
The Eyelids-I

Out-lines
1- Gross and details eyelid structures.
2- Congenital eyelid malformations.
3- Malposition of eyelid.
4- Inflammatory conditions of eyelid.
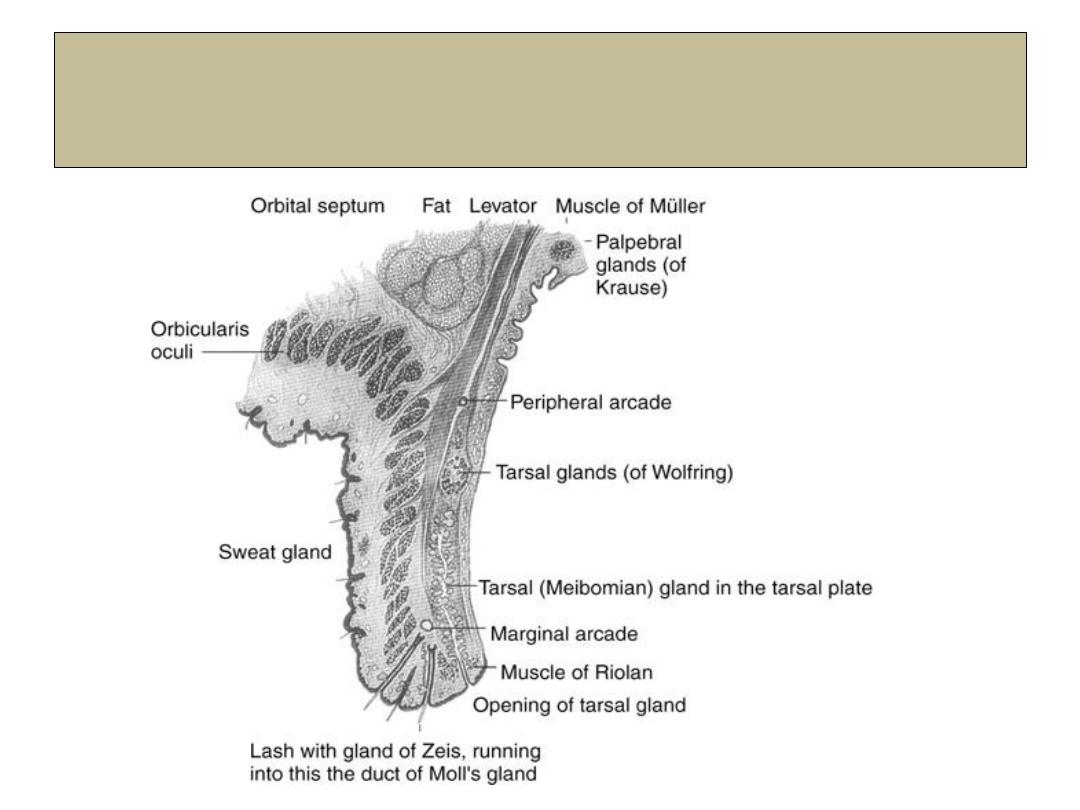
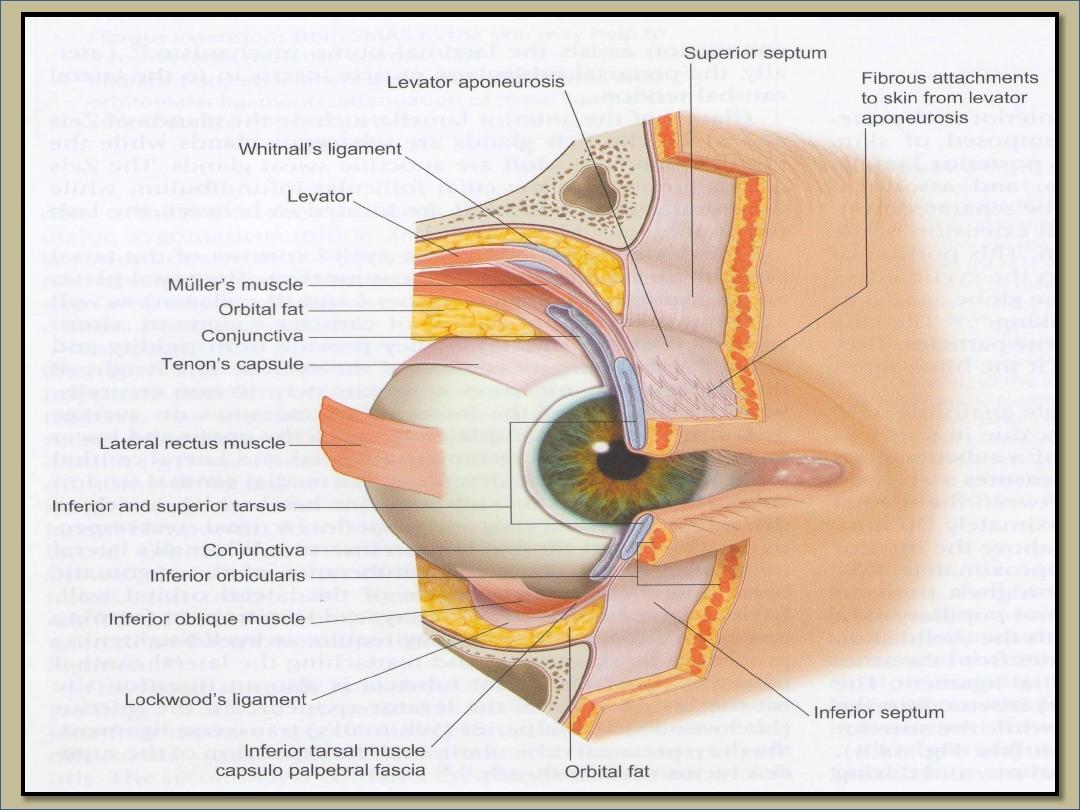
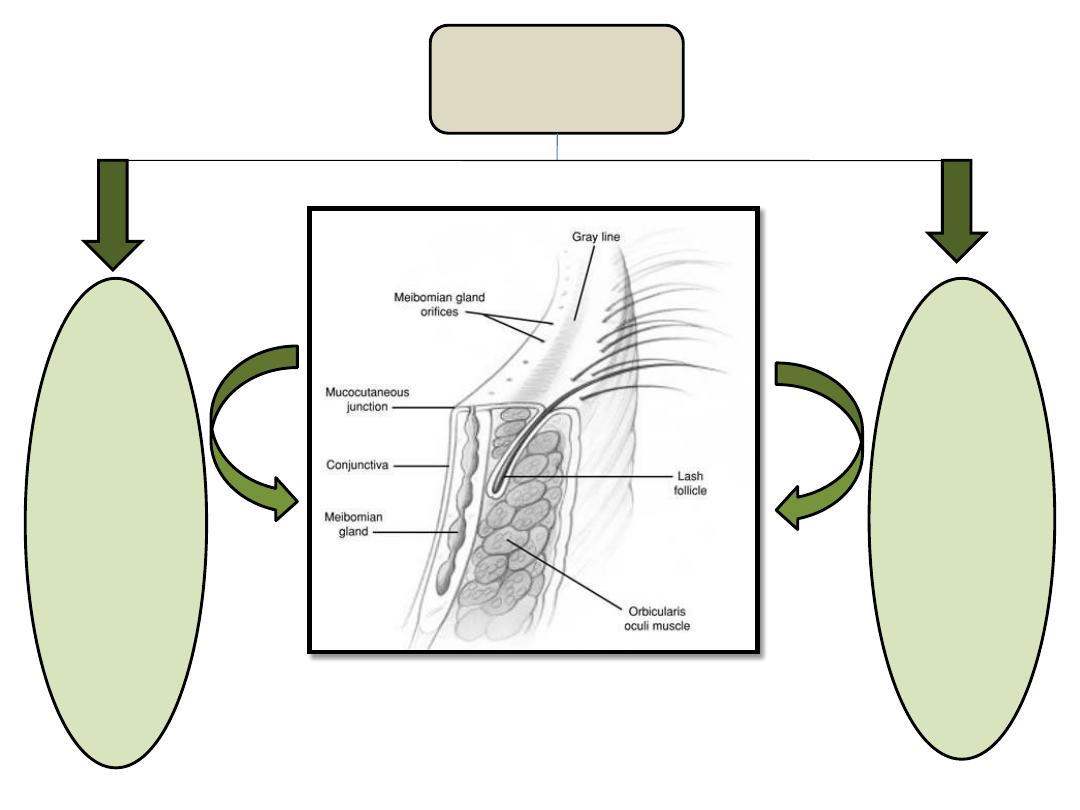
Gross and detailed eyelid structures
Anatomy
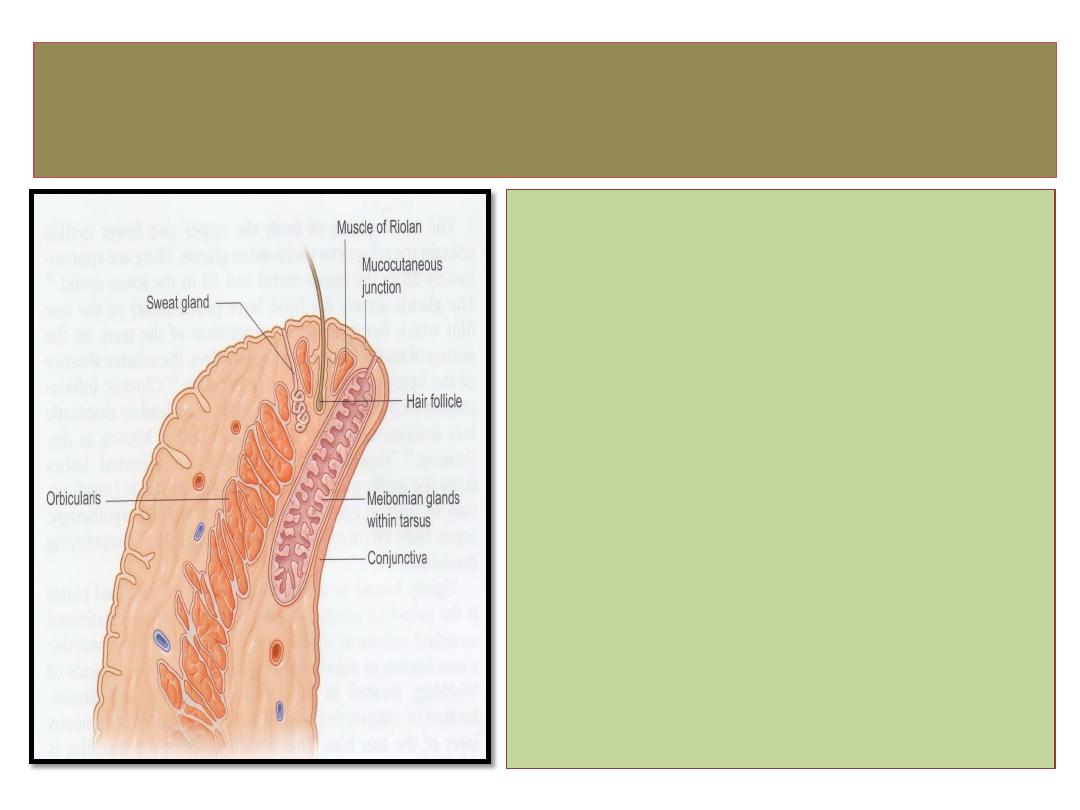
Structure of eyelid
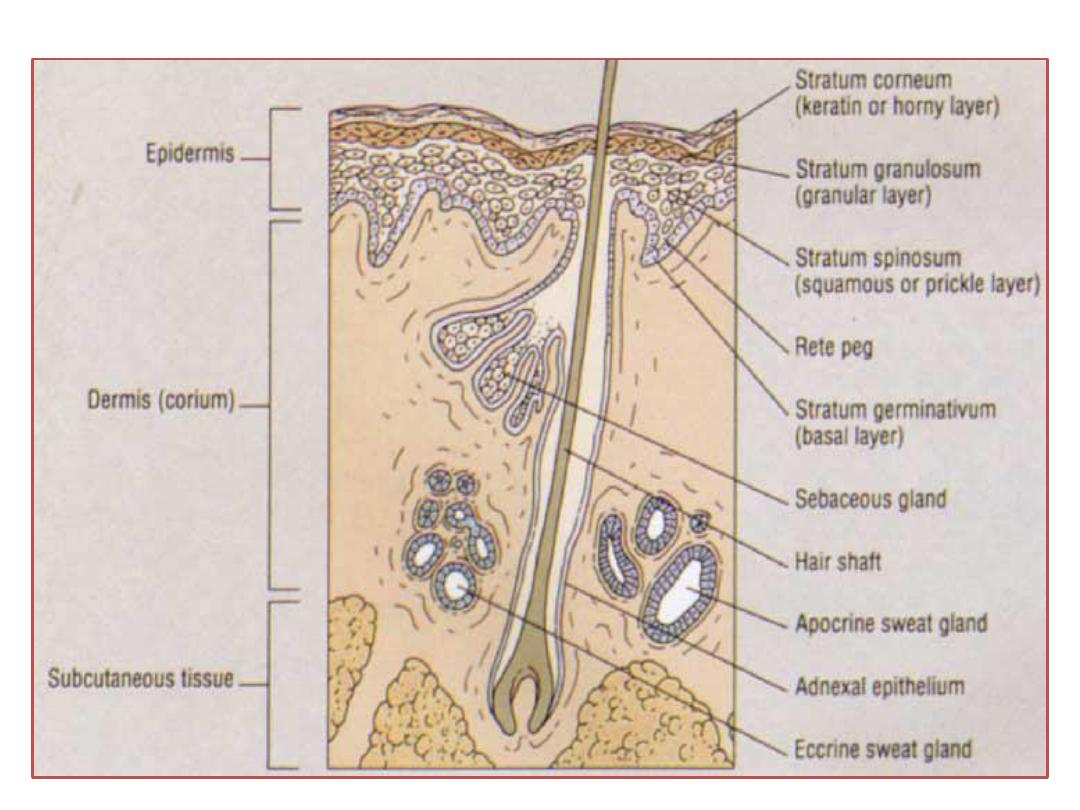
1-Skin
2- Subcutaneous fat.
3- Layer of stratified muscle
(
orbicularis oculi and LPS
