Viral infection3
Dr Anfal laythArab board of dermatology
Viral exanthemas
An exanthem is defined as a skin eruption occurring as a sign of a general disease.Viral exanthems may present with distinctive cutaneous features or in an entirely nonspecific fashion
Enanthems: rash on mucous membrane.
Incubational period
ProdromalEnanthem
Exanthem
Fade
The clinical types of viral exanthems
Viral exanthema
Differential diagnosis of morbilliform eruption
Viral infection: Measles, rubella, roseola, infectious mononucleosisBacterial infection: Scarlet fever
Reactive erythema: Urticaria, erythema multiforme
Drug eruption: Ampicillin, barbiturate, NSAIDs
MEASLESSynonym: ■ Rubeola
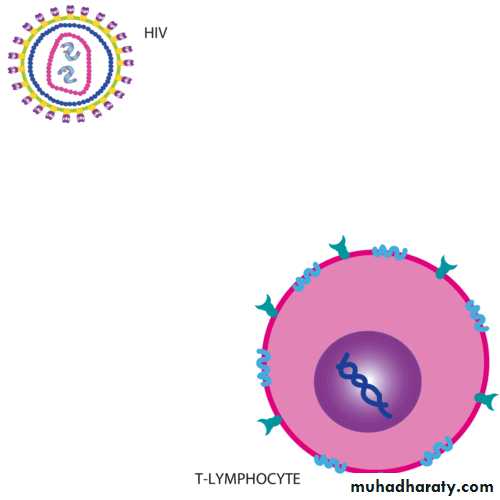
Measles is caused by an RNA virus in the Paramyxoviridae familyHumans are the natural host and reservoir of infection
Incidence greatly decreased with vaccination
pathogenesis
The incubation period of measles, which is highly contagious and spread via respiratory droplets, is 10–14 daysTarget populations were unvaccinated children younger than 5 years of age
replication of the virus within the epithelial cells of the respiratory tract spread to the lymphoid tissue and blood, resulting in viremia.
The virus can then disseminate to internal organs, including the lungs, liver, and gastrointestinal tract.
Clinical feature
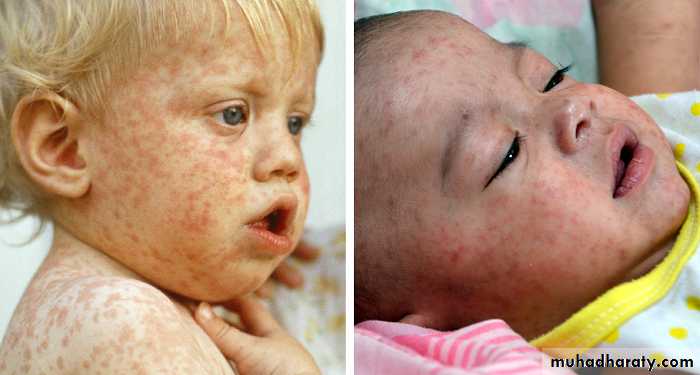
