
Dr. Hala Al- Salman
F.I.B.M.S. (derm.)

The key of successful treatment is an
accurate diagnosis
This will require:
a careful history.
a thorough physical examination.
the use of laboratory investigations.

Dermatology
differ from other
branches as its diseases can
easily be
seen
.
Its important to
examine
the
patient briefly
before
obtaining
a full history (
primary look
).

Lesion:
any abnormal area of skin,
it may be single or multiple.
Rash:
Widespread eruption of lesions
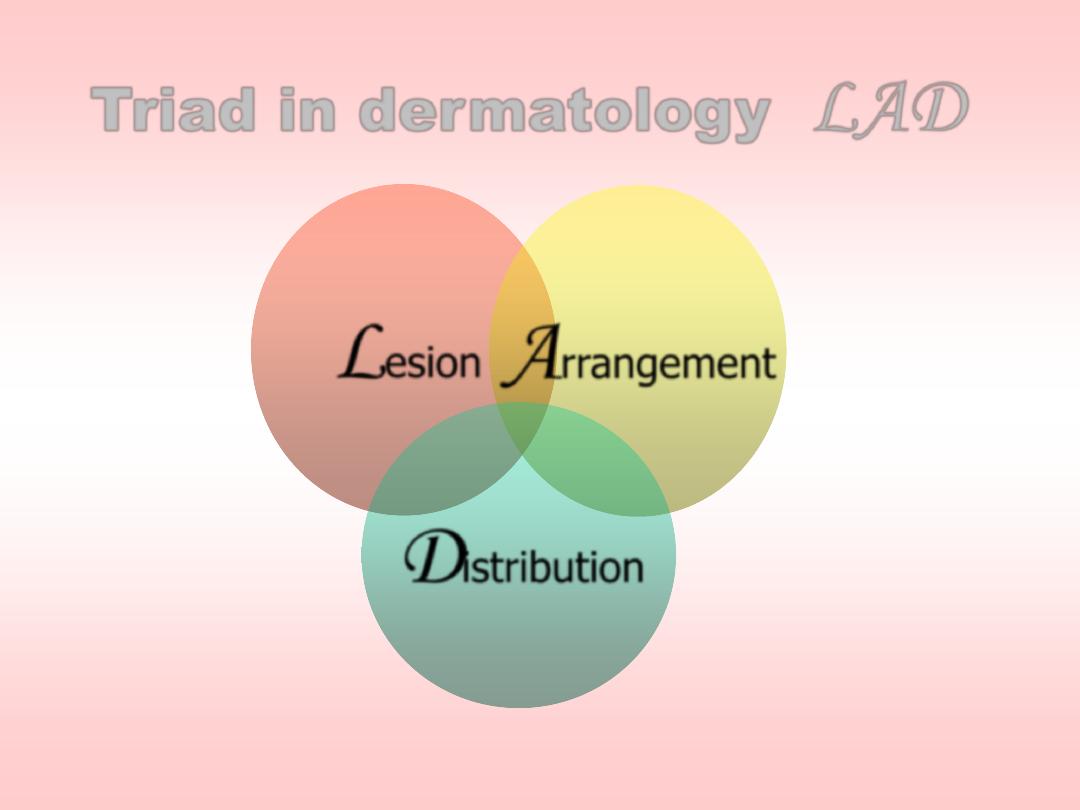
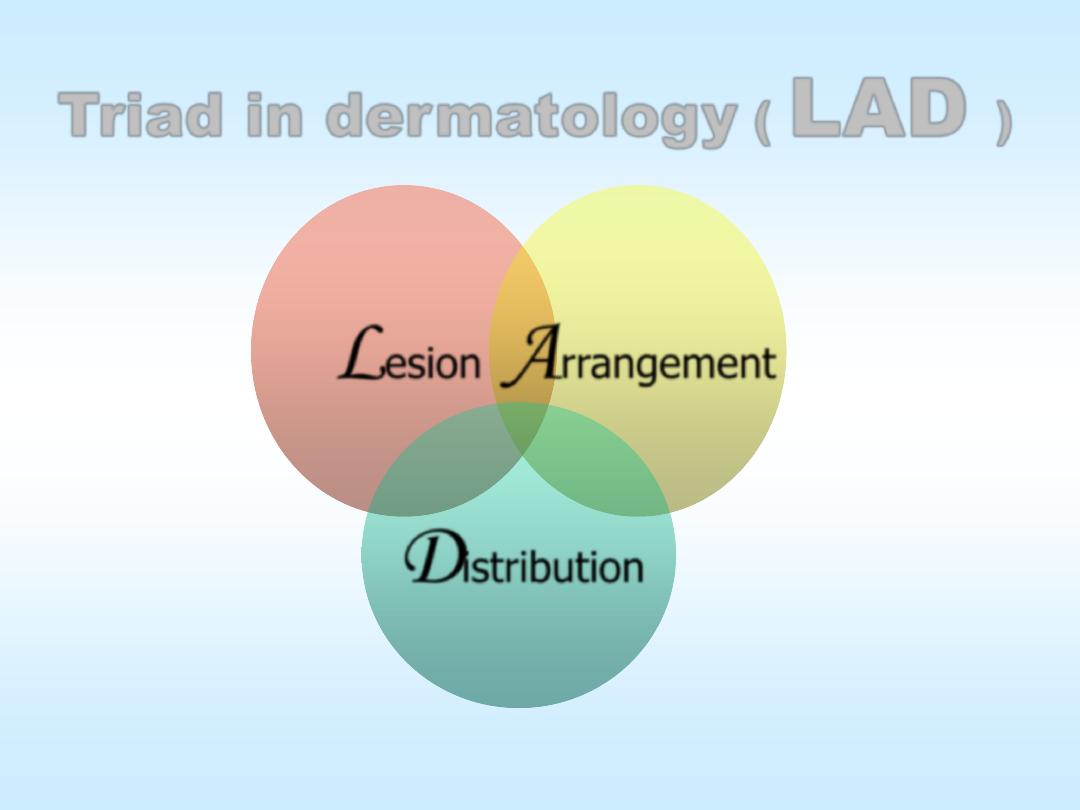
Triad in dermatology
(
LAD
)
L
esion
A
rrangement
D
istribution
Primary
Secondary
•
Macule
•
Papule
•
Vesicle
•
Pustule
•
Wheal
•
Nodule
•
Patch
•
Plaque
•
Bulla
•
Abscess
•
Angioedema
•
Scale
•
Crust
•
Ulcer
•
Erosion
•
Fissure
•
Excoriation
•
Sinus
•
Atrophy
•
Lichenification
•
Pigmentation

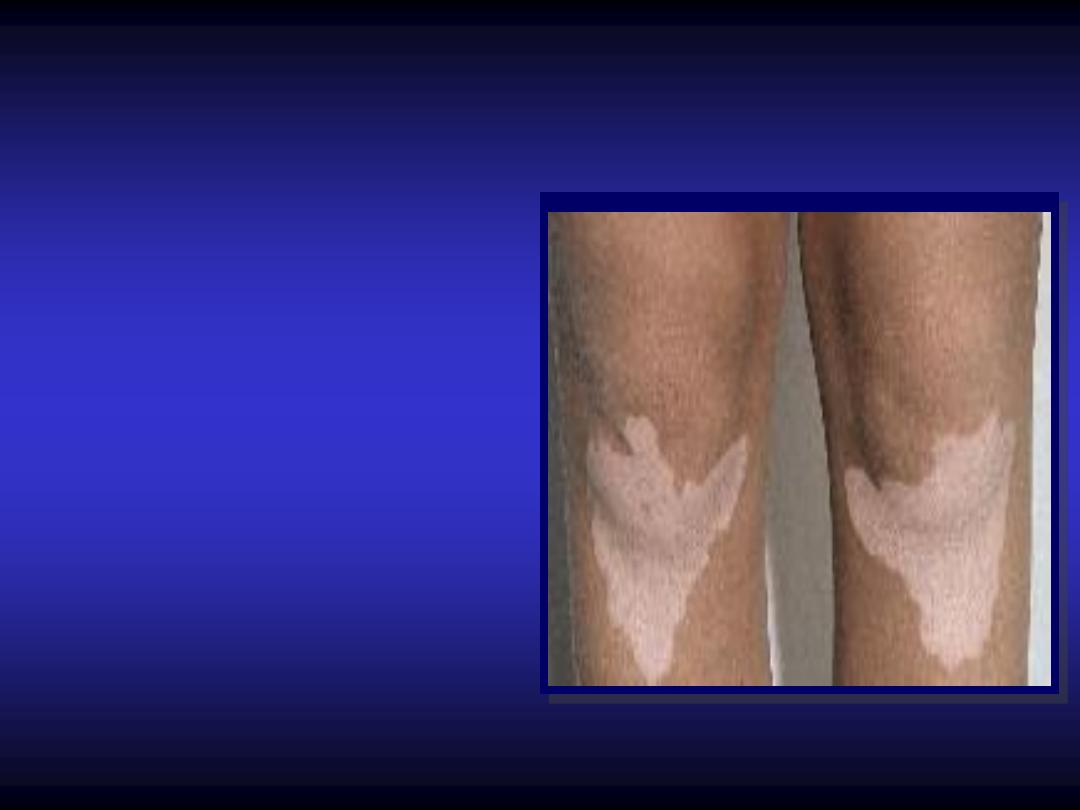
Macule / patch
-
Small
flat
area of
altered color less
than
0.5
cm.
