The Eyelids-II
Out-lines
1- Review of eyelid anatomy.
2- Eyelid malposition.
3- Eyelid tumours
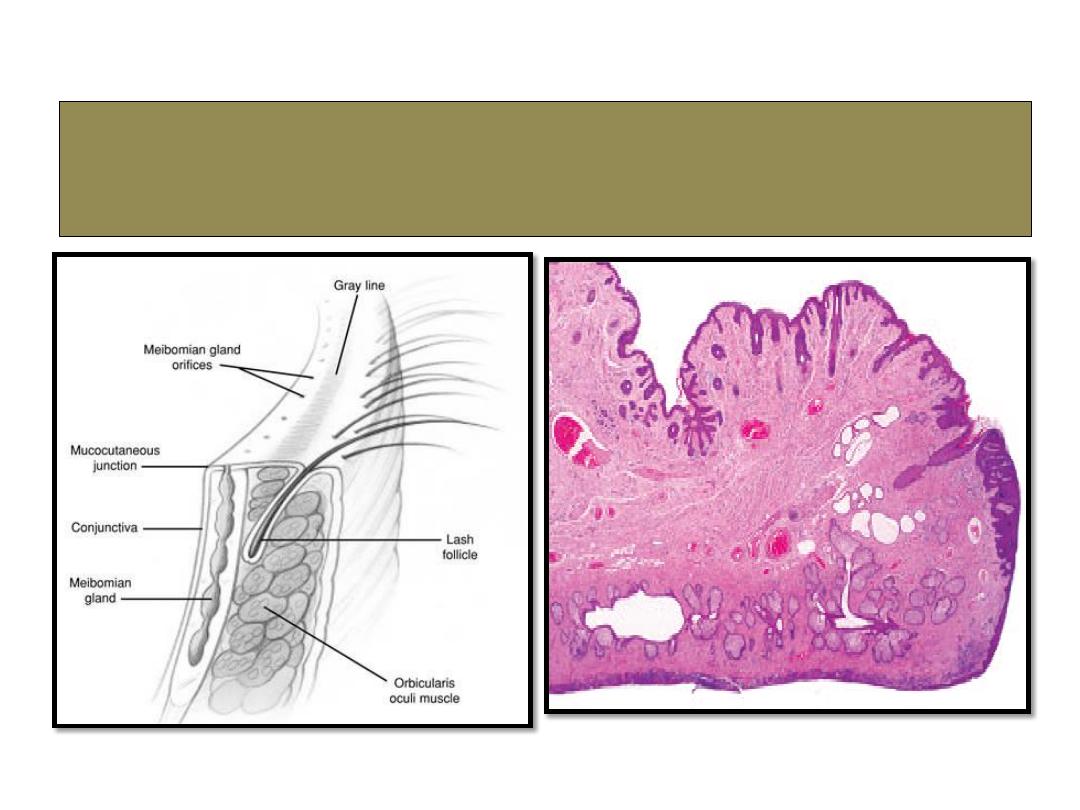
Anatomy of eyelid
Eyelid malposition
1- Ectropian.
2- Entropion.
3- Ptosis.
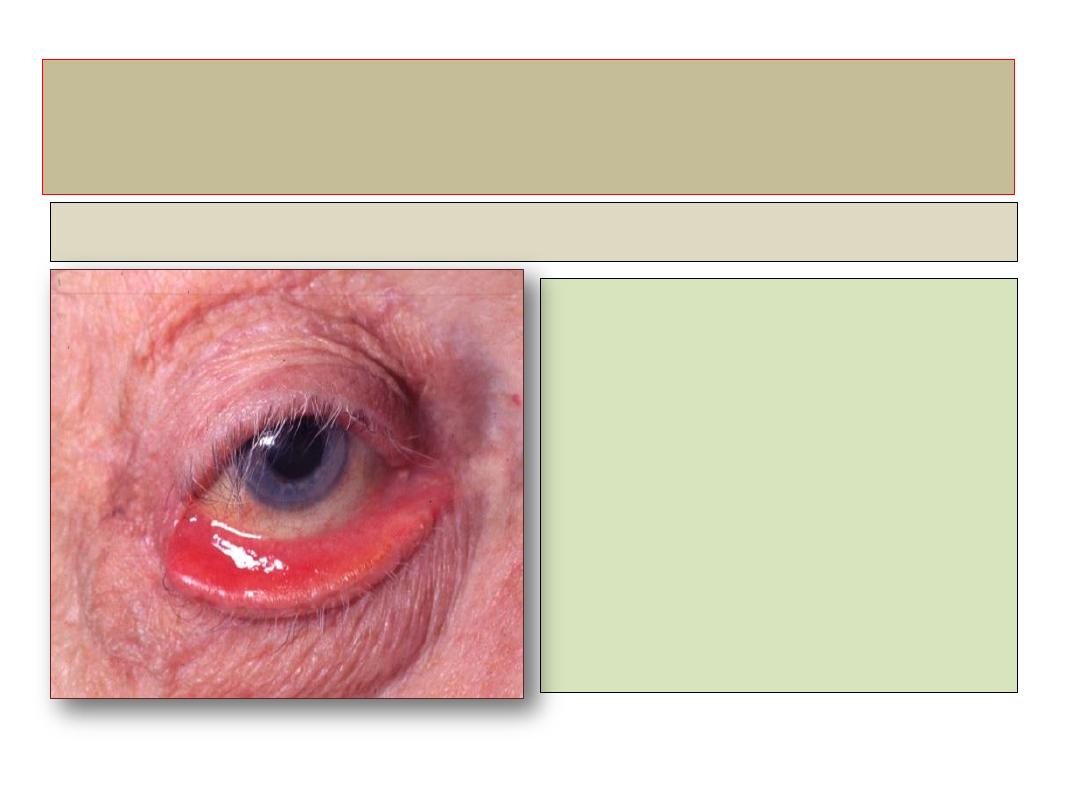
Ectropion
Definition
• An outward-turning eyelid,
virtually exclusively
involving the lower lid . If
sever and prolonged may
cause conjunctival
keratinization.
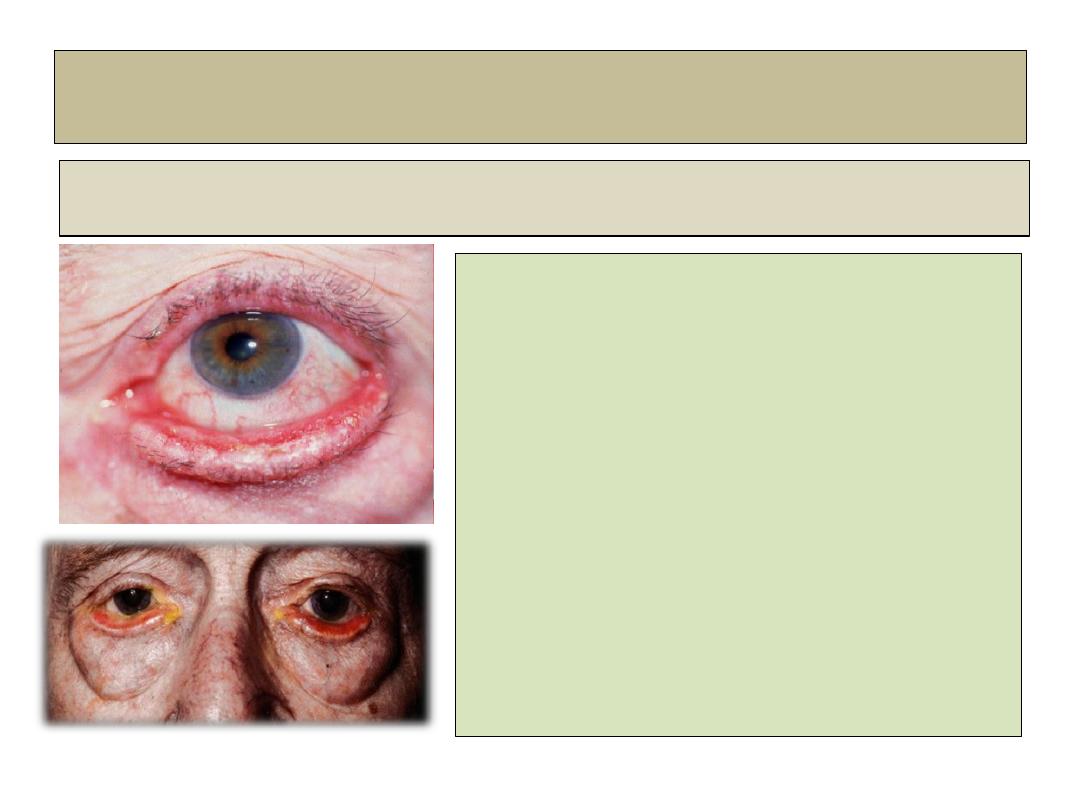
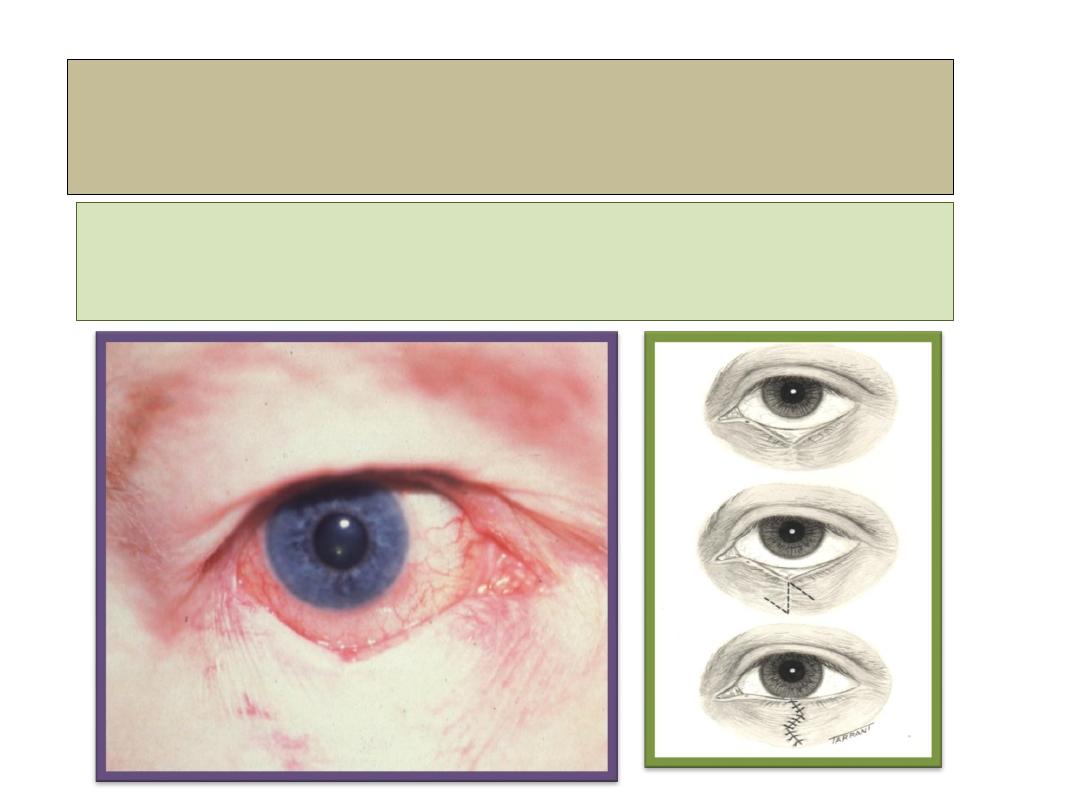
Ectropion
Involutional ectropion
• Pathogenesis:
Horizontal lid laxity associated with
laxity of medial and lateral canthal
tendons.