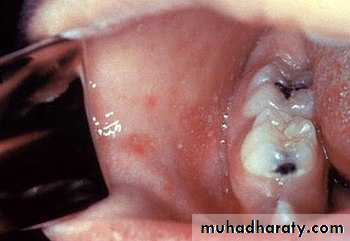
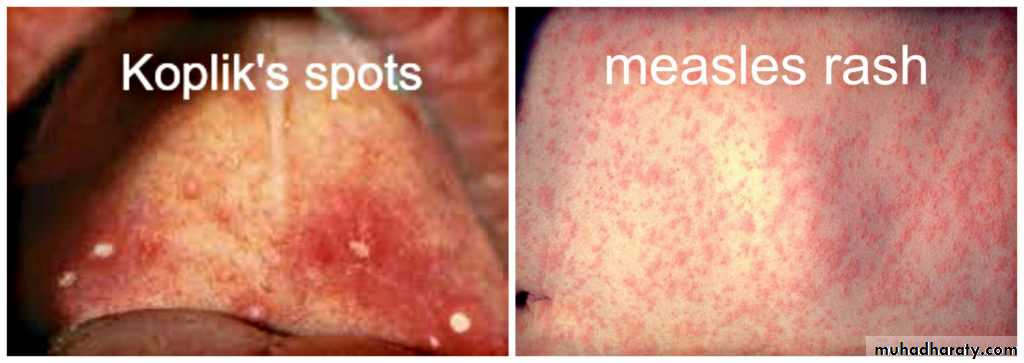
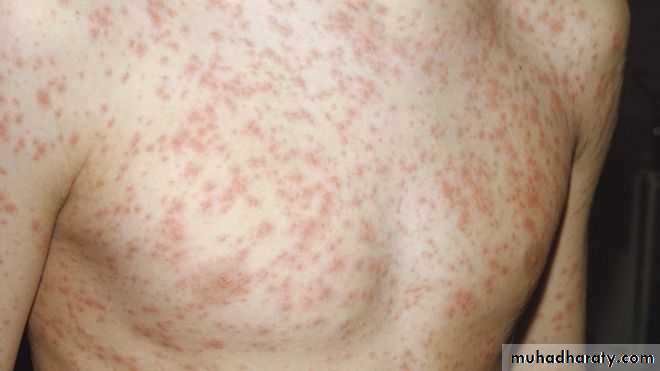
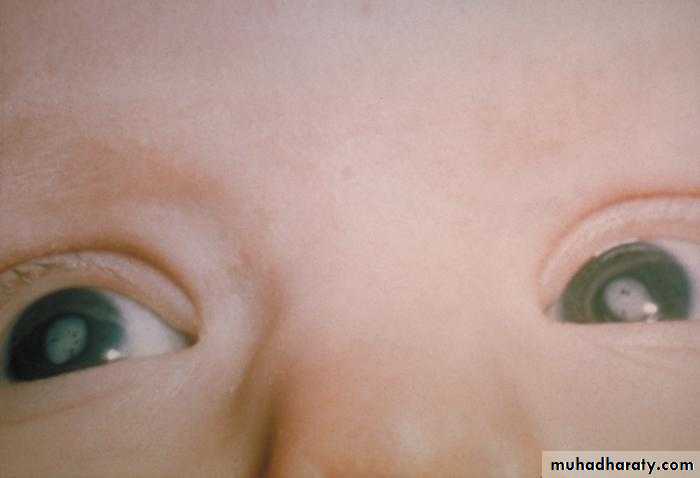
Measles classically presents with a prodrome of fever, cough, nasal congestion, and rhinoconjunctivitis.A pathognomonic enanthem, Koplik spots, appears during the prodrome and is composed of gray– white papules on the buccal mucosa.
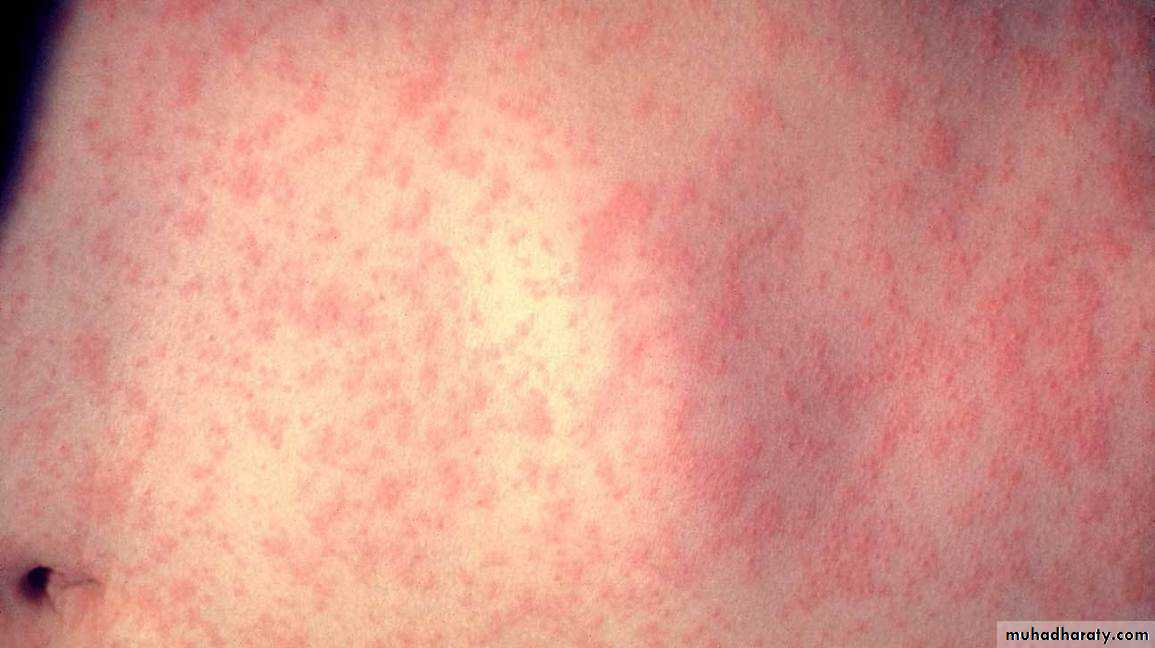
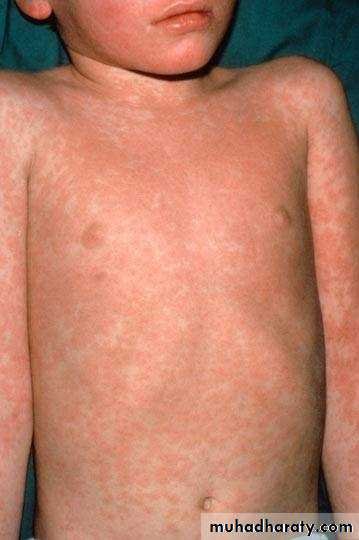
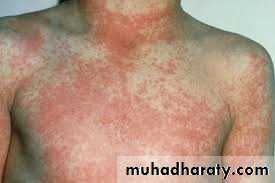
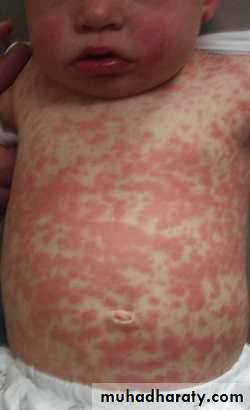
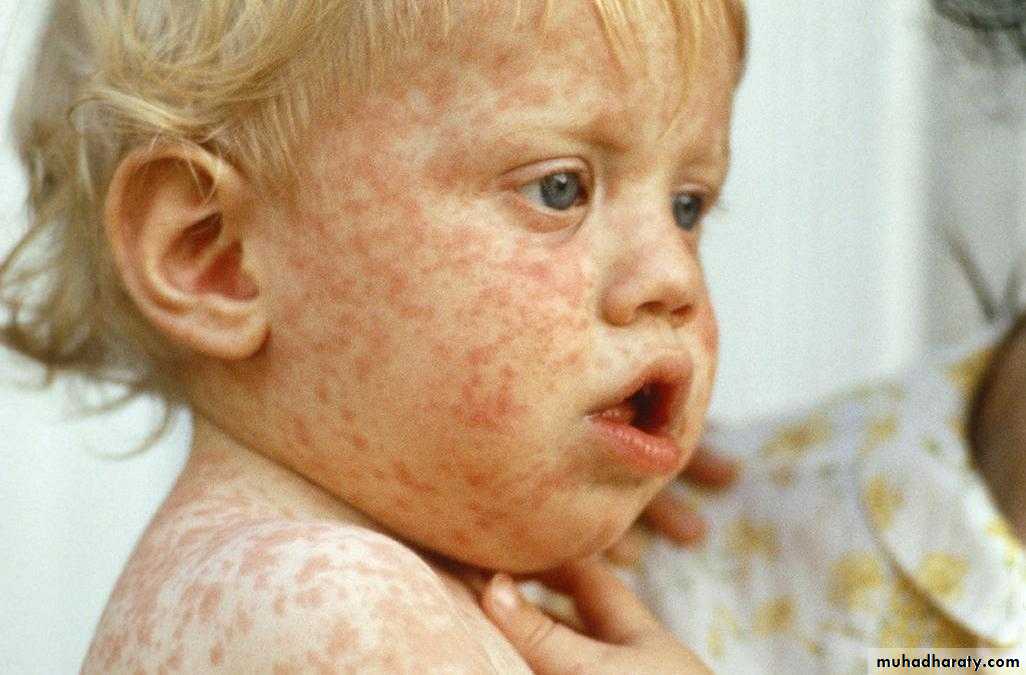
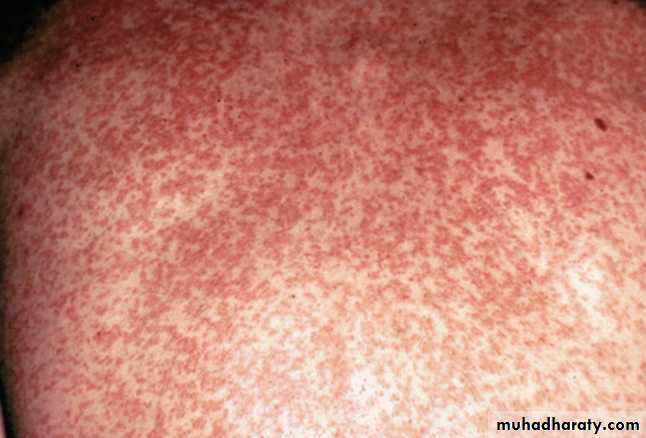
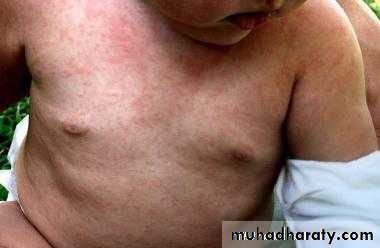