-
Patches are large
macule
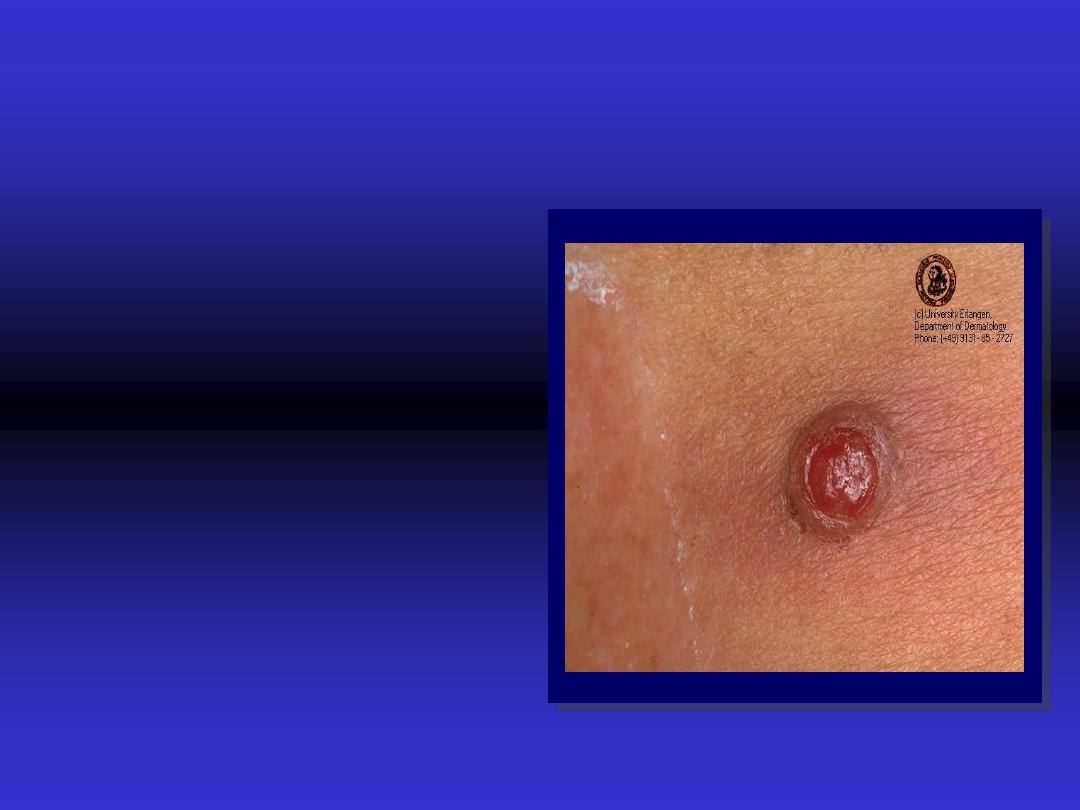
Papule
Elevated solid area
smaller than
0.5
cm
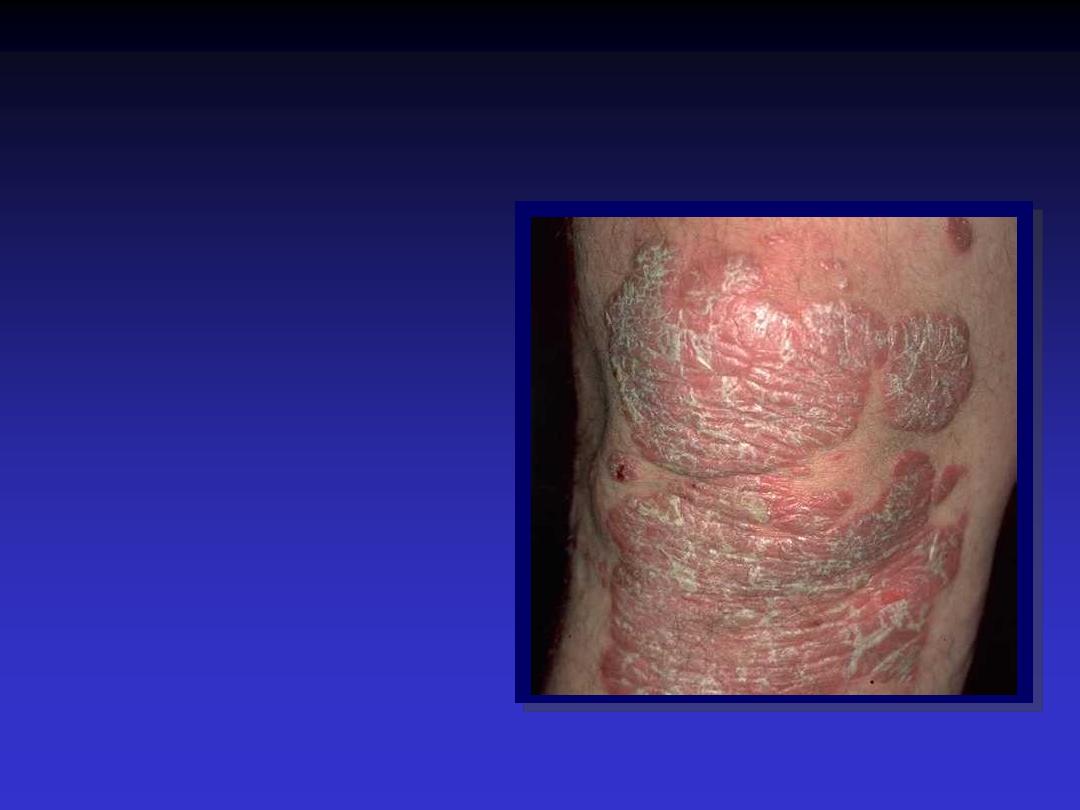
Plaque
Elevated solid area greater
than
0.5 cm
but without
substantial depth
Nodule
Elevated solid mass
greater than
0.5
cm in
width & depth.
