
Dr/
Dr/ Hebatallah
Hebatallah ADAM
ADAM
Associate Professor of Economics
Faculty of Commerce Ain Shams University

Chapter 3:
The Quantitative Aspects of
Human Resources (Human
Human Resources (Human
Investment, Human Capital)
2
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015

1. Meaning of Human Capital
1. Meaning of Human Capital
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
3

1. Definition of Human Capital
Economist Theodore Schultz* invented the term in the
1960s to reflect the value of our human capacities. He
believed human capital was like any other type of
capital; it could be invested in through education,
training and enhanced benefits that will lead to an
improvement in the quality and level of production.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
4
* Theodore W. Schultz, “Investment in Human Capital,” American Economic Review 51 (March 1961): 3

1. Definition of Human Capital (cont'd)
Human
Capital*
is
the
stock
of
competencies,
knowledge,
social
and
personality attributes, including creativity,
personality attributes, including creativity,
embodied in the ability to perform labor so
as to produce economic value.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
5
* Medard Nana Djomo Jules and Sikod Fondo, (2012). “The Effects of Human Capital on Agricultural Productivity and Farmer’s Income in
Cameroon”. International Business Research, Vol. 5, No.4. April, pp 149-159

1. Definition of Human Capital (cont'd)
Any efforts, and all types of spending aiming to increase
human productivity, skills, ability are considered to be a
“Human capital Investment”.
The main categories of human capital investments which
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
6
The main categories of human capital investments which
lead to improved human capabilities are:
1.
Education
2.
Training
3.
Healthcare and nutrition
4.
Manpower planning

2. Human Capital Index*
The Human Capital Index is a new measure for capturing and tracking
the state of human capital development around the world. It has four
different pillars:
1.
The Education
pillar contains indicators relating to
quantitative and qualitative aspects of education across
quantitative and qualitative aspects of education across
primary, secondary and tertiary levels and contains information
on both the present workforce as well as the future workforce.
2.
The Health and Wellness pillar contains indicators relating
to a population’s physical and mental well– being, from
childhood to adulthood.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
7
*World Economic Forum, (2013), “Human Capital Report, 2013”, http://www.weforum.org/reports/human-capital-report (4-9)

2. Human Capital Index (cont'd)
3.
The Workforce and Employment pillar is designed to
quantify the experience, talent, knowledge and training in
a country’s working–age population.
4.
The Enabling Environment pillar captures the legal
framework, infrastructure and other factors that enable
returns on human capital.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
8

3. Education and Human Capital
Education plays an essential role in human capital
formation and a necessary tool for sustainable socio-
economic growth.
Returns on education are both private to the individual in
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
9
Returns on education are both private to the individual in
the form of additional income, and to the general society in
the form of greater productivity provided by the educated.
(Becker G. S. 1964)*
* Becker, G. S. (1964), Human Capital: A Theoretical and Empirical Analysis with Special Reference to Education, New York: Columbia
University Press

3. Education and Human Capital (cont'd)
Education raises the productivity and efficiency of
individuals and thus produces skilled manpower
capable for leading the economy towards the path of
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
10
economic development.
Investment in education leads to a lower population
growth and a better health of population and labor
force. *
* Michaelowa, Katharina. (2000) “Returns to Education in Low Income Countries: Evidence for Africa.”
http://www.hwwa.de/Projects/Res_Programmes/RP/Development_Processes/VfS_EL_2000_Rev2.pdf

4. Main levels of Human investment
I.
Investment in children: All types of care which are
essential for the child mental and physical growth.
Childcare is directly related to the mother’s education
level.
level.
II.
Investment on Job-Training: Expenditure regarding
on-the-job training is a source of human capital
formation as the return of such expenditure in the form
of enhanced labor productivity is more than the cost of
it.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
11

4. Main levels of Human investment (cont'd)
III.
Investment in Education: Expenditure on education
considered as an investment since it is undertaken with
a view to increasing the future personal incomes (Return
on investment).
on investment).
IV.
Investment in Health: Includes all expenditure that
affect the life expectancy, strength and energy, of the
population. Medical advances, provision of clean
drinking water and good sanitation are various forms of
investment in health.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
12

5. Problems facing the decision making process
regarding human investment
1. Private investment:
A.
Problems facing the decision on the individual
level
level
B.
Problems facing the decision on the firm level
2. Public investment
C.
Problems facing the decision on the government
level
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
13

5. Problems facing the decision making process
regarding human investment (cont'd)
A. Problems facing the decision on the individual level:
1.
The risk and uncertainty: Calculating the expecting
returns is difficult because they occur in the future.
2.
Uniqueness: Every individual has his own experience of
2.
Uniqueness: Every individual has his own experience of
human capital investment.
3.
Education expenditures reasons are complex: They
could be considered as investment if the purpose of
acquiring skills is to develop a future professional career.
(Investment part of education spending). And, it could be
considered as spending, if education is just for studying
and learning for the self satisfaction. (Consumption part
of education spending)
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
14

