
Dr/
Dr/ Hebatallah
Hebatallah ADAM
ADAM
Associate Professor of Economics
Faculty of Commerce Ain Shams University

Chapter 2:
The Quantitative Aspects of
The Quantitative Aspects of
Labor's Role in Development
2
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM

1. Labor Productivity
1. Labor Productivity
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
3
A. Introduction: What is “Productivity”?
Productivity is a common measure of how well
resources are being used or a measure of the effective
use of resources usually expressed as the ratio of
output to input.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
4
Productivity =
Productivity =
Output
Output
Input
Input

B. Labor Productivity: Definition
“Labor productivity is equal to the ratio between a
volume measure of output (gross domestic product or
gross value added) and a measure of input use (the
gross value added) and a measure of input use (the
total number of hours worked or total employment)
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
5
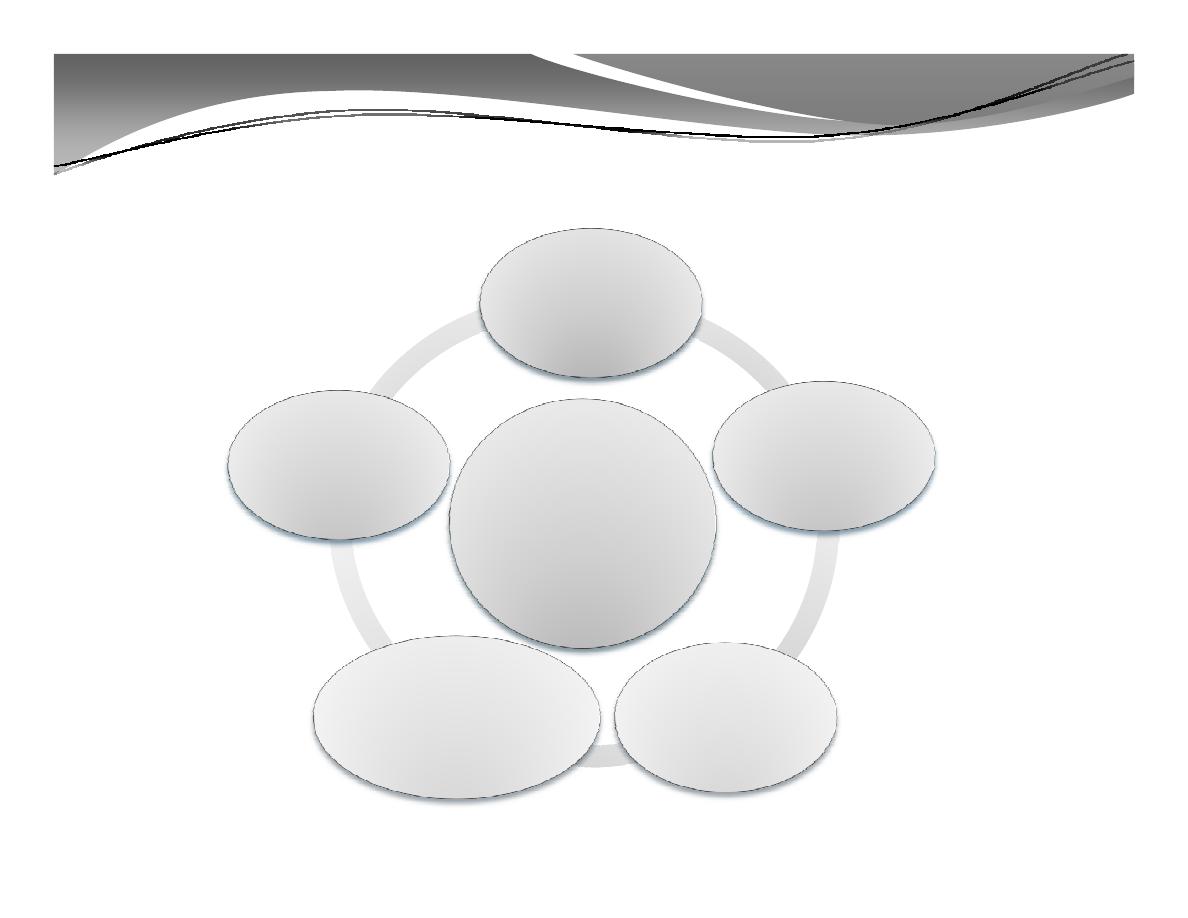
C. Factors Affecting Labor Productivity
Technical
Factors
Structure
Factors
Economical
and social
Labor
Productivity
Factors
Natural
Factors
Human and
psychological
Factors
and social
Factors
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
6