It can observed as
elevation or can be
palpated
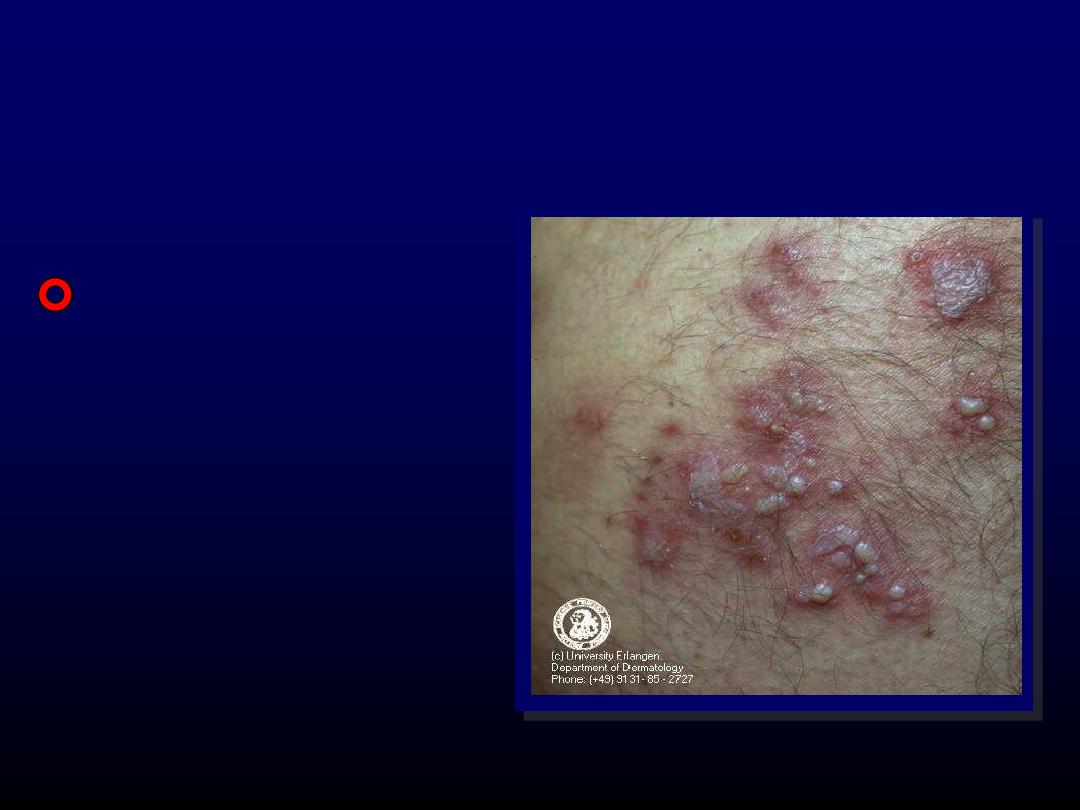
Vesicle
Circumscribed
elevation
of
skin,
less than
0.5
cm in
diameter, filled with
fluid
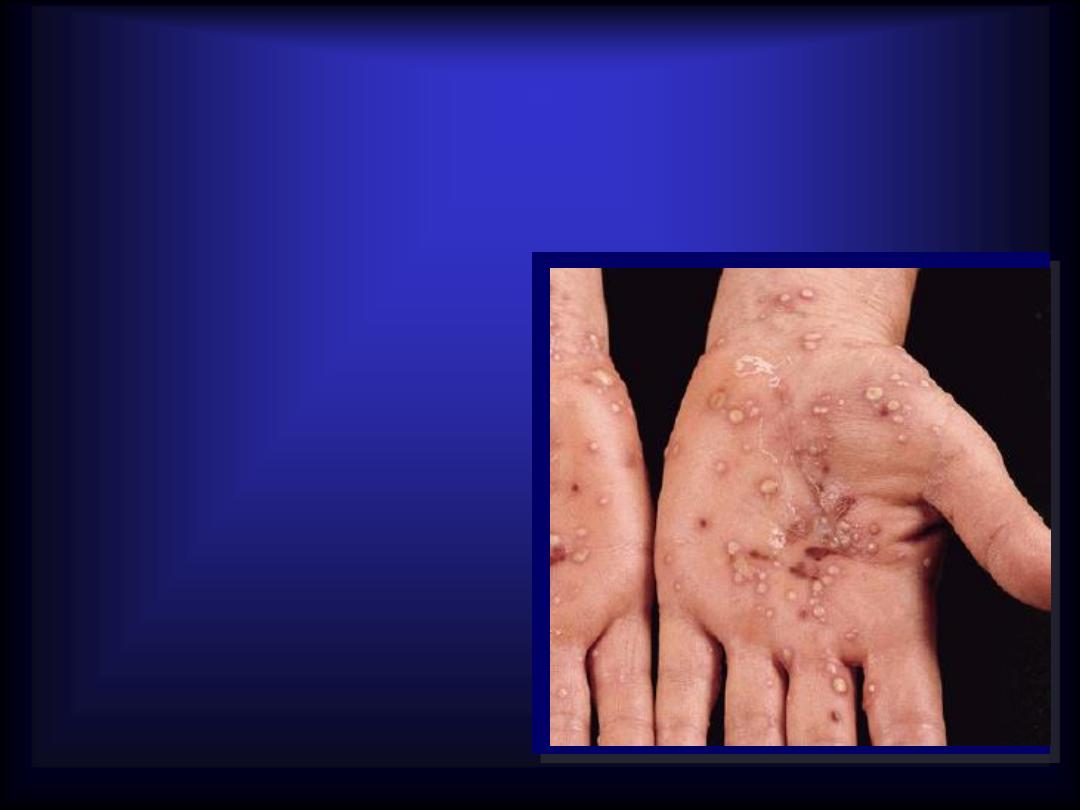
Pustule
Visible accumulation
of
pus
. The size is
smaller than
0.5
cm
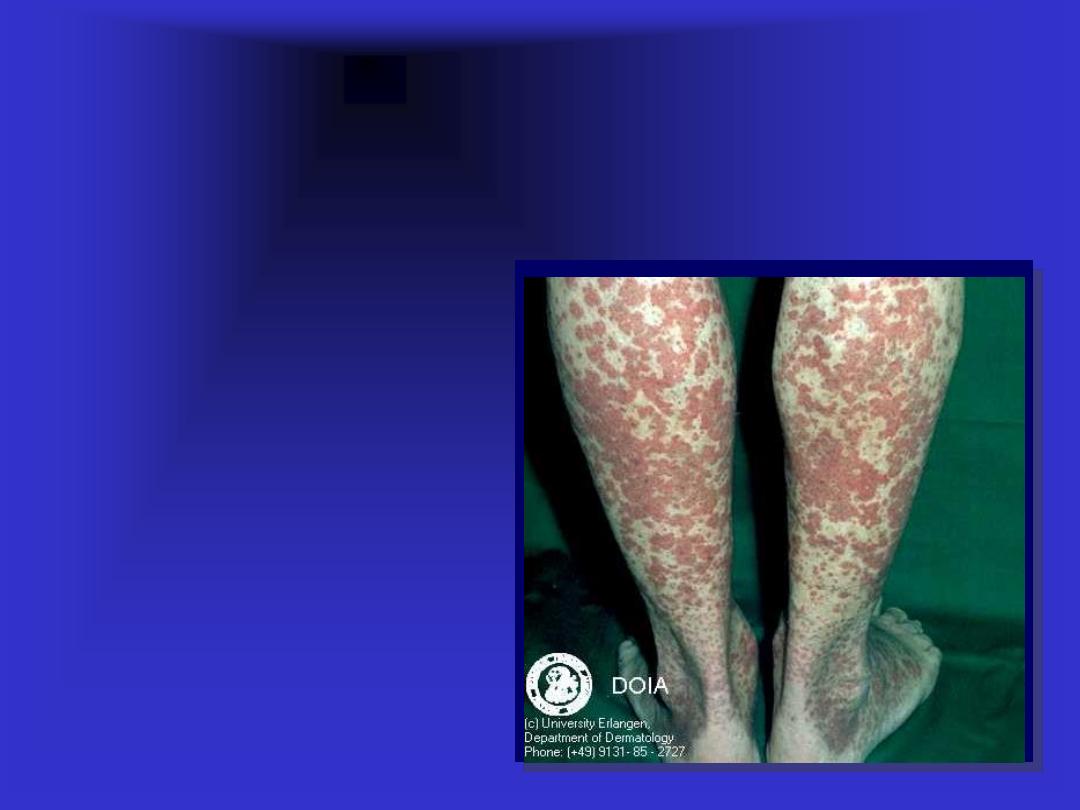
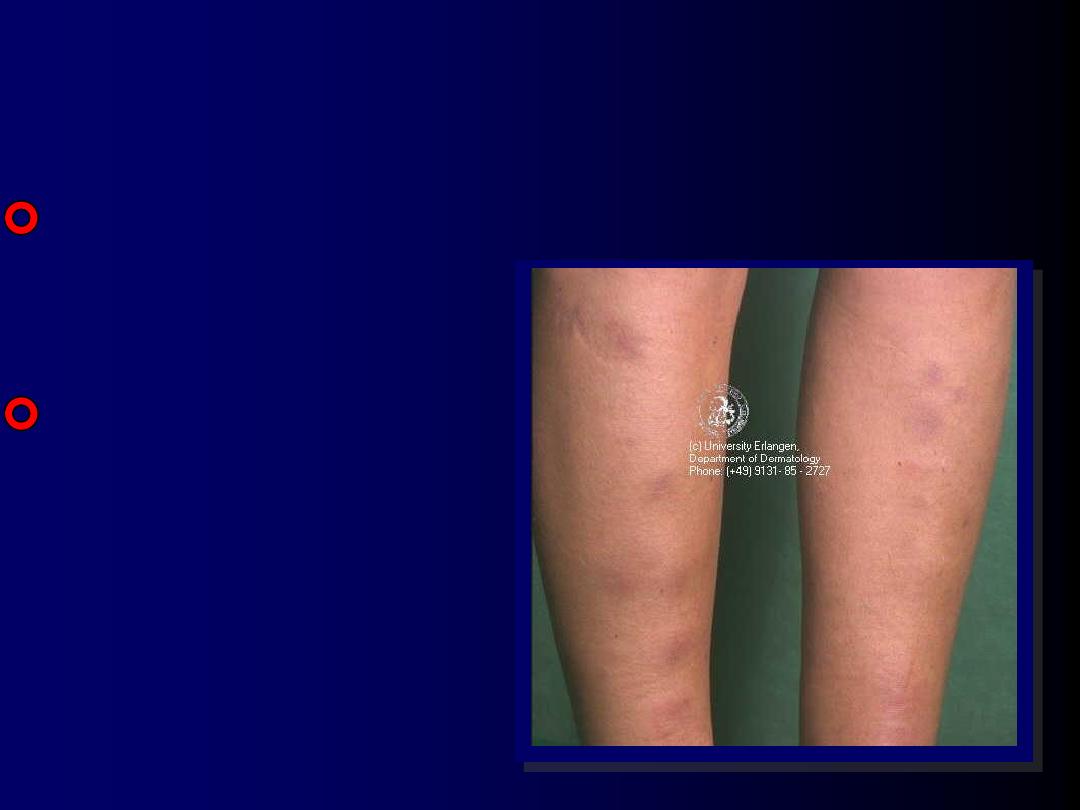
Petechiae – Purpura –
ecchymosis - Hematoma
All result from
extravasations of
blood
.
