
Dr/
Dr/ Hebatallah
Hebatallah ADAM
ADAM
Associate Professor of Economics
Faculty of Commerce Ain Shams University

Chapter 1:
The Quantitative Aspects of
The Quantitative Aspects of
Human Resources
2
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM

1. Introduction: Key Statistics
1. Introduction: Key Statistics
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
3
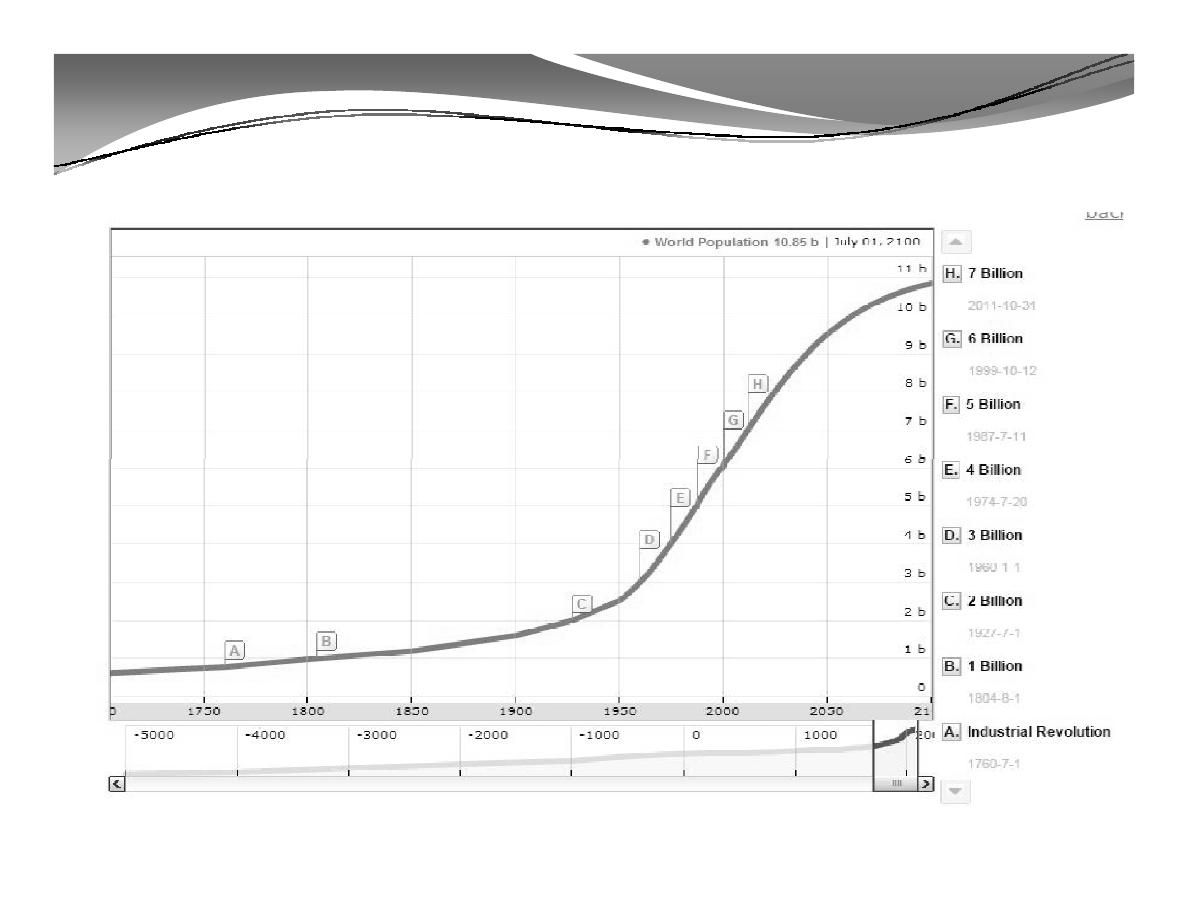
A. World Population: Past, Present, and Future
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
4

