MENISCAL CYST
Meni. Cyst may be caused by trauma to the meni. Or other opinion said it due to
infiltration of synovial cells between meni. And capsule .
The cyst is multilocular and containing gelatinous material .
It affect the lateral meni. More than the medial
It is located at the joint line on the lateral meni.
Treatment : excision .
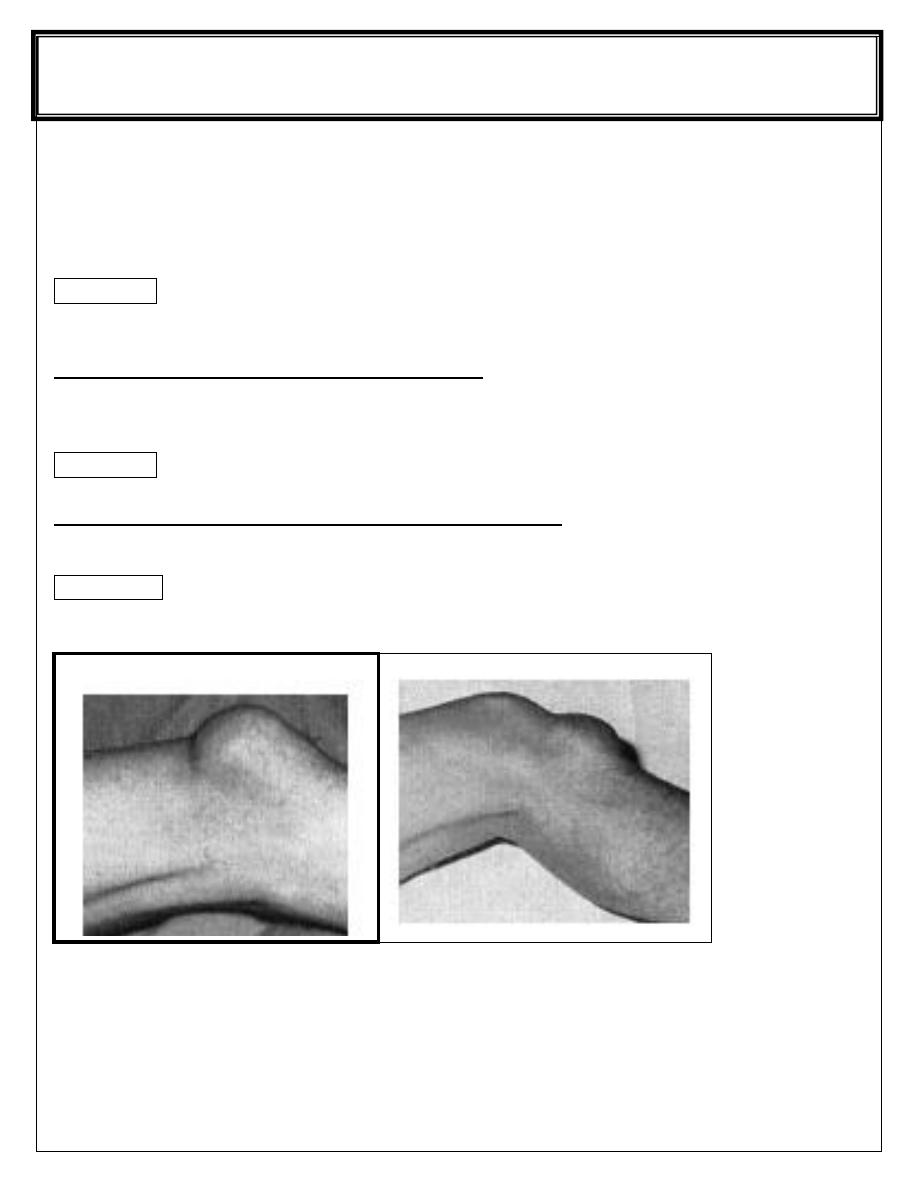
Bursitis around the knee
1- prepatellar bursitis( house maid
’s knee).