The difference in
size.
All are non
blanchable.

Burrow
Liner or curvilinear papule caused
by burrowing of the scabies mite
into skin.
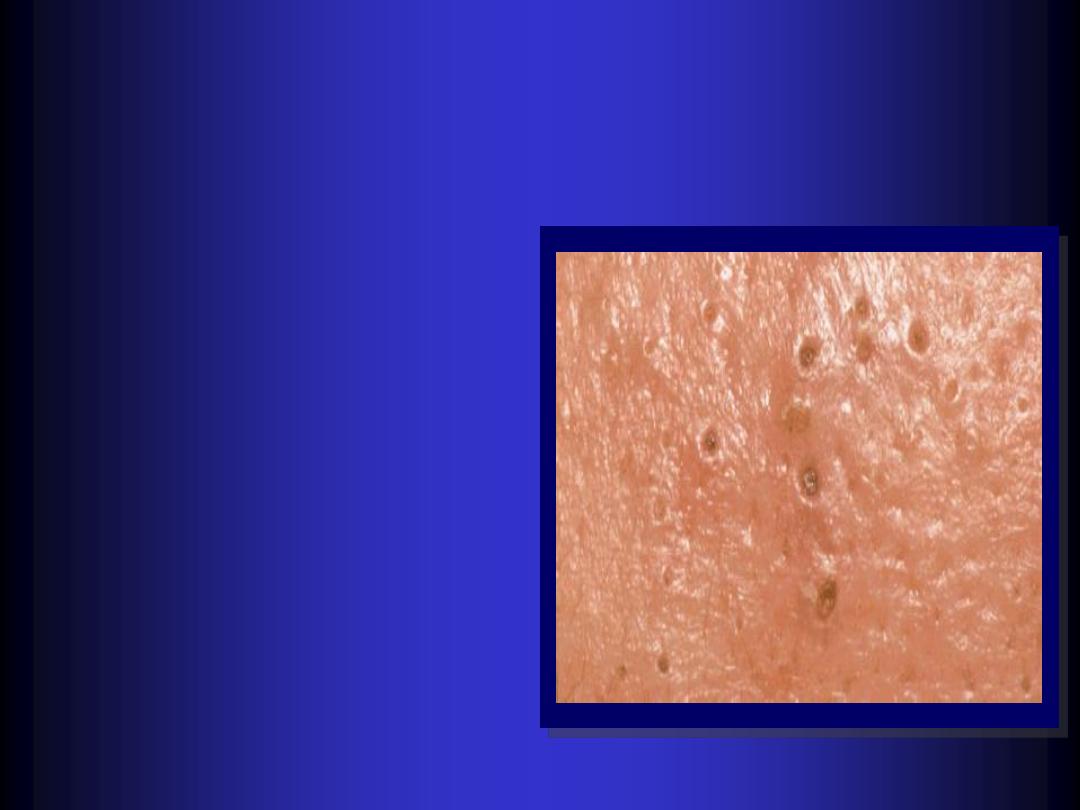
Comedo
-
A
plug
of greasy keratin &
sebum wedged in a dilated
pilosebaceous orifice.
-
Open comedones are
black heads.
-
Closed comedones are
white head.
-
(pathognomonic)
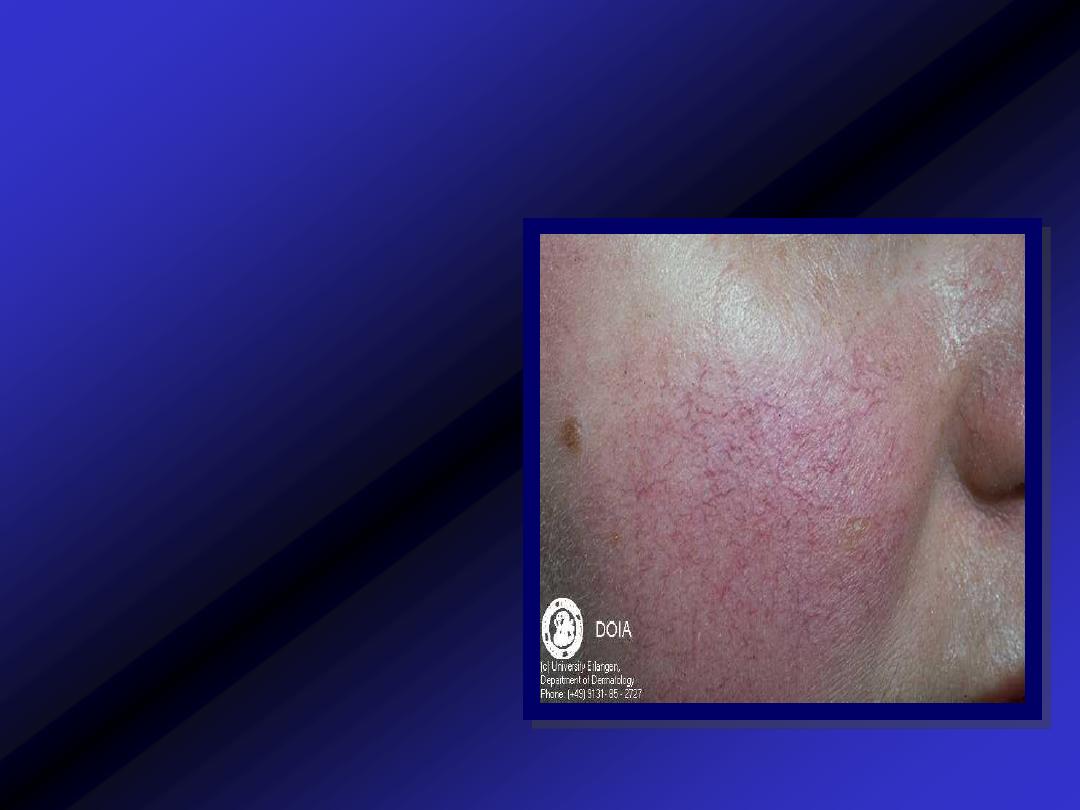
Telangiectasia
Visible dilatation of
cutaneous
blood
vessels
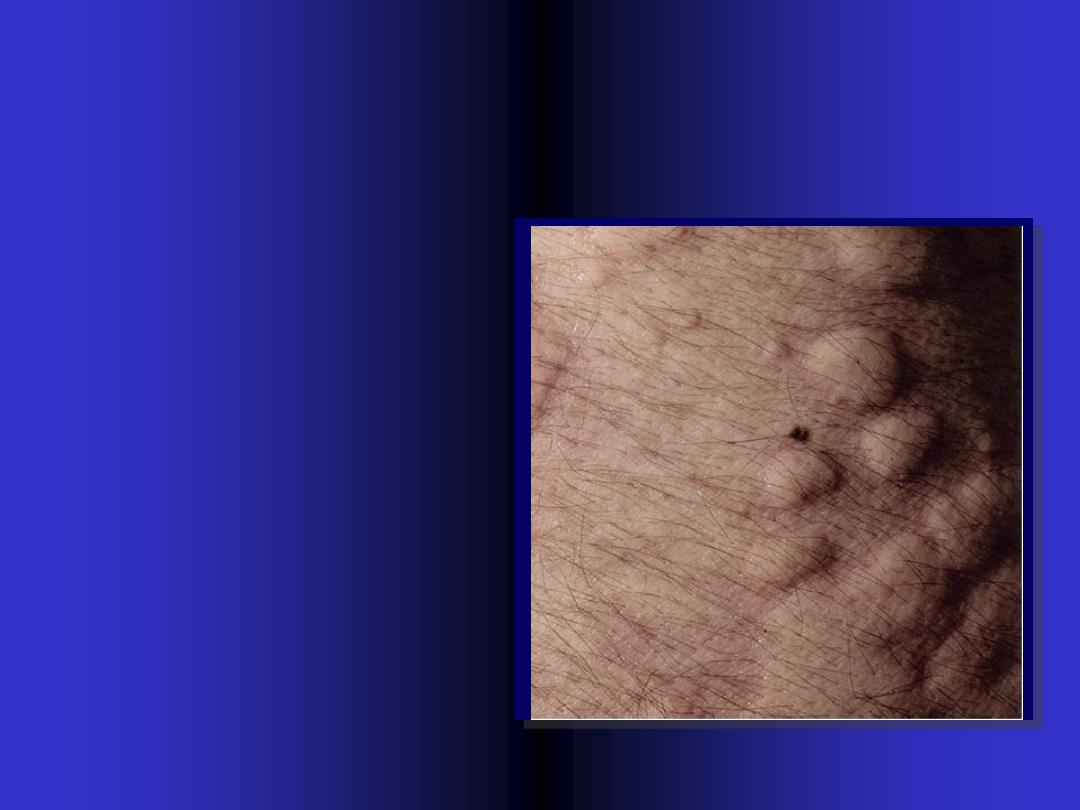
Wheal
Elevated white
compressible,
evanescent
area.
