RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
Prof. Fakhir Yousif2
Definition
EpidemiologyRheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common form of inflammatoryarthritis, occurring throughout the world and in all ethnic groups.The prevalence of RA is approximately 0.8–1.0%, with a female-to-male ratio of 3 : 1.The prevalence is lower in South-east Asia (0.4%). The highest prevalencin the world is in Pima Indians (5%).
Etiology
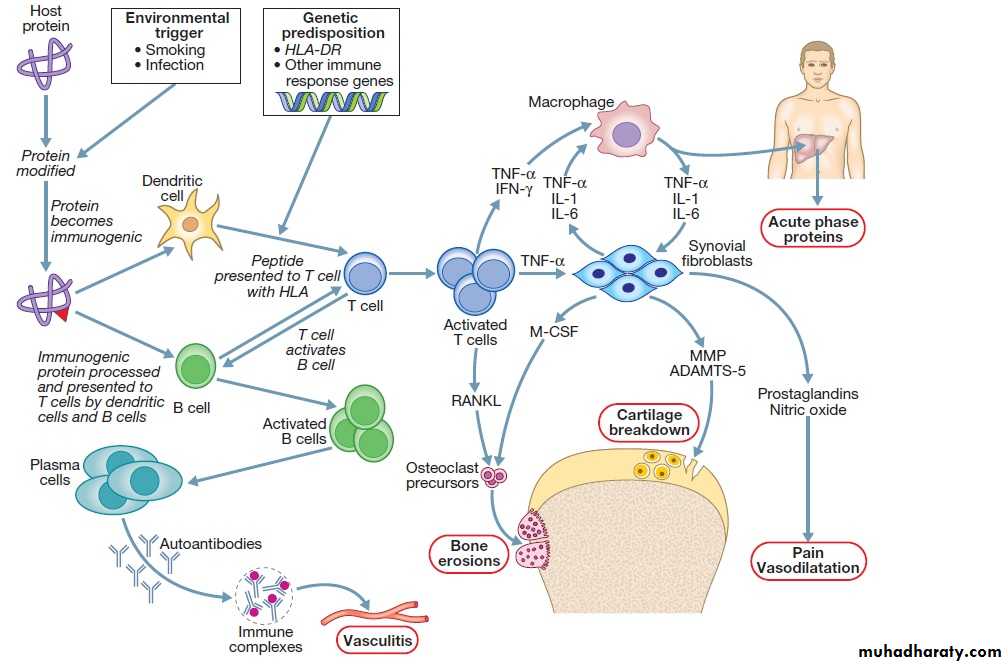
Genetic factors in RA are important in defining disease susceptibility and severity.Family studies have demonstrated an increased risk for disease in siblings of persons affected with RA. Concordance has been found to be 12% to 15%
in monozygotic and 4% in dizygotic twins, strong evidence for a major influence of genetic factors in disease causation . The strongest association is with variants in the HLA region. Recent studies have shown that the
association with HLA is determined by variations in three aminoacids in the HLA-DRβ1
Enviromental
• viruses (e.g., parvovirus B19, Epstein-Barr virus), Mycoplasma, and other bacteria (e.g., streptococci).cigarete smoking
Rheumatoid factor (RF), an immunoglobulin M (IgM) auto-antibody against the Fc portion of an IgG molecule first described by Waaler in 1940, is the main serologic marker, found in 75% to 80% of patients
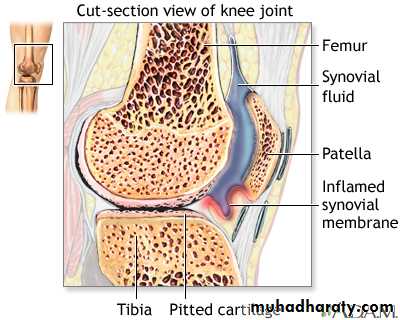
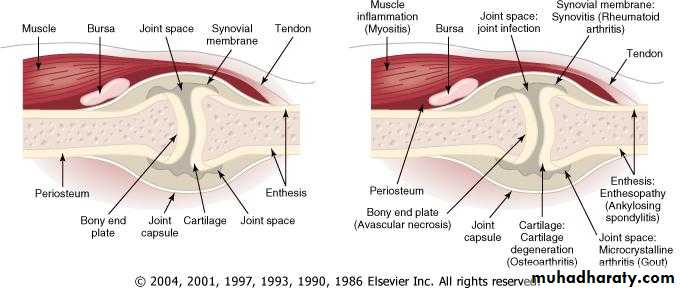
The synovium of RA assumes the appearance of a reactive lymph node because of the extensive infiltration by plasma cells, macrophages, and lymphocytes in the form of large lymphoid follicles.