It is uninfected bursitis , not due to pressure , but to constant friction between skin and
patella ; it is seen in carpet layers and miners .
Swelling is well circumscribed and fluctuant , joint is normal .
Treatment :avoid kneeling ; bandaging , occasionally aspiration; and in chronic case
excision .
2- INFRAPATELLAR BURSITIS(clergyman
’s knee) .
The swelling is superficial to infrapatellar tendon (more distal to prepatellar bursitis) .
Gout may play a role in developing this type of bursa .
Treatment :the same as the prepatellar bursitis
PREPATELLAR AND INFRAPATELLAR BURSA
F
F
i
i
f
f
t
t
h
h
s
s
t
t
a
a
g
g
e
e
Lec-
DR.Yaqthan
Surgery
/ /2017
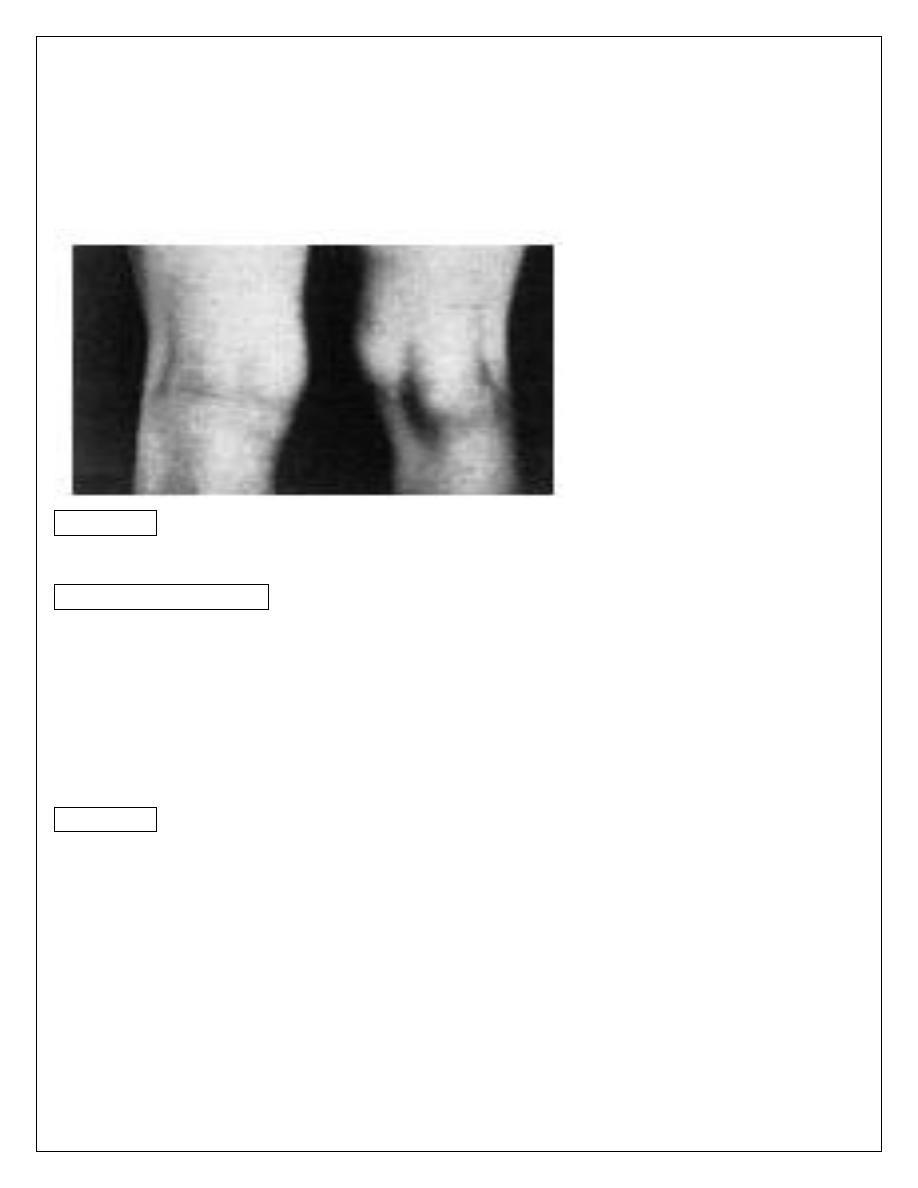
Semi membrenosus bursa :
Normally there is bursa between the semimembrenosus muscle and the medial head
of the gastrocnemeous muscle ; this bursa may become enlarged and the patient
presented with painless lump behind the knee slightly to the medial side of the midline ;
the joint is normal
Semi membrenosus bursa
Treatment :
The bursa may disappear spontaneously , if not and there is pain then excision should
be done .