produced by
dermal edema.
It is surrounded
by red axon-
mediated flare

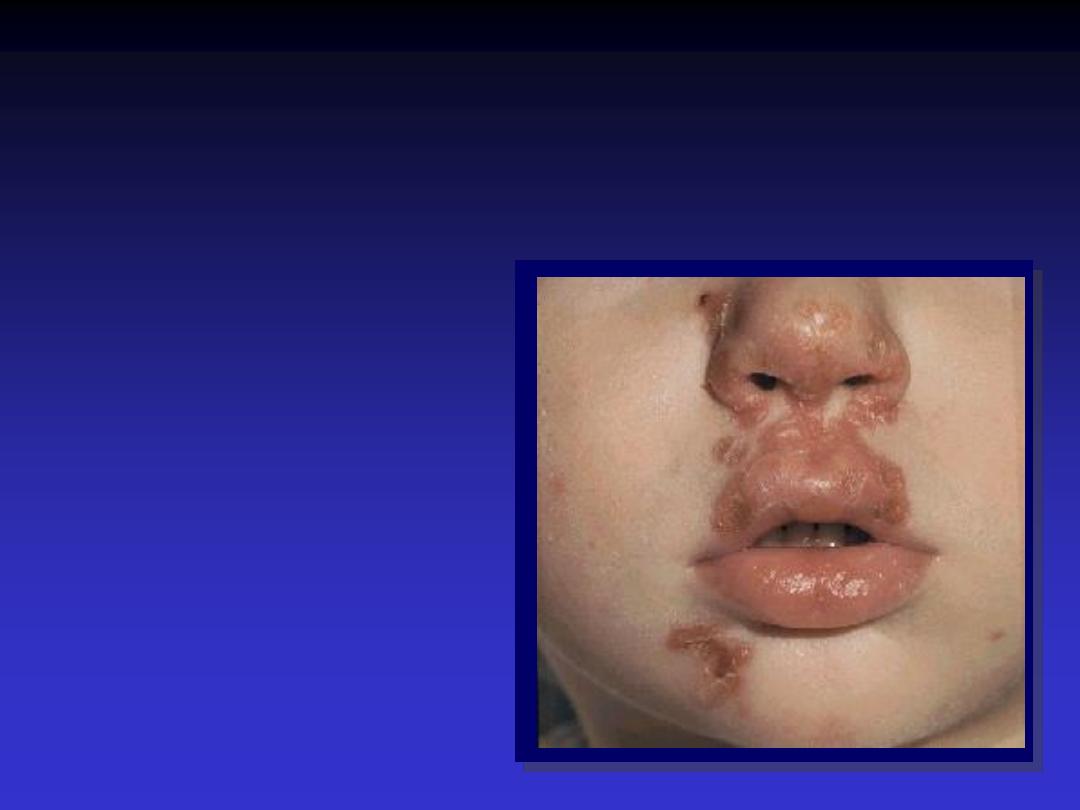
Crust
Dried
fluid or blood
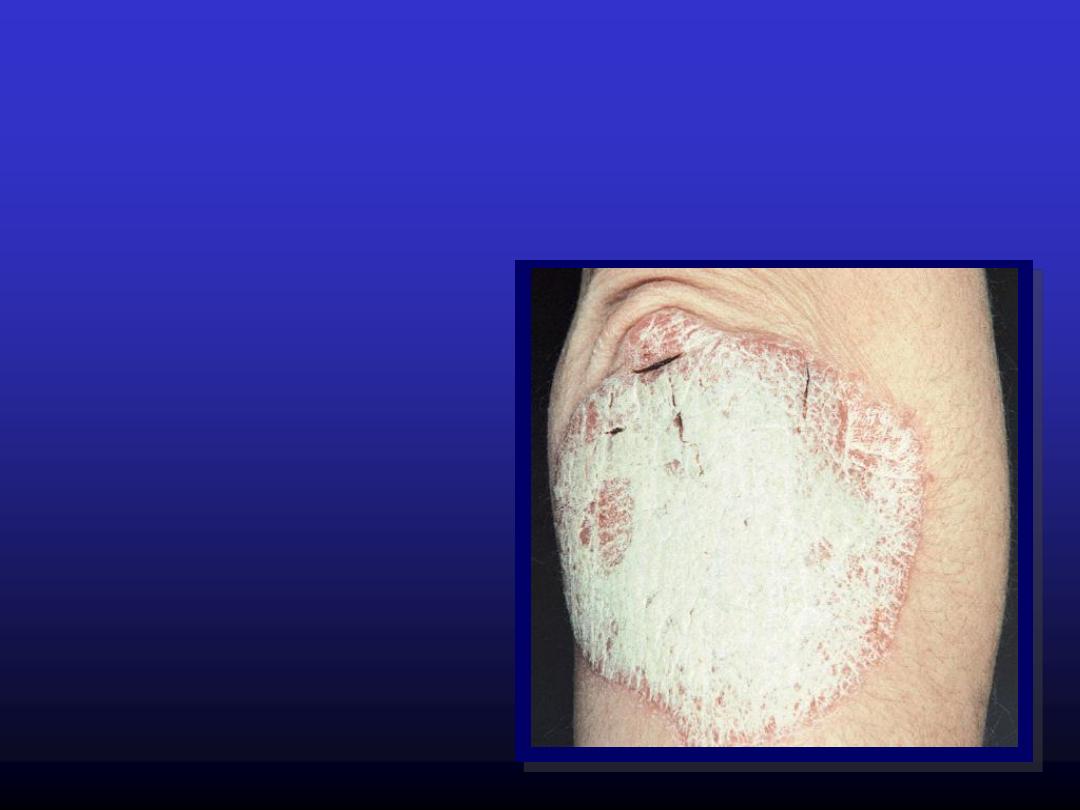
Scale
Flakes
arising from
the horny layer
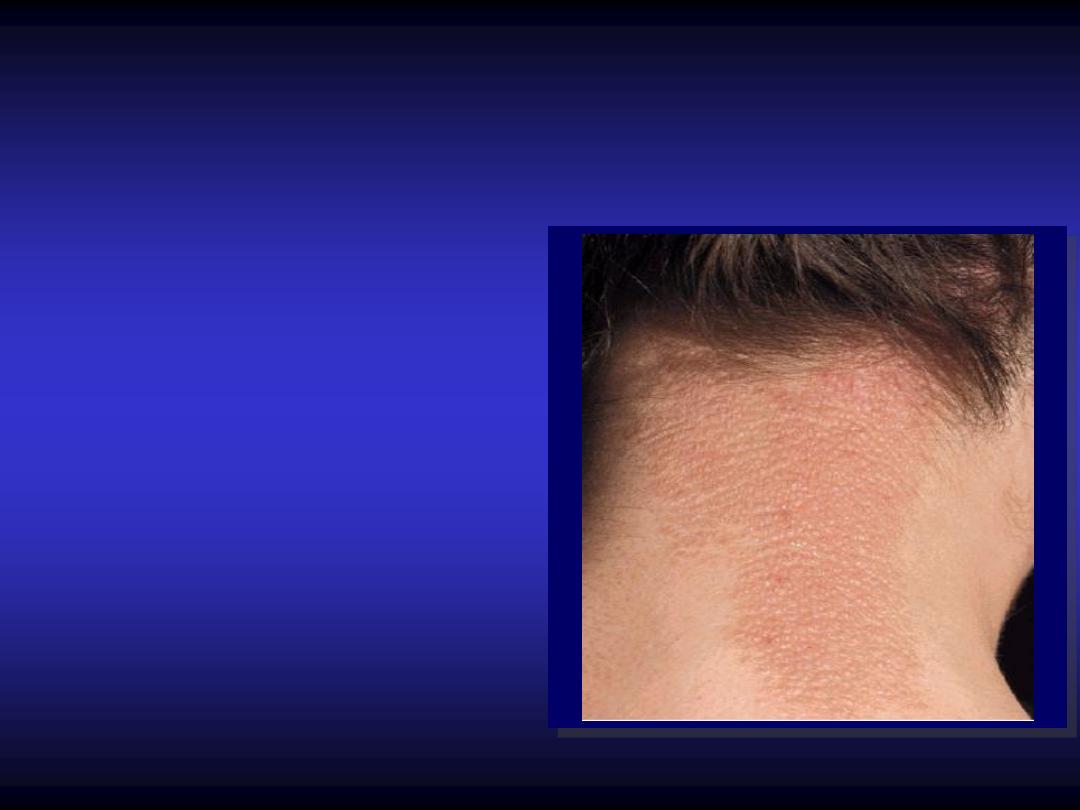
Lichenification
Thickened skin.