C. Factors Affecting Labor Productivity (cont'd)
1.
Technical Factors: having regard to the level
reached by the science, engineering, technology at a
given time;
2.
Economic
and
social
Factors:
bound
by
organization of production and related work at both
micro and
macro level,
working
and
living
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
7
organization of production and related work at both
micro and
macro level,
working
and
living
conditions;
3.
Human and psychological Factors: related to
educational
preparation,
level
of
culture,
adaptability to working conditions, satisfaction that
they offer it, family, religion and tradition influence
the choice of profession;

C. Factors Affecting Labor Productivity (cont'd)
4.
Natural factors: that refer to climatic conditions,
soil fertility, availability of natural resources;
4.
Structural Factors: which affects labor productivity
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
8
4.
Structural Factors: which affects labor productivity
through changes in the structure of branches and
under-branches of national economy.

2. Patterns of Labor in
developing countries
developing countries
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
9

2. Patterns of Labor in developing countries
1.
Dual labor markets (formal/informal)
2.
Large share of agriculture and rural labour
3.
Non-wage labor (self employment and unpaid family
workers) more important
workers) more important
4.
Earnings levels are very low despite long work hours.
5.
Women are disadvantaged in developing country
labor markets. Women’s earnings are lower, women’s
work is more likely to be informal
6.
Labor force growth is higher
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
10

2. Patterns of Labor in developing countries
(cont'd)
7.
What
the
developing
countries
have
is
an
employment problem – that is, poverty among those
who work – rather than an unemployment problem.
(85% of the world’s poor are working).
8.
Labor force participation rates among the 15-64 are
8.
Labor force participation rates among the 15-64 are
higher (because of lower school enrollment rates and
pervasive poverty)
9.
Human capital investments are lower
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
11