Differential diagnosis :
1- popliteal cyst .
2- popliteal aneurism .
Popliteal cyst
This type of cyst is follow synovial rupture or herniation so the joint is abnormal ; it may
be osteoarthritis then the term BAKER
’S CYST is applied or more commonly
rheumatoid in origin .
Usually the cyst is in the midline of the popliteal fossa .
Treatment : it is the treatment of the underlying causes ; aspiration and injection of
methylprednesolone is helpful .
Excision is not advisable because recurrence is high , unless the underlying cause is
treated
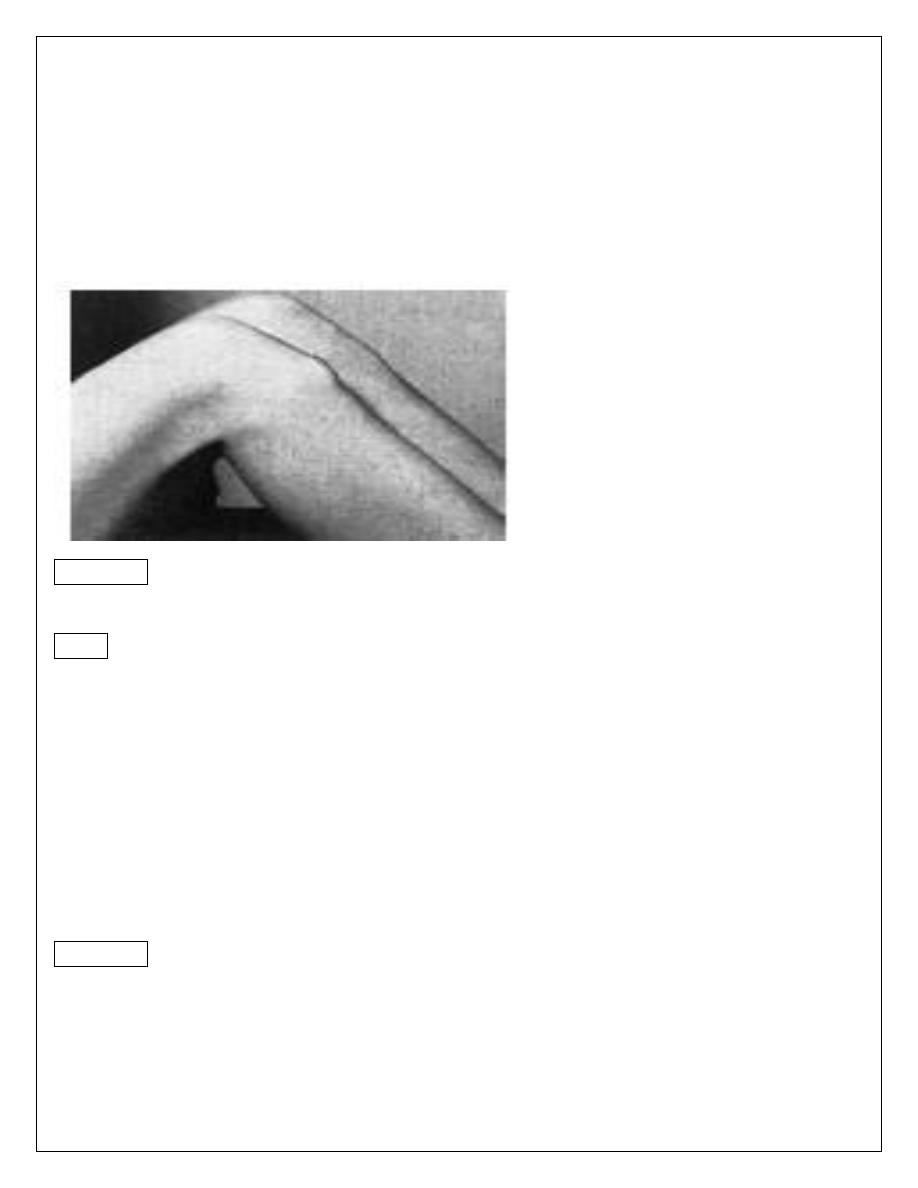
Osgood-schlatter
’s disease
Apophysitis
’of the tibial tubercle
Osgood- sch.
