Antipsychotic drugs
Dr. Safeya AlchalabiAntipsychotic drugs
neurolepticsmajor tranquillizers
Antipsychotic drugs
reduce psychomotor excitement and control symptoms of psychosisAntipsychotic drugs
The main therapeutic uses of antipsychotic drugs are:To reduce hallucinations, delusions, agitation, and psychomotor excitement in schizophrenia, mania, or psychosis secondary to a medical condition.
The drugs are also used prophylactically to prevent relapses of schizophrenia and other psychoses.
Antipsychotic drugs
Chlorpromazinein
1952
Antipsychotic drugs
Pharmacology
psychosis is associated with increased dopamine release in striatal regions
Antipsychotic drugs
Pharmacologythese agents block the ability of increased dopamine release to attribute abnormal salience to irrelevant stimuli.
A list of antipsychotic drugs
PhenothiazinesChlorpromazine
Trifluoperazine
Thioxanthenes
Flupenthixol
Clopenthixol
Butyrophenones
Haloperidol
Dibenzodiazepines
Clozapine
Olanzapine
Dibenzothiazepine
Quetiapine
Substituted benzamides
Sulpiride
Amisulpride
Benzisoxazole
Risperidone
Quinolinone
Aripiprazole
Antipsychotic drugs
PharmacologyAntipsychotic effect is obtained when D2 -receptor occupancy lies in the range 60–70%.
Higher levels are associated with extrapyramidal movement disorders and hyperprolactinaemia, but not with greater efficacy.
Distinction between typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs
Atypical antipsychotic agents have a lower likelihood of causing extrapyramidal side effects within their usual therapeutic range.Distinction between typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs
The risk of tardive dyskinesia appears to be lower with the newer antipsychotic drugs.Distinction between typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs
atypical antipsychotic drugs is improved efficacy relative to typical agents.
Pharmacology of typical (conventional) antipsychotics
PhenothiazinesChlorpromazine is the prototypic phenothiazine.
Pharmacology of typical (conventional) antipsychotics
ChlorpromazineAntagonizes
α1 – adrenoceptors sedation, hypotension.
histamine H1 –receptors sedation,
muscarinic cholinergic receptors dry mouth, urinary difficulties, and constipation.
• Drug
• EPS*• Prolactin elevation
• Weight gain
• Adverse effects
• Amisulpride
• +
• +++
• +
• Insomnia, agitation, nausea, constipation, QT prolongation
• Sulpiride
• +
• +++
• +
• Insomnia, agitation, abnormal liver function tests
• Clozapine
• 0
• 0
• +++
• Agranulocytosis—white cell monitoring mandatory, myocarditis and myopathy (rare), fatigue, drowsiness, dry mouth, sweating, tachycardia, postural hypotension, nausea, constipation, ileus, urinary retention, seizures, diabetes
• Olanzapine
• +/0
• +
• +++
• Somnolence, dizziness, oedema, hypotension, dry mouth, constipation, diabetes, QT prolongation
• Risperidone
• ++
• +++
• ++
• Insomnia, agitation, anxiety, headache, impaired concentration, nausea, abdominal pain, diabetes, QT prolongation
• Quetiapine
• 0
• 0
• ++
• Somnolence, dizziness, postural hypotension, dry mouth, abnormal liver function tests, QT prolongation, diabetes
• Aripiprazole
• +
• 0
• 0
• Agitation, insomnia, nausea, vomiting
Atypical antipsychotics
Depot antipsychotic drugs
Slow-release preparations
esters of conventional antipsychotic
fluphenazine decanoate, flupenthixol decanoate, and haloperidol decanoate.
given intramuscularly in an oily medium
Slow-release injections of atypical antipsychotic drugs such as risperidone, paliperidone (an active metabolite of risperidone), aripiprazole, and olanzapine are also available.
Pharmacokinetics
Drug interactionscentral sedatives
tricyclic antidepressants
antiepileptic drugs
antihypertensive drugs, including ACE inhibitors
antiarrhythmics, astemizole and terfenadine, cisapride, and tricyclic antidepressants, clarithromycin and erythromycin.
carbamazepine, co-trimoxazole, and penicillamine.