1. World Population: Past, Present, and Future*
A remarkable change occurred with the industrial
revolution: whereas
it had taken all of human
history until around 1800 for world population to
reach one billion, the second billion was achieved in
only 130 years (1930), the third billion in less than 30
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
5
only 130 years (1930), the third billion in less than 30
years (1959), the fourth billion in 15 years (1974), and
the fifth billion in only 13 years (1987).
The population of the world is 7.28 billion people as of
January 2015.
*
Sources: Historical Estimates of World Population - US Census Bureau. & The World at Six Billion, World Population,
Year 0 to near stabilization [Pdf file] - United Nations Population Division
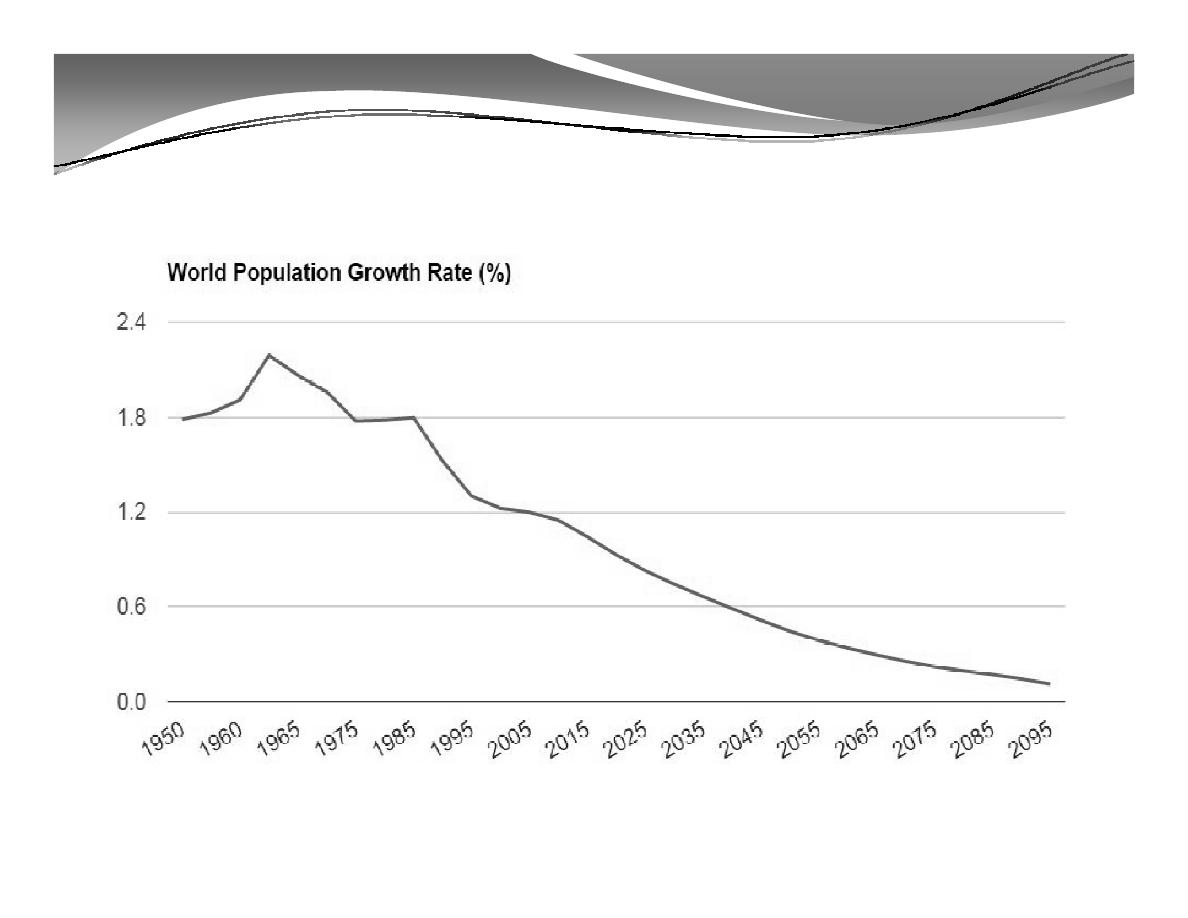
B. World Population Growth Rate
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
6