It is a common disorder in which the tibial tubercle in adolescence become painful and
swollen .
It is also called osteochondritis of the upper tibial apophysis or apophysitis .
It is traction injury of the apophysis into which part of the patellar tendon is inserted .
It could be unilateral or bilateral
osgood schlatter disease
Clinically :
Young adolescent complains of pain after activity and of a lump.
The lump is tender and it
’s situation over the tibial apophysis is diagnostic .
X-ray : show fragmentation of the apophysis.
Spontaneous recovery is usual but it take a time ; restriction of certain activities like
cycling and soccer is advisable ; if no response then immobilization by p.o.p; if it is
more sever then surgery is indicated
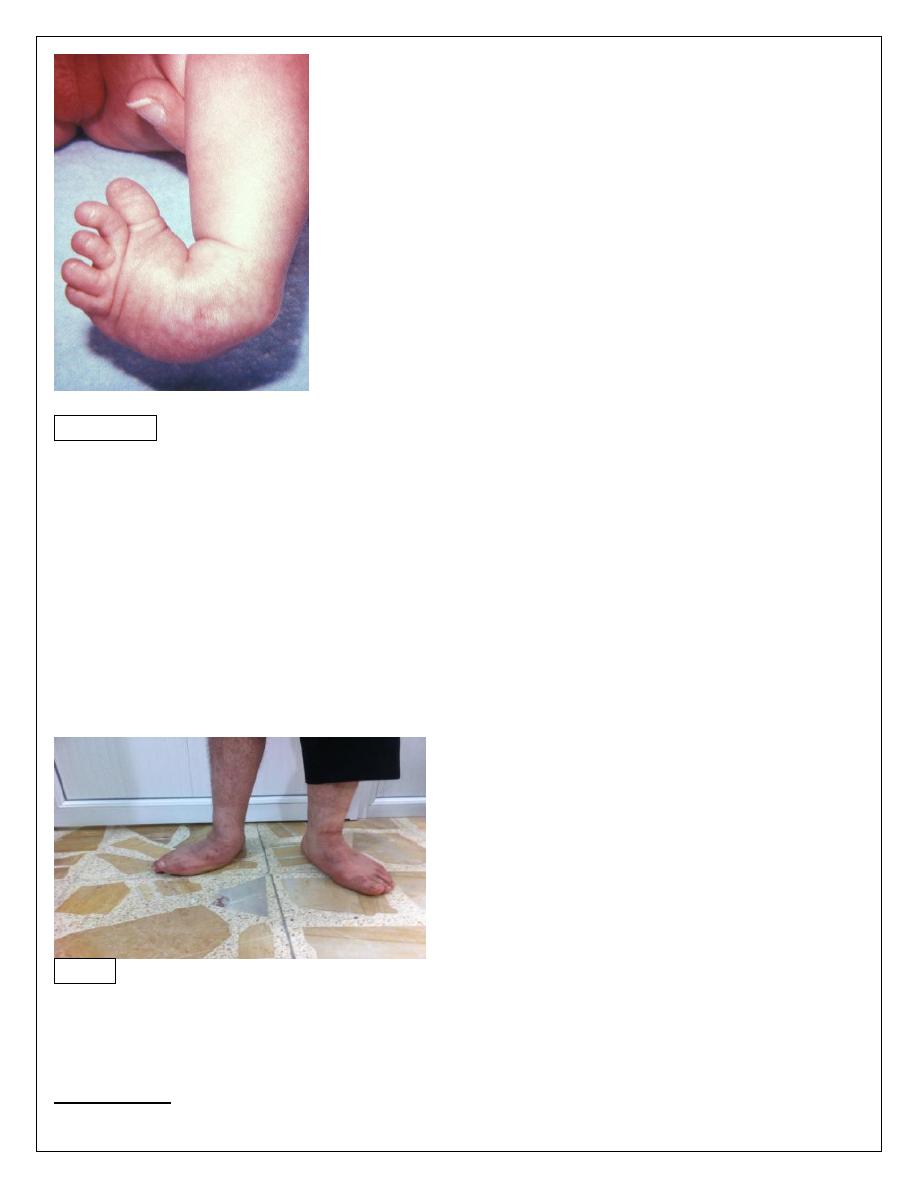
Congenital club foot
Talipoequinovarus foot
It is common abnormality . Incidence 1-2 / 1000 birth .Male to female ratio is 2:1 .
One third of the cases are bilateral .
It could be due to congenital defect , or secondary to neurological disorder e.g
myelomeningocele ; or could be postural due to mal position in intrauterine life
(crowded uterus) .
Clinically :
The deformity is as follow :
Ankle is in equinus (fixed planter flexion) .
Heel is in varus .
Forefoot in adduction .
The deformity is obvious at birth ; the foot is turned and twisted inward
Treatment :
It should be started from the birth and within few days :
1
– by repeated manipulation and adhesive strapping which maintains the correction.
2
– correction of the deformity by holding the foot in correct position in plaster cast .
3
– resistant cases and that not respond to conservative treatment , surgical correction