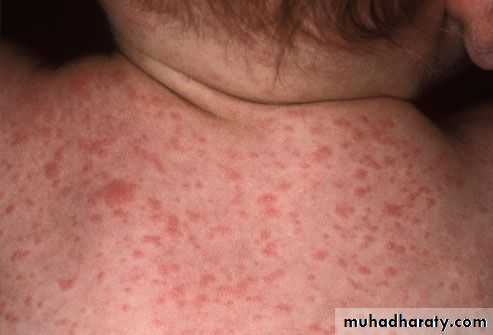
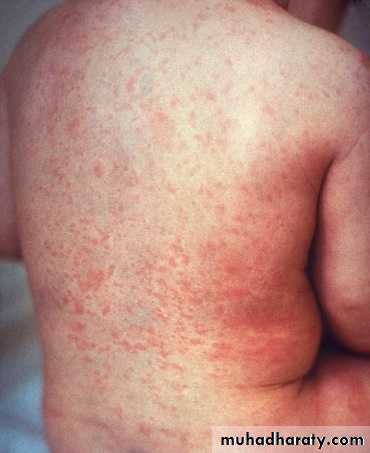
The exanthem develops over 2–4 days and consists of erythematous macules and papules that begin on the forehead, hairline, and behind the ears and then spread in a cephalocaudad direction
On the fifth day, the exanthem starts to fade in the same order as it appeared.
Treatment:
1. Symptomatic: bed rest, antipyretics, analgesics.2. High dose vitamin A.
3. Vaccination at 15 months.
4. Immunoglobulin.
Rubella(German measles)(3 days measles)
Rubella is caused by an RNA virus in the Togaviridae familyThe disease is spread via respiratory droplets,
with an incubation period of 16–18 days.