)
.
4- Submuscluar areolar tissue.
5- Fibrous layer (tarsal plate).
6- Layer of mϋller muscle.
7- Conjunctiva.
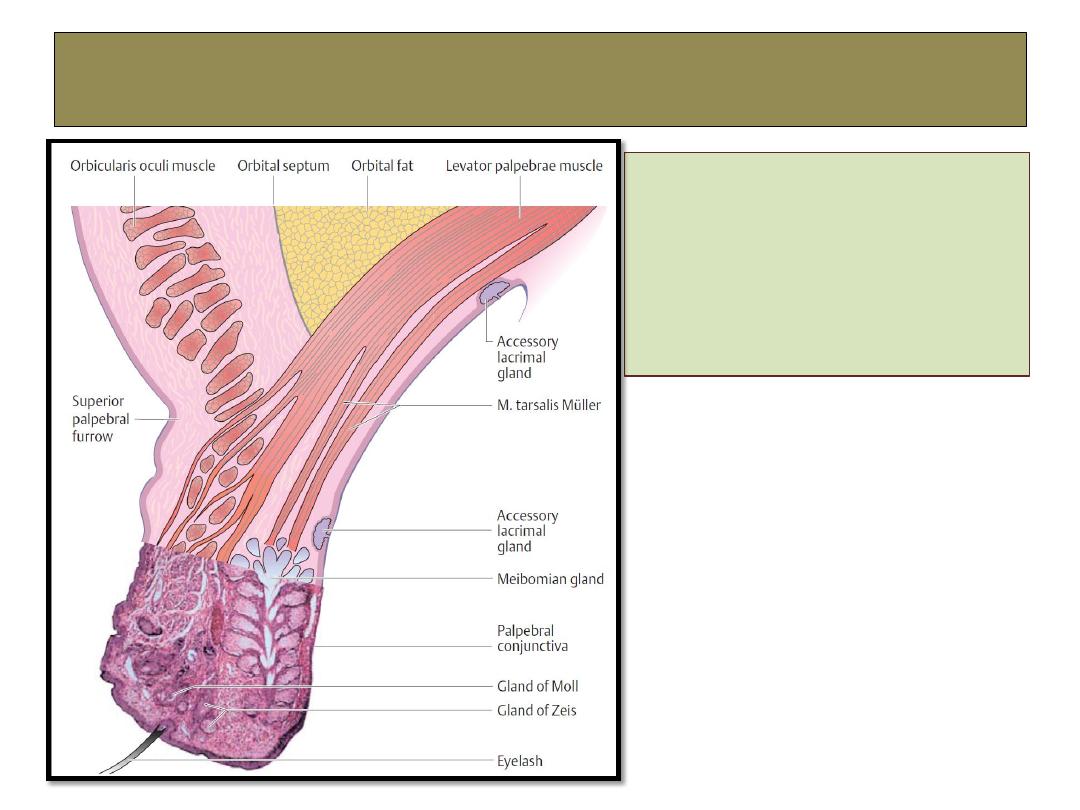
Glands of the eyelid
1- Meibomian glands.
2- Glands of Zeis.
3- Gland of Moll.
4- Accessory lacrimal gland
of Wolfring.
Congenital eyelid malformations
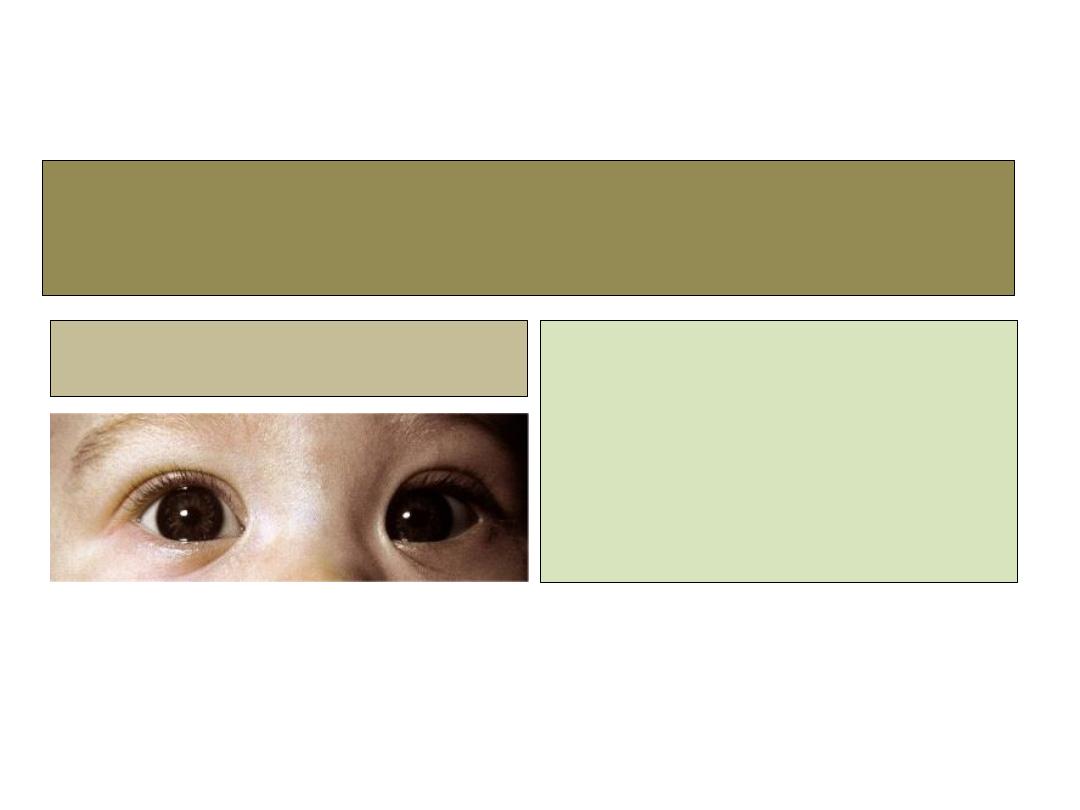
Congenital malformations
1- Epicanthal folds
• Bilateral vertical folds of
skin that extend from upper
or lower lids towards the
medial canthi.
• Treatment: Y-V plasty.
