Practical Immunology
and Serology
Lab.7
Hawler Medical University
College of Health Sciences
Clinical Biochemistry Dept.
Ass. Lec. Amer Ali Khaleel
(M.Sc. Medical Immunology)
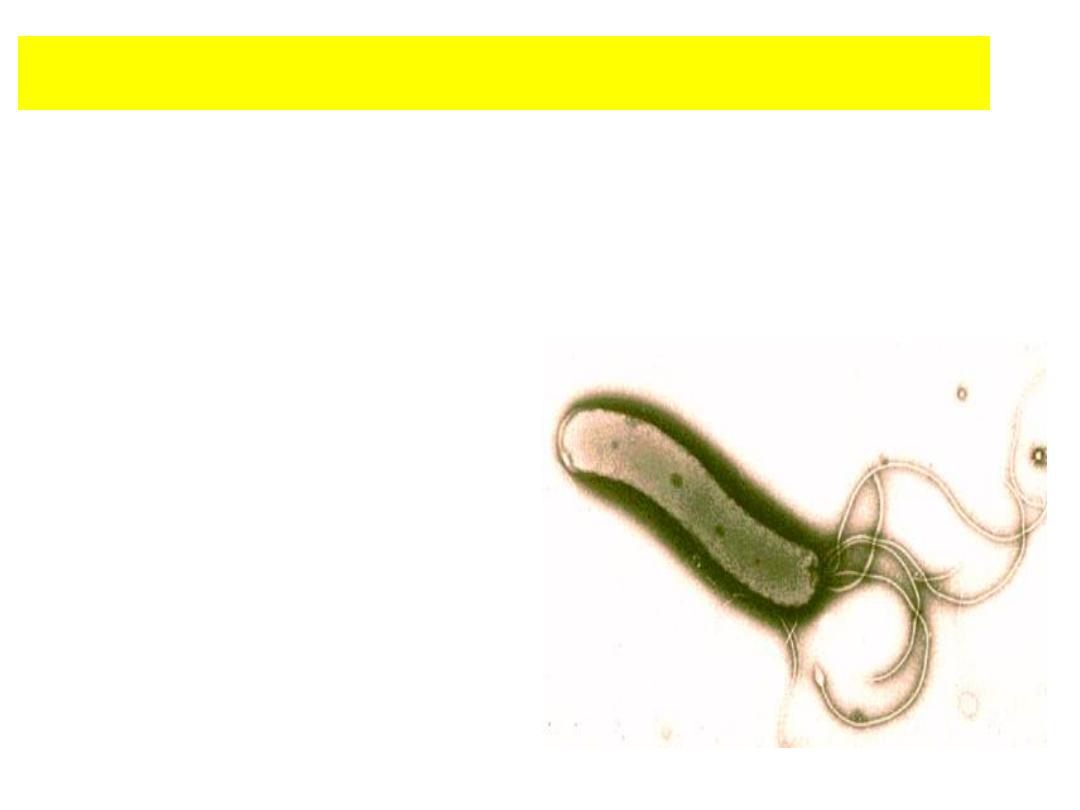
Helicobacter pylori