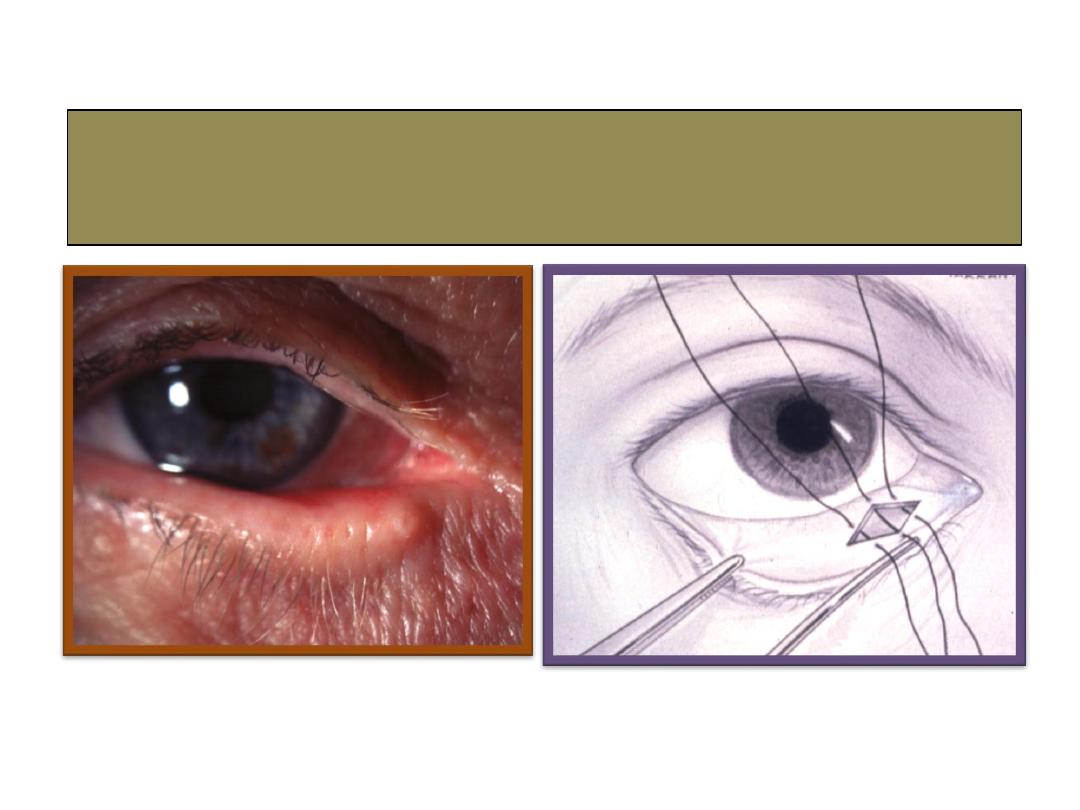
Medial spindle with everting sutures
for medial Ectropion
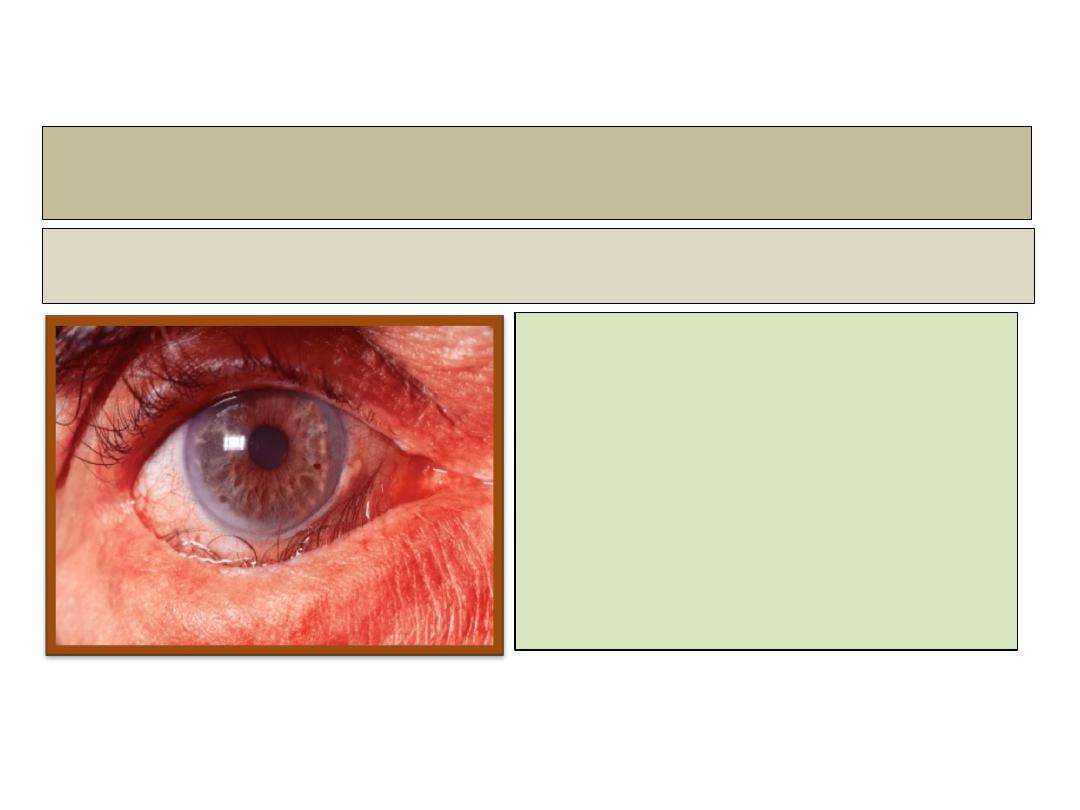
Cicatricial ectropion
• Ectropian associated with scarring and contracture.
Entropion
Definition:
• An inward-turning of eyelids.
If sever or prolonged may
cause corneal scarring.
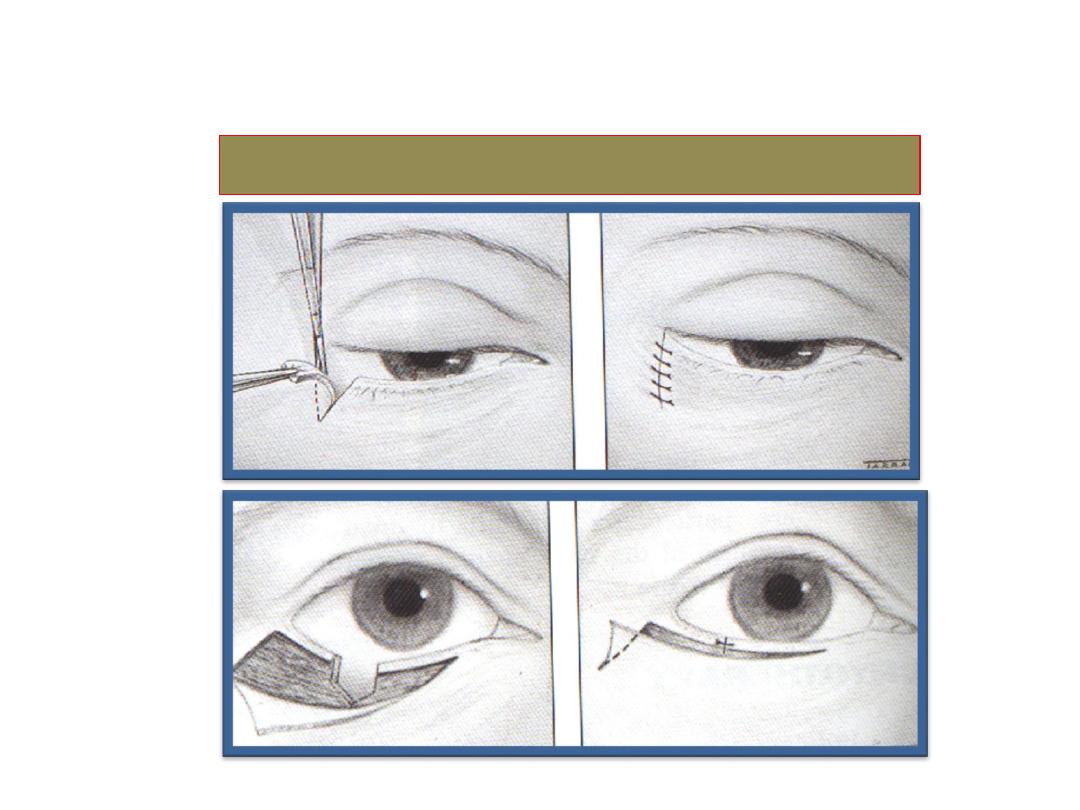
Surgical correction
Ptosis
Definition
• The upper eyelid rest at a lower position than normal (drooping of eye lid).