Clinical features
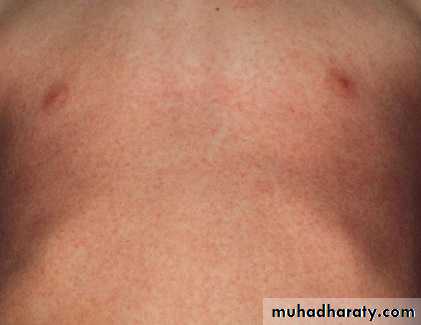
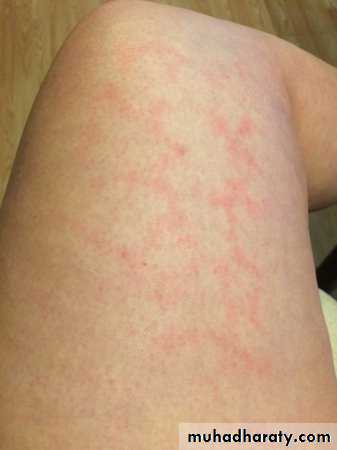
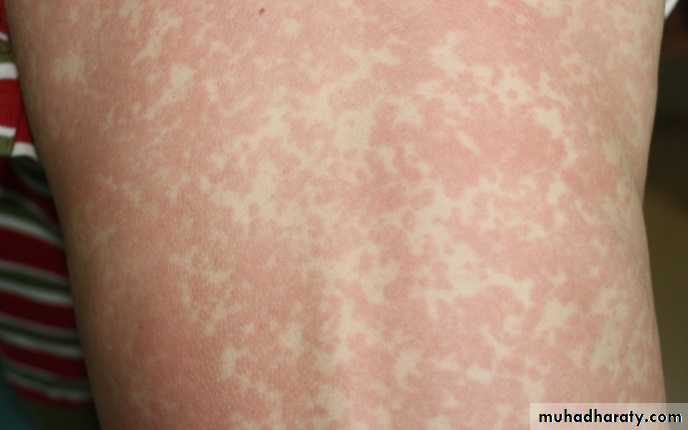
Rubella typically presents with a mild prodrome that includes fever, headache, and upper respiratory symptoms. In children, many cases are subclinical.One to 5 days following the prodrome, an eruption of erythematous macules and papules appears on the face, spreading in a cephalocaudad direction.
Erythematous petechial macules may also be present on the soft palate (Forchheimer spots).
The eruption is often accompanied by tender lymphadenopathy, especially of the occipital, posterior auricular, and cervical regions.
The cutaneous eruption tends to fade in 2–3 days in the same order as it appeared
Note
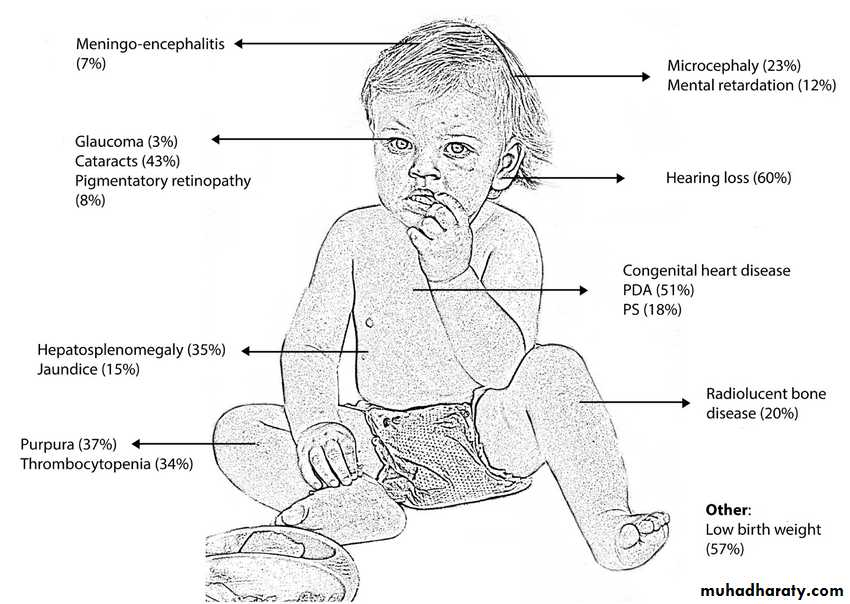
Rubella during pregnancy (1st trimester) associated with congenital abnormalities in the fetus in the form of cataract, cardiac defect and deafness.
Treatment and prevention
Treatment of rubella is supportive.The current recommended immunization schedule for rubella vaccine, which is given in conjunction with the measles and mumps vaccines (MMR vaccine), is an initial dose at 12–15 months and a second dose at 4–6 years16
Characteristics
MeaslesRubella
Etiology
Paramyxovirus
TogavirusI.P.