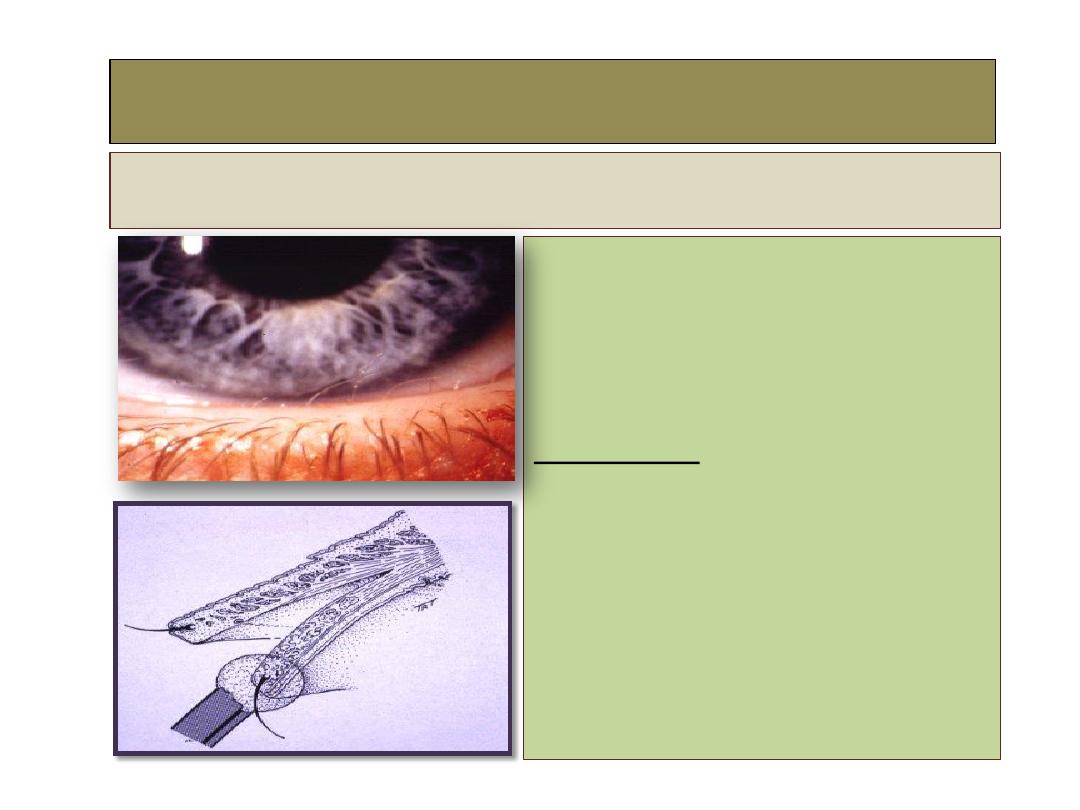
2- Distichiasis
Definition:
•
Second row of lashes
arising from meibomian
gland orifices.
•
Congenital, Occasionally
dominantly inherited.
Treatment:
•
Division into anterior and
posterior lamellae.
•
Cryotherapy to posterior
lamella.
•
Reapposition of lamellae.
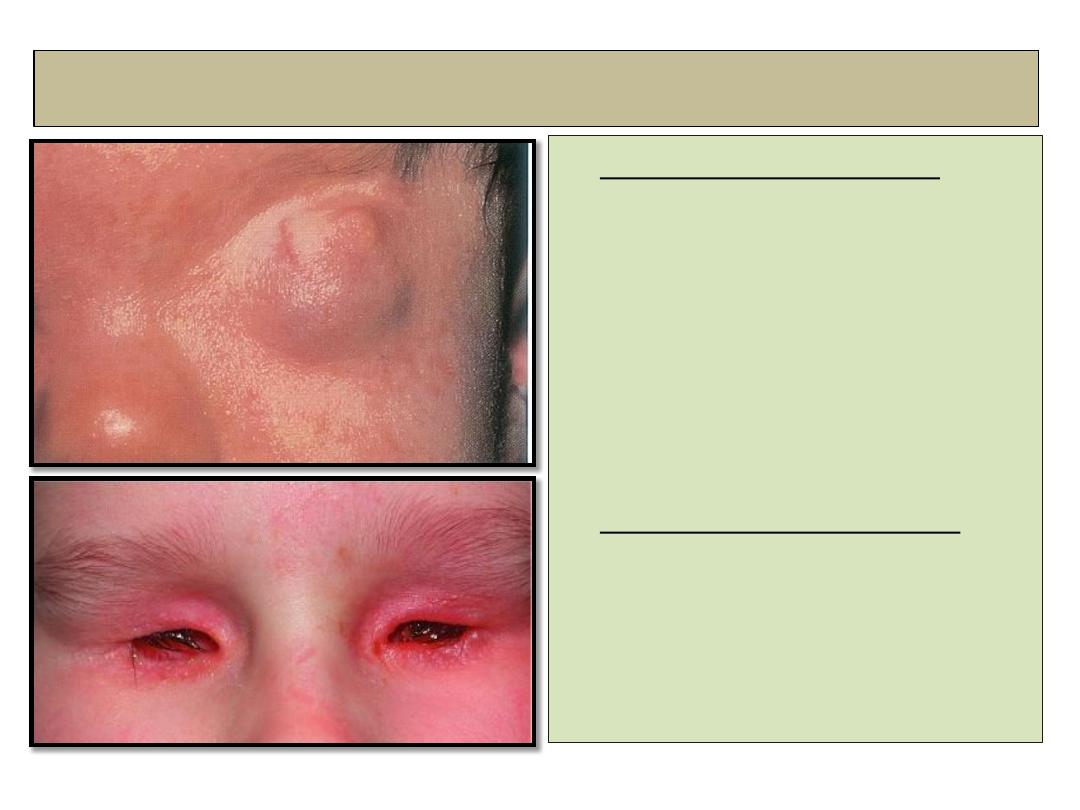
3- Cryptophthalmos
• Complete cryptophthalmos
: the
lids are replaced by a layer of
skin which fused with
microphthalmic eye.
• Incomplete cryptophthalmos
:
Microphthalmos,
rudimentary lids and small
conjunctival sac.
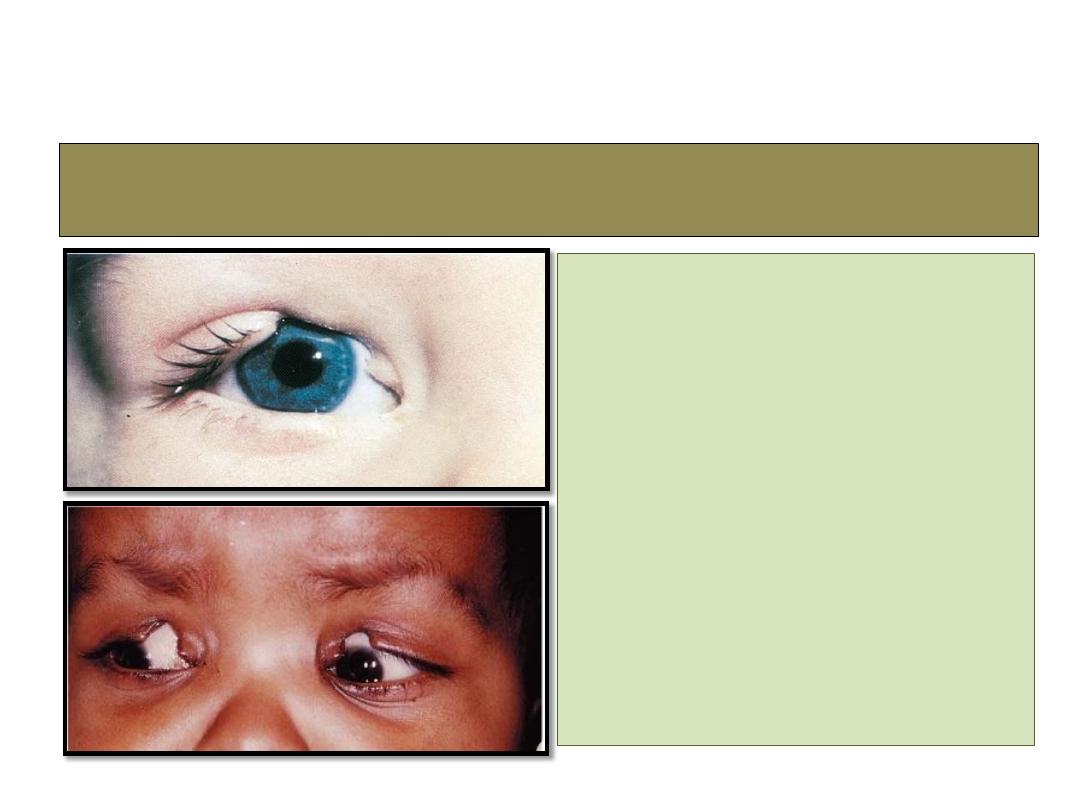
4- Eyelid coloboma
• Uncommon unilateral or
bilateral partial or full
thickness eyelid defect.
• Treatment: small defect:
direct closure
• Large defect: skin graft or
rotational flap.
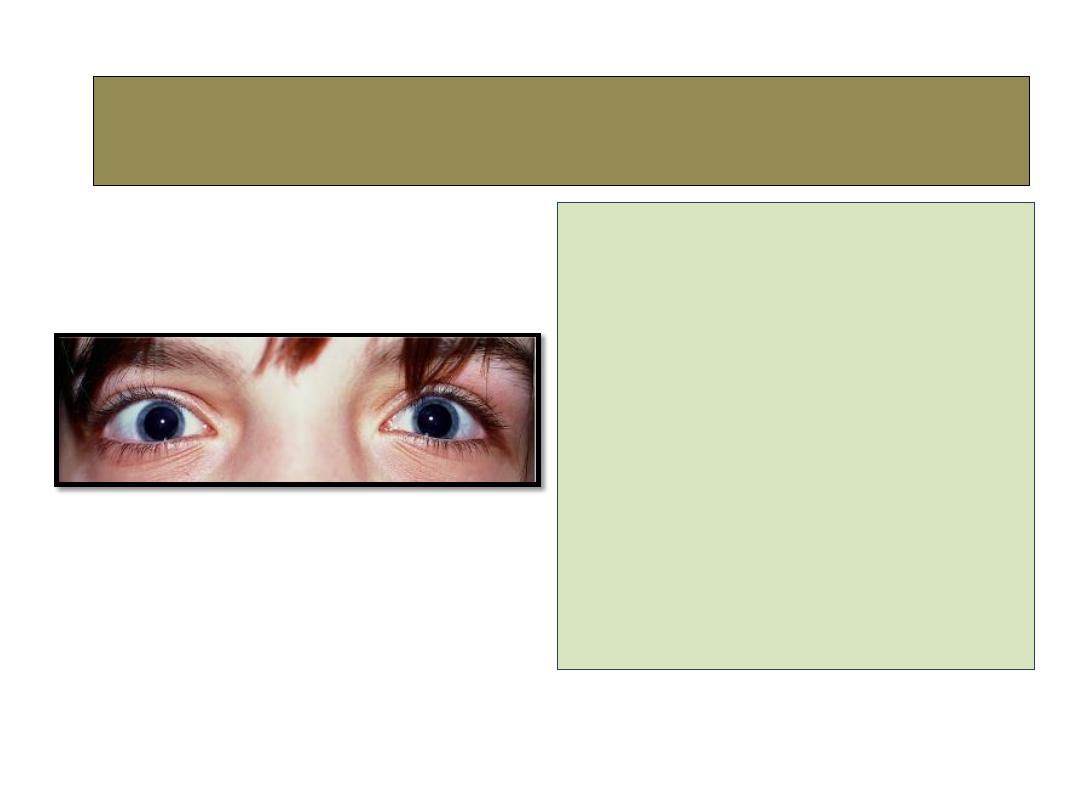

• Increased distance between
the medial canthi due to
abnormal long medial
canthal tendons.