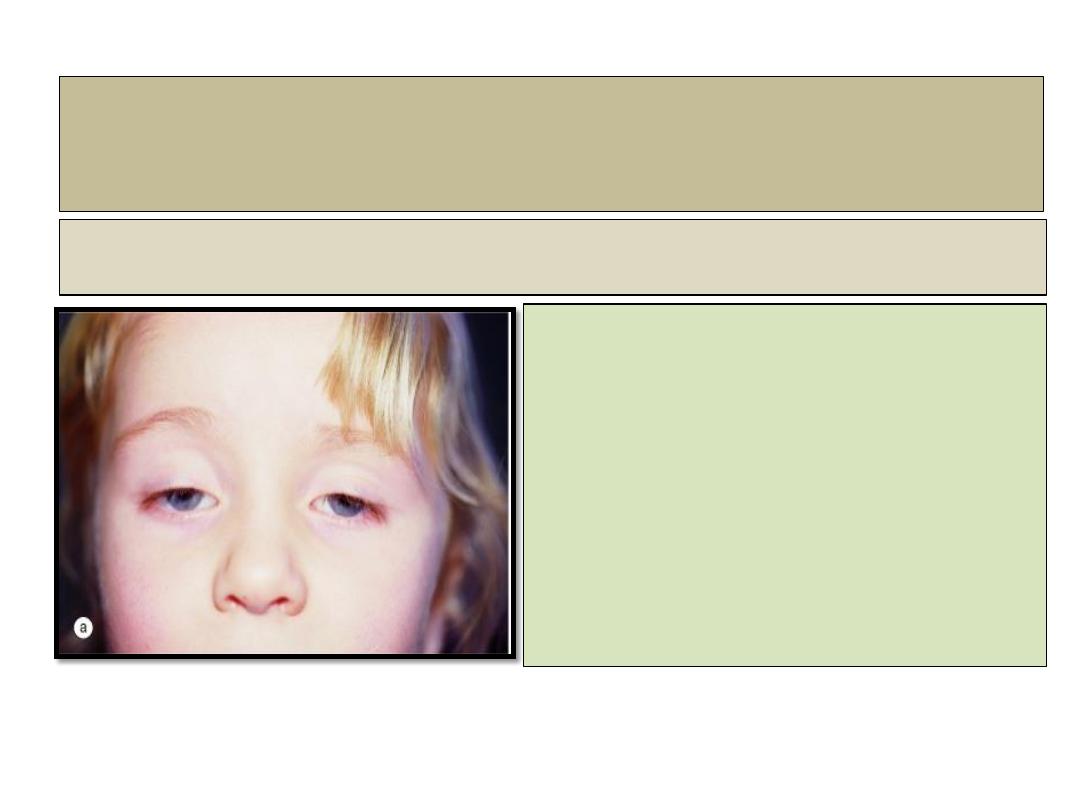
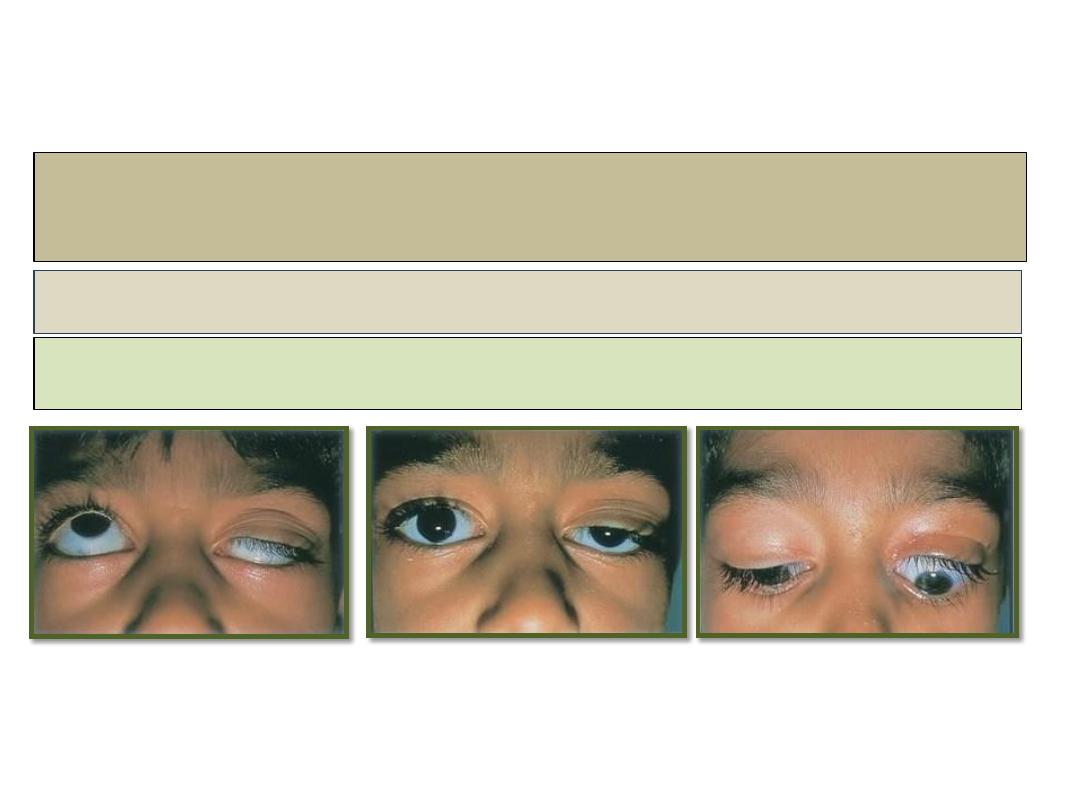
Congenital ptosis
Signs:
• Unilateral or bilateral ptosis of variable
severity.
• Absent upper lid crease and poor
levator function.
• In lower gaze the ptotic lid is higher
than normal.
• Superior rectus weakness may be
present because of close embryological
association with levator.
• Compensatory chin elevation in sever
bilateral cases.
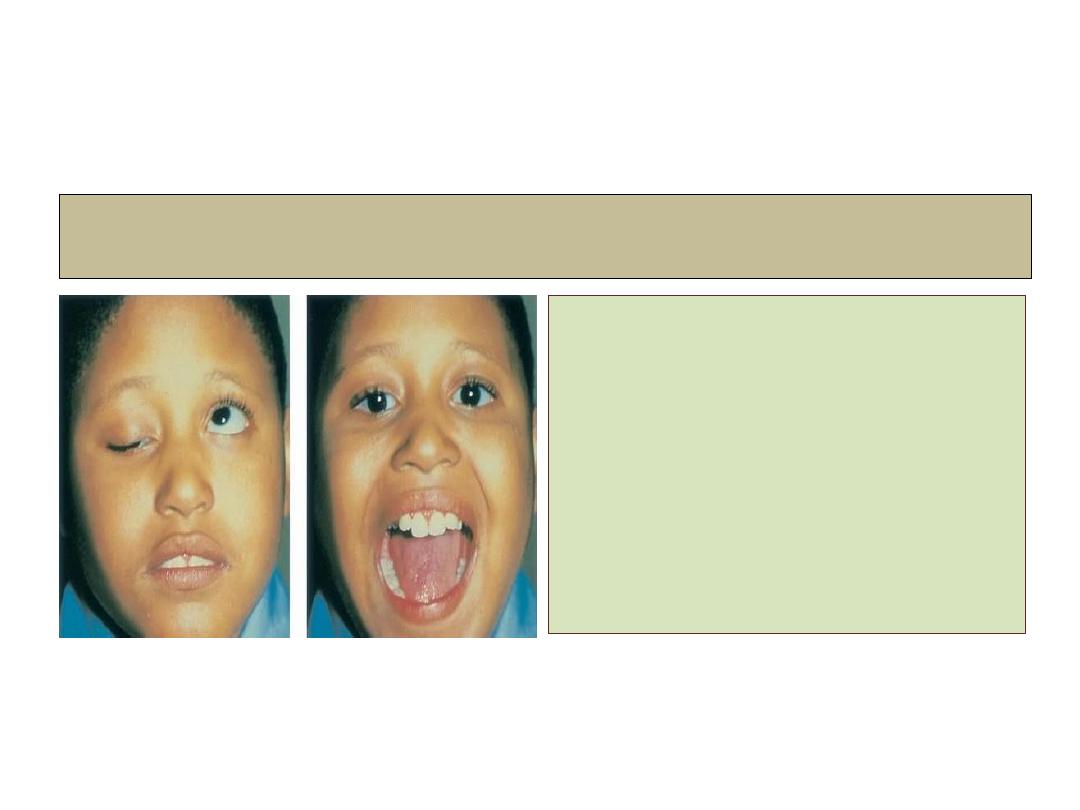
Marcus gunn jaw winking syndrome
• Unilateral.
• About 5% of ptosis cases.
• A branch of mandibular
division of the 5
th
cranial
nerve is misdirected to
levator muscle.