One characteristic feature of RA is the invasion of and damage to cartilage, bone, and tendons by an infiltrating inflammatory synovial tissue mass called the pannus
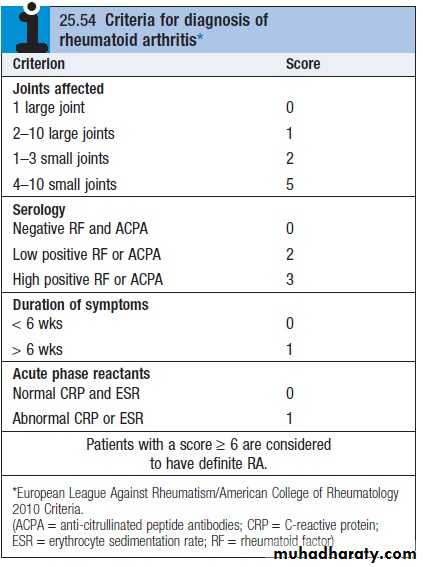
Diagnosis of RA is made with four or more of the following
Morning stiffness (> 1 hourArthritis of three or more joint areas
Arthritis of hand joints
Symmetrical arthritis
Rheumatoid nodules
Seropositive - Rheumatoid factor OR Anti-CCP (citrullinated C peptide)
Radiological changes
Duration of 6 weeks or more
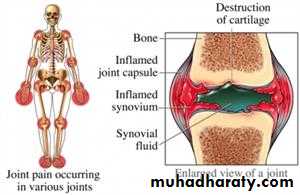
The typical presentation is with pain, joint swelling and stiffness affecting the small joints of the hands, and wrists in a symmetrical fashion. Large joint involvement, systemic symptoms and extra-articular features may also occur