Introduction:
• Helicobacter pylori
is major human pathogen associated with gastric
antral epithelium in patients with active chronic gastritis.
• H. pylori
is the bacterium (germ) responsible for causing most stomach
and duodenal ulcers and many cases of stomach inflammation (chronic
gastritis) & cancer.
• H. pylori
testing is used to diagnose an infection due to the bacteria
and to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
• The organism is present in 95% to 98% of patients with duodenal ulcers
and 60% to 90% of patients with gastric ulcers.
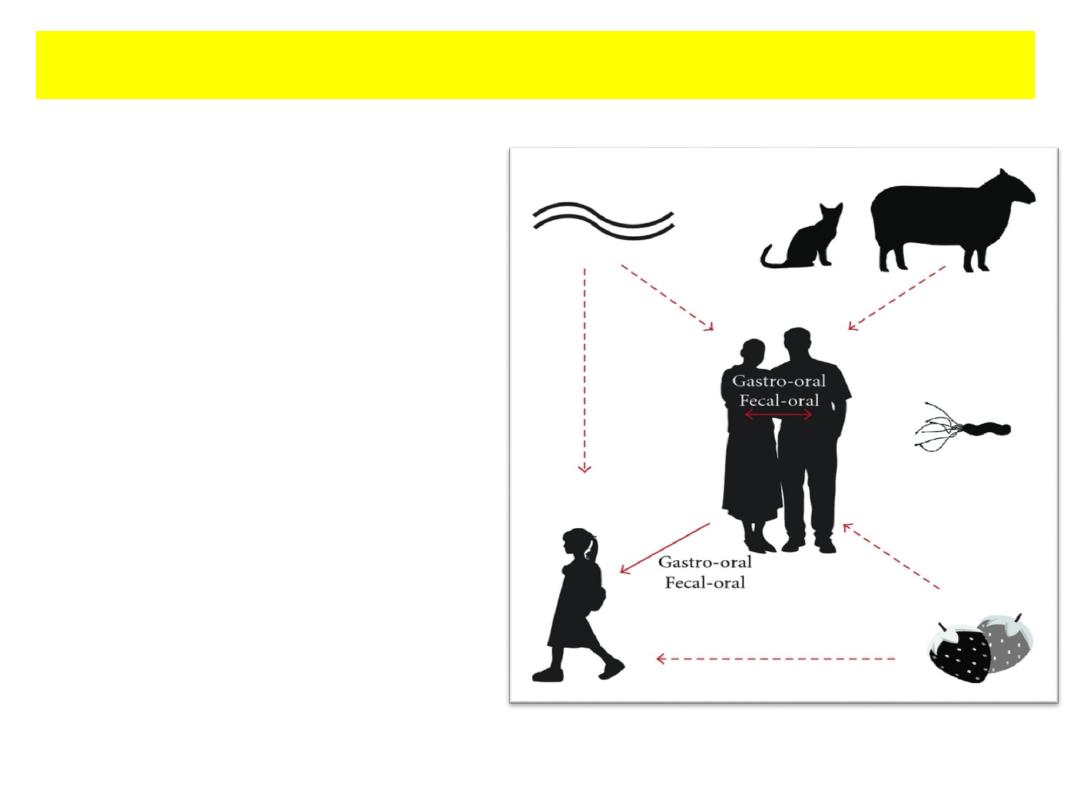
• Transmissible
• Oral-oral and oral-fecal
• Infects the human
stomach.
• Produces inflammatory
response.
• This brings up the point of
the importance of “hand
washing”.
H. pylori Infection transmission:

Symptoms of H. pylori infection:
• Abdominal pain with burning or gnawing sensation.
• Pain is often made worse with empty stomach; night time pain is
common.
• Poor appetite.
• Weight loss.
• Heart burn.
• Indigestion (dyspepsia)
• Belching.
• Nausea.
• Vomiting.
• Blood in stool.
Whole Blood
Serum
Plasma
Stool
Breath Test
Biopsy.
Specimens:

Time
Consuming
Methods
No.
Serology level
10-15 min
H. pylori Antibody Test Cassettes or Strips by Immunochromatography assay
1
10-15 min
H. pylori Antigen Stool (fecal) Strips test by chromatographic Immunoassay
2
10-15 min
H. pylori Urea Breath Test (UBT)
3
2 hours
ELISA (IgG/ IgM/ IgA)
4
45 minutes –
2 hours
ECL (IgG/ IgM)
5
Molecular level
7-10 days
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
6
Laboratory Diagnosis of
Helicobacter pylori :

• Widely available.
• Positive result may reflect previous (old) rather than current (recent)
infection not recommended for confirming eradication.
• Blood tests are used to measure antibodies to
H. pylori.
• Test not recommended for routine diagnosis or for evaluation of
treatment effectiveness.
• Blood tests for
H. pylori
cannot tell if you have a current infection or
how long you have had it, This is because the test can be positive for
years even if the infection is cured.
1-H. pylori
antibody
test cassette or strips by ICA.

1-H. pylori
antibody
test cassette or strips by ICA.
• Detects
to the bacteria and will not distinguish previous
infection from a current one.
• If test is negative, then it is unlikely that a person has H. pylori
infection.
• If ordered and positive, results should be confirmed using stool antigen
or breath test.
• As a result, blood tests cannot be used to see if the infection has been
cured after treatment.

