
Dr/
Dr/ Hebatallah
Hebatallah ADAM
ADAM
Associate Professor of Economics
Faculty of Commerce Ain Shams University

Chapter 1:
The Quantitative Aspects of
Human Resources
Human Resources
(cont'd)
2
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM

3. The Causes of Population
Growth - Theories
Growth - Theories
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
3
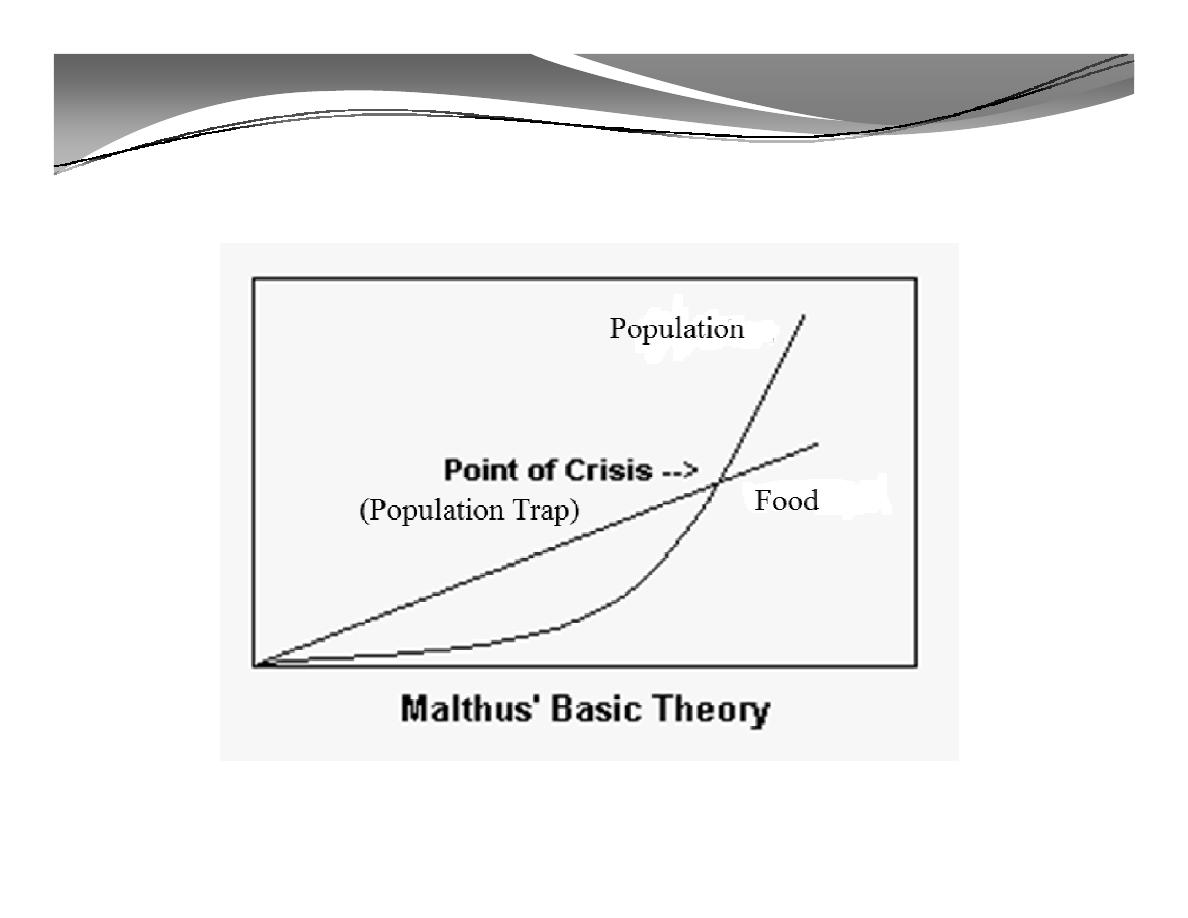
A. Malthus’ Theory of Population Growth
In An Essay on the Principle of Population, published
in
1798, Malthus claimed that “the population was
growing more rapidly than the Earth’s food supply
because population increased geometrically, whereas
food supply increased arithmetically”.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
4

A. Malthus’ Theory of Population Growth
(cont'd)
Malthus theory has TWO basic principles:
1.
Population grows at a geometric rate
2.
Food production increases at an arithmetic rate
Malthus noticed that farming improvements could
raise food production by a certain amount each year –
in an arithmetic rate of increase (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6)
Whereas population tends to increase at a ‘geometric
rate’ (1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 32) with each generation (a
generation=25years)
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
5