Sometimes RA has an acute onset, with severe early morning stiffness, polyarthritis and pitting oedema. This occurs more commonly in old age. Another presentation is with proximal muscle stiffness imicking polymyalgia rheumatica Occasionally, the onset is palindromic, with relapsing and remitting episodes of pain, stiffness and swelling that last for only a few hours or days
Examination typically reveals swelling and tenderness of the affected joints. Erythema is unusual and its presence suggests coexistent sepsis. Characteristic deformities may develop with long-standing uncontrolled disease
Joints Affected :
Typically involves elbows, wrists, MCP, and PIP joints1st & 2nd cervical vertebrae frequently involved
Unaffected joints :
Thoracolumbar spine, DIPs & SI joints
Rheumatoid Arthritis: PIP Swelling
Swelling is confined to the area of the joint capsuleSynovial thickening feels like a firm sponge
20
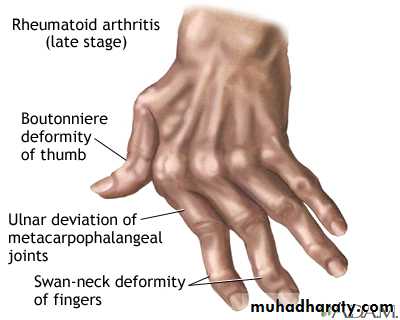
Rheumatoid HAND
An across-the-room diagnosisProminent ulnar deviation in the right hand
MCP and PIP swelling in both hands
MCP sublaxation
Synovitis of left wrist
21
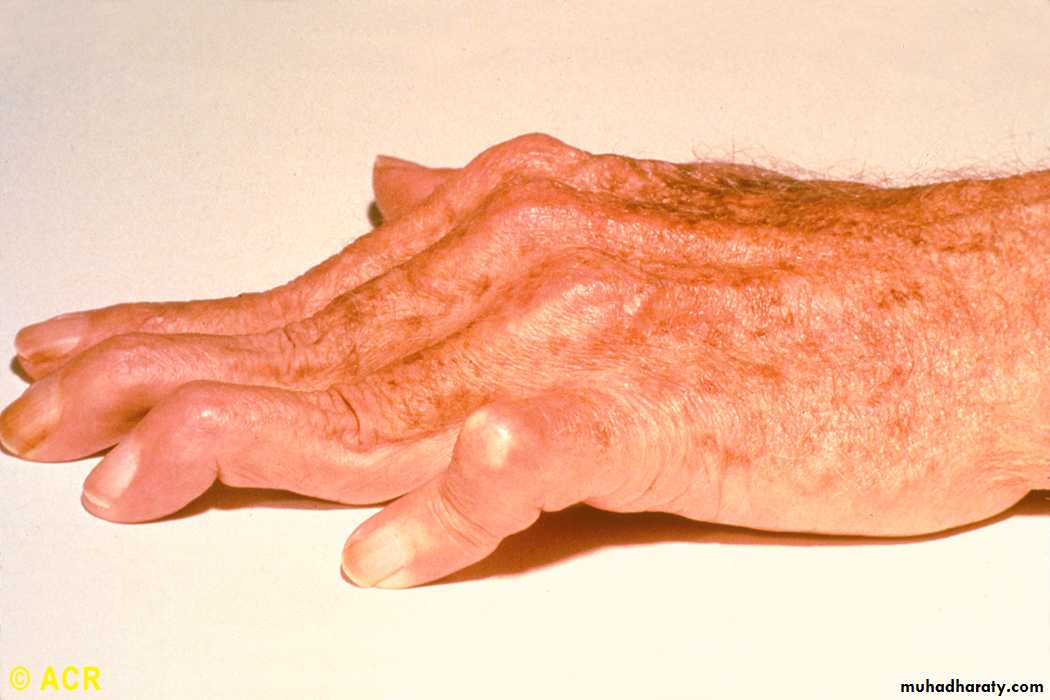
Rheumatoid arthritis: swan-neck and boutonnière deformity, hand
22
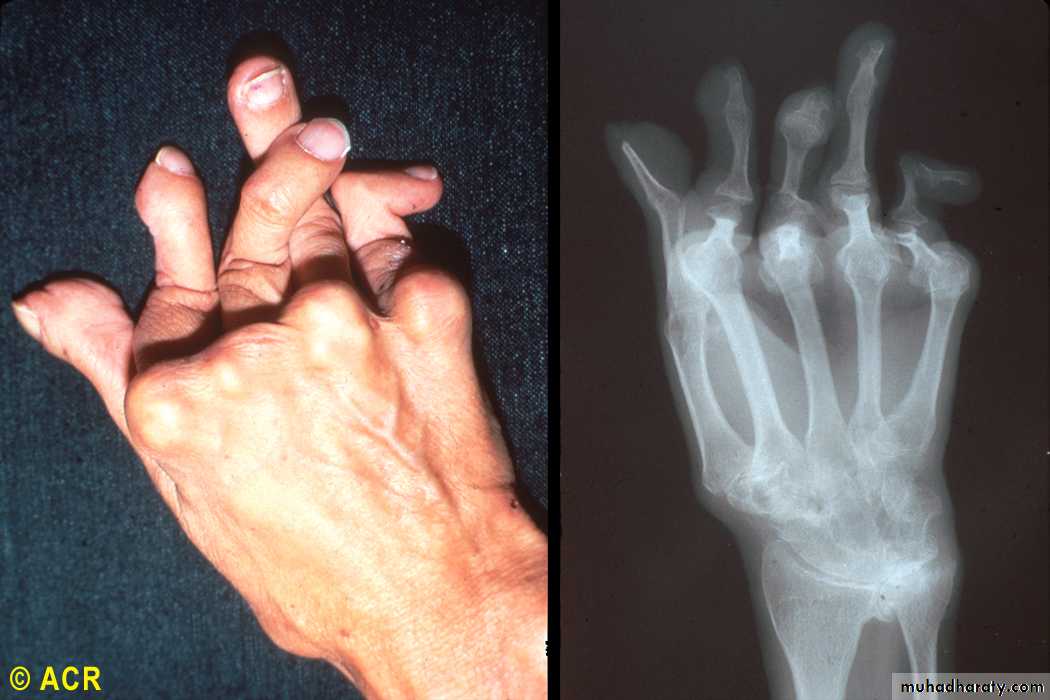
Rheumatoid arthritis: arthritis mutilans, hand (clinical and radiograph)
23
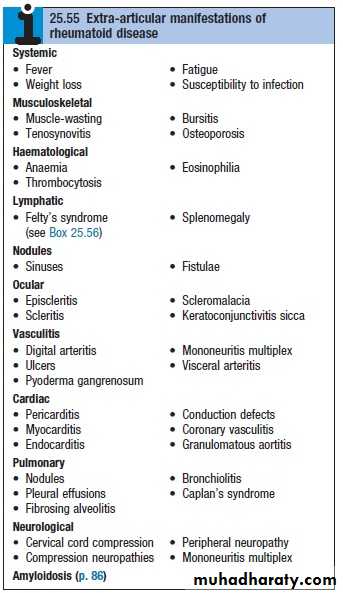