• Please note hypertelorism
:wide separation of the
orbits.
• Treatment: shortening and
re-fixation of medial canthal
tendons.
5- Telecanthus
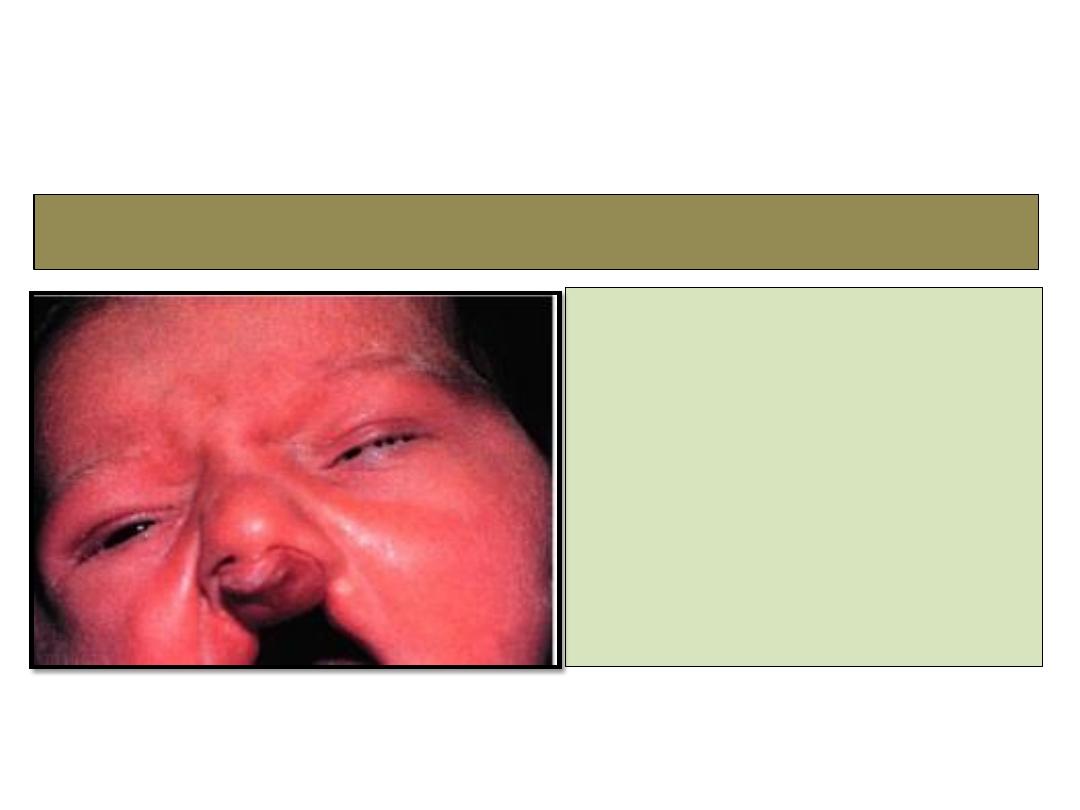
6- Ankyloblepharon filiform adantum
• Sporadic cases
• Upper and lower eye lids
are joined by thin tags
• Treatment: transection with
scissors.

Inflammatory conditions of the eyelid
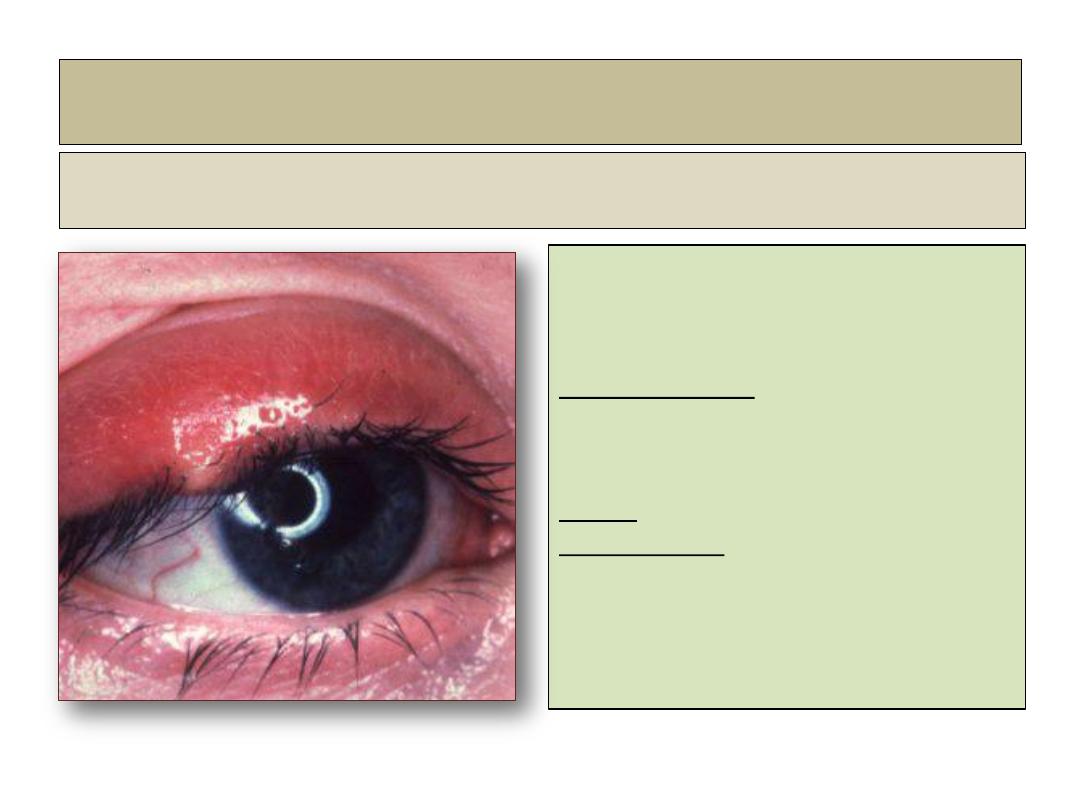
External hordeolum (stye)
Definition
• Acute suppurative inflammation of
Zeis glands characterized by tender
swelling at lid margin.
Clinical features:
•
An acute painful inflamed swelling
on the anterior lid margin, usually
pointing through the skin.
Cause: :
staphylococcus auras
Management:
removal of associated lash, and hot
bathing. Topical antibiotic
ointment. Large lesions may require
incision.
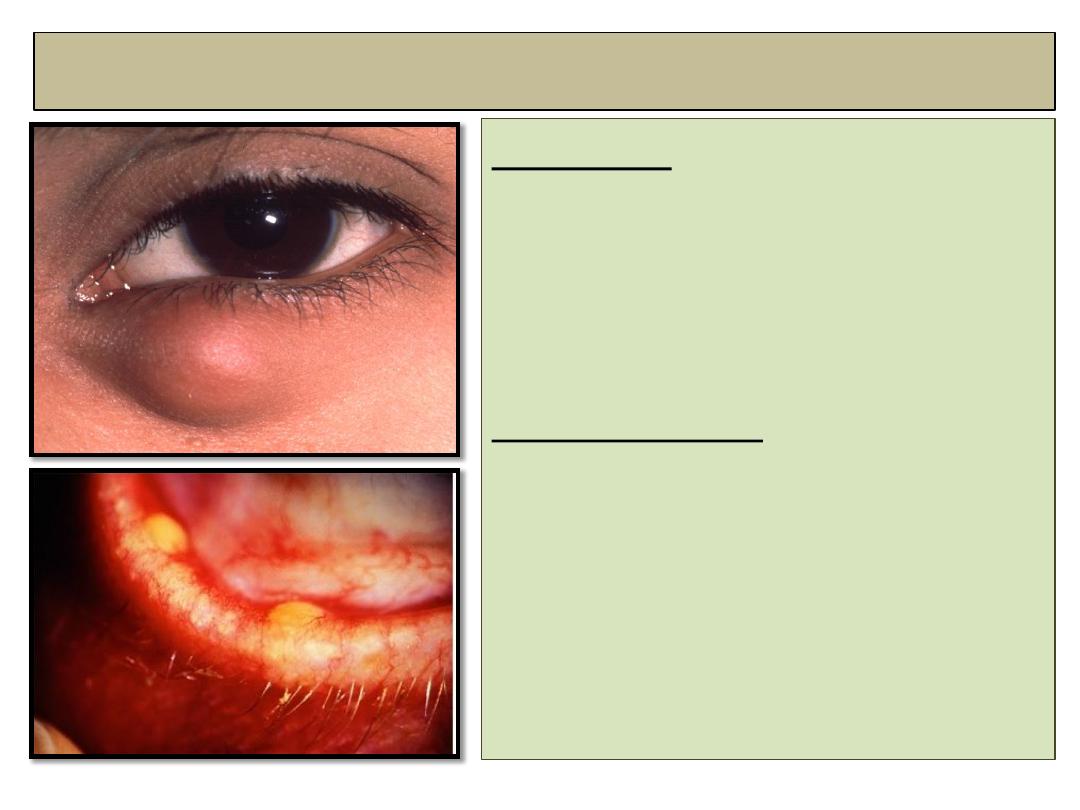
Internal hordulum (Chalazion)
Definition:
• Sterile lipogranulomatous
inflammatory reaction caused
by leaking of retained
meibomian gland secretions.
Predispositions:
1-
chronic posterior blepharitis.
2-
Acne Resaca.
3-
Seborrheic dermatitis.
