Gursharan Singh Tatla
mailme@gursharansingh.in
www.eazynotes.com
Introduction to Microprocessors
03-Aug-2011
1
www.eazynotes.com

Introduction to Microprocessors
The microprocessor is one of the most important components of
a digital computer.
It acts as the brain of the computer system.
As technology has progressed, microprocessors have become
faster, smaller and capable of doing more work per clock cycle.
Sometimes, microprocessor is written as
µ
P.
( µ is pronounced as Mu )
03-Aug-2011
2
www.eazynotes.com

Introduction to Microprocessors
Definition:
Microprocessor is the controlling unit or CPU of a micro-computer,
fabricated on a very small chip capable of performing ALU
operations and communicating with the external devices connected
to it.
03-Aug-2011
3
www.eazynotes.com

A Computer
A computer:
Accepts the data from the user.
Stores the data and the set of instructions supplied by the user in
memory.
Processes the data according to the instructions in the processing
unit.
Communicates the result to the user or stores it for further
reference.
03-Aug-2011
4
www.eazynotes.com
A Computer
A computer has the following units:
Input Unit
Output Unit
Memory Unit
Central Processing Unit
03-Aug-2011
5
www.eazynotes.com

A Computer
INPUT UNIT
The input unit consists of the devices which accept the data and instructions from
the user and communicates it to the CPU.
The various input devices are: keyboard, mouse, joystick, trackball etc.
OUTPUT UNIT
It provides the result of the various operations performed by the CPU to the user.
The various output devices are: printers, monitors, loudspeakers etc.
03-Aug-2011
6
www.eazynotes.com

A Computer
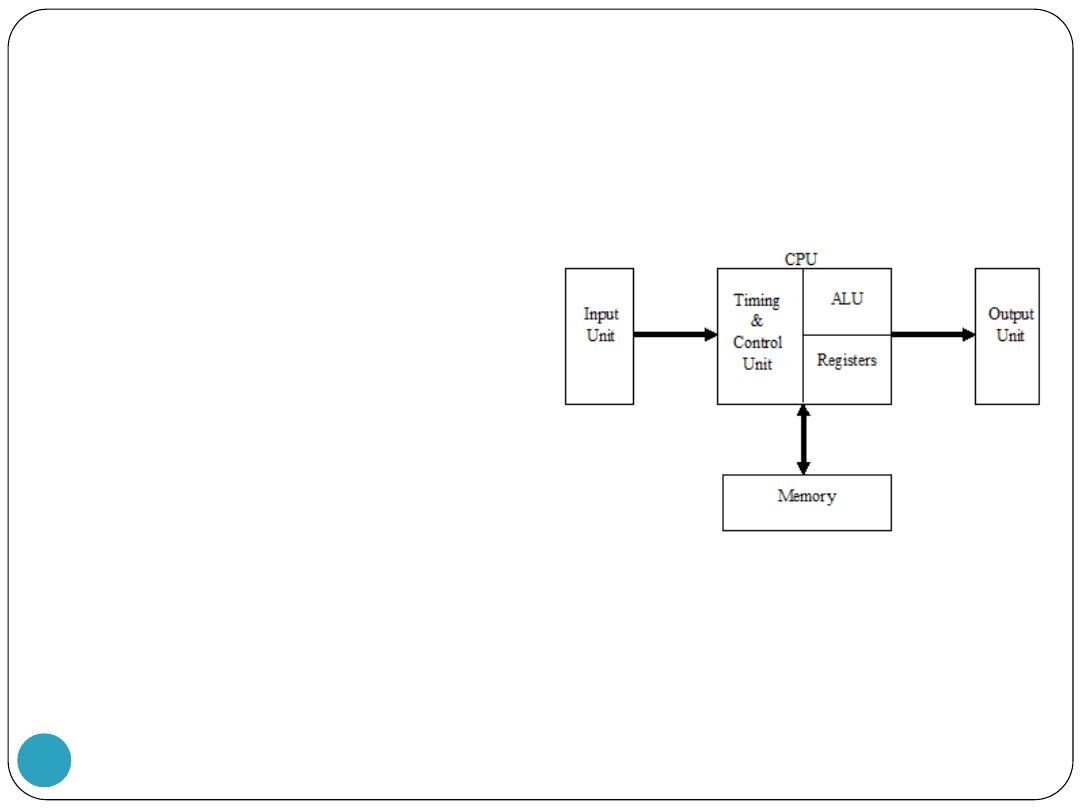
CENTRAL PROCESSING UNIT (CPU)
The CPU is the heart and nerve centre of the computer.
It fetches the instruction and data from the peripheral devices and
performs all the arithmetic operations, takes logical decision and control
the operation of all other units.
Various sub-blocks of the central processing unit are:
Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU)
Timing & Control Unit
Registers
03-Aug-2011
7
www.eazynotes.com