SSRIs (notably fluoxetine and paroxetine)
Unwanted effects
Antidopaminergic movement effectsAntiadrenergic effects
Anticholinergic effects
Antihistaminic effects
Unwanted effects
Antidopaminergic movement effects
Acute dystonia
Akathisia
Parkinsonism
Tardive dyskinesia
Antiadrenergic effects
Sedation
Postural hypotension
Inhibition of ejaculation
Anticholinergic effects
Dry mouth
Reduced sweating
Urinary hesitancy and retention
Constipation
Blurred vision
Precipitation of glaucoma
Antihistaminic effects
Sedation
Weight gain
Other effects
Cardiac arrhythmias
Metabolic syndrome and diabetes
Amenorrhoea
Galactorrhoea
Hypothermia
Pulmonary embolus
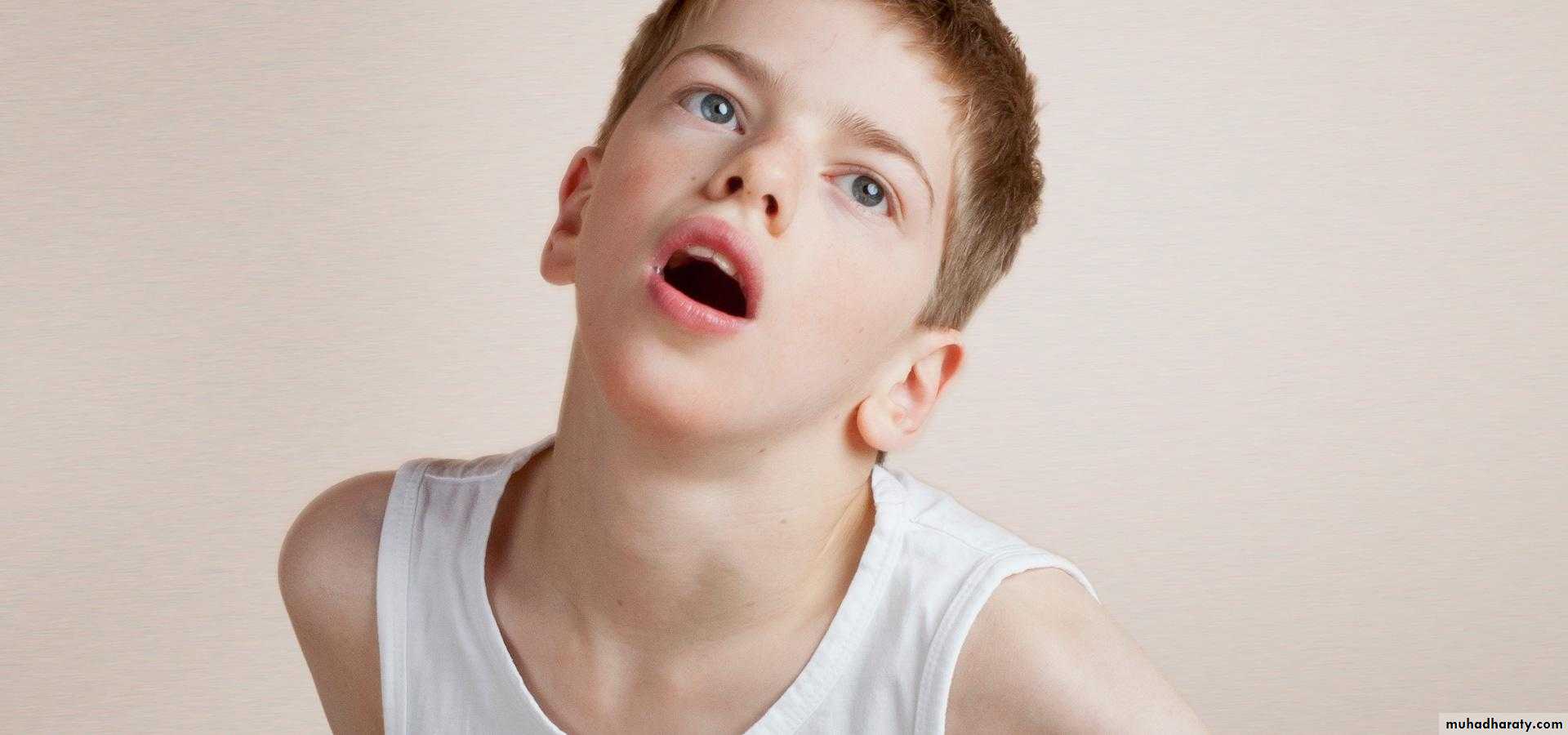
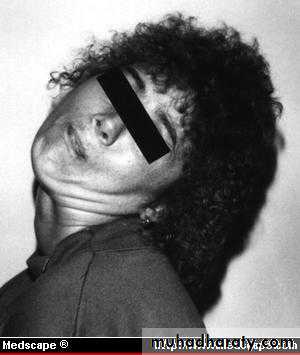
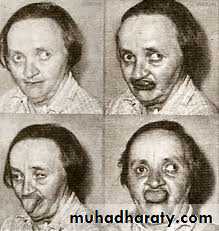
Acute dystonia
Acute dystonia
Acute dystonia
Acute dystoniaAcute dystonia
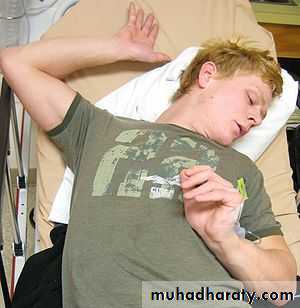
Akathisia
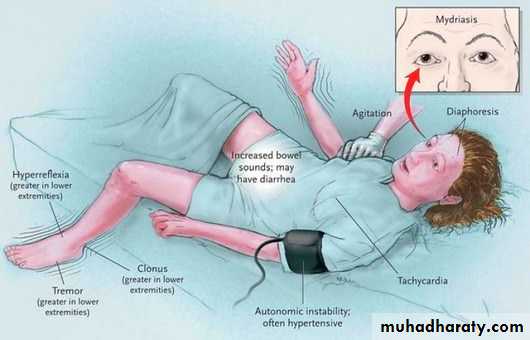
This is an unpleasant feeling of physical restlessness and a need to move, leading to an inability to keep still.Agitation with suicidal ideation can also occur.
Akathisia may wrongly be mistaken for a worsening of psychosis
occurs during the first 2 weeks of treatment with antipsychotic Akathisia is not reliably controlled by antiparkinsonian drugs.