B. World Population Growth Rate (cont'd)
Population in the world is currently growing at a rate
of around
1.14% per year. The average population
change is currently estimated at around 80 million per
year.
Annual growth rate reached its peak in the late 1960s,
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
7
Annual growth rate reached its peak in the late 1960s,
when it was at 2% and above.
The annual growth rate is currently declining and is
projected to continue to decline in the coming years.
Currently, it is estimated that it will become less than
1% by 2020 and less than 0.5% by 2050.
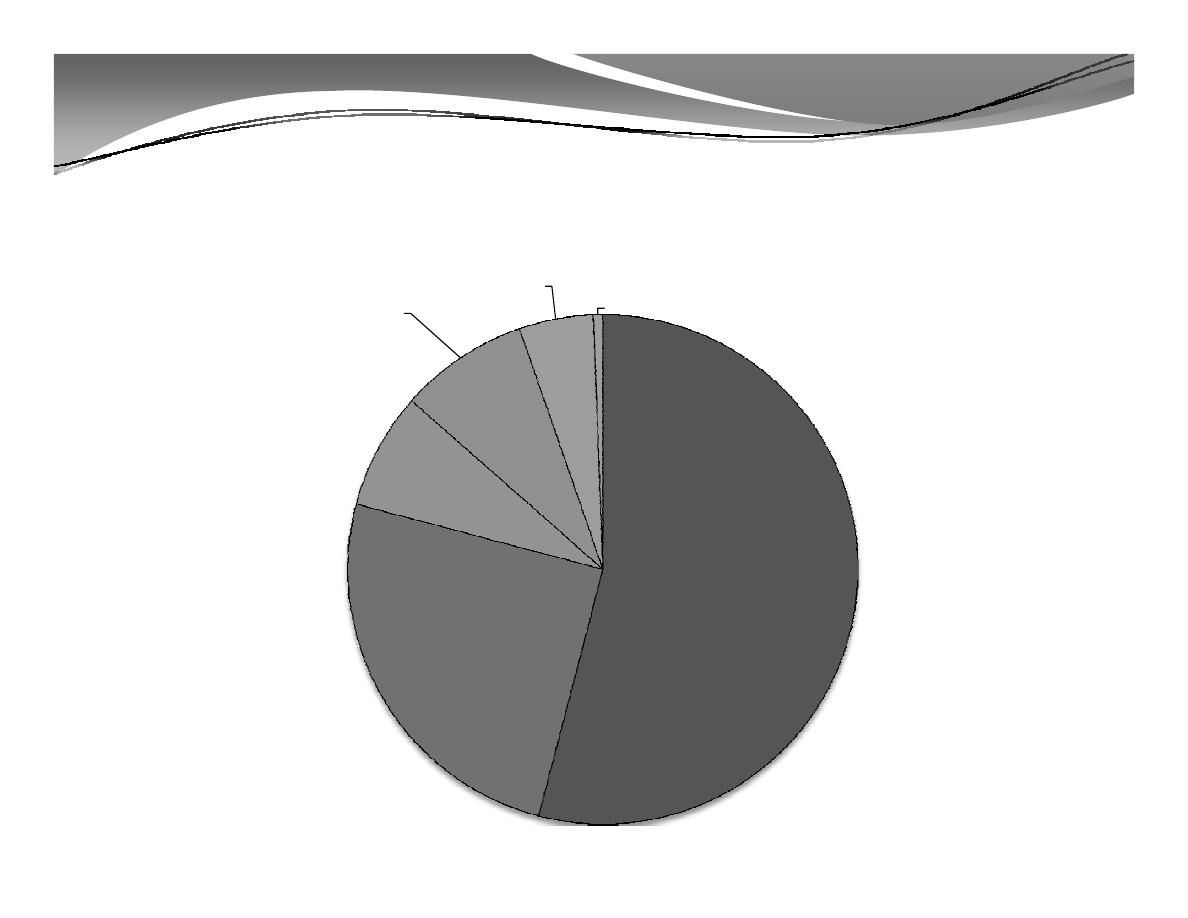
C. World Population by Region, 2013
Europe
Latin America and
Caribbean
8%
Northern America
5%
Oceania
1%
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
8
Asia
54%
Africa
25%
Europe
7%
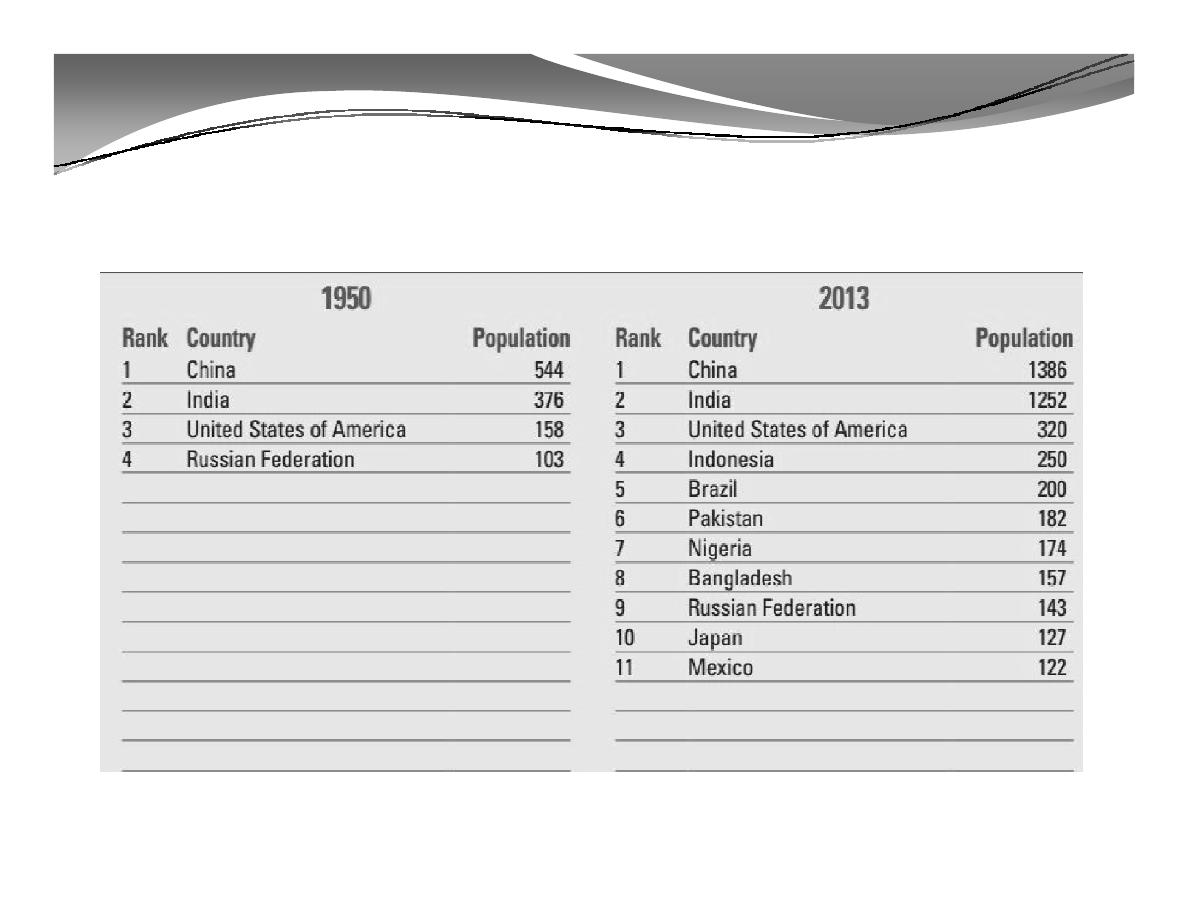
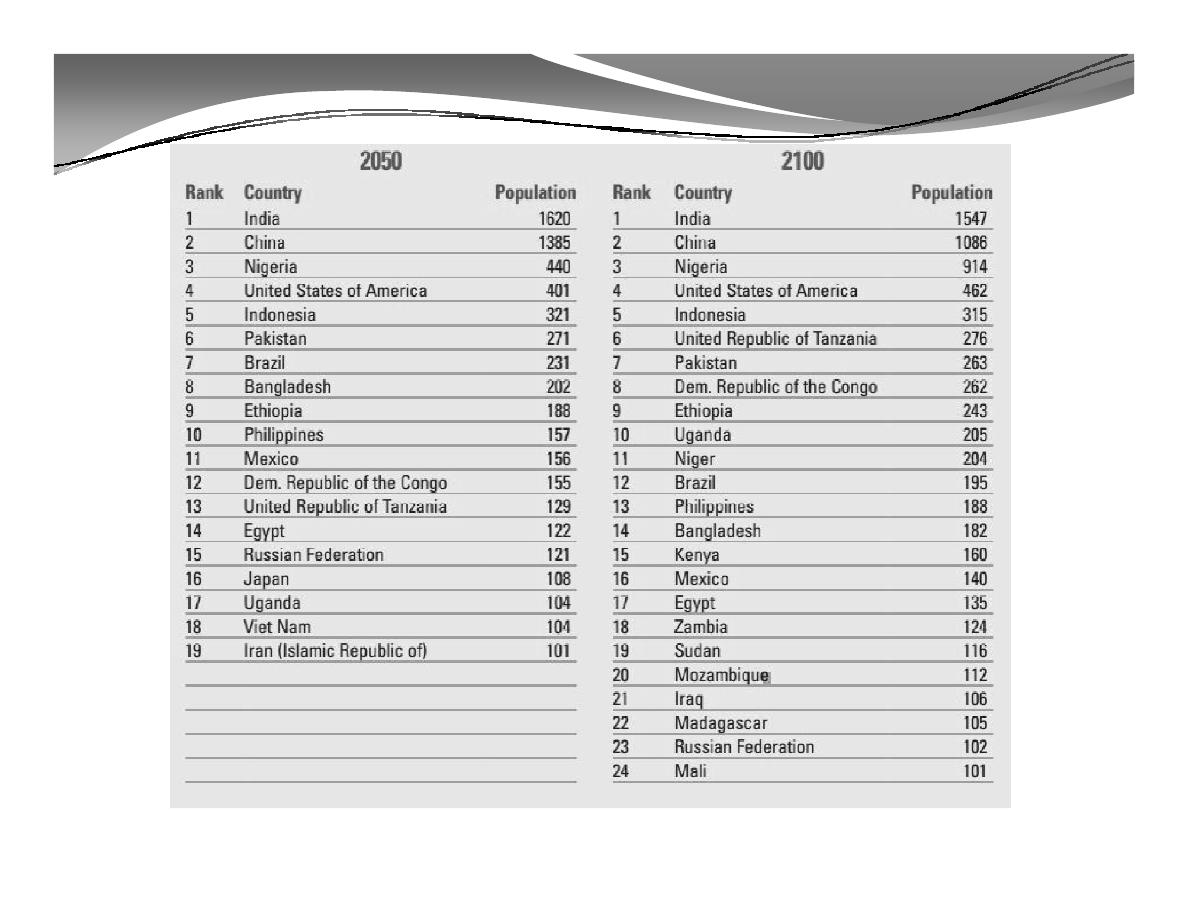
D. World Population by Country:
Countries with more than 100 million inhabitants in 1950, 2013, 2050 and 2100
(population in millions)*
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
9
* Source: WorldPopulation2012, www.unpopulation.org
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
10