3. The Structure of Labor
Markets in developing
countries
countries
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
12
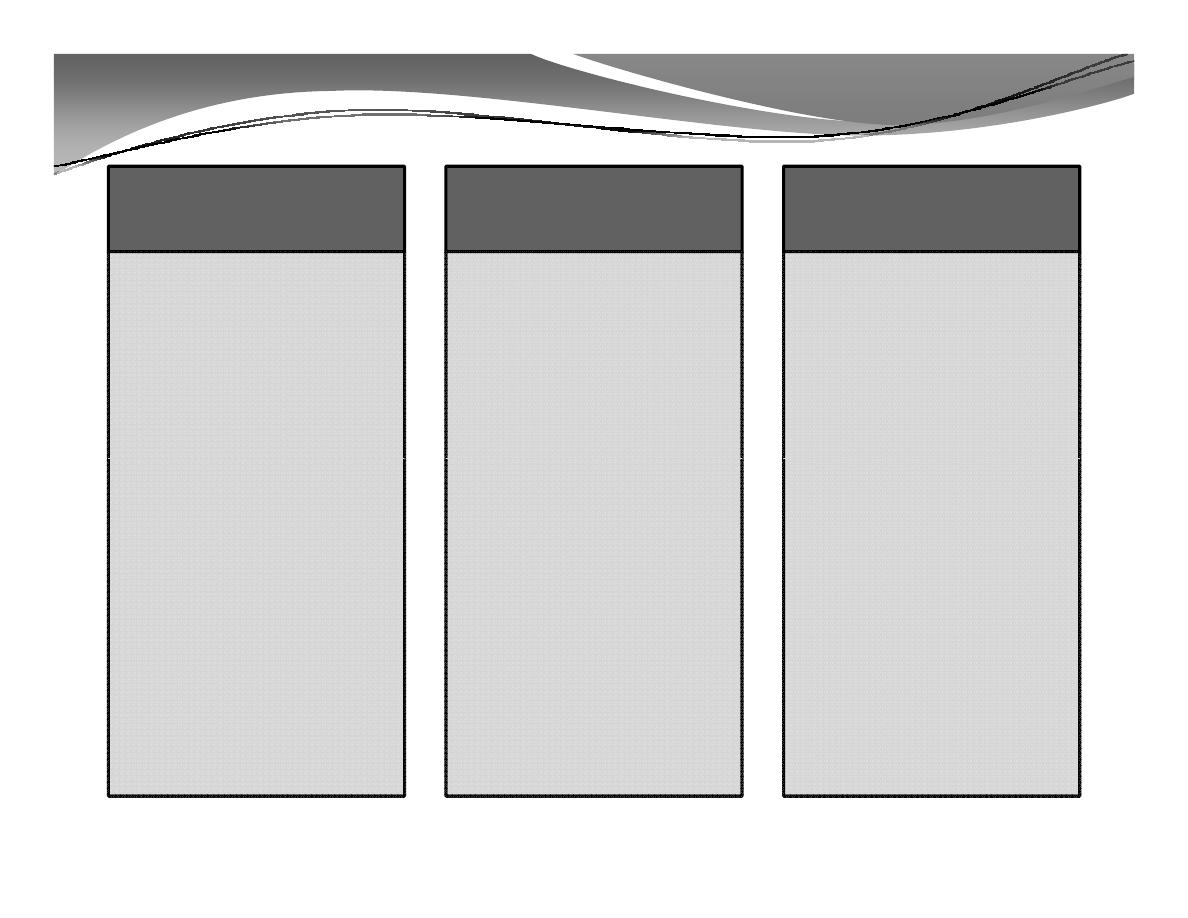
Urban Formal
Labor Market
• Public & Private
Sectors
• Highest wages
• Social Security
Protection
Urban Informal
Labor Market
• The informal
economy refers to
activities and
income that are
partially or fully
outside
government
Rural Labor
Market
• The rural labor
market is
undergoing
significant
changes mainly
due to rising
employment
outside
government
regulation,
taxation, and
observation.
• Provides jobs for
migrants
• Wages are lower
than the formal
sector
due to rising
employment
opportunities
outside
agriculture.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
13

4. Measuring the Labor Supply
4. Measuring the Labor Supply
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
14

4. Measuring the Labor Supply
The Supply of Labor is determined by:
Size and structure of the population – age, gender
Skill levels required (in developing countries: shortage in skilled
labor)
Education and training
Education and training
Number in higher education
School leaving age
Qualification types
Opportunity cost of work – income and substitution effects
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
15

5. Unemployment Problem
5. Unemployment Problem
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
16

A. Definition of Unemployment
As defined by the International labor organization,
"unemployed workers" are those who are currently not
working but are willing and are able to work for pay,
working but are willing and are able to work for pay,
currently available to work, and actively searching for
work.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
17