Hyperpigmented.
Increased skin marking.
result from excessive
rubbing.
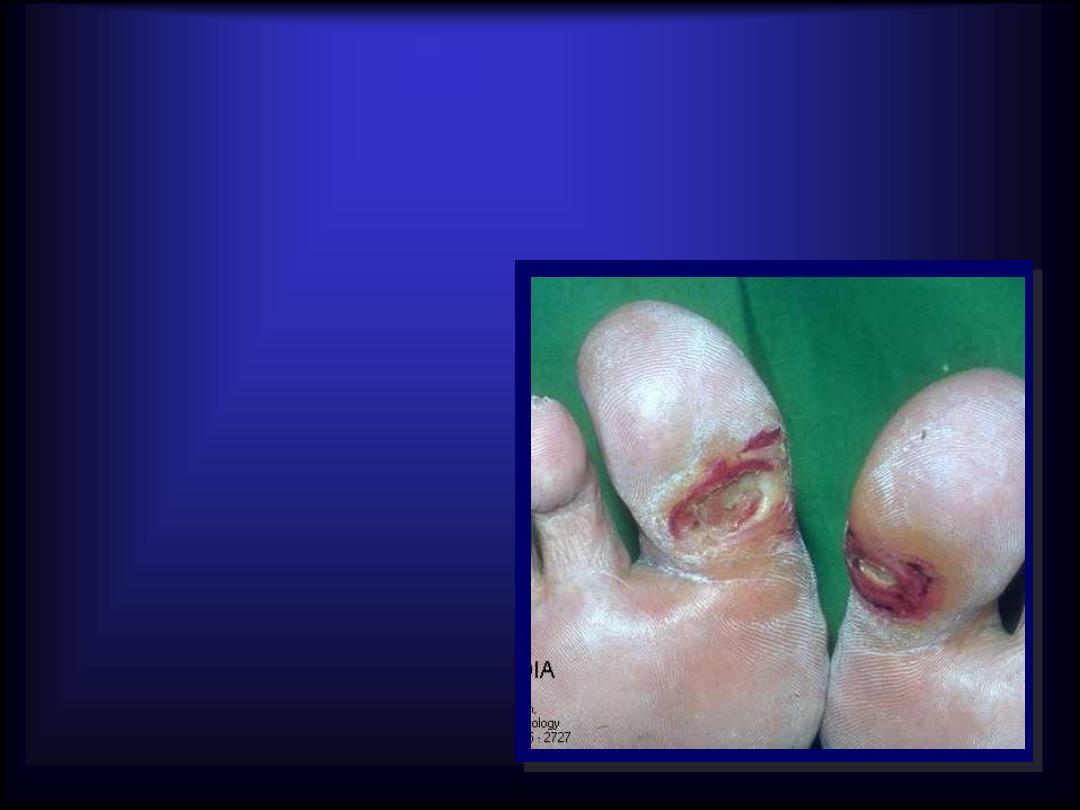
Ulcer
Area of skin from
which
whole
epidermis
& dermis is lost.
It heal with
scarin
g
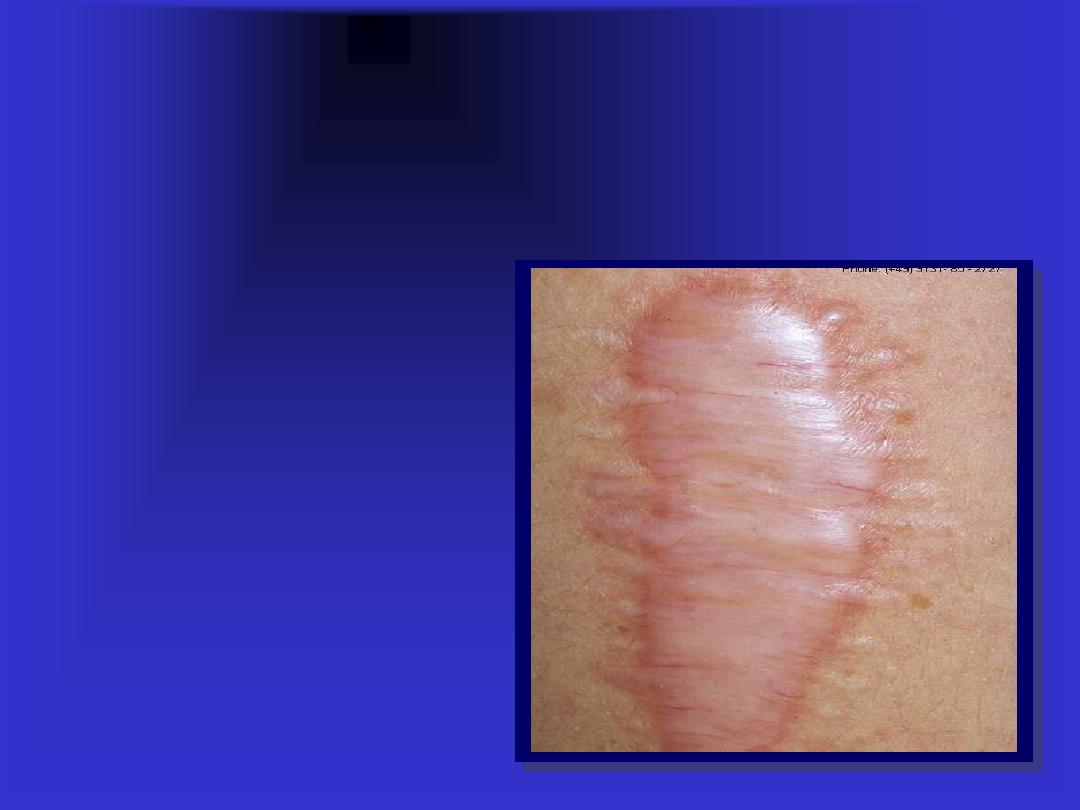
Scar
Is a result of
healing
in which
normal structure is permanently
replaced by connective tissue
cm
0.5
>
cm
0.5
<
Plaque &
nodule
Papule
Elevated solid lesion
Patch
Macule
Flat area of change in color or
texture
Bulla