Video
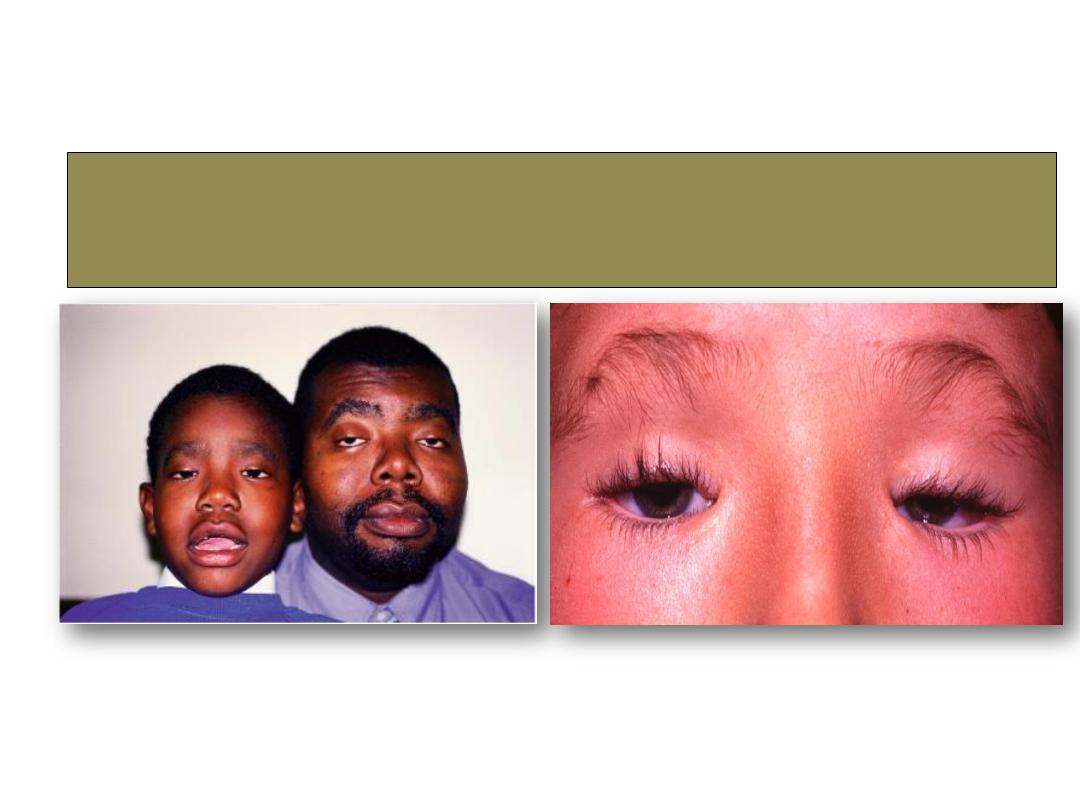
Ptosis:
Blepharophymosis syndrome
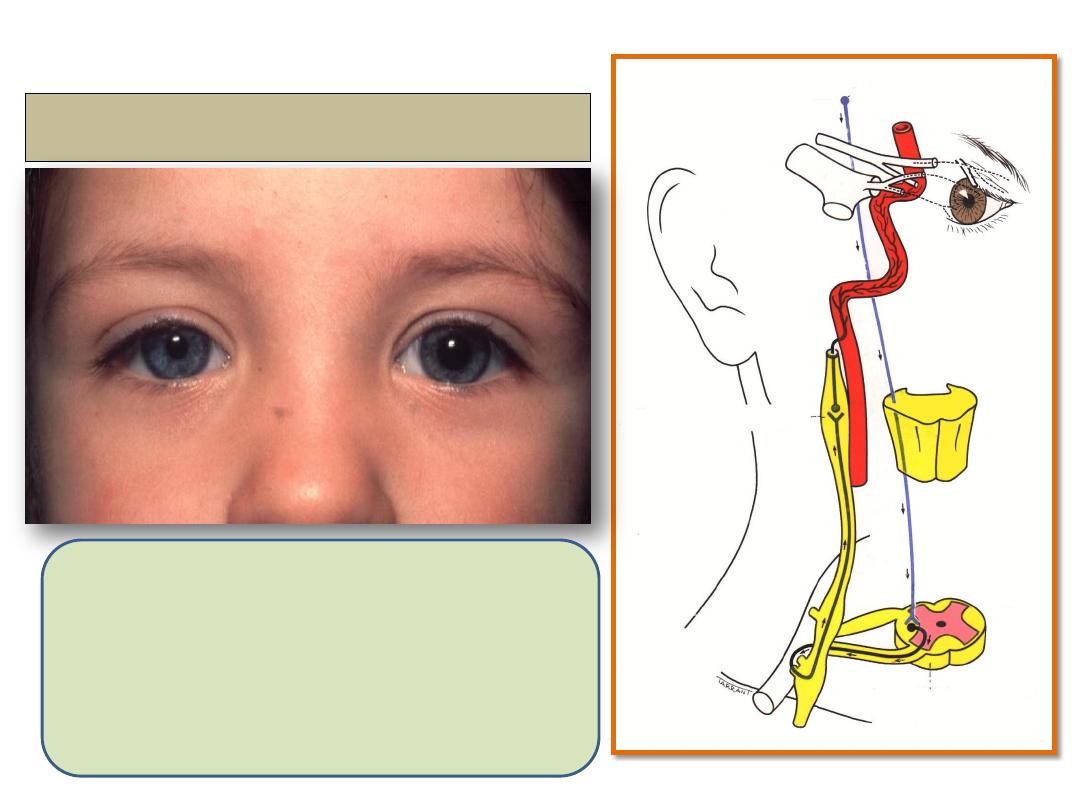
Horner syndrome
1- Ptosis
2- Miosis
3- Anhydrosis
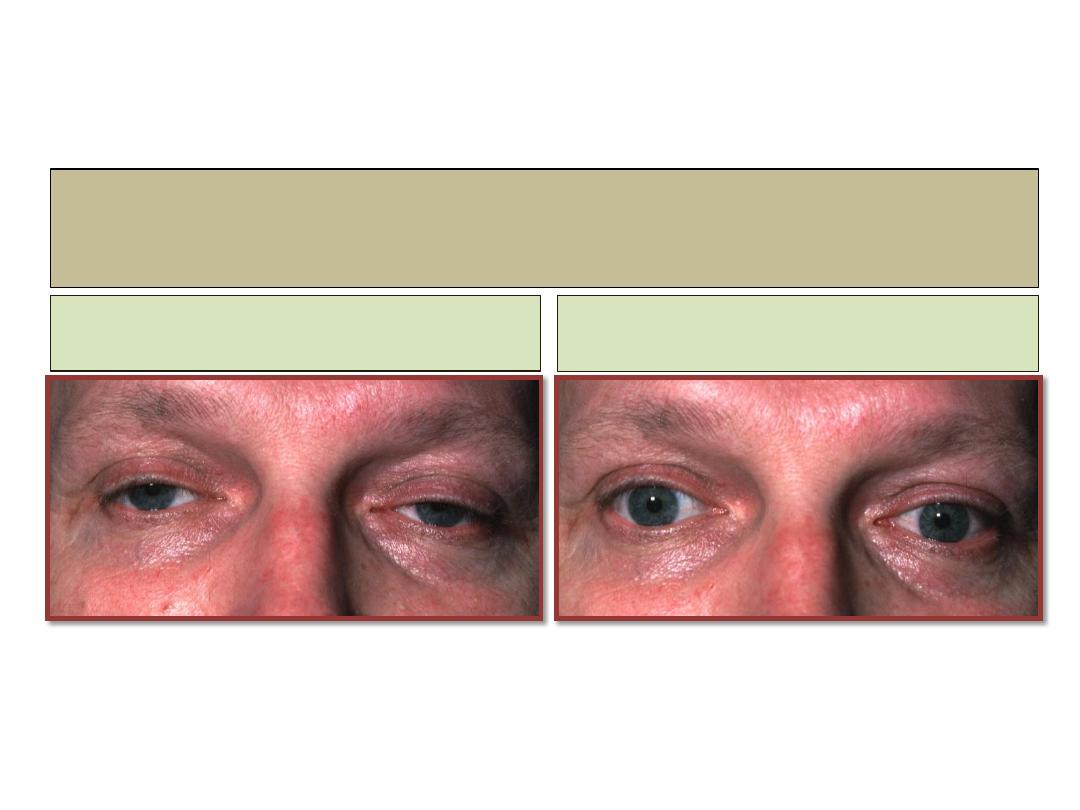
Myasthenia gravis
Before injection
After injection
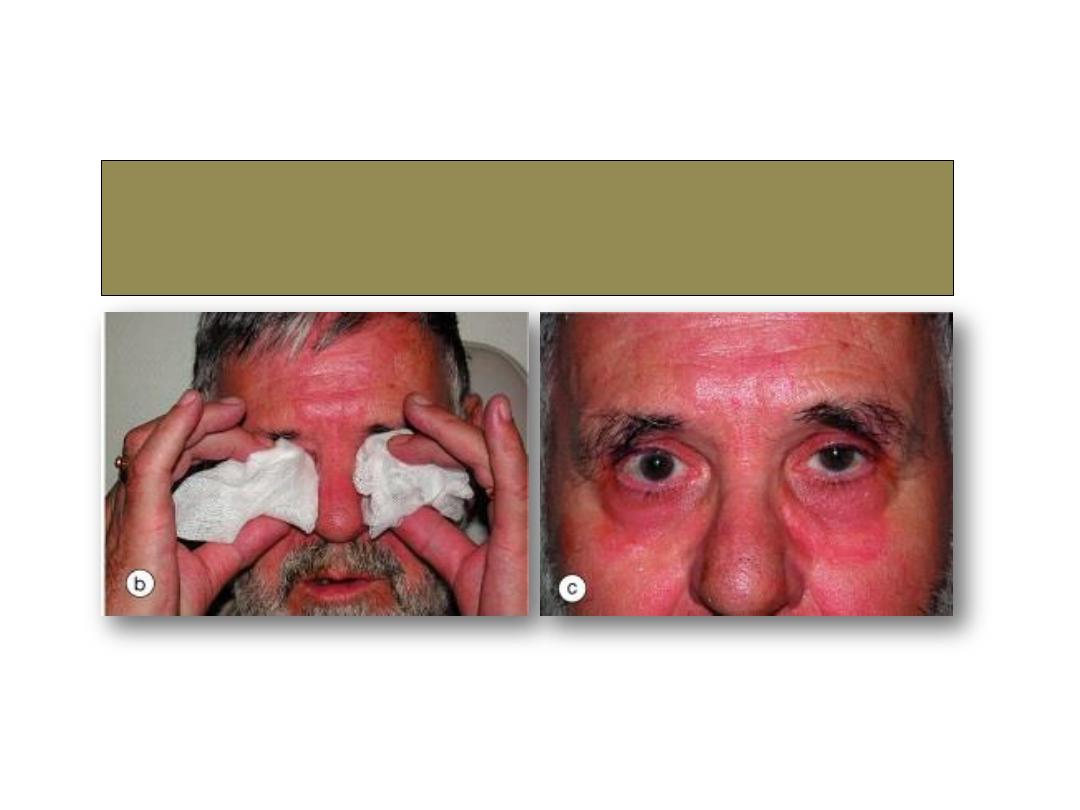
Ice test
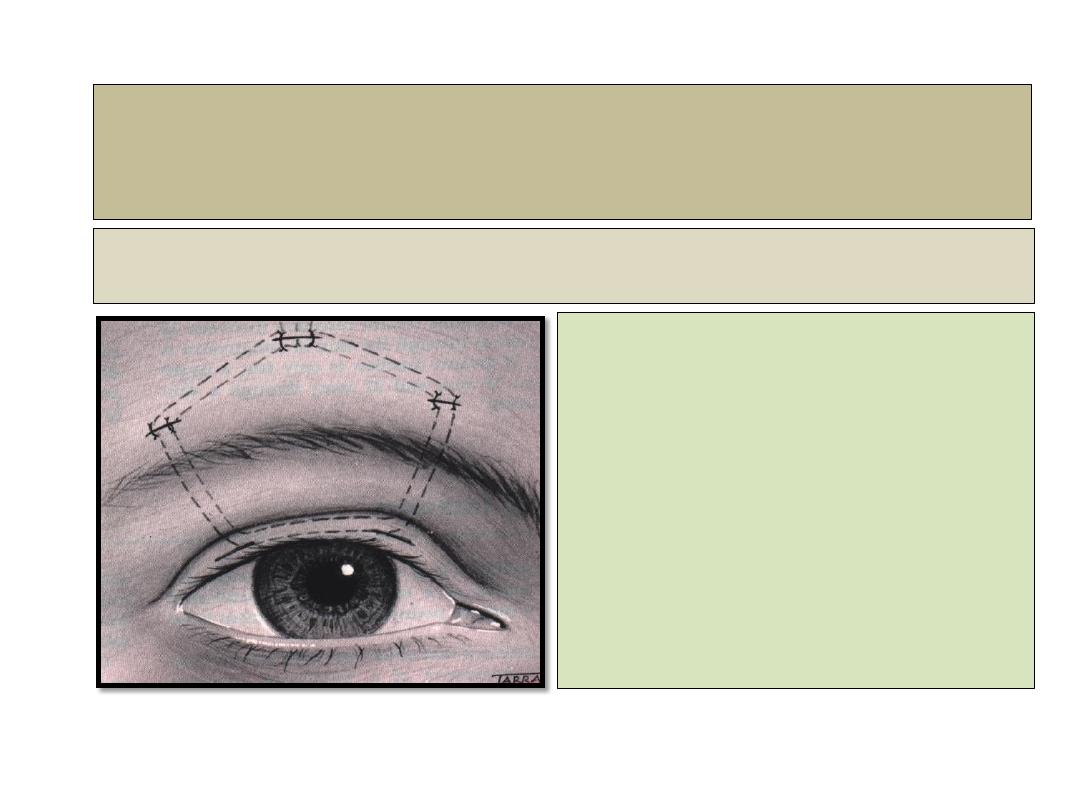
Frontalis brow suspension
Main indications
• Sever ptosis with poor
levator function.