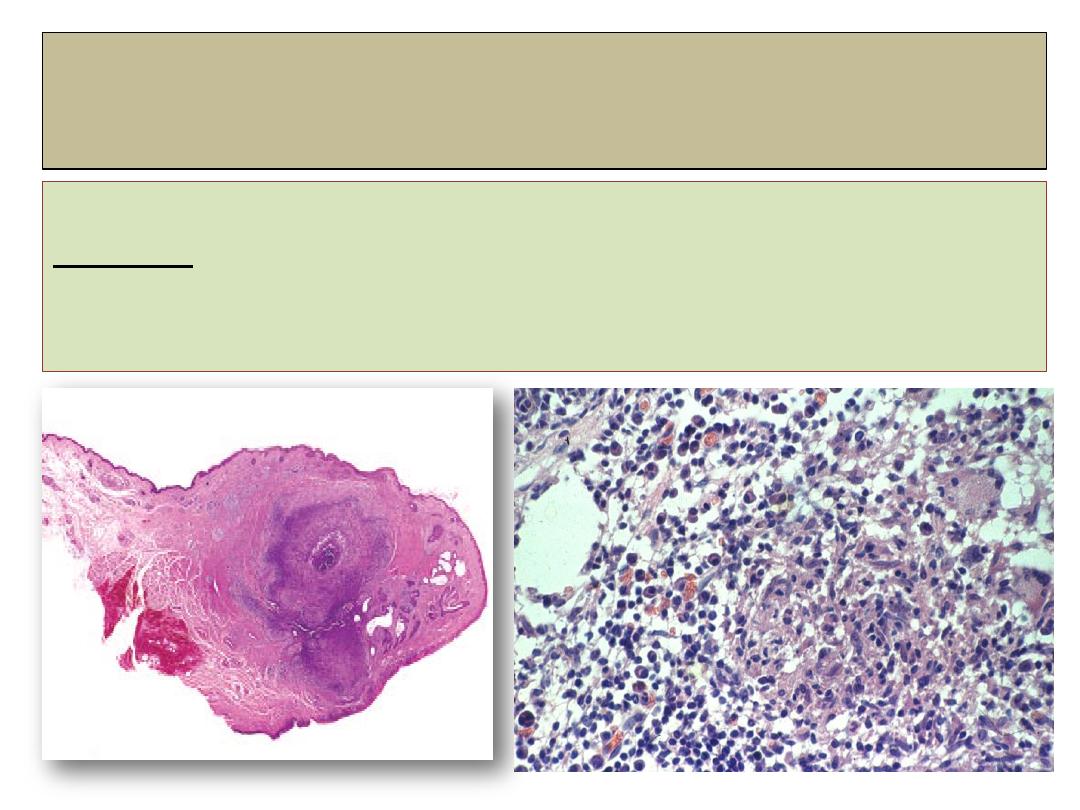
Chalazion
histopathology
Histology:
shows lipogranulomatous inflammatory reaction containing
epithelial histiocytes, multinucleated giant cells and plasma cells.
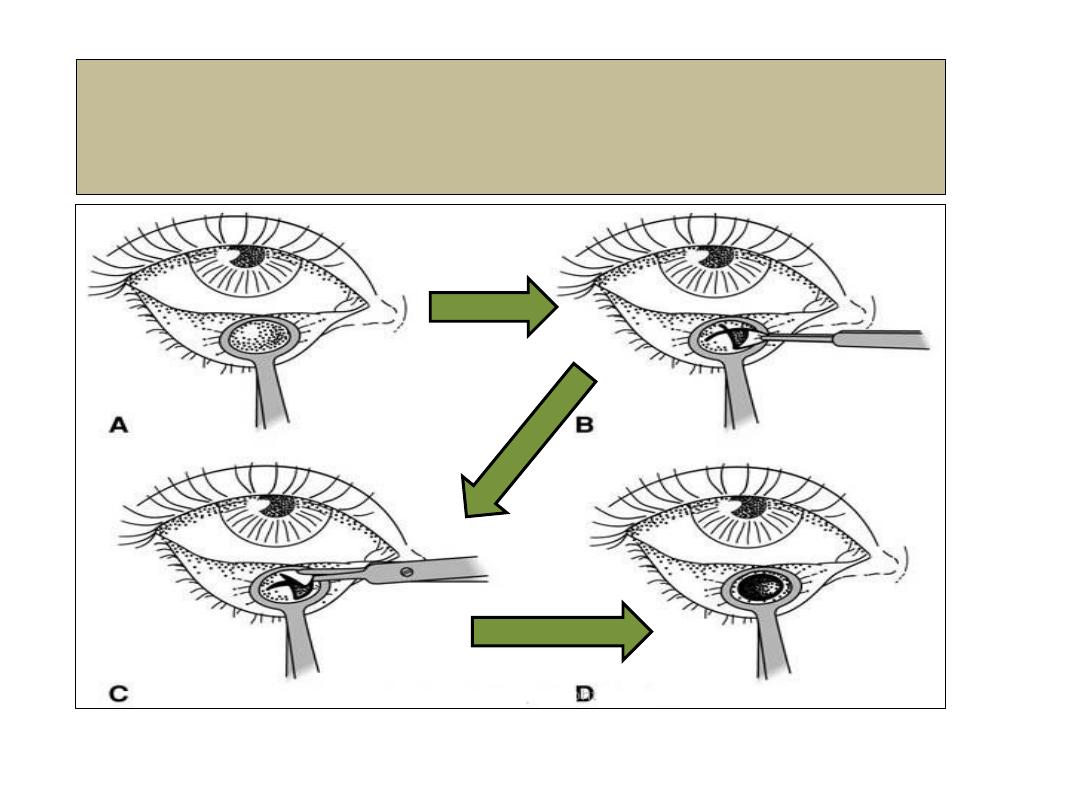
Chalazion- incision and curate
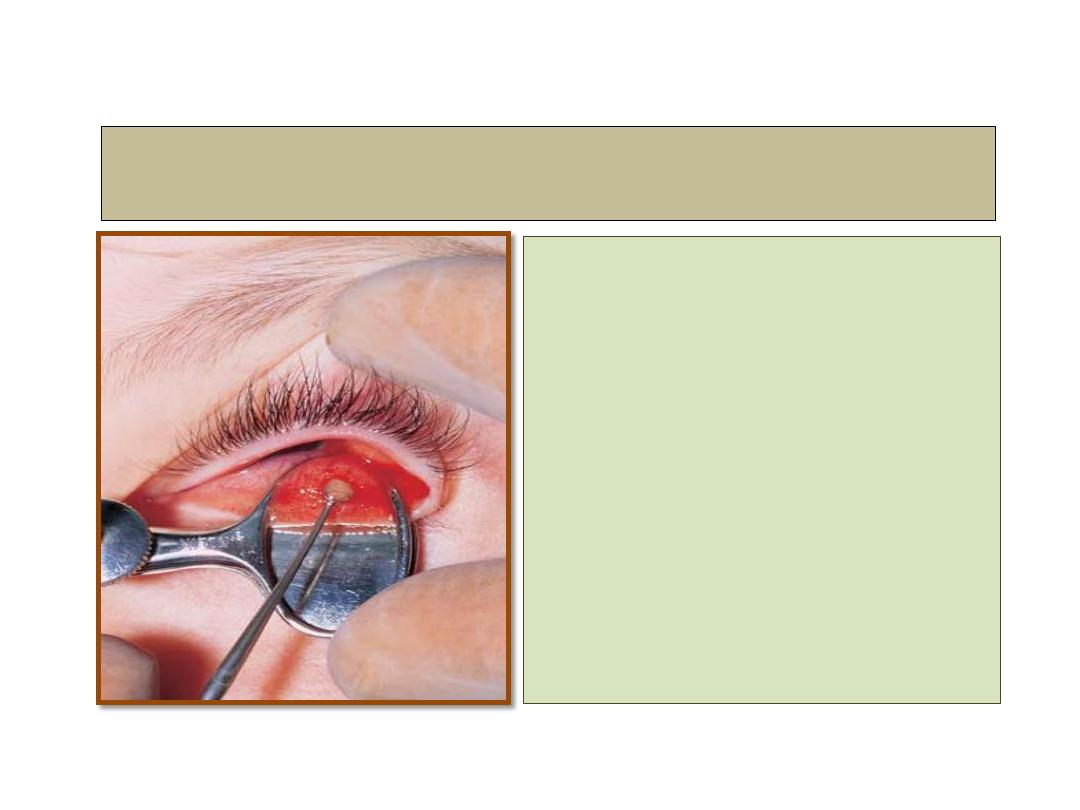
Treatment
1- Observation of small lesion
in anticipation of
spontaneous resolution.
2- Incision and curettage.
3-Steroid injection into the
lesion.
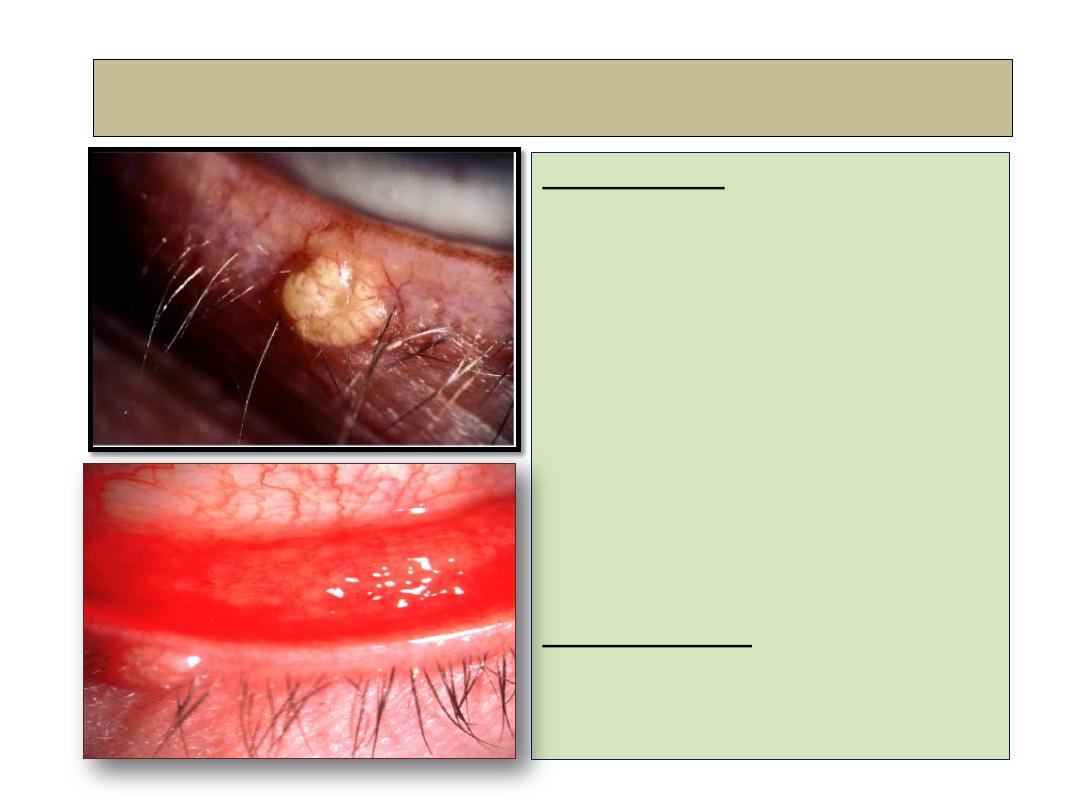
Molluscum contagiosum
Description:
Single or multiple, small, pale,
waxy umbilicated nodules,
which may cause a secondary
chronic ipsilateral follicular
conjunctivitis.