Vesicle
Fluid-filled blister
Abscess
Pustule
Pus-filled lesion
Ecchymosis
hematoma
Petechia/
purpura
Extravasations of blood
Angioedema
Wheal
Accumulation of dermal edema

Adjectives add to describe lesion
Shape
Color
Sharpness of border
Temp., smell, etc
Consistency
Surface contour
1
2
3
6
4
5
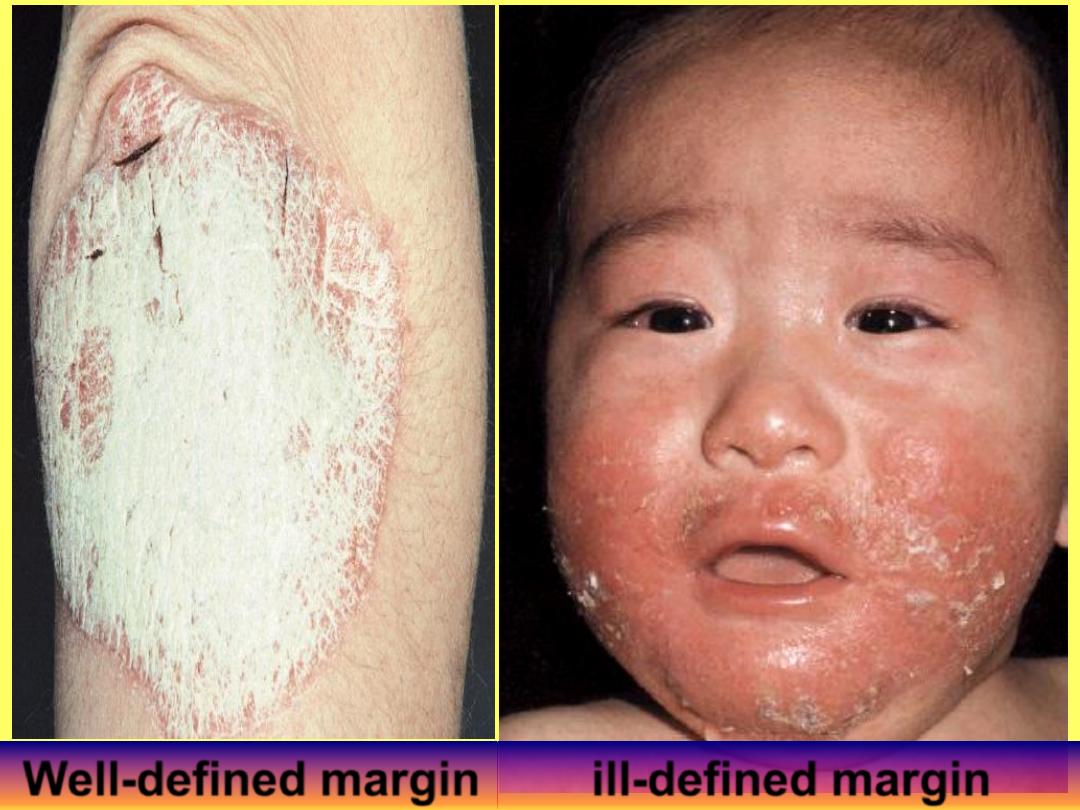
Well-defined margin
ill-defined margin
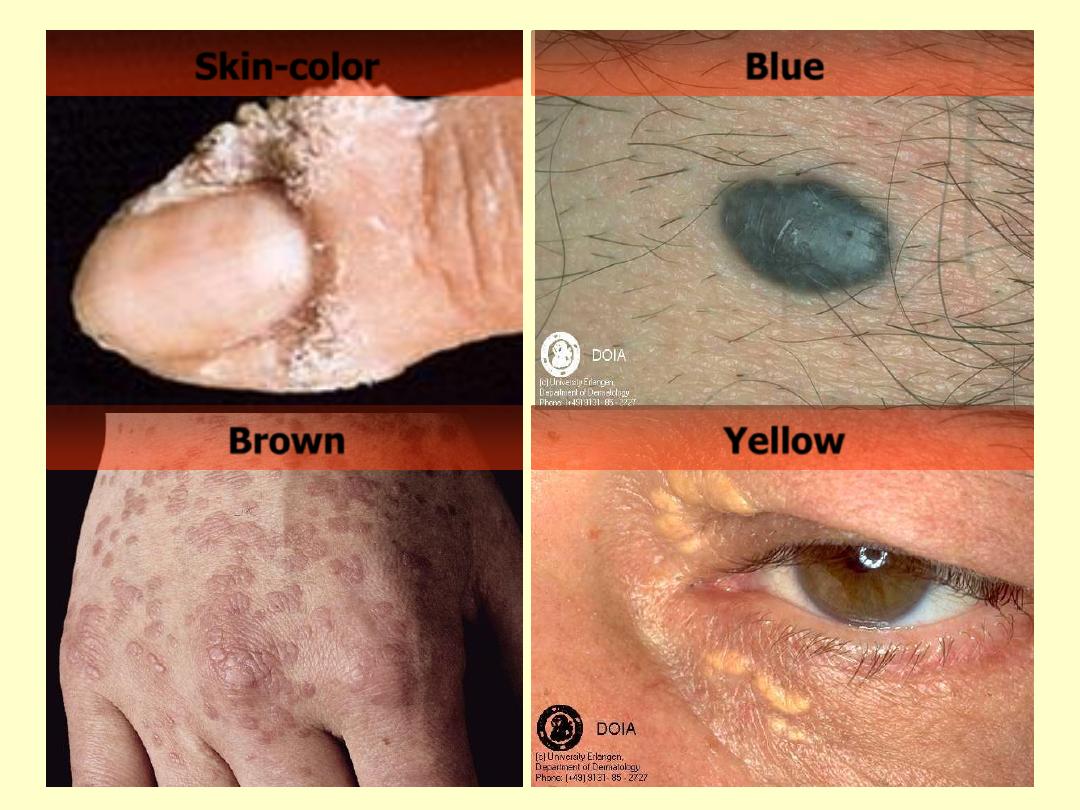
Skin-color
Blue
Brown
Yellow