1. Population Size
1. Population Size
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
11
1. Population Size
Population size increases because of births and
immigration, and decreases through deaths and
emigration.
Population size change:
Population size change:
1.
Births: fertility
2.
Deaths: mortality
3.
Migration
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
12
Population change =
(births + immigration) – (deaths + emigration)

A.
Population Death – Birth Rates
Birth rate=
The number of live babies born per thousand of the
population per year.
Death rate=
When the birth rate is higher than the death rate, more
people are being born than are dying, so the population
grows. This is called
Natural increase
When the death rate is higher than the birth rate it is called
the
natural decrease.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
13
Death rate=
The number of deaths per thousand of the population per
year.

A.
Population Death – Birth Rates (cont'd)
The average number of children born to women in a
population (total fertility rate) is the key factor that
determines population size.
Fertility rate = number of children born to a woman
during her lifetime
Total fertility rate (TFR) = Average number of
children born to women in a population
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
14

A.
Population Death – Birth Rates (cont'd)
Factors Affecting Birth Rates and Fertility Rates:
1.
Children as part of the labor force
2.
Cost of raising and educating children
3.
Availability of private and public pension
4.
Urbanization
4.
Urbanization
5.
Educational and employment opportunities for
women
6.
Average age of a woman at birth of first child
7.
Availability of legal abortions
8.
Availability of reliable birth control methods
9.
Religious beliefs, traditions, and cultural standards
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
15

A.
Population Death – Birth Rates (cont'd)
Factors Affect Death Rates:
1.
Life expectancy
2.
Infant mortality rate
3.
Number of live births that die in first year
Why are people living longer?
1.
Increased food supply and distribution
2.
Better nutrition
3.
Medical advances
4.
Improved sanitation
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
16

B.
Population Migration
Migration is the movement of people from one area to
another.
When people move into an area its called
immigration.
When people leave an area its called
emigration.
Migration happens because of push and pull factors:
Migration happens because of push and pull factors:
1.
Push factors are the things about a persons place of
origin that make them decide to move. (ex. Not being
able to find a job, Poor living conditions, Natural
disasters)
2.
Pull factors are things about a persons destination that
attracts them to it. (ex. Job opportunities, Better
standards of living)
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
17
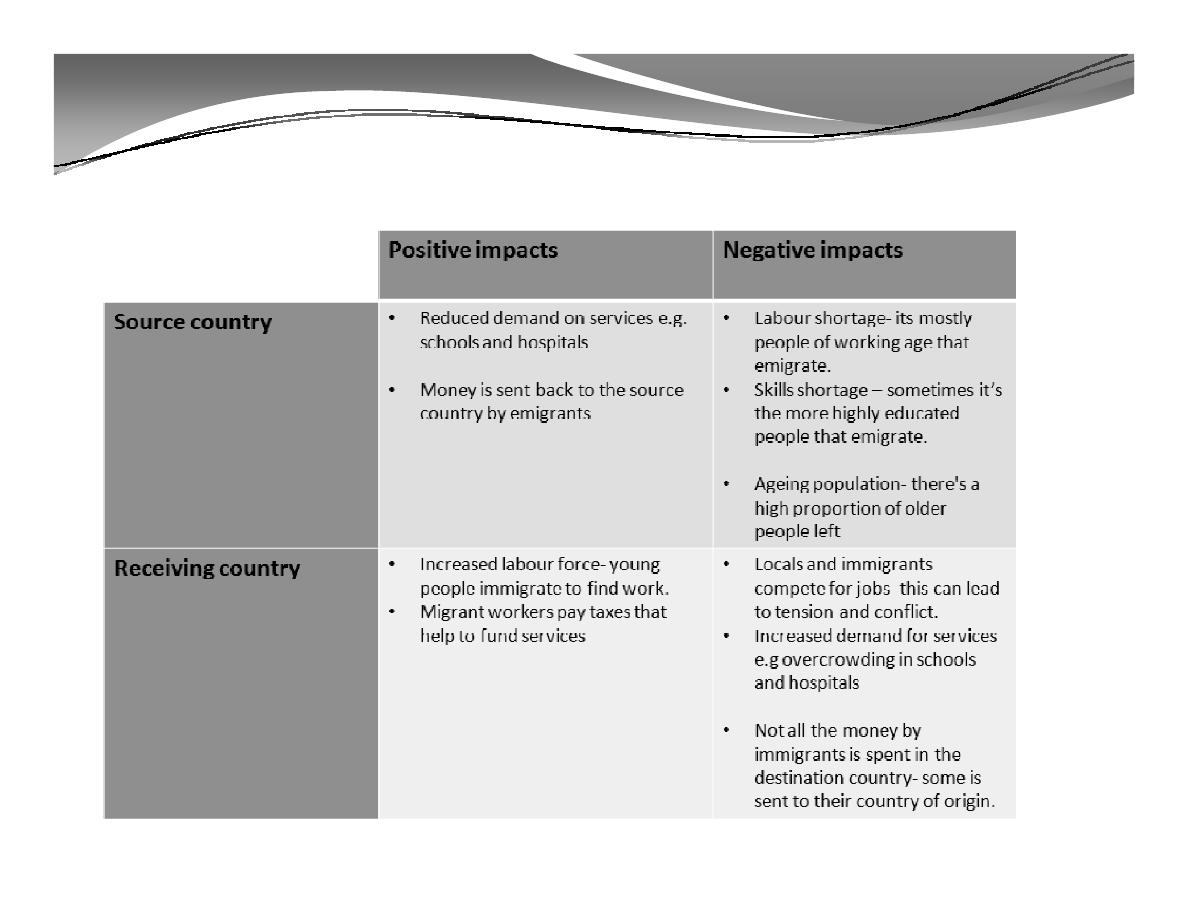
B.
Population Migration (cont'd)
effects on population
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
18