EXTRA-ARTICULAR MANIFESTATIONS OF RHEUMATOID DISEASE
Haematological
AnaemiaThrombocytosis
Eosinophilia
Lymphatic
Splenomegaly
Felty's syndromeOcular
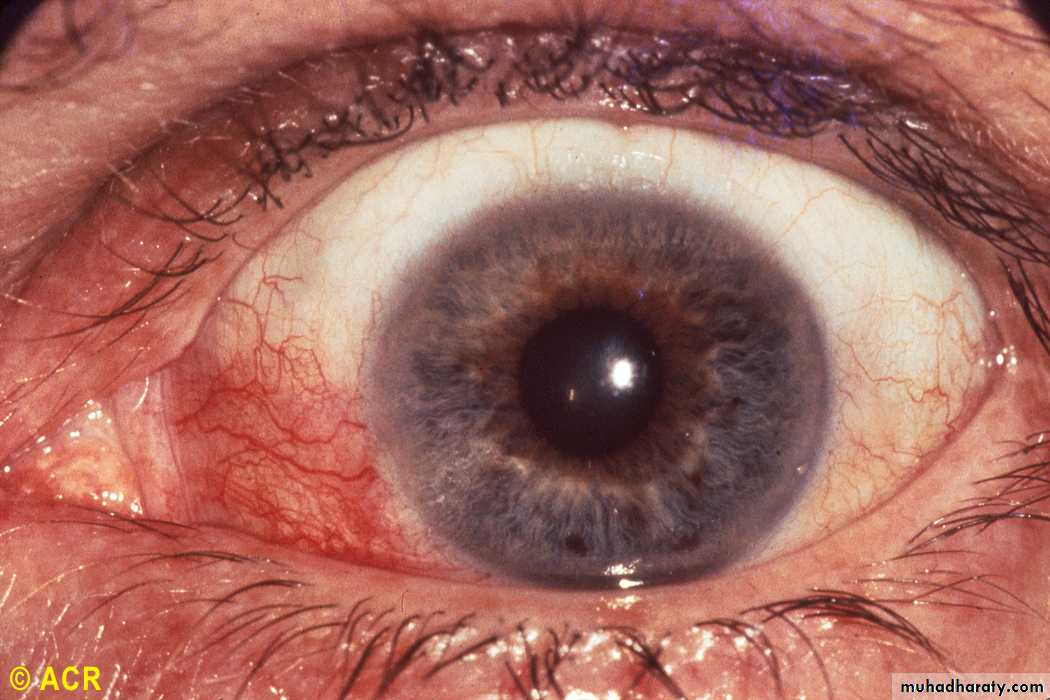
EapiscleritisScleritis
Scleromalacia
Keratoconjunctivitis sicca
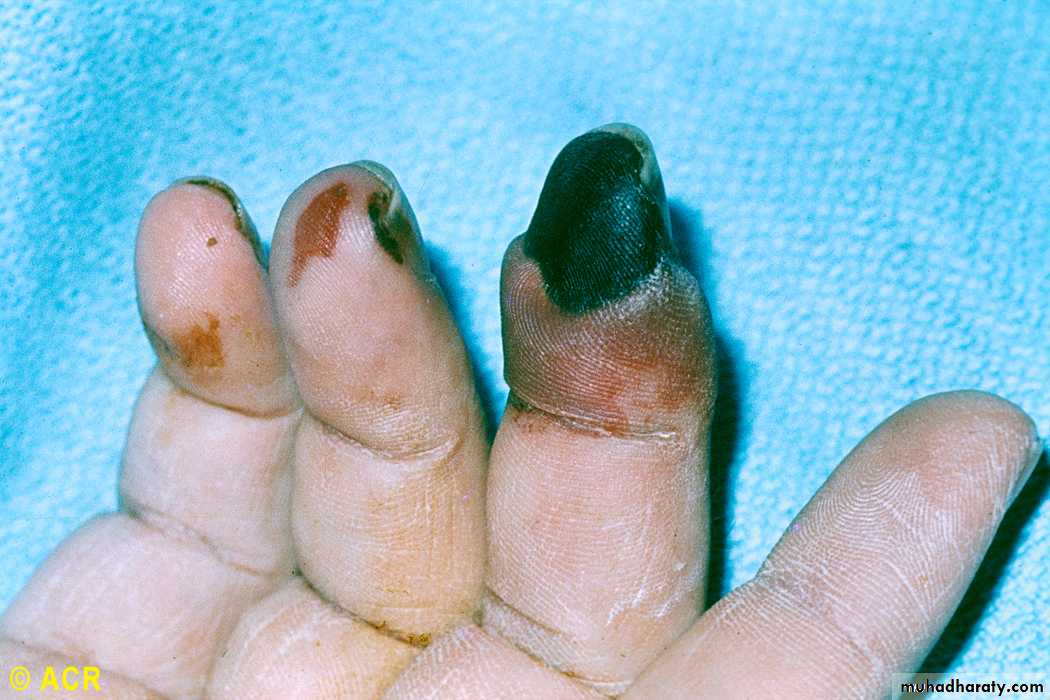
Vasculitis
Digital arteritisUlcers
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Mononeuritis multiplex
Visceral arteritis
Cardiac
Pericarditis
Myocarditis
Endocarditis
Conduction defects
Coronary vasculitis
Granulomatous aortitis
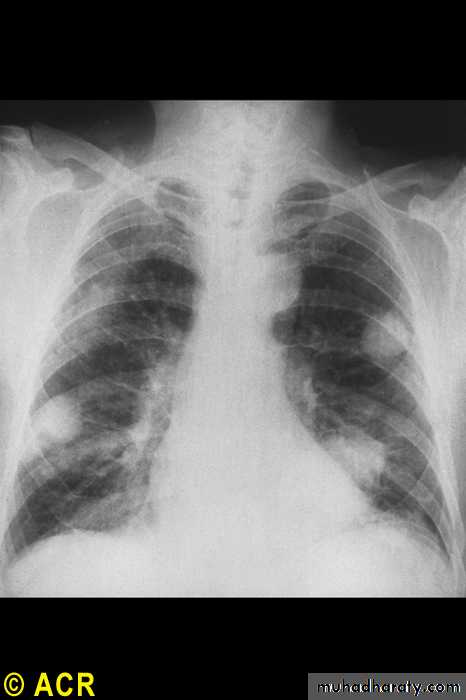
Pulmonary
NodulesPleural effusions
Fibrosing alveolitis
Bronchiolitis
Caplan's syndrome
Neurological
Cervical cord compressionCompression neuropathies
Peripheral neuropathy