These virally transmitted
lesions (pox virus) are common
and more sever in AIDS
patients.
Management:
expression or cautery.
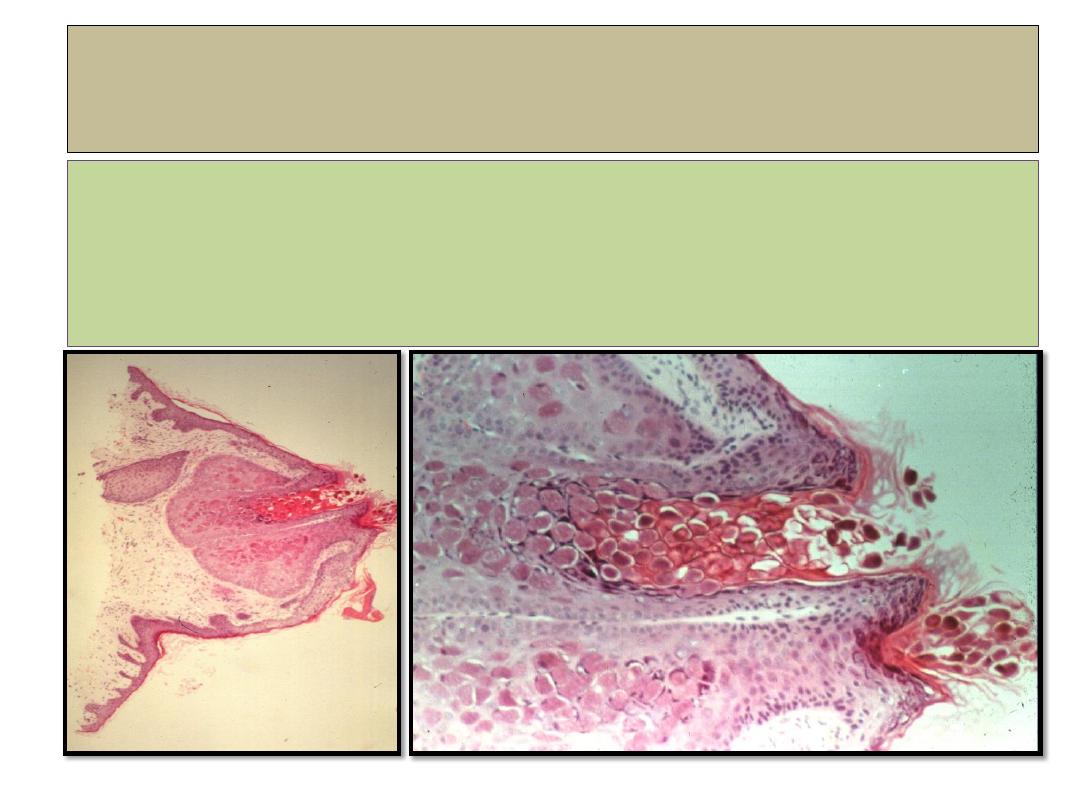
Molluscum contagiosum
histopathology
•Lobules of hyperplastic epithelium
.
•Intracytoplasmic (Henderson-Patterson
) inclusion bodies
•
Deep within lesion bodies are small and eosinophilic.
• Near surface bodies are larger and basophilic
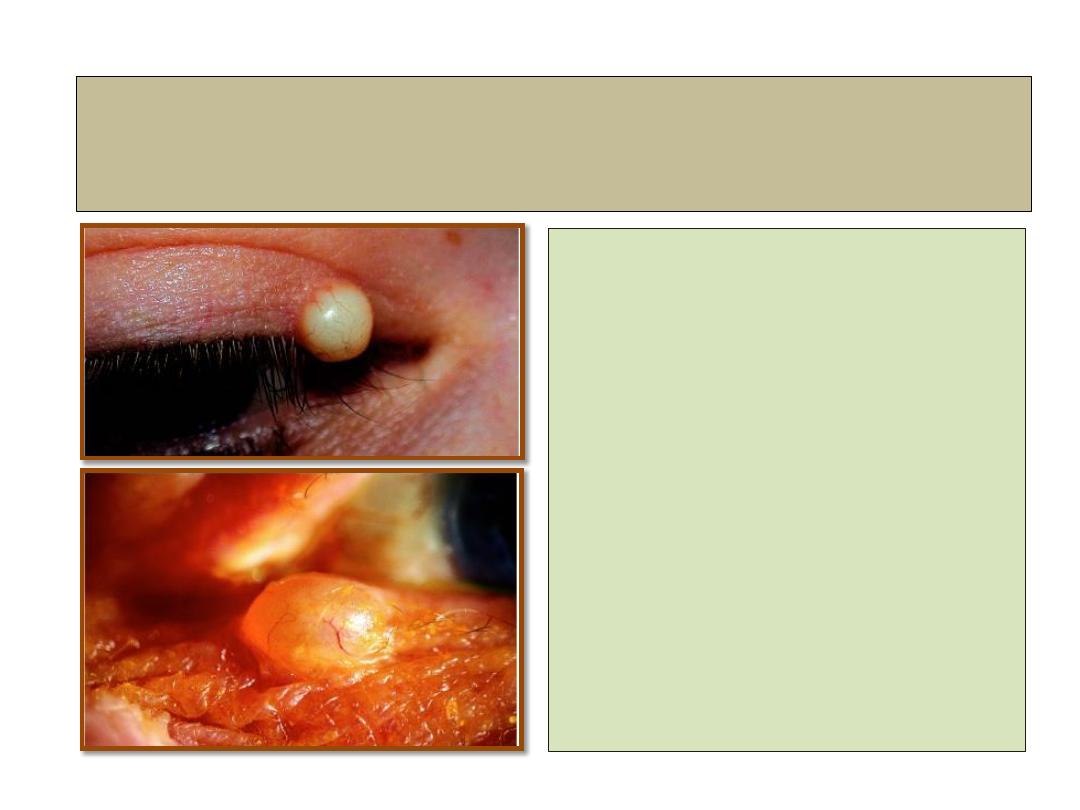
Cyst of Zeis and Moll
• Is small, whitish, chronic,
painless, opaque nodule on
lid margin.
• A cyst of Moll is similar
but translucent.
• Management:
simple excision.
Blepharitis
Anterior
blepharitis
Posterior
blepharitis
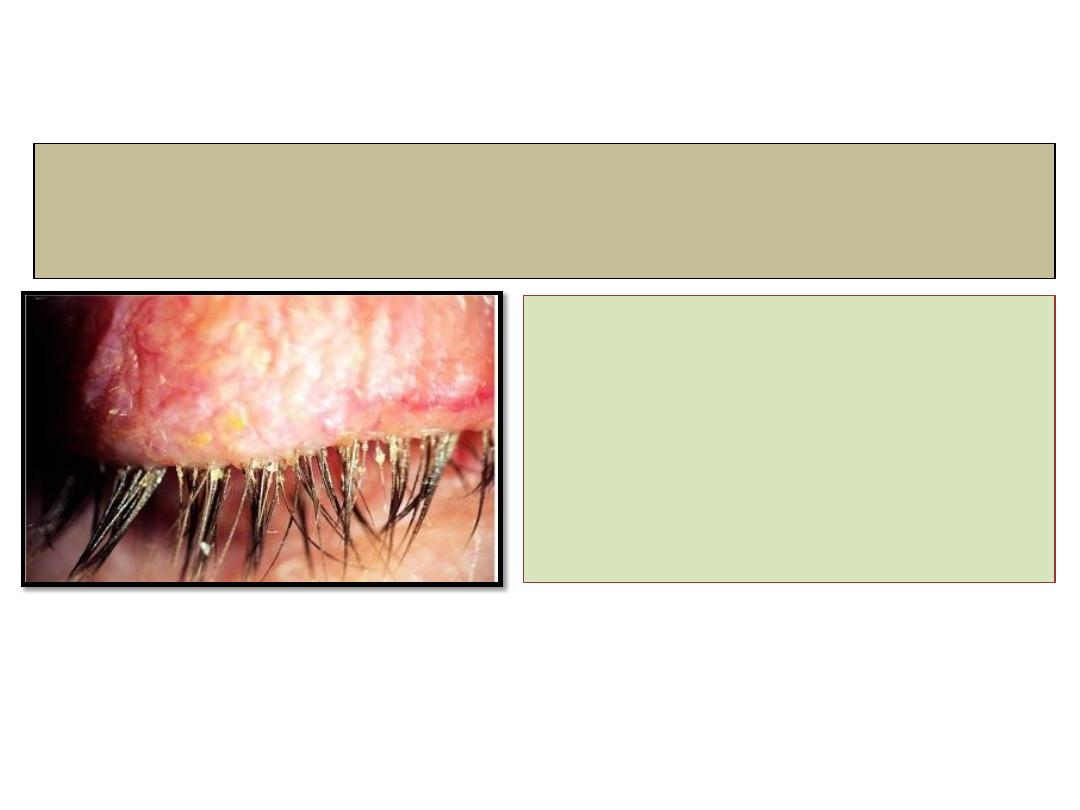
Blepharitis
Chronic anterior blepharitis
• Is very common cause of
ocular discomfort and
irritation, usually it is
bilateral and symmetrical.

Treatment
• 1- lid hygiene: to mechanically remove
crusts involve scrubbing the lid margin with
cotton buds dipped in a diluted solution of
baby shampoo or sodium bicarbonate.
• 2- Antibiotics:
A- topical fucidic acid, bactracin or
chloramphenicol.
B- oral azithromycin 500mg daily for
3 days.
• 3- weak topical steroids
such as fluorometholone.
• 4- tear substitutes.