10 days
2-3 wks
Route of transmission
Respiratory droplet
Respiratory dropletProdrome
High fever, malaise, cough, coryza, sneezing, conjunctivitis, adenopathy
Absent or mild or low grade fever, upper respiratory symptoms, adenopathy & eye painExanthems
Onset
7 days after prodrome
5 days after prodrome
Shape
Large, coalescing morbilliform rashesSmall morbilliform or scarlet-like lesion
Distribution
Forehead & behind ear; extend centrifugally & caudally in 3 days; fade in same mannerForehead & behind ear; extend centrifugally & caudally in 1 day; fade in same manner
Duration
Last 7 days
Last 3 days
Enanthems
Name
Koplik’s spot
Forscheimer’s sign
Shape
White papules on red baseTiny red macules or petechiae
Site
Buccal mucosaSoft palate & uvula
Complication
Otitis media, pneumonia, encephalitis, thrombocytopenia
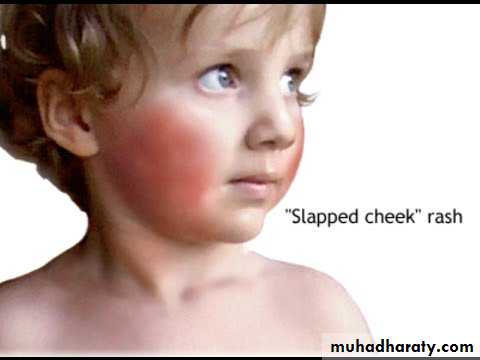
Arthritis & congenital rubella infection syndrome if occur in 1st trimester of pregnancyERYTHEMA INFECTIOSUMFifth disease ■ “Slapped cheek” disease ■ Parvovirus B19 infec
Human parvovirus B19 (B19), the only parvovirus known to infect humans, it is small single-stranded DNA viruspeak incidence of erythema infectiosum during the winter and spring.
Age of patient: children
Clinical features
Mild prodromal symptoms such as a low-grade fever, myalgias, and headache may develop 7–10 days before the characteristic exanthem appears
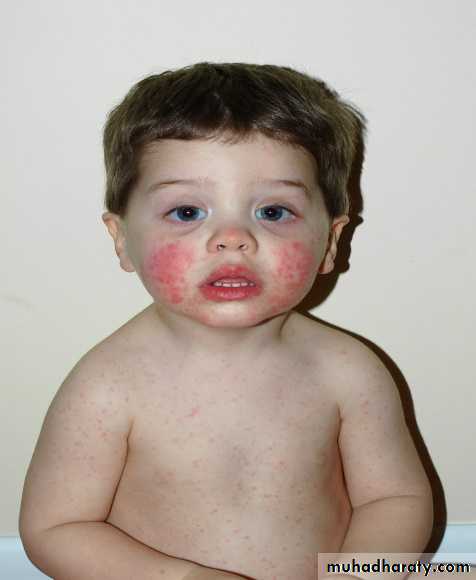
initial stage of the exanthem consists of bright red macular erythema of the cheeks, with sparing of the nasal bridge and circumoral regions Slapped check stage
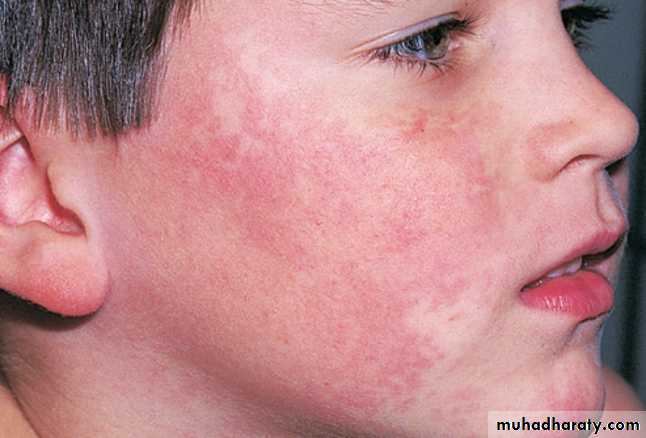
One to 4 days later, the second stage appears as erythematous reticulated pattern on extermities lasts 1–3 weeks Lacy erythema stage
Recurrent stage : after completely resolution of the condition in 5-6 days, child develop recurrent facial erythema after exposure to heat or sun
Roseola infantumExanthem subitum ■ Sixth disease
is a common febrile illness of infancy that is primarily caused by human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) infection and is occasionally associated with human herpesvirus-7 (HHV-7) infectionAge of patient: infant
Clinical picture: infant suffer from prodrome of high fever & lymphadenopathy for 4 days.