B. Unemployment Measurement
Unemployment rate =
unemployed worker/total labor force*1oo
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
18
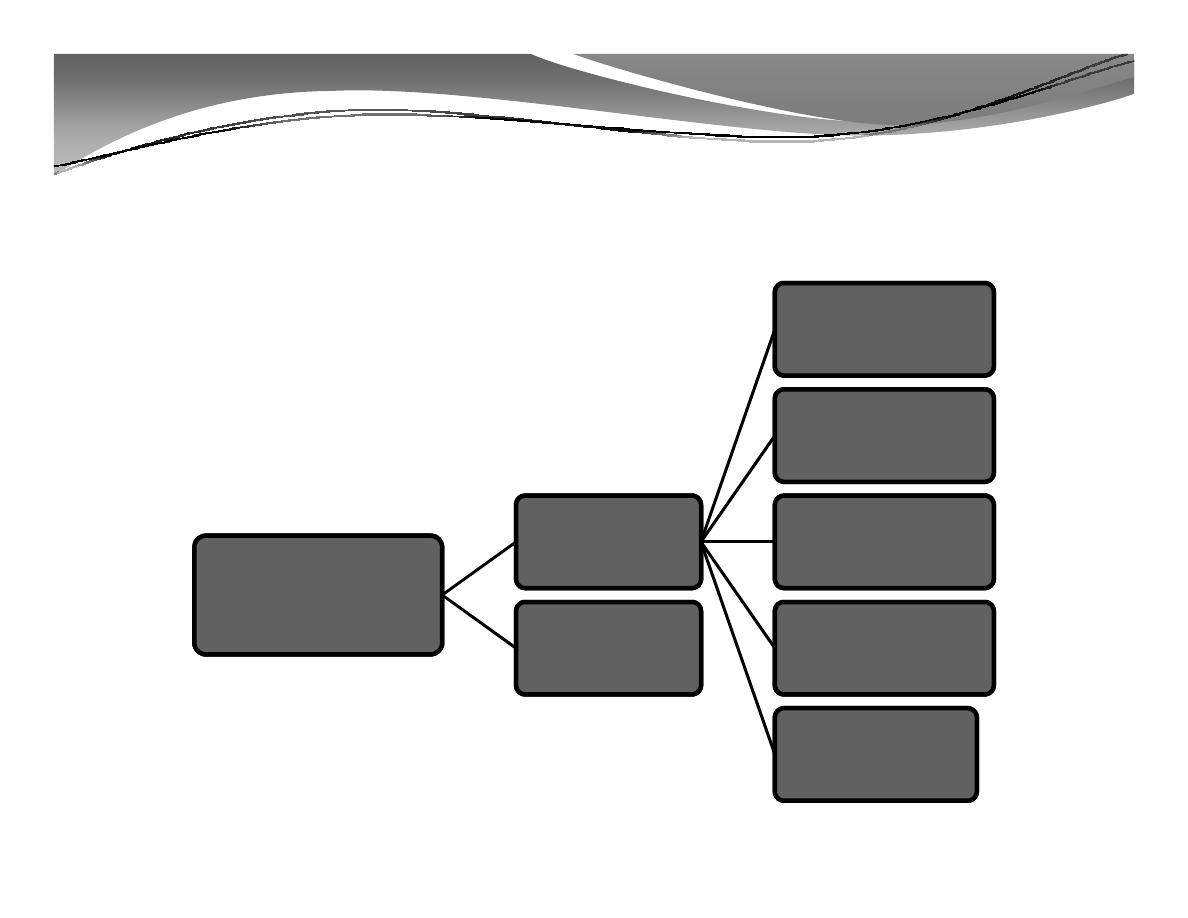
C. Types of Unemployment
Cyclical
Technological
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
19
Unemployment
Involuntary
Structural
Seasonal
Frictional
Voluntary
C. Types of Unemployment (cont'd)
• A person is out of job because of
his own desire to not to work on
the prevalent or prescribed wages.
Voluntary
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
20
• A person is separated from
remunerative work and devoid of
wages although he is capable of
earning his wages and is also
anxious to earn them.
Involuntary

D. Types of Involuntary Unemployment
Frictional unemployment is a brief period of
unemployment
experienced
by
people
moving
between jobs or into the labor market. People have
the skills and knowledge necessary to get a job, and the
jobs are available.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
21
jobs are available.
Structural unemployment is unemployment caused
by a mismatch between the skills or location of job
seekers and the requirements or location of available
jobs. Jobs may be available in other geographic areas or
for individuals with specific skills and abilities.

D. Types of Involuntary Unemployment (cont'd)
Cyclical unemployment is unemployment caused by
a lack of job vacancies; an inadequate level of
aggregate demand. Cyclical unemployment commonly
occurs during recessions. Companies cut back on
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
22
occurs during recessions. Companies cut back on
workers due to reduced sales, fears of an economic
recession, and insufficient consumer demand.
Technological unemployment: It results of from the
introduction of new techniques on a large scale.
Seasonal unemployment is unemployment due to
seasonal changes in employment or labor supply.

E. Causes of unemployment in developing
countries
Rapid Population Growth
Poor economic performance and slowing down
economic growth
Economic Recession
Demand for highly skilled labor
Global Competition
Illiteracy: Over 70% of total labor force is illiterate or
educated below primary level
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
23

D. The main characteristics of
unemployment in Egypt
To be presented by groups research with
“unemployment problem” as a topic.
“unemployment problem” as a topic.
Until then read pages 63-64.
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
24

Thank You
Thank You
Economics Resources - Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM
25