5. Problems facing the decision making process
regarding human investment (cont'd)
B. Problems facing the decision on the firm level
Firms invest in human capital through on-job training.
If the employer didn’t take all his precautions to
guarantee his investments, he will take the risk to not to
get the planned return on his investments.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
15

5. Problems facing the decision making process
regarding human investment (cont'd)
C. Problems facing the decision on the government
level
The largest investor in human capital formation is
The largest investor in human capital formation is
the government, through public spending on
education and health care.
The main problem facing the government human
investment spending is “the quantity-quality trade
off”.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
16
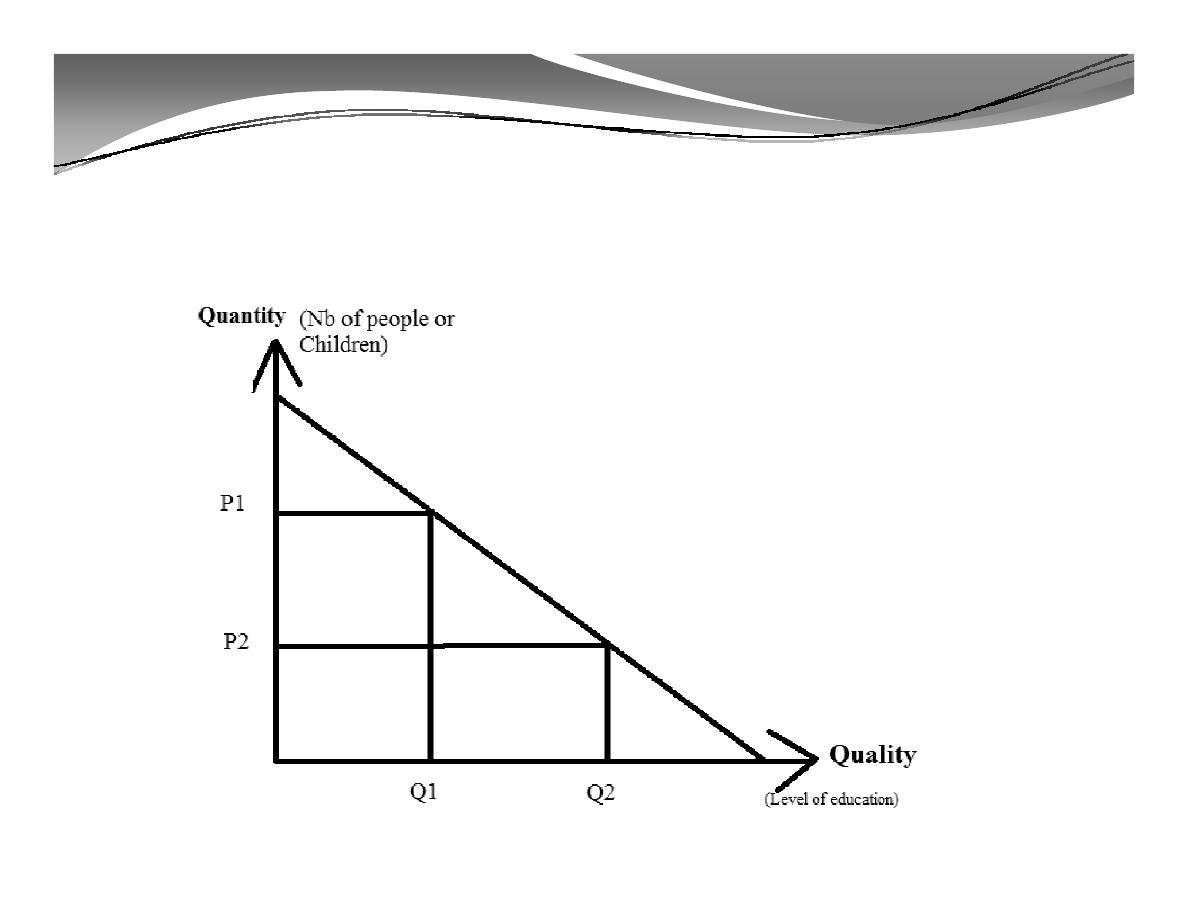
5. Problems facing the decision making process regarding human
investment (cont'd)
The quantity-quality trade off
Q1: Primary education
Q2: Secondary or
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
17
Q2: Secondary or
higher education
5. Problems facing the decision making process regarding human
investment (cont'd)
The quantity-quality trade off
Given the total government resources, we can compare between
two situations on the curve:
At (P1), the society has the choice to get more people (children)
with very limited level of education (Primary education Q1).
At (P2), with a less size of population, we can increase the level of
education to (higher education Q2).
A significant reduction in population growth rates is absolutely essential
for visible improvements in human capital investment.
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
18

Recommended Reading:
Farag Ezzat & Hebatallah Adam, (2015),
“Economics
Resources”,
Ain
Shams
University, Faculty of Commerce, Chapter 3
University, Faculty of Commerce, Chapter 3
Pages (70-87).
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
19

Thank You
Thank You
Dr/ Hebatallah ADAM - Economics Resources - 2015
20