In the fourth day fever suddenly drop & morbilliform exanthems appear distributed on the trunk.
The rash will disappear completely in two days
treatment supportive
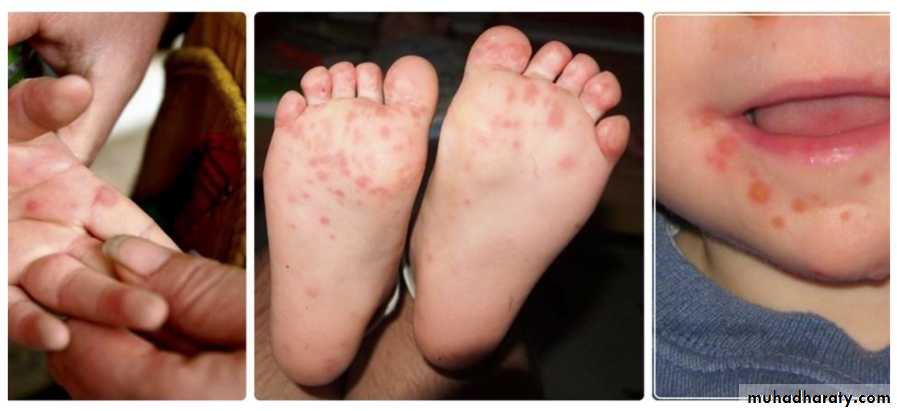
Hand, foot and mouth disease
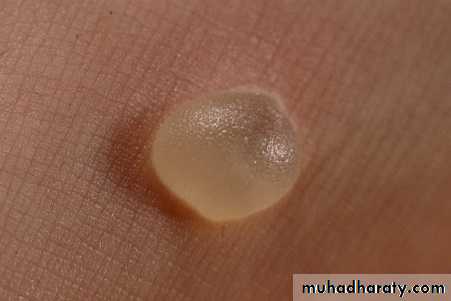
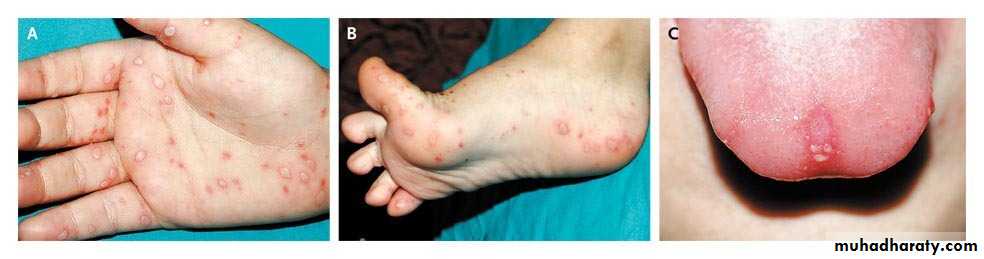
Caused: coxsackie A16 virusThis disorder is characterized by a vesicular eruption on the palms and soles in conjunction with an erosive stomatitis.
Oral lesions: consist of small vesicles which rapidly ulcerate surrounded by erythema.
Hand and feet lesions: are red papules which quickly become small gray vesicles with red halo, oval and run parallel with skin line.
Lesions improve spontaneously and treatment is supportive
Herpangina
Acute infectious illness.Cause: coxsackie virus (group A).
Age: child.
Clinical picture: A child presented with fever and severe sore throat, covered with many small vesicles, which rapidly become superficial ulcers.
The episode resolve in about a week