2. Population Structure
2. Population Structure
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
19

2. Population Structure
The numbers of males and females in young, middle,
and older age groups determine how fast a population
grows or declines.
These profiles help demographers project how
These profiles help demographers project how
populations will change over time.
Age structure categories:
1.
Pre-reproductive ages (0-14)
2.
Reproductive ages (15-44)
3.
Post-reproductive ages (45 and older)
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
20
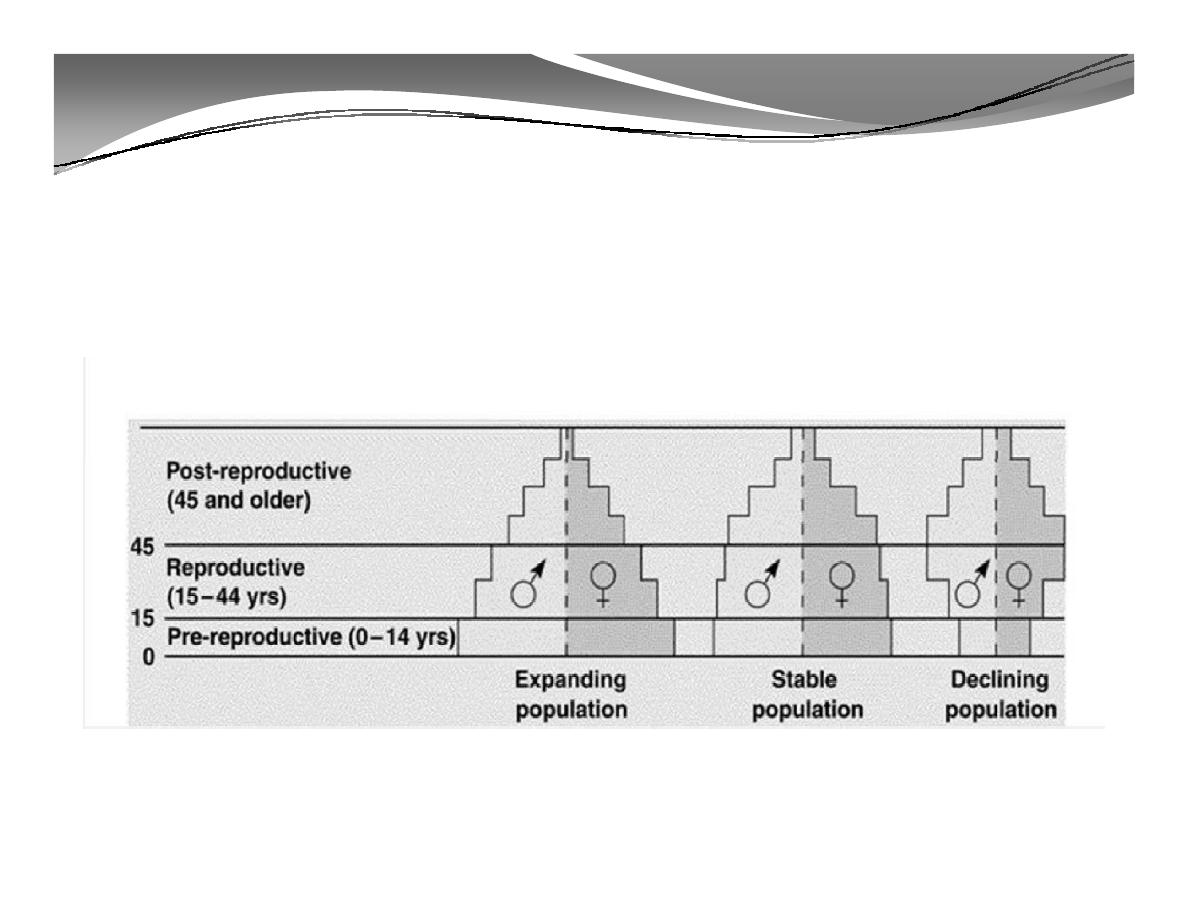
2. Population Structure (cont'd)
Generalized Population Age-Structure Diagrams
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
21
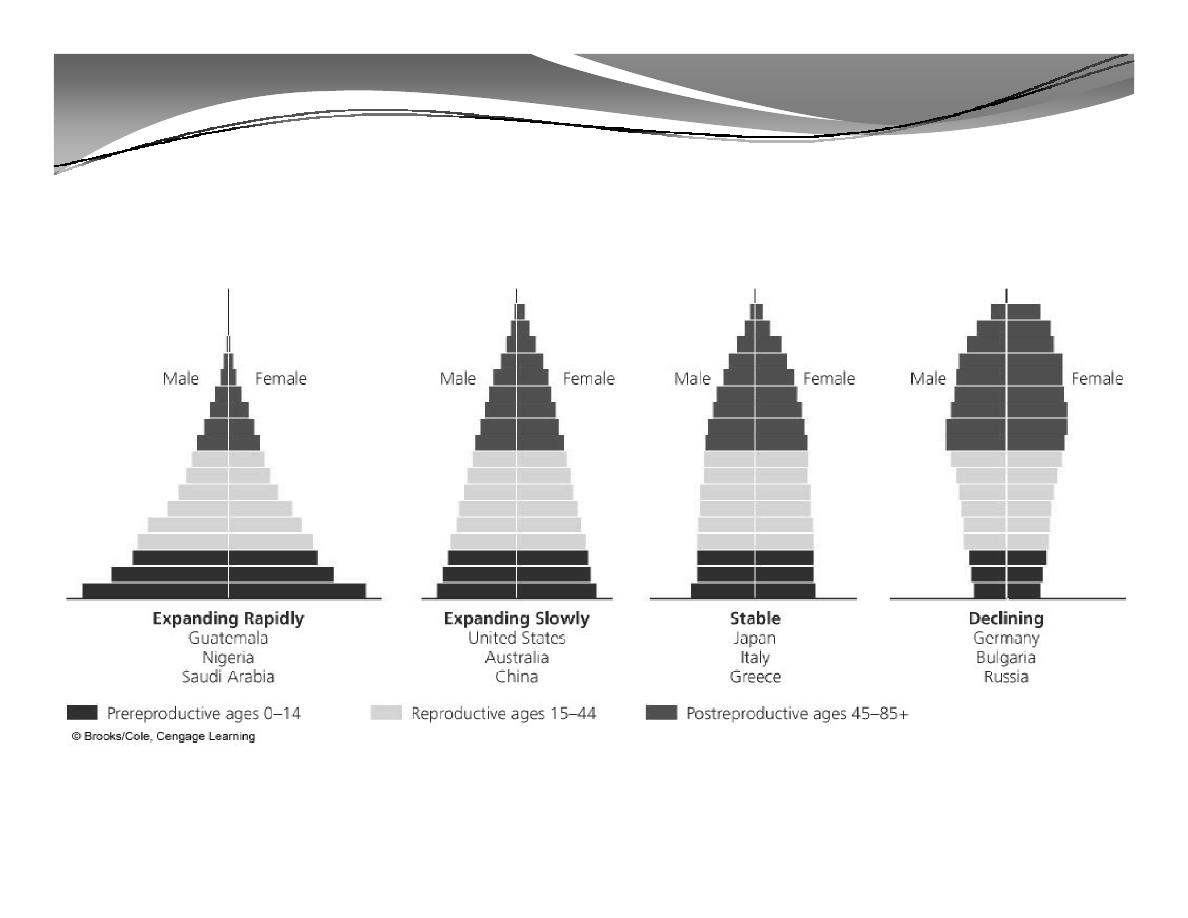
2. Population Structure (cont'd)
Generalized Population Age-Structure Diagrams
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