2- H. pylori
antigen
stool (fecal)
stripes test ICA
• Detects directly the presence of
H. pylori
antigen in a stool sample.
•
A stool test can detect traces of
H. pylori
in the feces.
• This test can be used to diagnose the infection and confirm that it has
been cured after treatment.
•Useful before and after treatment.
•Process of stool collection may be distasteful to patient.
•False positive result possible with recent use of antibiotics or bismuth
preparation.
•The test is for qualitative detection of H. pylori antigen in stool sample
and dose not indicate the quantity of the antigens.

• H. pylori
Ag Rapid test kit result window has 2 pre-coated lines, "T"
(
H. pylori
Ag Test Line) and "C" (Control Line).
• Both the Test Line and the Control Line in result window are not visible
before applying any samples.
• The Control Line is used for procedural control and should always
appear if the test procedure is performed correctly.
• H. pylori
Ag Rapid test kit can identify Helicobacter pylori antigen in
human fecal specimen with a high degree of sensitivity and specificity.
Principle:
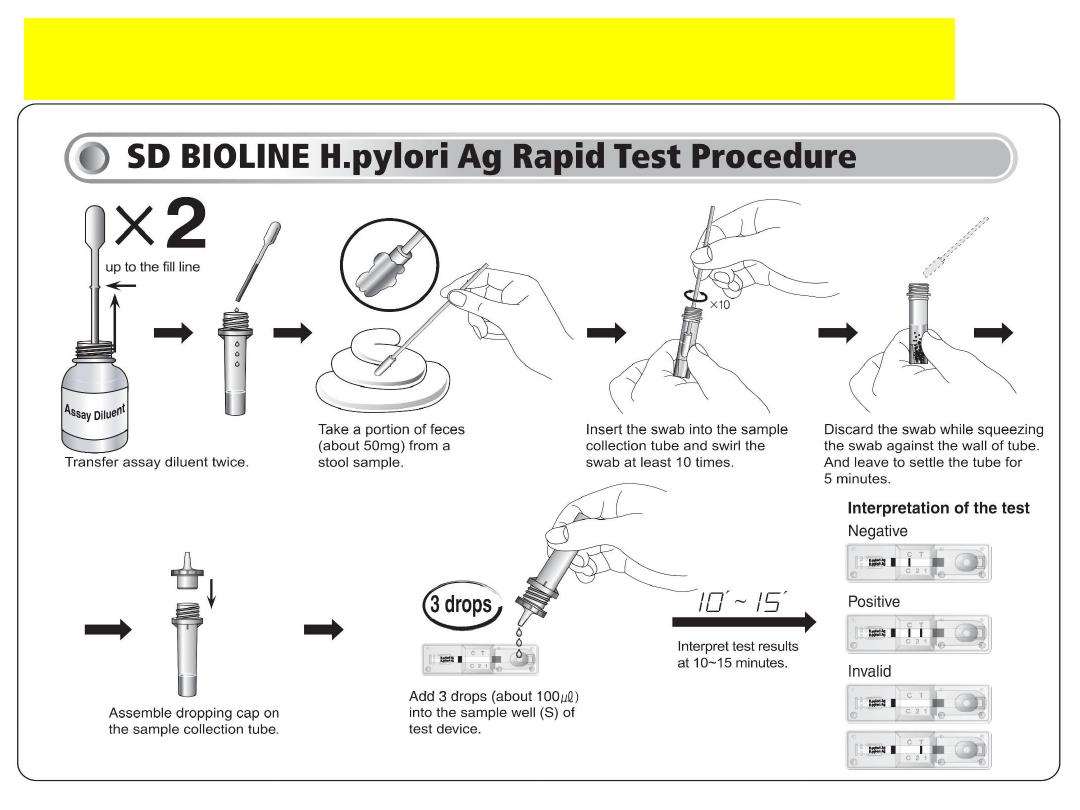
Procedure of the Test (Refer to figure):

The results are to be interpret as follows:
• One green line = negative (control test)
• One green line AND one red line = positive
• No line = invalid*
* The absence of the control line, which is the upper green
line, makes the result invalid. In this case, the sample must be
retest.
Interpreting the results:

3- H. pylori
breath Test
(Carbon Isotope-urea
Breath Test, or UBT).
• A person drinks a liquid containing a low level of
radioactive material that is harmless or a nonradioactive
material.
• If H. pylori is present in the person's gastrointestinal tract,
the material will be broken down into "labeled" carbon
dioxide gas that is expelled in the breath.
Biopsy:
Biopsy most accurate way to detection of
H. pylori
infection.
• To remove the tissue sample, you have a procedure called
The procedure is done in the hospital or private sector.
• Usually a biopsy is done if endoscopy is needed for other reasons.
Reasons include diagnosing the ulcer, treating bleeding, or making sure
there is no cancer.
• The test may also be recommended for a condition called dyspepsia.