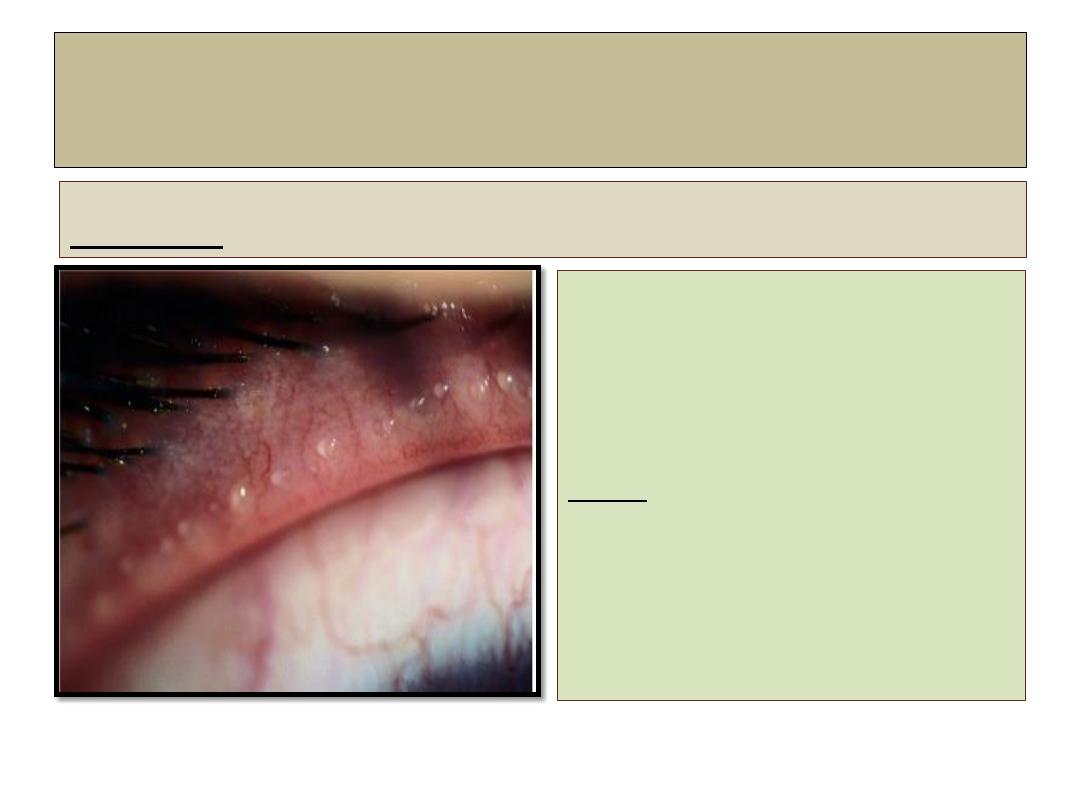
Chronic posterior blepharitis
Diagnosis:
• Poor correlation between
severity of symptoms and
clinical signs.
• Symptoms: similar to chronic
anterior blepharitis.
Signs:
• Excessive and abnormal
meibomian gland secretion
manifest as capping of
meibomian gland orifices with
oil globules.
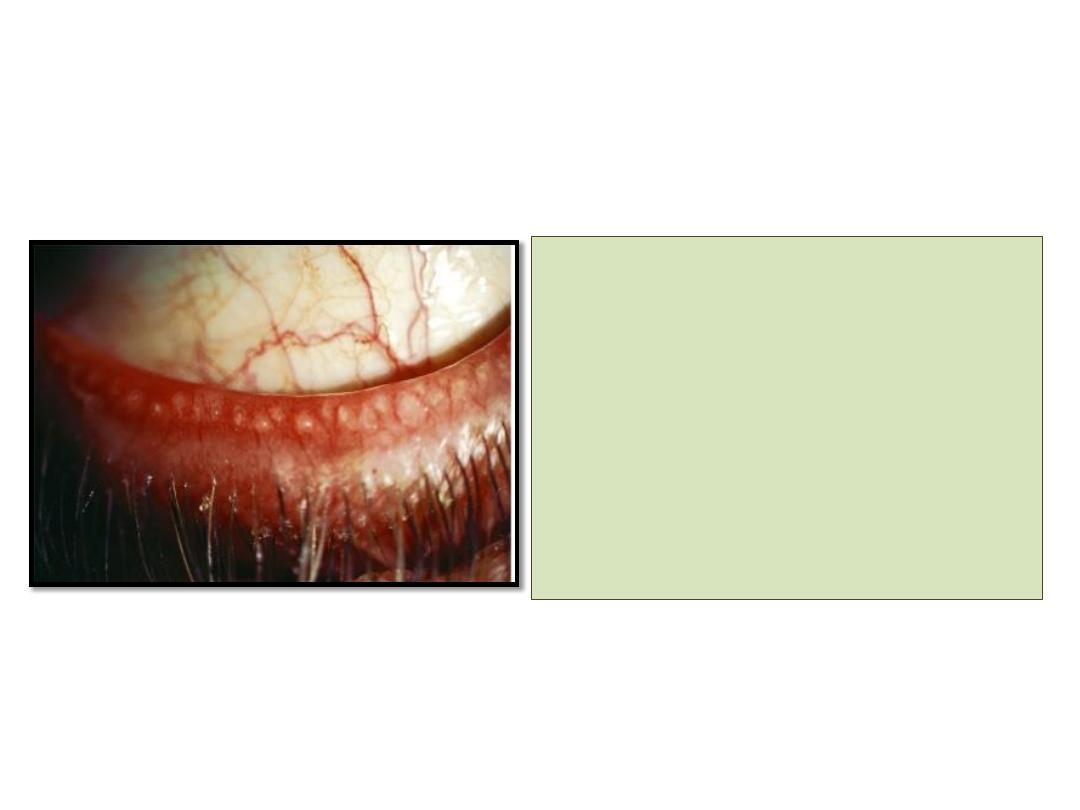
• Pouting or plugging of
meibomian gland orifices.
• Hyperemia and
telangectasia of posterior
lid margin.
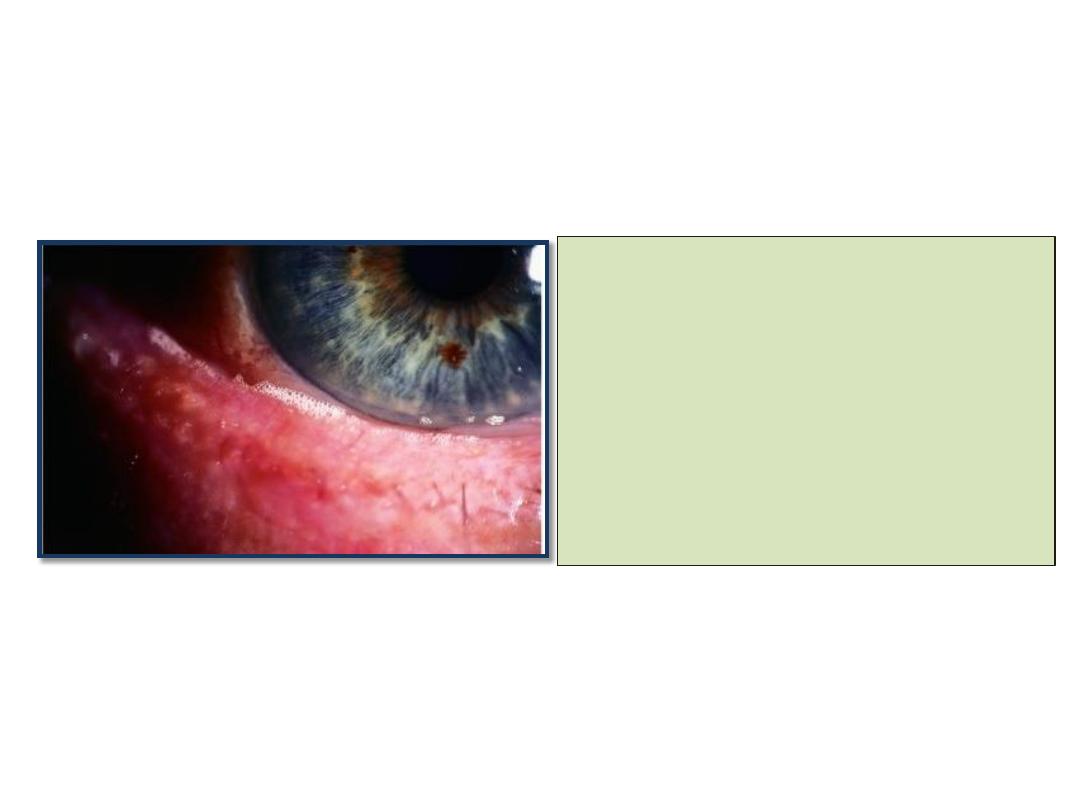
• The tear film is oily and
foamy and froth may
accumulate on the lid
margins or inner canthi.
• Secondary changes include
papillary conjunctivitis and
inferior punctate epithelial erosions.
• Pressure on lid margin
results in expression of
meibomian fluid that
may be turbid or tooth
past-like.
Treatment
• 1- lid hygiene.
• 2- systemic tetracyclines:
Oxytetracycline 250 mg b.d,
6-12 weeks.
doxcycycline 100mg daily for
6-12 weeks
Erythromycin 250mg b.d (in children).
• 3- topical therapy:
antibiotics, steroids and
tear substitutes.