Mononeuritis multiplex
Cutaneous features
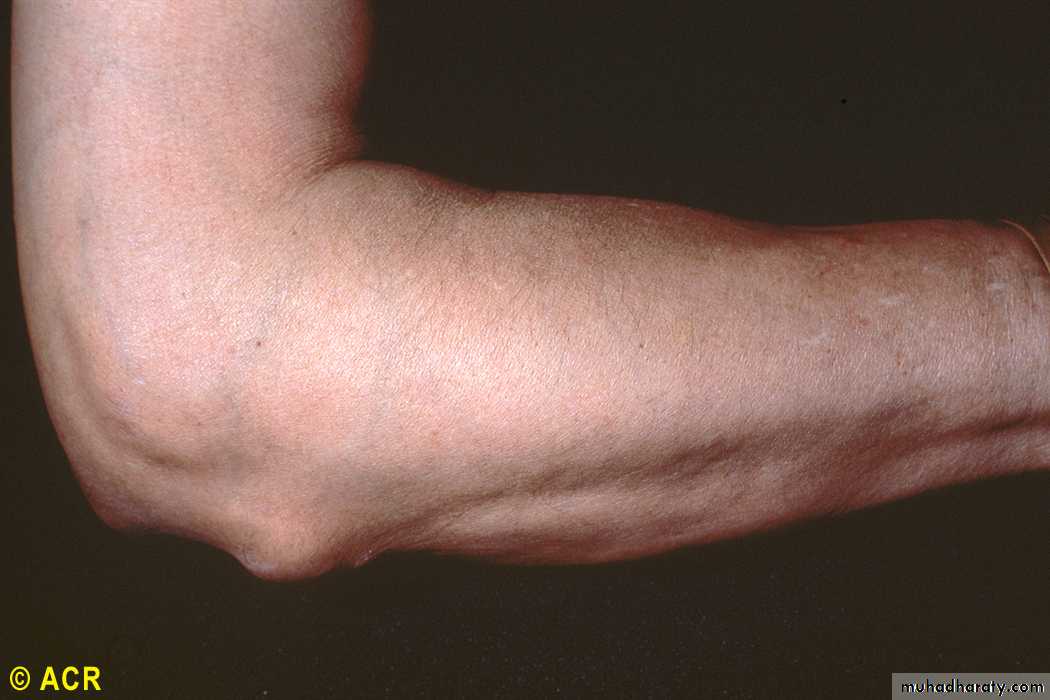
Subcutaneous rheumatoid nodules occur almost exclusively in seropositive patients, usually at sites of pressure or friction such as the extensor surfaces of the forearm, sacrum, Achilles tendon and toes
Rheumatoid arthritis: subcutaneous nodule, olecranon
35
Rheumatoid arthritis: episcleritis
36
Rheumatoid arthritis: vasculitis and gangrene, fingers
37
Rheumatoid arthritis: pulmonary nodules
38
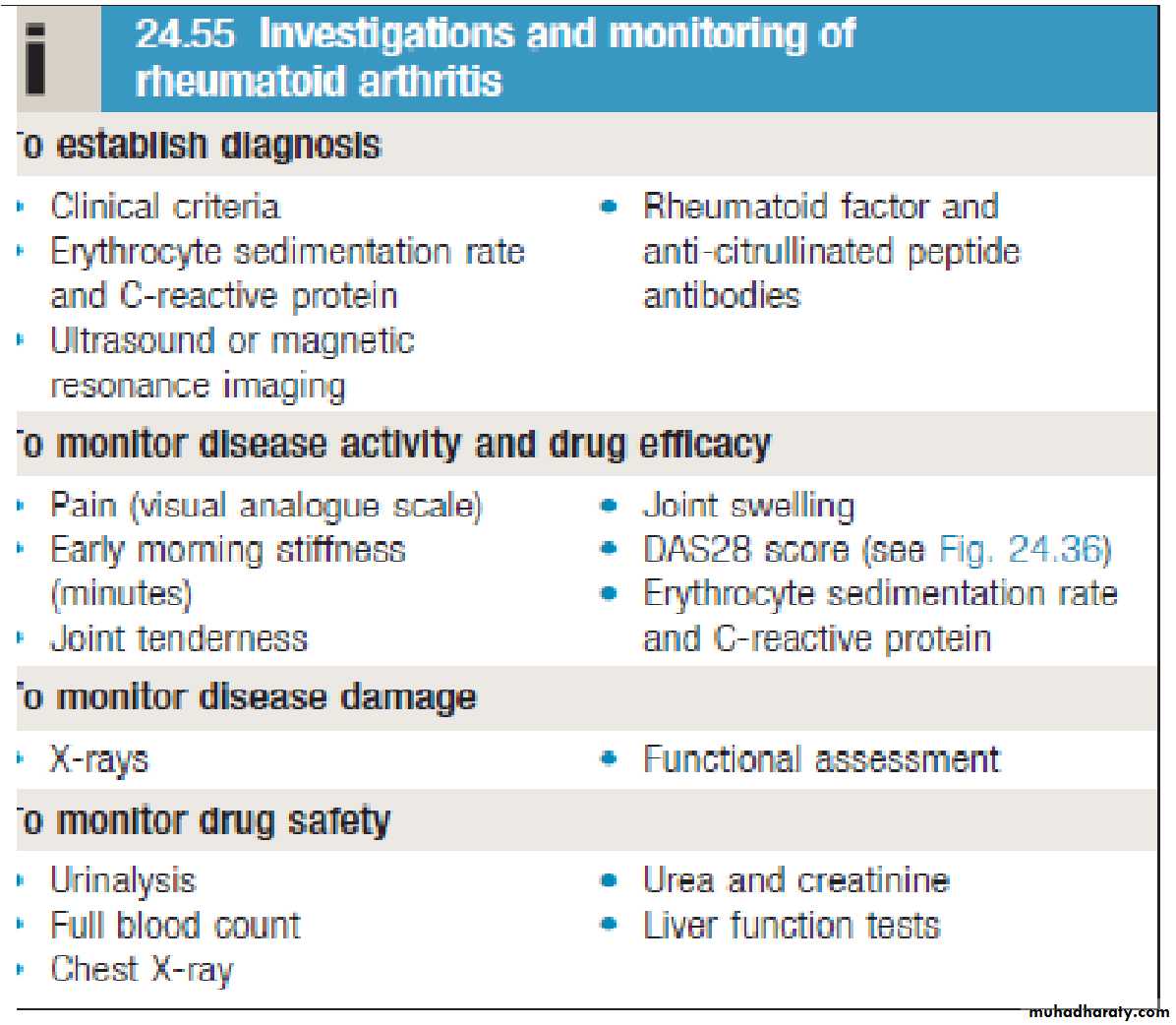
Investigations
The diagnosis of RA is essentially clinical but investigationsare useful in confirming the diagnosis and assessing disease
activity
Raised inflammatory markers . Reasonable correlation with clinical activity