A. Malthus’ Theory of Population Growth
(cont'd)
Today:
1 person, 1 unit of food
25 years from now:
2 persons, 2 units of food
50 years from now:
4 persons, 3 units of food
50 years from now:
4 persons, 3 units of food
75 years from now:
8 persons, 4 units of food
100 years from now:
16 persons, 5 units of food
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
6
A. Malthus’ Theory of Population Growth
(cont'd)
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
7

A. Malthus’ Theory of Population Growth
(cont'd)
The
consequence of these two principles is that
eventually, population will exceed the capacity of
agriculture to support the new population numbers.
Population would rise until a limit to growth was reached.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
8
Population would rise until a limit to growth was reached.
Further growth would be limited by:
1.
Positive checks : anything that increases mortality (war,
disease, famine, poor living standards), would increase
the death rate between the excess population.
2.
Preventive checks : anything that limit the number of
children born (Postponement of marriage, birth control).

A. Malthus’ Theory of Population Growth
(cont'd)
Main Criticism of the Malthusian model:
Ignores the impact of technological progress.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
9
Rapid
technological
improvement:
Increasing
returns to scale rather than decreasing returns to
scale.

B. The microeconomic household theory of
fertility
Children are considered as a special kind of consumption
(and in LDC: investment) good so that
Fertility becomes a rational economic response to family’s
demand for children relative to other goods, depending on:
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
10
demand for children relative to other goods, depending on:
1.
Household income
2.
Net price for children (benefits such as potential child
income minus costs such as education and
opportunity costs for mothers)
3.
Price of other consumer goods
4.
Tastes

B. The microeconomic household theory of
fertility (cont'd)
Demand for Children Equation:
Where:
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
11
Where:
C
d
is the demand for surviving children
Y is the level of household income
P
c
is the “net” price of children
P
x
is price of all other goods
t
x
is the tastes for goods relative to children

B. The microeconomic household theory of
fertility (cont'd)
Income & Substitution effects
:
If other factors are held constant, the desired
number of children can be expected to vary
directly
with household income and
inversely with the cost
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
12
with household income and
inversely with the cost
(price) of children.
1.
Income effect: Higher income allows for larger
family size
2.
Substitution effect: Higher cost of children
implies smaller family size

B. The microeconomic household theory of
fertility (cont'd)
Why are there so many children in poor countries?
Because children are an “investment” rather than a
“consumption good”
the “expected return of the
investment” is given by child labor and financial
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
13
investment” is given by child labor and financial
support for parents in old age.
Parents have children up to the point at which their
marginal economic benefit is equal to marginal cost

4. Policy Approaches of
population growth problem
population growth problem
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
14

A. Rising the net price of children or Decrease
“marginal economic benefit of children”, this will
be through:
1.
Increase the minimum-age child labor
Policy approach to deal with the high population
growth:
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
15
1.
Increase the minimum-age child labor
2.
provide better old-age social security
3.
Increase “marginal cost of children”
4.
Increase education, employment and wages for
women (which will increase opportunity costs of
having children)

Policy approach to deal with the high population
growth:
B. Other policy options:
1.
Better water and public health programs in rural and
urban poor areas.
2.
Implementation of family-planning programs
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
16
2.
Implementation of family-planning programs
3.
Improvement of quality of care of health and family
planning programs
4.
Monetary subsidies to poor families
5.
Political commitment and role of religious leaders

5. The relationship between
population and the economy
population and the economy
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
17

First question: How the population size can
affect the economy?
The effect of any increase in the size of the population depends
mainly on the demographic stage of the economy:
1.
Over-population stage: the increase in the size of population
will be negative on both consumption and production (higher
inflation rates, increased imports, decrease in real per capita
income, government budget deficit)
income, government budget deficit)
2.
Under-population stage: the effect of the increasing size
population will depend on the nature of the population
increase:
a)
Natural increase: High level of dependency and high level of
consumption in short run. High level of production in long
run.
b)
Immigration: High level of production and high standard of
living.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
18

Second question: How the population
structure can affect the economy?
1.
The impact of Age structure: the more is the
percentage of children and older the higher will
be the dependency ratio.
be the dependency ratio.
2.
The impact of gender structure: Gender
distribution affects the economy through labor
Market supply – It depends on the status of
women empowerment in the country.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
19

Thank You
Thank You
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
20