will be the next choice of the treatment followed by serial casting and splint .
pes planus (flat foot)
The medial border (arch of the foot) is in contact with the ground, the
longitudinal
arch of the foot is reduced (eversion or valgus deformity).
Flatfoot is common among children. The causes may be congenital , muscle
weakness or paralysis. Symptom mainly pain
Pes planus (flat foot)
Types:
1- Flexible flatfoot: normal variation usually disappears spontaneously.
2- Rigid flatfoot: cannot be corrected passively.
3- Compensatory flatfoot e g. short tendo achillis, or external rotation of lower limbs
(Charlie Chaplin look) .
Treatment:
Conservative by modifying the shoes and in sever cases surgery is indicated

Hallux Valgus
It is lateral deviation of the great toe at the metatarso-phalangeal joint. It is
usually bilateral.
Family history usually posative ,more common in female, narrow pointed
shoes and the wearing of high heels forced toes into the narrow pointed part
of the shoe .
Symptoms:
early symptoms arise are pain and tenderness over the bunion from pressure
against the shoe . There is also difficulty in getting comfortable footwear.
Later, additional symptoms arise from osteoarthritis of the
metatarso-phalangeal joint.
HALLUX VALGUS
Treatment:
conservative treatment for asymptomatic, mild and non-progressive
deformity by comfortable footwear with low heels, foot wear selected with
care to obtain adequate width, protect the bunion with pads of felt, and to
wear a wedge of plastic foam between the great toe and the second toe to
reduce the deformity.
surgical treatment for Severe, progressive and painful deformity is
required . Variable surgical procedures used depend on age, severity, and
presence of arthritis.