Mild anemia & thrombocytosis
S. Rheumatoid factor (Agglutination method). Positive in near 70-80% cases (western countries). Not specific
ACPA
antibodies. Similar sensitivity to RF but more specific (up to 95%)
39
Examination of joint fluid
the most helpful laboratory procedure. The fluid is inflammatory, with more than 10,000 white blood cells and a predominance of polymorphonuclear leukocytes, typically 80% or more. Rheumatoid factor, an IgM antibody directed to IgG, is found in 80 to 90% of patients with RA.... XR-Findings
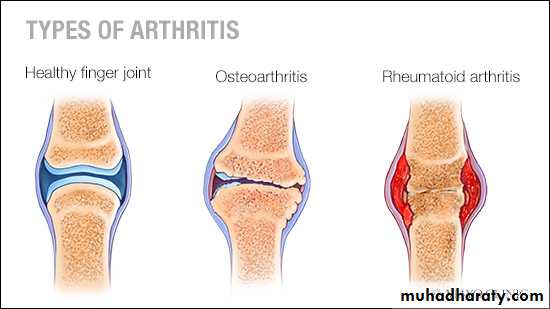
Peri articular osteopenia
Marginal erosions (at least months of persistent activity)
Joint space narrowing (cartilage loss)
Ankylosis (wrists)
Deformities
42