A Computer
ARITHMETIC AND LOGIC UNIT (ALU)
This unit perform all the logical and arithmetic operations.
Various arithmetic operations are: addition, subtraction, increment and decrement etc.
Various logical operations are: AND, OR, NOT, XOR, etc.
TIMING AND CONTROL UNIT
This unit controls the entire operations being performed by the system.
It controls the operations of ALU, input/output devices and memory unit.
This unit interprets the instructions and generates various timing and control signals.
REGISTERS
A register is a very small amount of very fast memory that is built into the CPU in order to store
the current data and instructions which are being executed by the CPU.
03-Aug-2011
8
www.eazynotes.com

A Computer
MEMORY UNIT
It stores the program statement and the data i.e. the information supplied
from the input unit.
It also stores the final output.
This is connected to the CPU by means of a bidirectional bus.
The CPU processes the information as taken from the memory and
performs the operations in the ALU section.
The results are either transferred to the output unit or stored in the
memory for later use by the CPU.
03-Aug-2011
9
www.eazynotes.com
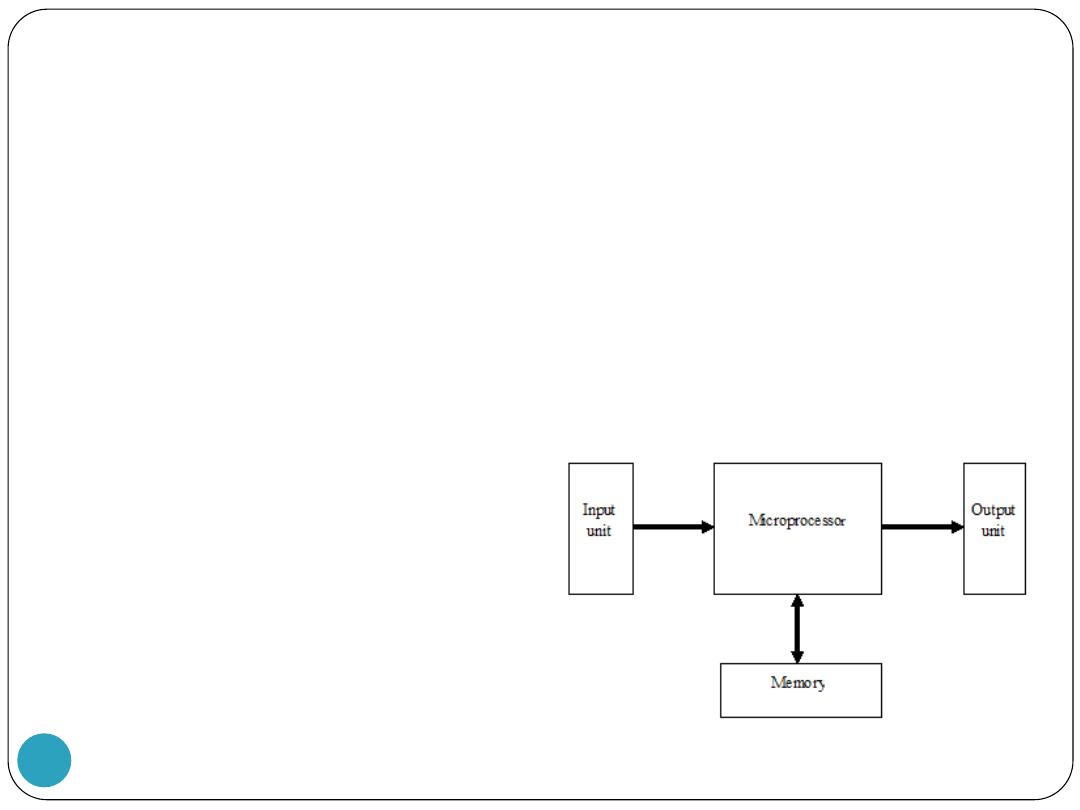
A Micro-Computer
As the name implies, microcomputers are small computers.
The block diagram of the microcomputer is similar to the
computer except that the central processing unit of the
microcomputer is contained in a single IC called the
microprocessor.
03-Aug-2011
10
www.eazynotes.com

A Micro-Computer
A microprocessor is a LSI (Large Scale Integration) IC that does almost
all the functions of the CPU.
It is also defined as a CPU contained in a single chip.
The basic function of the microprocessor is:
to fetch the instructions stored in the main memory
identify the operations and the devices involved in it
and accordingly generate control signals to determine when a given action
is to take place.
We can say that a computer with a microprocessor as its CPU, is
known as Microcomputer.
03-Aug-2011
11
www.eazynotes.com

Some Definitions
Microprocessor:
The central processing unit built on a single IC is called
Microprocessor.
A microprocessor (sometimes abbreviated as µP) is a digital
electronic component with miniaturized transistors on a single
semiconductor integrated circuit (IC).
One or more microprocessors typically serve as a central processing
unit (CPU) in a computer system or handheld device.
03-Aug-2011
12
www.eazynotes.com