Beta-adrenoceptor antagonists and short-term treatment with benzodiazepines may be helpful.
The best strategy is to reduce the dose of antipsychotic drug,
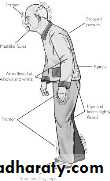
Parkinsonian syndrome
akinesia,an expressionless face,
lack of associated movements when walking,
rigidity,
coarse tremor,
stooped posture,
in severe cases, a festinant gait.
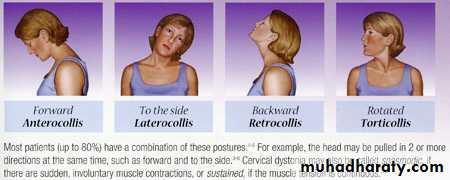
Tardive dyskinesia
chewing and sucking movements, grimacing, choreoathetoid movements, and possibly akathisia.The movements usually affect the face, but the limbs and the muscles of respiration may also be involved.
• hyperprolactinaemia:
menstrual disturbances,• increased risk of malignancy,
• increased galactorrhea,&
• increased osteoporosis.
Prolactine sparing is aripiprazole
sedation• Increased sedation with high affinity to histamine& muscarinic receptors
• E.g.CPZ,olanzapine,clozapine
• Helpful in acute state
Histamine & 5HT R block
• (>olanzapine) less with resperidone,& aripipraz>clozapine &olanzapine
• Should be monitored by Bd sugar,lipid profile& weight.through their effect on the lipid profile ,Wt,& insulin resistance.
• Some produce prolonge QT interval.• olanzapine& resperidone