22
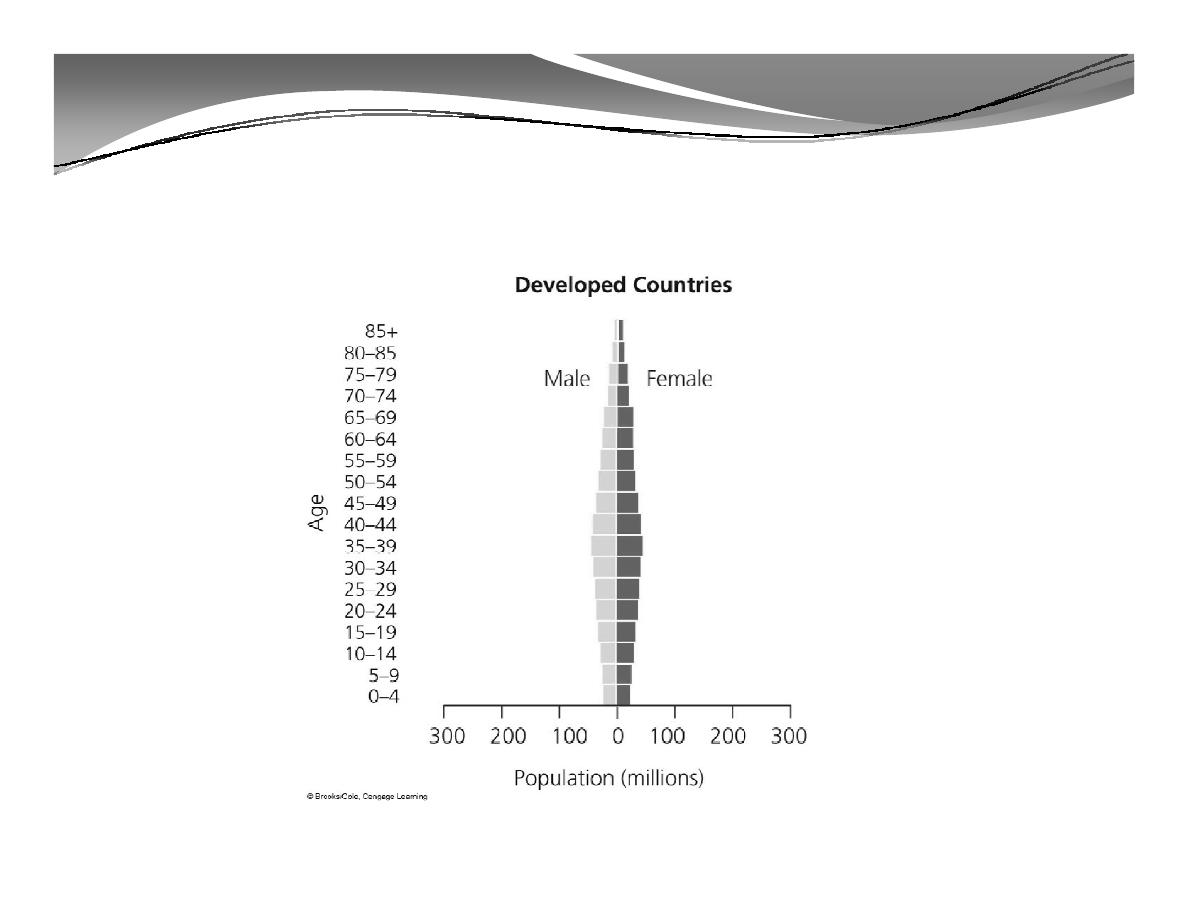
2. Population Structure (cont'd)
Population Structure by Age and Sex in Developing and Developed
Countries
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
23
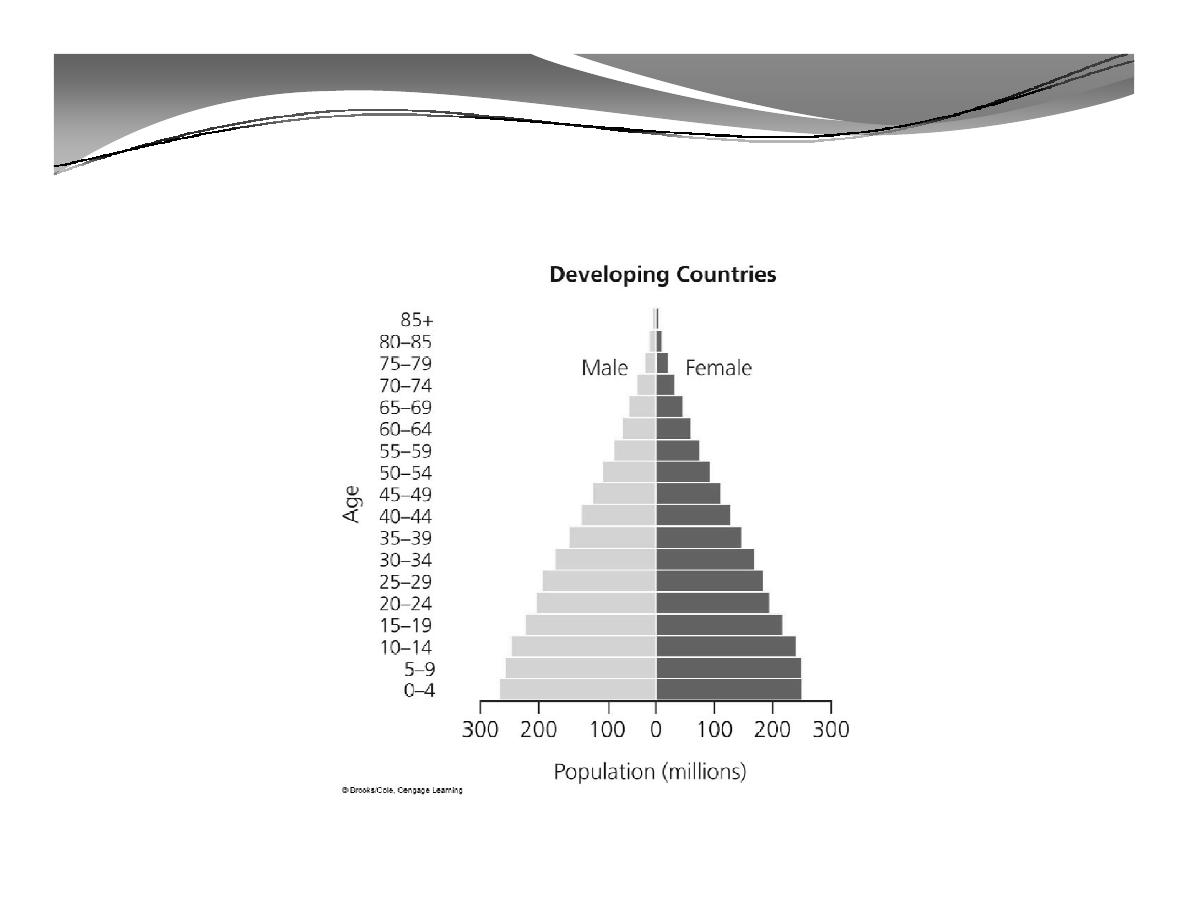
2. Population Structure (cont'd)
Population Structure by Age and Sex in Developing and Developed
Countries
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
24

2. Population Structure (cont'd)
Populations Made Up of Mostly Older People Can
Decline Rapidly.
Slow decline is Manageable
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
25
But Rapid decline is not:
1.
Severe economic problems
• How pay for services for elderly
• Proportionally fewer young people working
• Labor shortages
2.
Severe social problems

2. Population Structure (cont'd)
How Can We Slow Human Population Growth?
We can slow human population growth by reducing
poverty, elevating the status of women, and
encouraging family planning.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
26
Empowering Women Can Slow Population
Growth:
Education, healthcare, equal opportunity in labor
market.

Main ideas in today’s lecture
The human population is increasing rapidly and may
soon bump up against environmental limits.
Even if population growth were not a serious problem,
Even if population growth were not a serious problem,
the increasing use of resources per person is
expanding the overall human ecological footprint and
putting a strain on the earth’s resources.
We can slow population growth by reducing poverty
through economic development, elevating the status
of women, and encouraging family planning.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
27

Thank You
Thank You
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
28