Some Definitions
Microcomputer:
A digital computer, in which one microprocessor has been provided
to act as a CPU, is called Microcomputer.
A desktop computer, laptop, notebook, palmtop, etc. contain one
microprocessor to act as a CPU and hence they come under the
category of microcomputer.
The term microcomputer is generally synonymous with personal
computer.
03-Aug-2011
13
www.eazynotes.com

Some Definitions
Multiprocessor System:
The CPU of a large powerful digital computer contains more than
one microprocessor.
High-end powerful servers, mainframe computers, supercomputers,
etc. contain more than one microprocessor to act as CPU.
A computer whose CPU contains more than one microprocessor is
called Multiprocessor System.
03-Aug-2011
14
www.eazynotes.com

Some Definitions
Microcontroller:
A highly integrated chip that contains all the components such as
CPU, RAM, some form of ROM, I/O ports, and timers is called
Microcontroller.
Unlike a general-purpose computer, which also includes all of these
components, a microcontroller is designed for a very specific task to
control a particular system.
03-Aug-2011
15
www.eazynotes.com

Microprocessor Characteristics
Instruction Set:
The set of instructions that a microprocessor can understand.
Bandwidth:
The number of bits processed in a single instruction.
Capability:
It depends upon the number of instructions and capability of each
instruction.
03-Aug-2011
16
www.eazynotes.com

Microprocessor Characteristics
Clock Speed:
The clock speed determines how many operations per second the processor can
perform.
It is also called Clock Rate.
Every computer contains an internal clock that regulates the rate at which instructions
are executed and synchronizes the various computer components.
The faster the clock, the more instructions the CPU can execute per second.
Clock speeds are expressed in megahertz (MHz) or gigahertz (GHz).
The microprocessors of personal computers have clock speeds of anywhere from 300
MHz to over 3.8 GHz.
03-Aug-2011
17
www.eazynotes.com

Microprocessor Characteristics
Word Length:
It depends upon the width of internal data bus, registers, ALU etc.
An 8-bit microprocessor can process 8 bit data at a time.
A processor with longer word length is more powerful and can
process data at a faster speed as compared to processor with shorter
word length.
The word length ranges from 4 bits for small microprocessor, to 64
bits for high-end microcomputers.
03-Aug-2011
18
www.eazynotes.com

Microprocessor Characteristics
Width of Data Bus:
This is the size of the data bus. It defines the number of bits that can be transferred through data
bus.
Width of Address Bus:
This parameter decides the memory addressing capability of the microprocessor. The maximum
size of the memory unit is decided by this parameter.
Input/Output Addressing Capability:
The maximum number of the input/output ports accessed by the microprocessor depends upon
the width of the input/output address provided in the input/output instruction.
03-Aug-2011
19
www.eazynotes.com

Microprocessor Characteristics
Data Types:
The microprocessor handles various types of data formats like binary,
BCD, ASCII, signed and unsigned numbers.
Interrupt Capability:
Interrupts are used to handle unpredictable and random events in the
microcomputer.
It is used to interrupt the microprocessor.
Interrupt driven input/output improves the throughput of a system.
03-Aug-2011
20
www.eazynotes.com

Features of Microprocessor
Cost:
The most important feature of a microcomputer is its low cost.
Because of the widespread use of microprocessors, the volume of production is
very high.
That is why, microprocessor chips are available at fairly low prices.
Size:
The second important feature of a microprocessor is its small size.
As a result of improvement in fabrication technology, VLSI, electronic circuitry
has become so dense that a minute silicon chip can contain hundred and thousands
of transistors.
03-Aug-2011
21
www.eazynotes.com

Features of Microprocessor
Power Consumption:
Another important feature is its low power consumption.
Microprocessors are normally manufactured by Metal-Oxide semiconductor technology, which
has the feature of low power consumption.
Versatility:
The microprocessors are versatile.
Keeping the same basic hardware, a microprocessor-based system can be configured for a
number of applications by simply altering the software program.
Reliability:
Another important property of microprocessors is its extreme reliability.
It has been established that the failure rate of an IC is fairly uniform at the package level,
regardless of its complexity.
03-Aug-2011
22
www.eazynotes.com

Micron
A unit of length equal to one millionth of a meter.
It is denoted by
µ
(Mu)
.
For Example:
If we pluck a hair from the head, it is very thin.
But a hair is more than 2000 times wider than a transistor on a microprocessor.
Wires between transistors are even thinner.
They're more than 4000 times thinner than a hair.
A hair is about 100 microns in diameter.
That means, a transistor is just 0.045 microns wide.
03-Aug-2011
23
www.eazynotes.com

03-Aug-2011
24
www.eazynotes.com