Limitation of the test:
• A negative result does not preclude the possibility of
infection with H. pylori. Other clinically available tests are
required if questionable results are obtained.
• As with all diagnostic tests, a definitive clinical diagnosis
should not be based on the results of a single test, but should
only be made by the physician after all clinical and
laboratory findings have been evaluated.
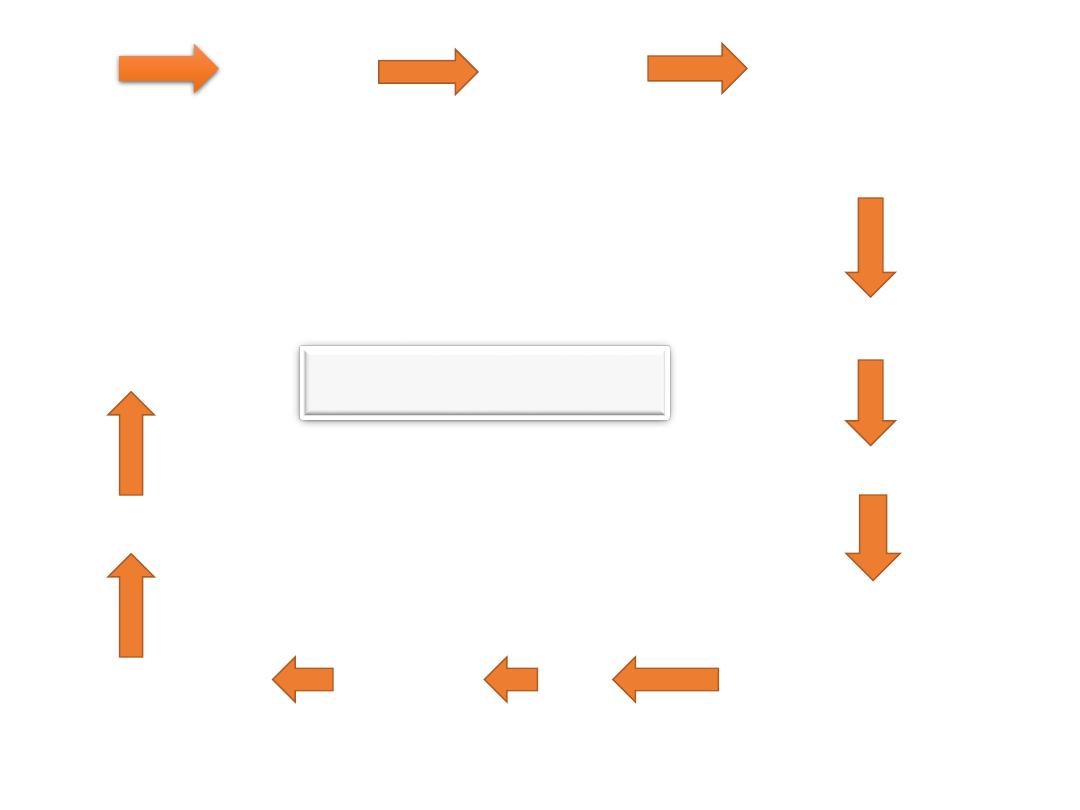
Patient physician laboratory Detection
Helicobacter pylori
in the specimen (Serum)
Positive
Medication
after one month
Detection
Send the biopsy into
Endoscopy +VE
Helicobacter pylori
histological laboratory
(take Biopsy)
in the specimen (Stool)
Eradication therapy
Flow-chart
Confirmation
of cure

1- Trying to drawing of blood sample from your colleagues.
2- Preparation of serum.
3- Do H. pylori for your colleagues.
4- Report the result and interpretation.
Practical Part
Safety Guidelines
1-You must wear a lab coat (and do it up) in all Immunology labs.
2-At the end of the lab. clean your lab bench and equipment.
Any Questions