•
Mrcus gunn jaw winking syndrome
.

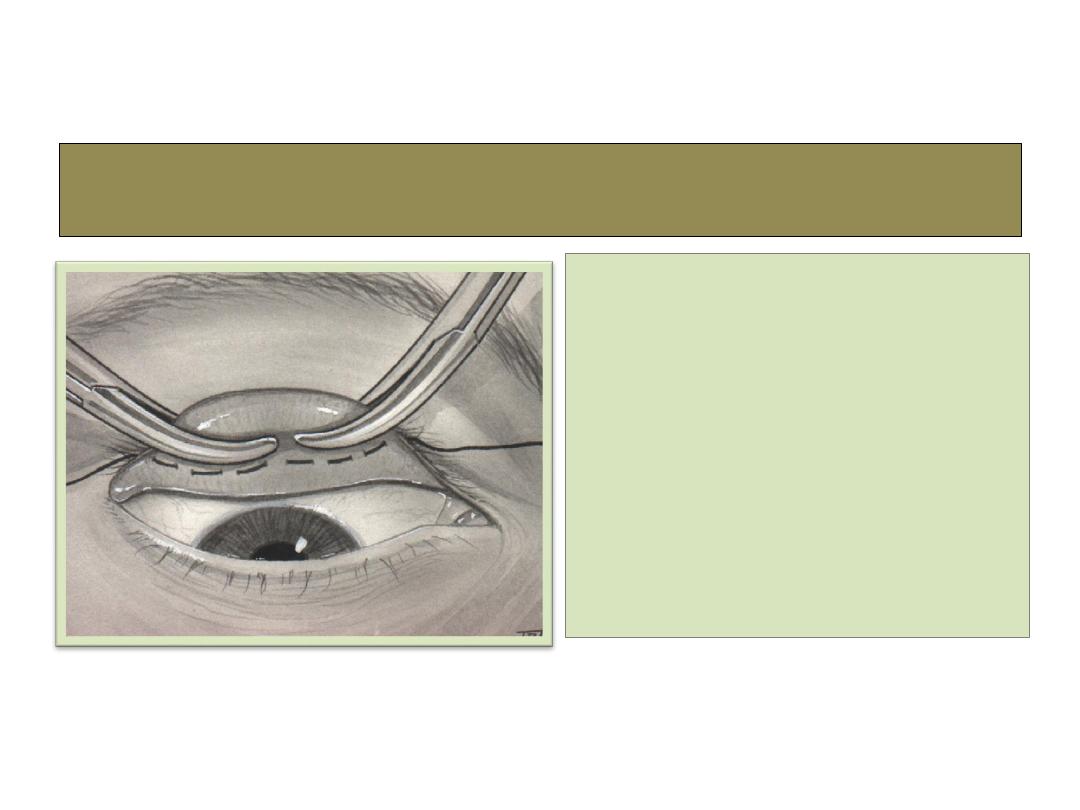
Levator resection
• Indicated for any
ptosis with levator
function at lease
5mm of action.
Fasanella-Servat procedure
• Indicated for mild
ptosis with good
levator function.
Eyelid tumours
1- Benign
2- Malignant
Benign eyelid tumours
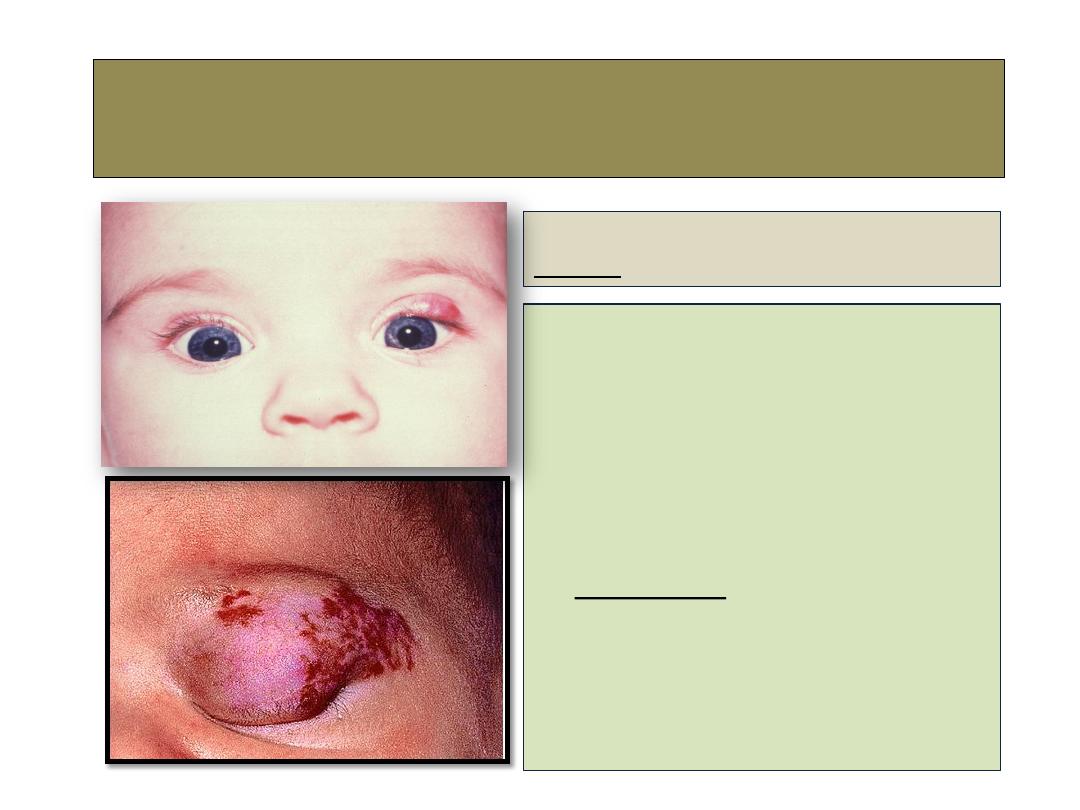
Capillary haemangioma
(strawberry nevus)
Signs:
Unilateral, raised bright red lesion
which blanches on pressure
and may swell on crying.
• A large lesion on upper lid may
cause mechanical ptosis and
amblyopia.
• Treatment:
local steroids if necessary, but
frequently undergoes gradual
spontaneous involution.