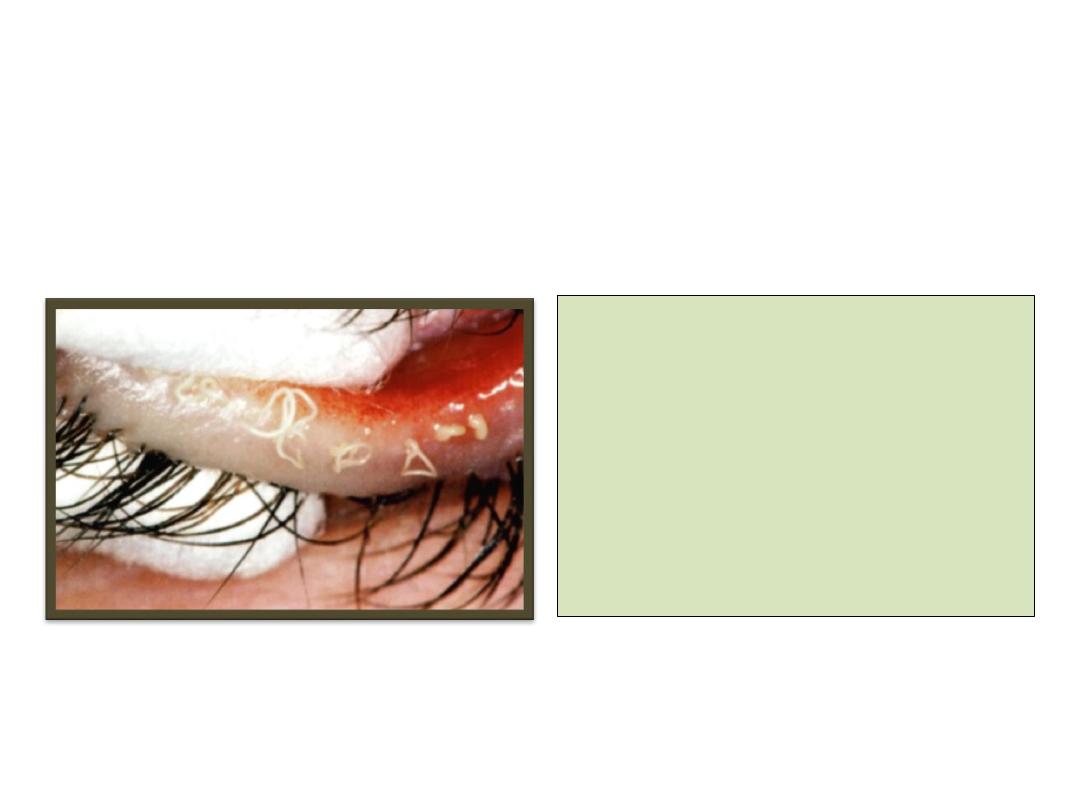
Phthiriasis palpebrarum
Eyelid malposition
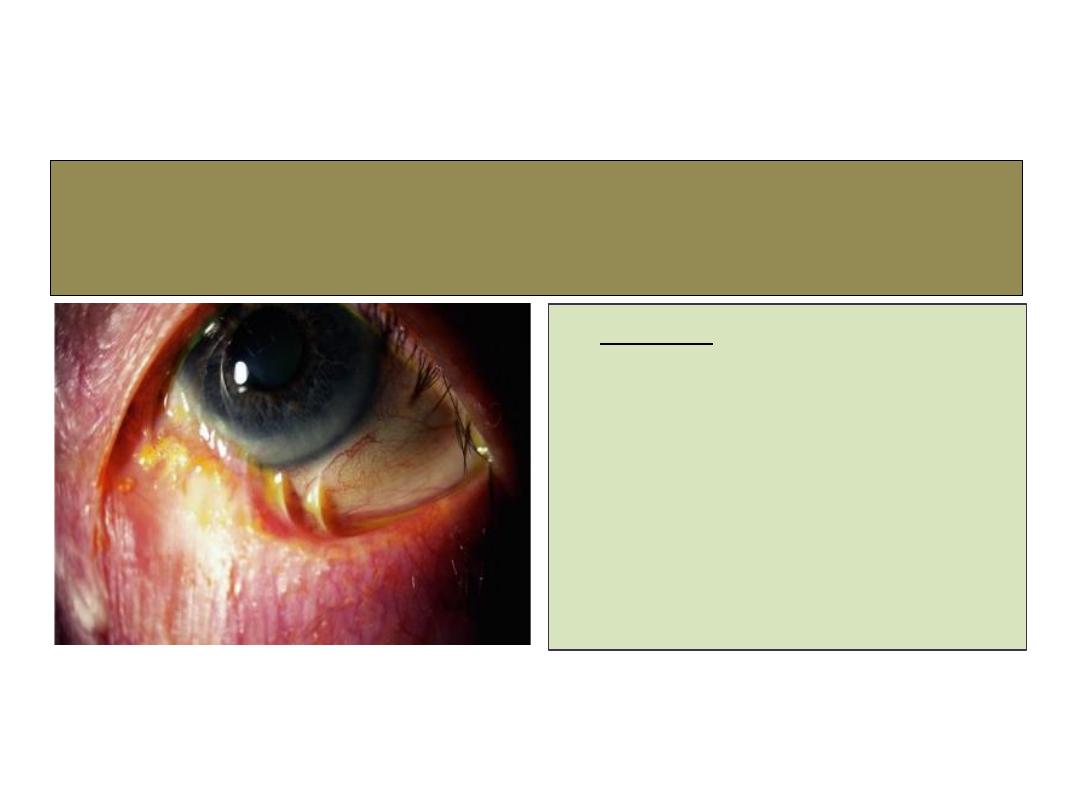
Symblepharon
Causes:
1- Chemical burn.
2- Thermal burn.
3- Membranous conjunctivitis
.
4- Conjunctival injury.
5- Ocular pimphigus.
6- S
teven-johnson syndrome
.
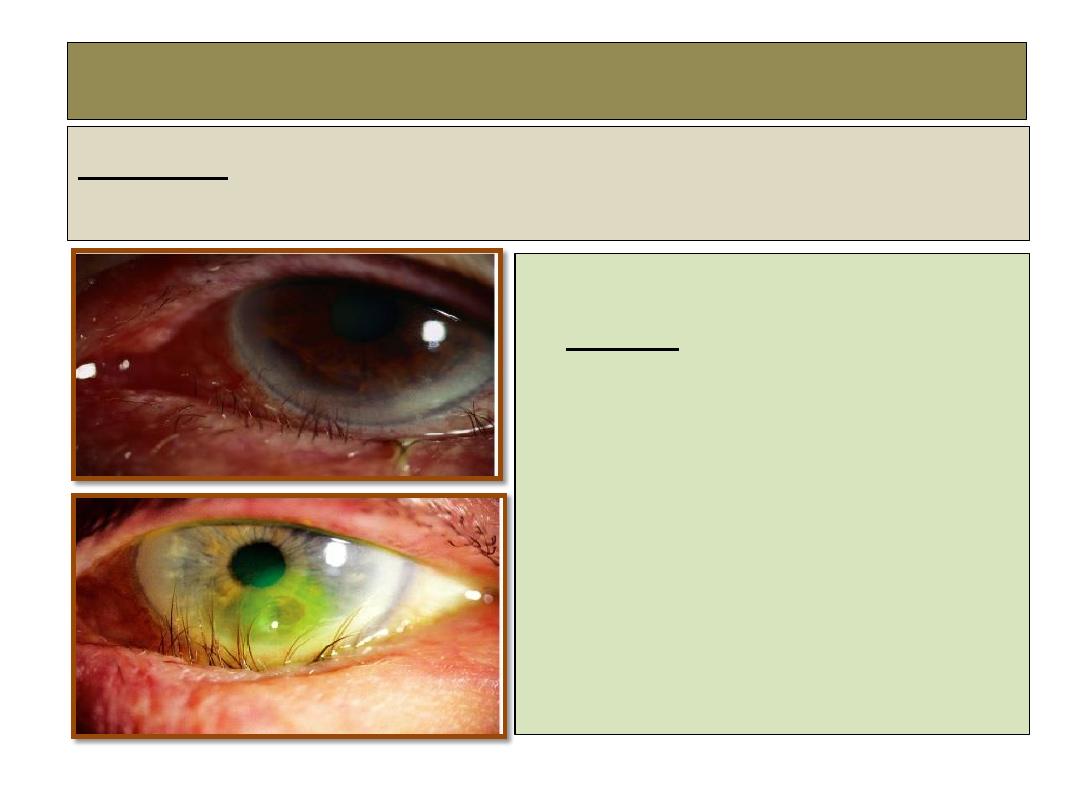
Trichiasis
Definition:
Inward misdirection of cilia which rub against the eyeball.
Causes:
1- Cicatrizing trachoma.
2- Ulcerative blepharitis.
3-
Healed membranous conjunctivitis.
4- Healed hordulum externum.
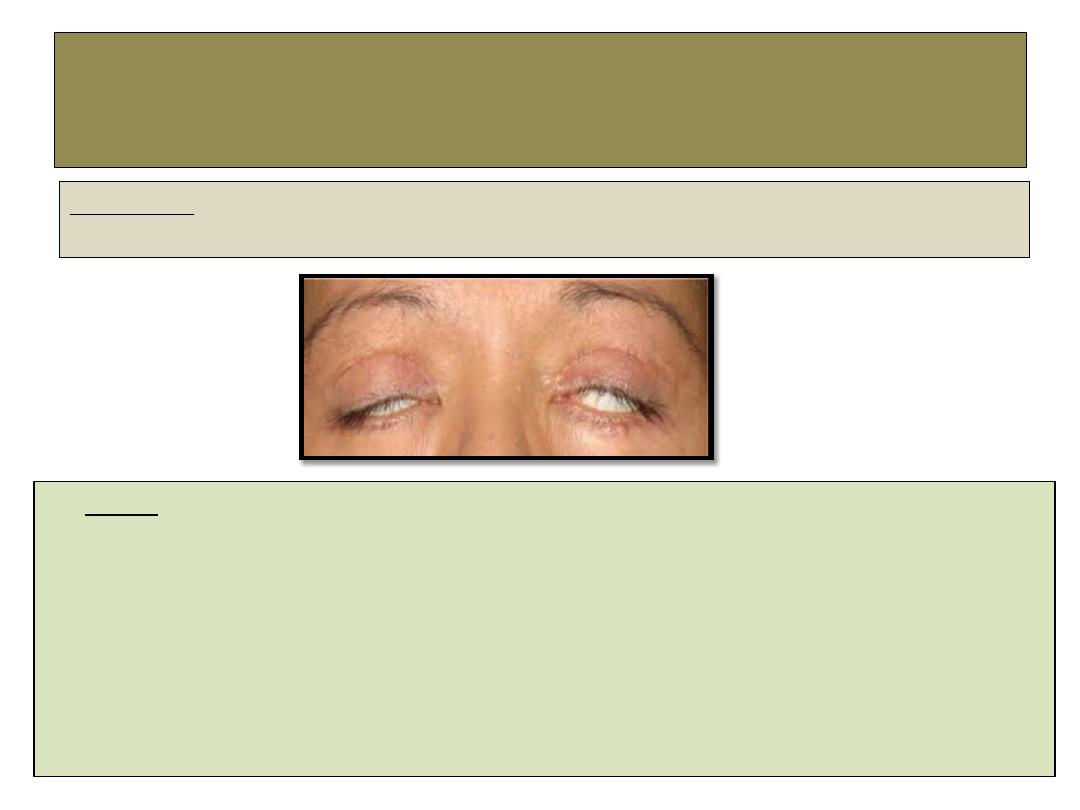
lagophthalmos
Definition:
Inability to voluntary close the eyelids.
•
Causes
:
1- Facial nerve palsy.
2- Marked proptosis.
3- Cicatricial contraction of the lid.
4- Following over resection of levator palpebri superioris muscle in ptosis surgery.
5- Symblepharon.
6- Comatose patient.
The End