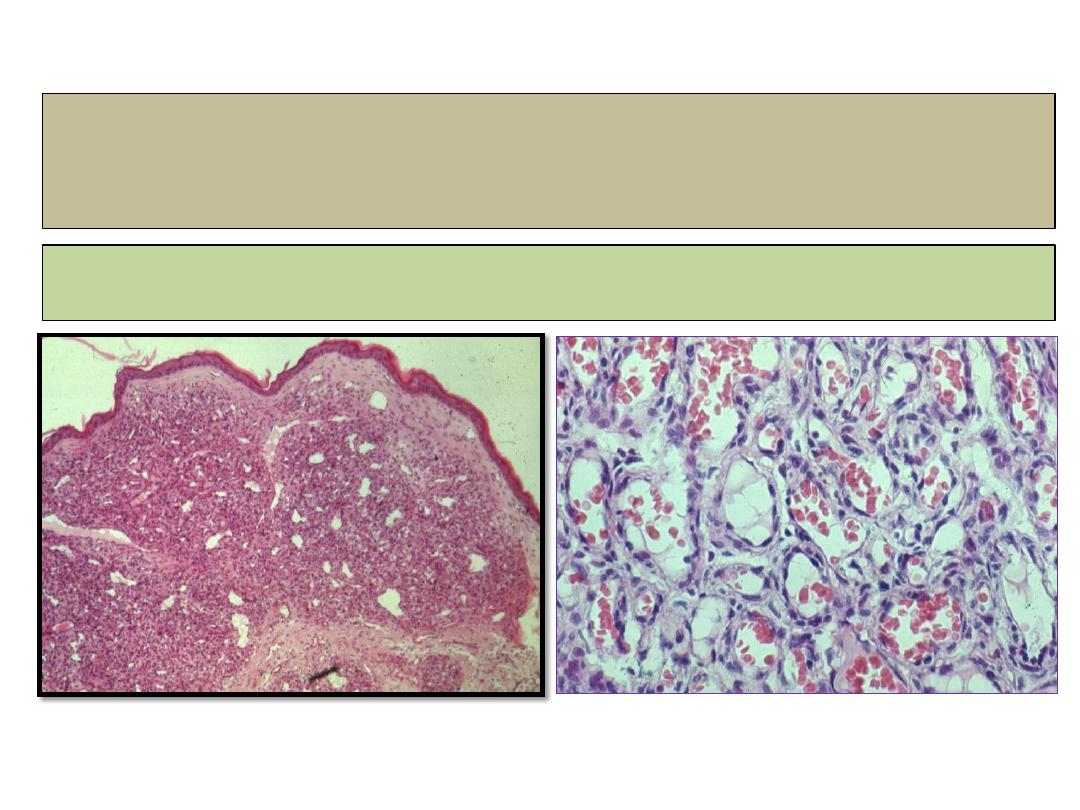
Capillary haemangioma
histopathology
Lobules of capillaries with fine fibrous septa.
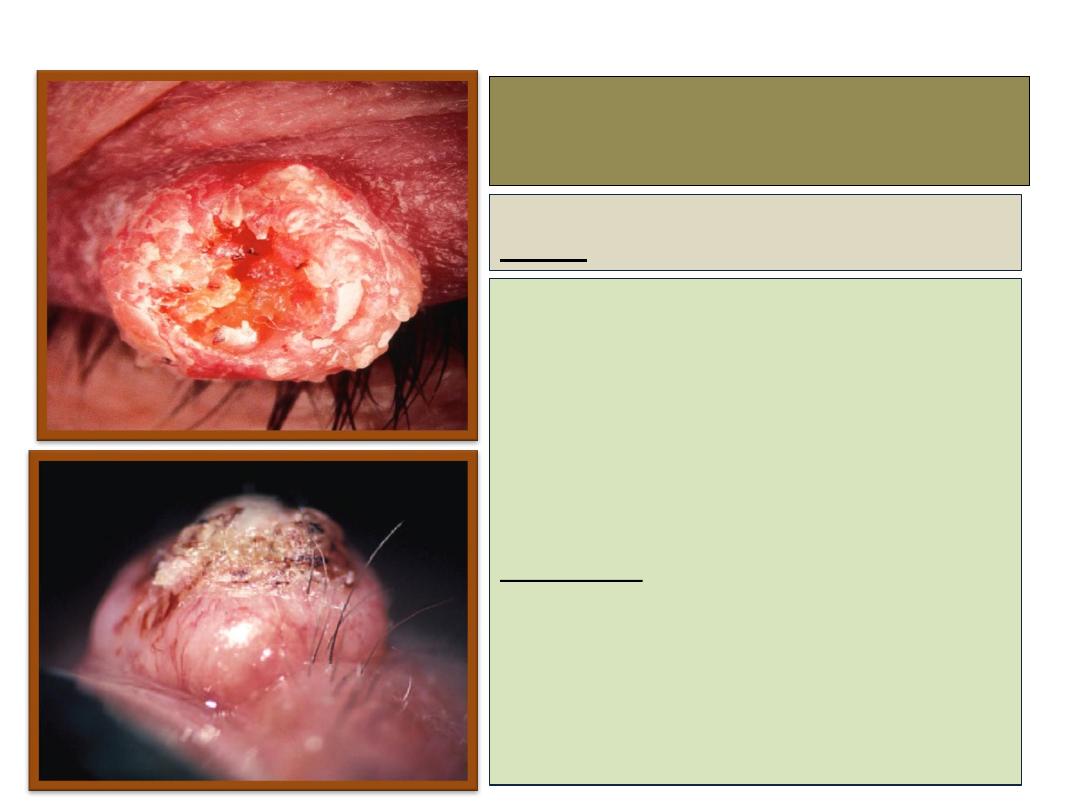
Keratoacanthoma
Signs:
• A pink, rapidly growing,
hyperkeratotic lesion, often on the
lower lid which may double or
treble in size within weeks.
• Growth cease for 2-3 months,
after which spontaneous
involution occurs.
Treatment:
Complete surgical excision, or
radiotherapy, cryotherapy and
topical or intralesional 5-
fluorouracil.
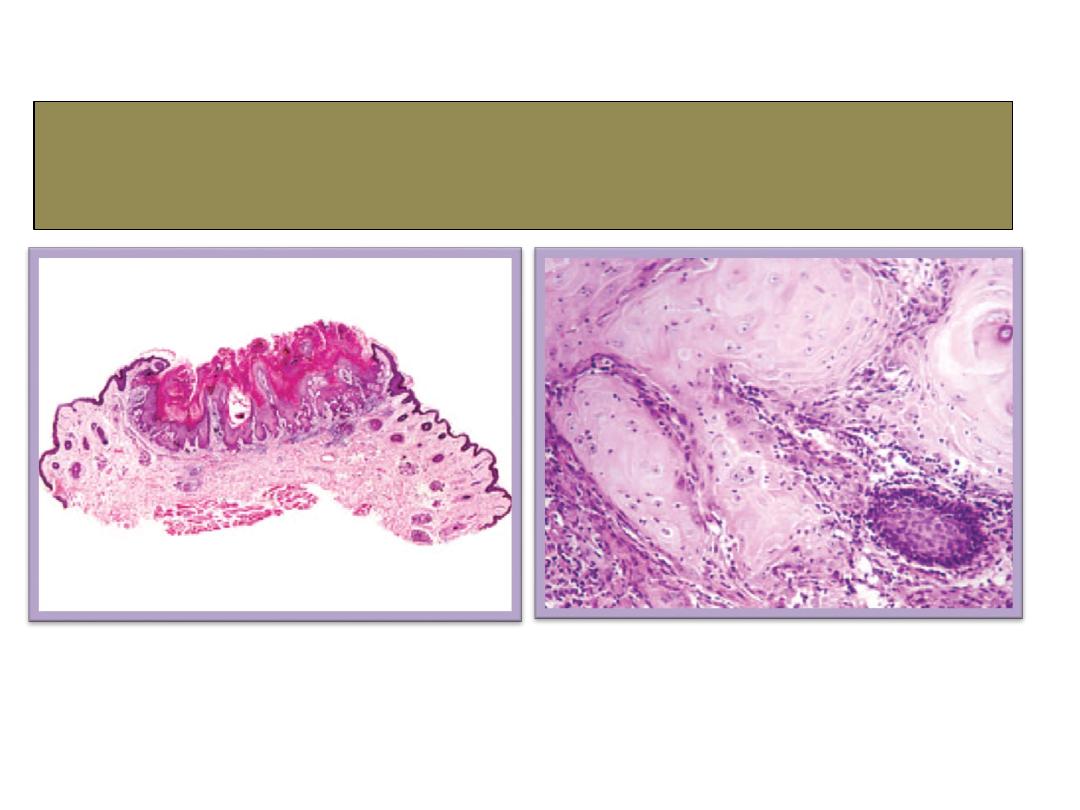
Keratoacanthoma
histopathology
Malignant eyelid tumours
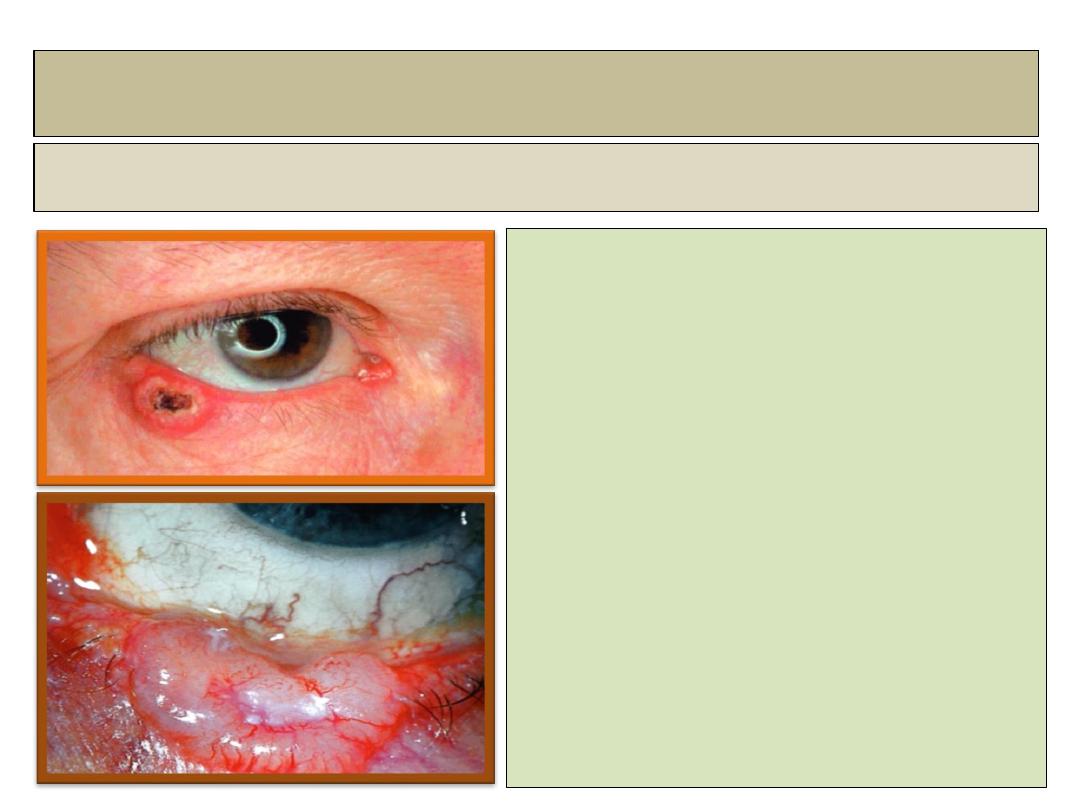
Basal cell carcinoma BCC
Clinical features:
• The most common eyelid
malignancy.
• It is locally invasive, but dose
not metastasize.
• About 50% involve the lower lid,
30% the medial canthal area.
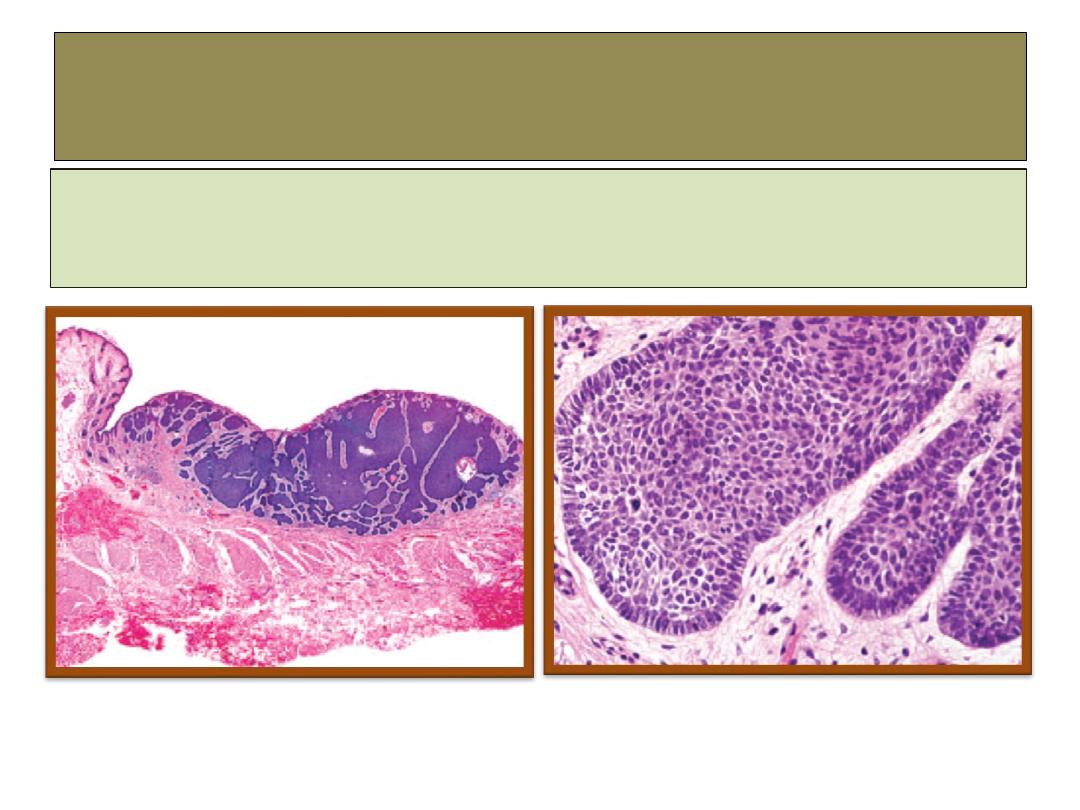
BCC
histopathology
The most important diagnostic feature in basal cell carcinoma is
the “palisading” arrangement of the cells at the periphery of the
nests.
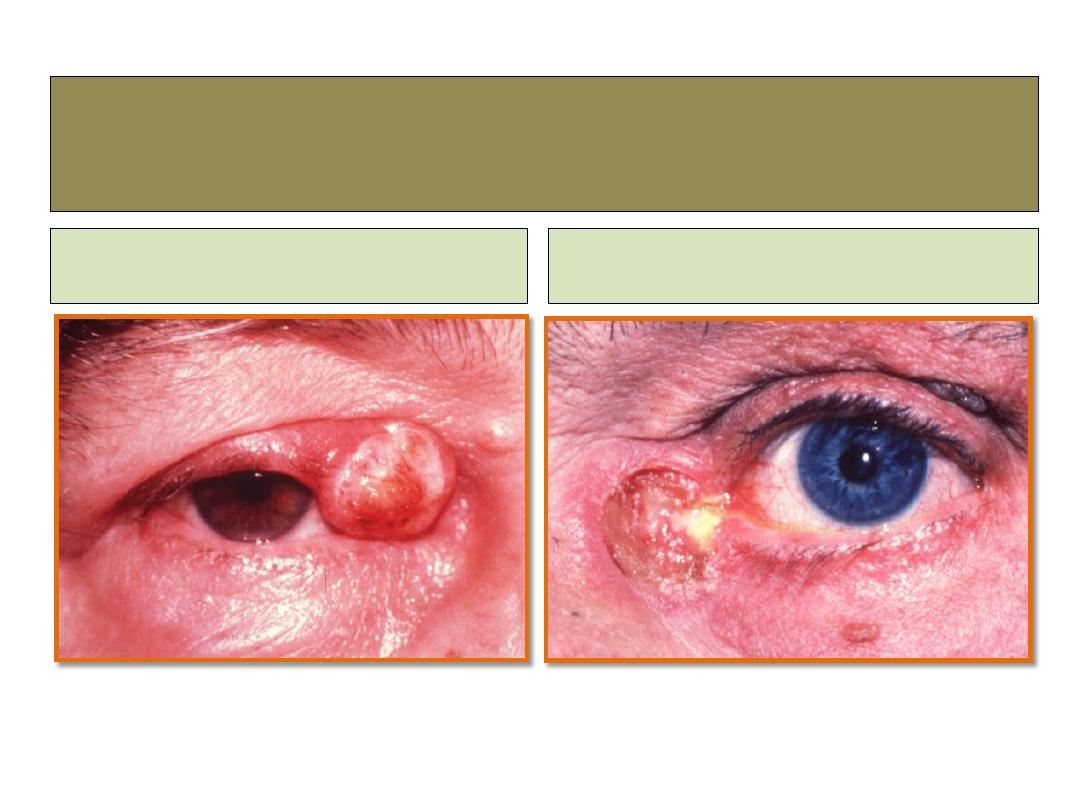
Squamous cell carcinoma-SCC
nodular
ulcerative
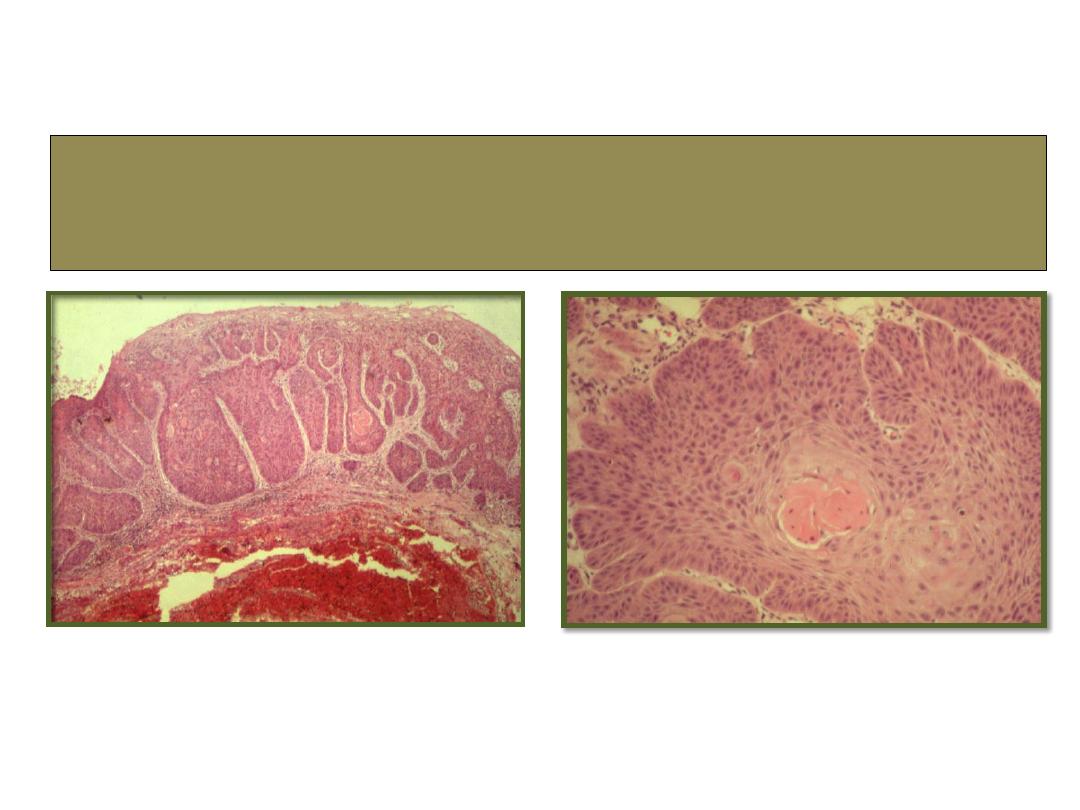
SCC
histopathology
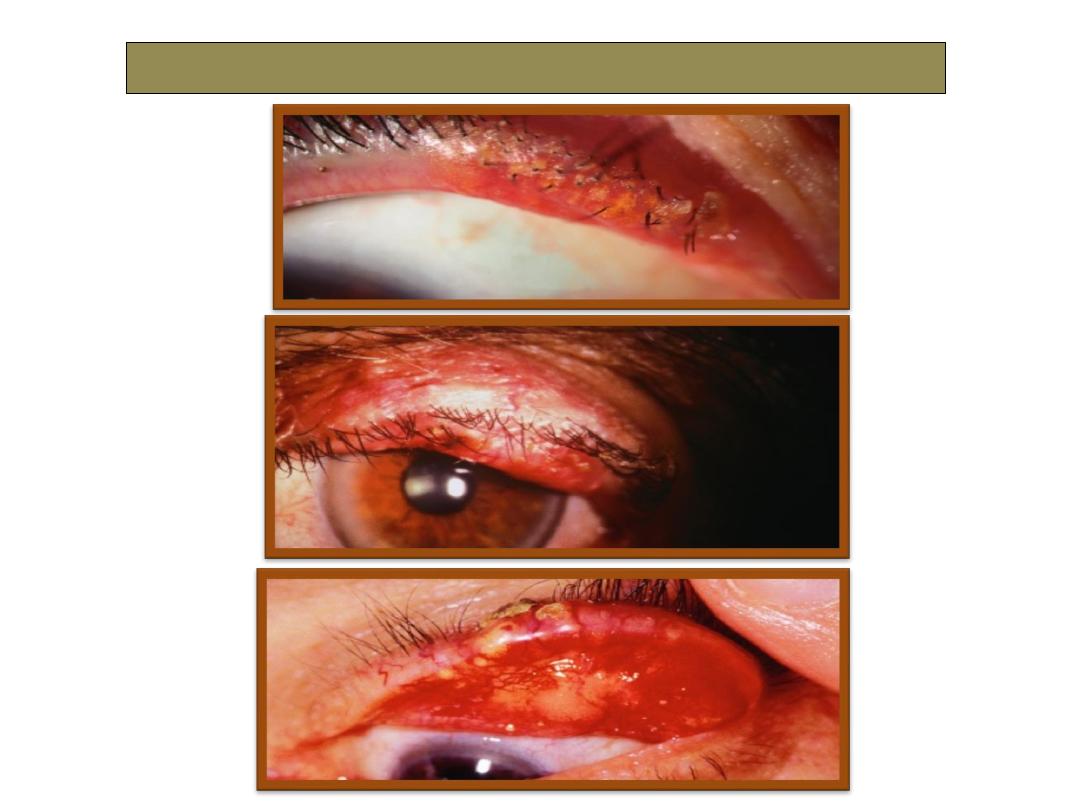
Sebaceous gland carcinoma SGC
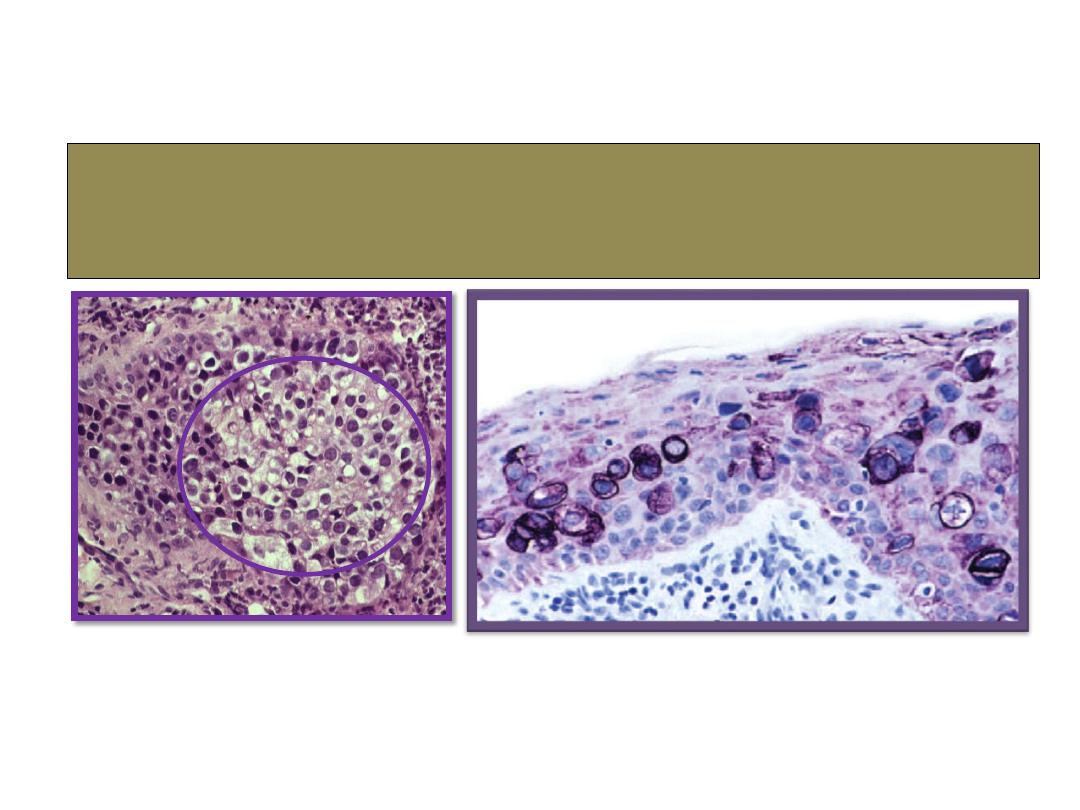
SGC
histopathology
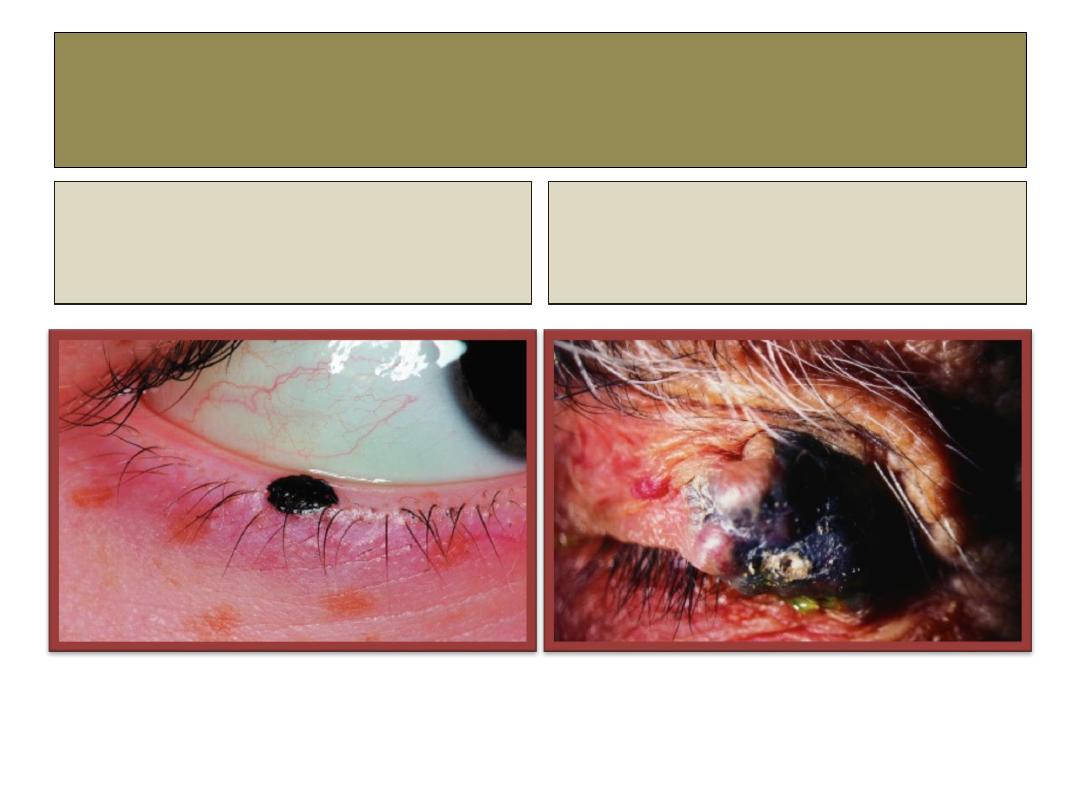
Malignant melanoma
Superficial spreading melanoma:
Plaque with irregular outline and
variable pigmentation.
Nodular melanoma
Blue-black nodule surrounded by
normal skin.
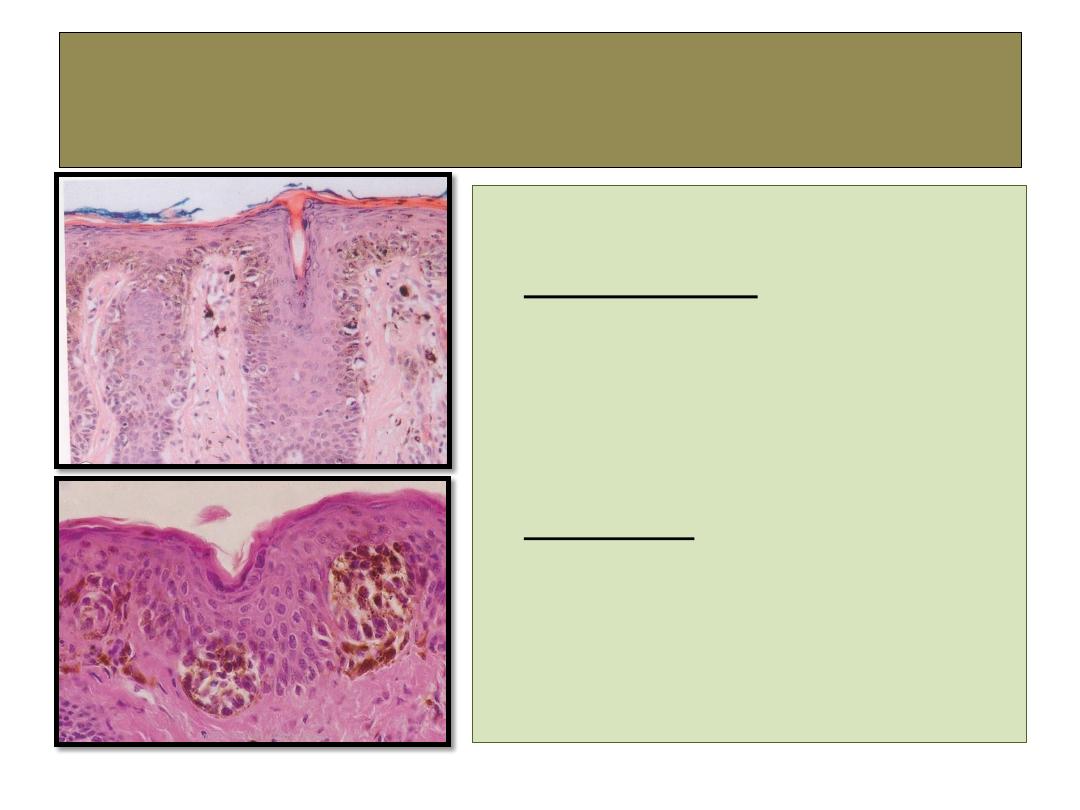
Malignant melanoma
histopathology
• Clinical types:
1-
superficial spreading melanoma .
2- nodular melanoma.
• Histology: shows atypical
melanocytes within the
dermis.
The End