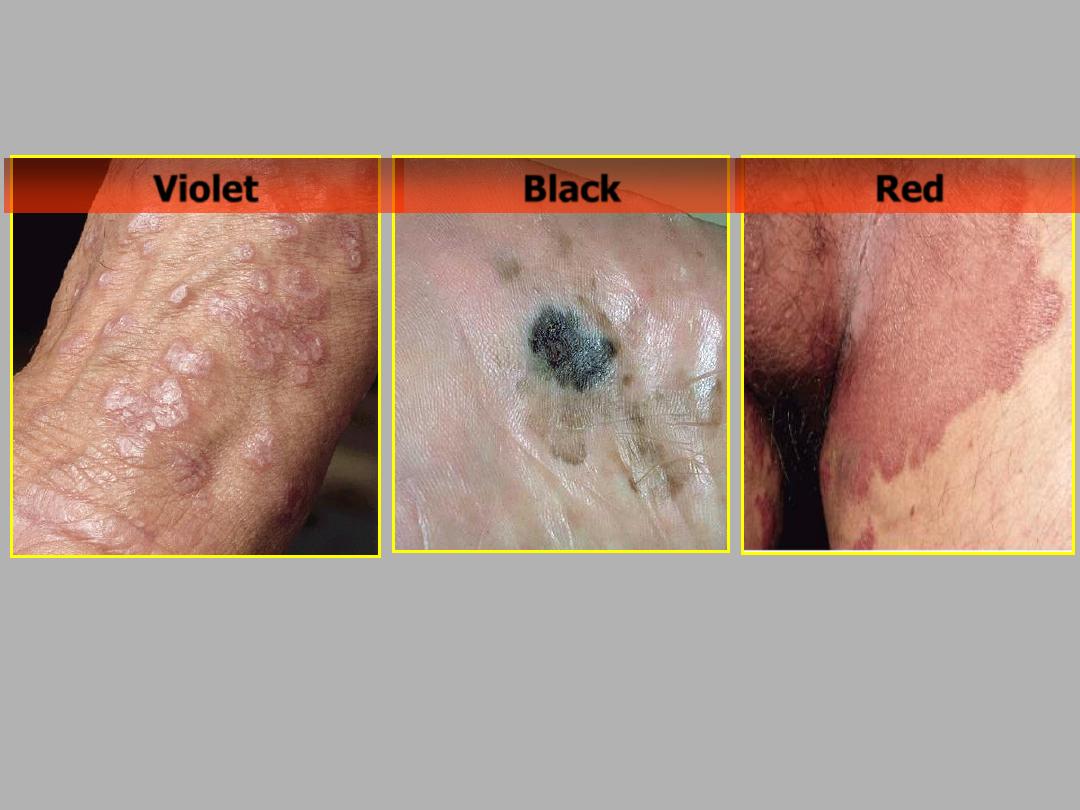
Red
Violet
Black
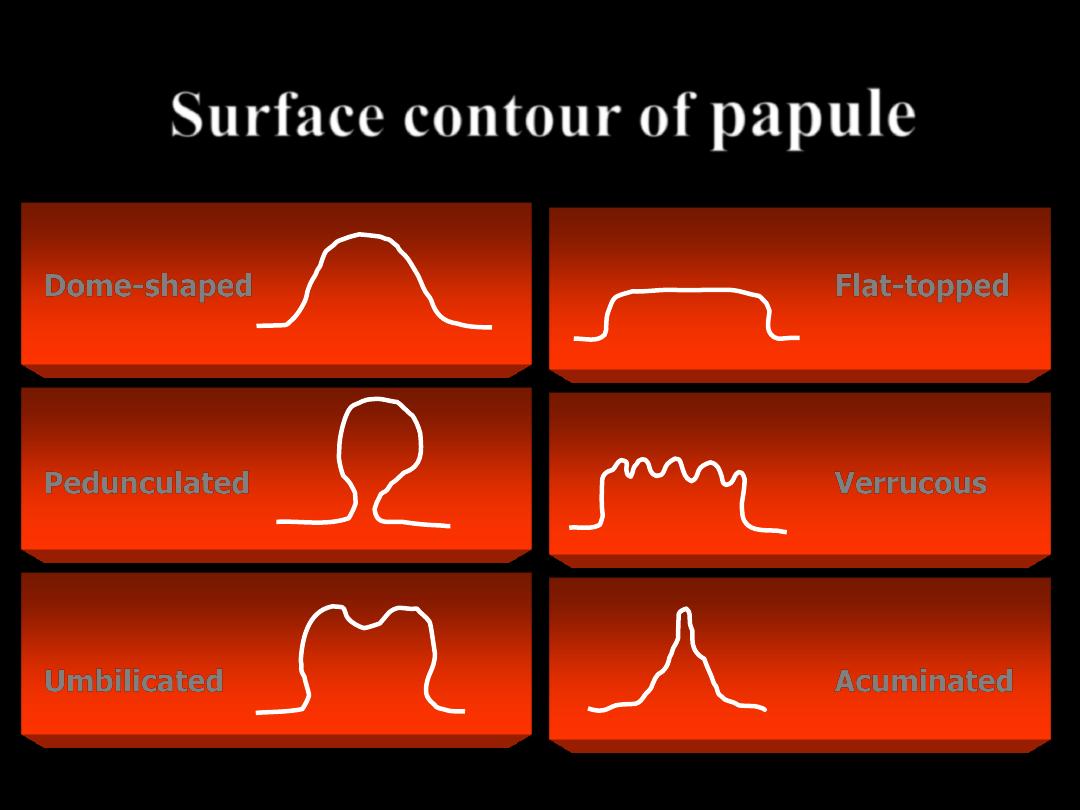
Surface contour of
papule
Dome-shaped
Pedunculated
Umbilicated
Flat-topped
Verrucous
Acuminated
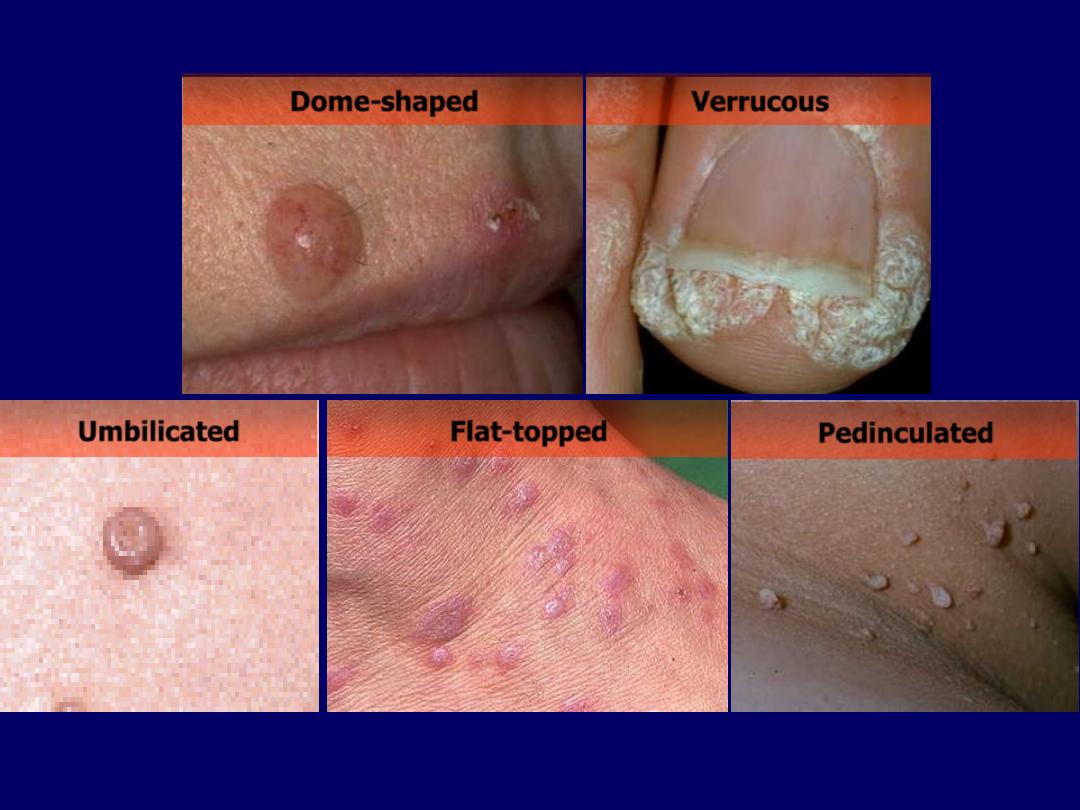
Umbilicated
Flat-topped
Pedinculated
Verrucous
Dome-shaped
Triad in dermatology
(
LAD
)
L
esion
A
rrangement
D
istribution
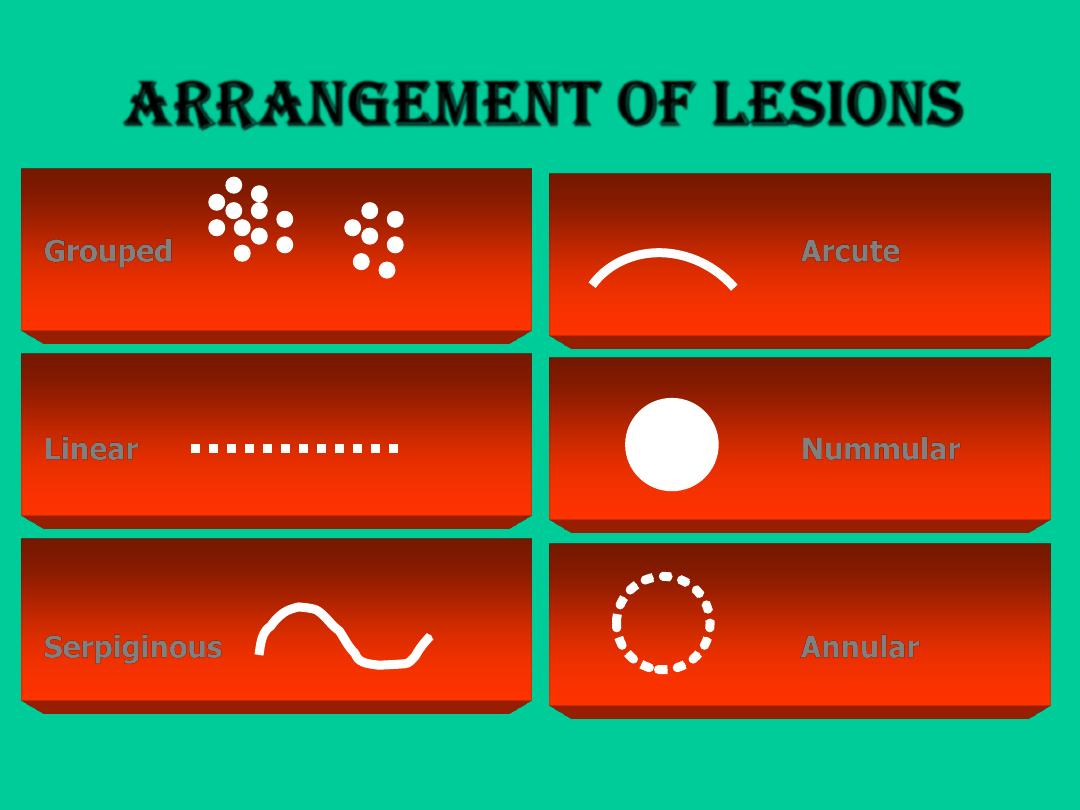
Arrangement of lesions
Grouped
Linear
Serpiginous
Arcute
Nummular
Annular
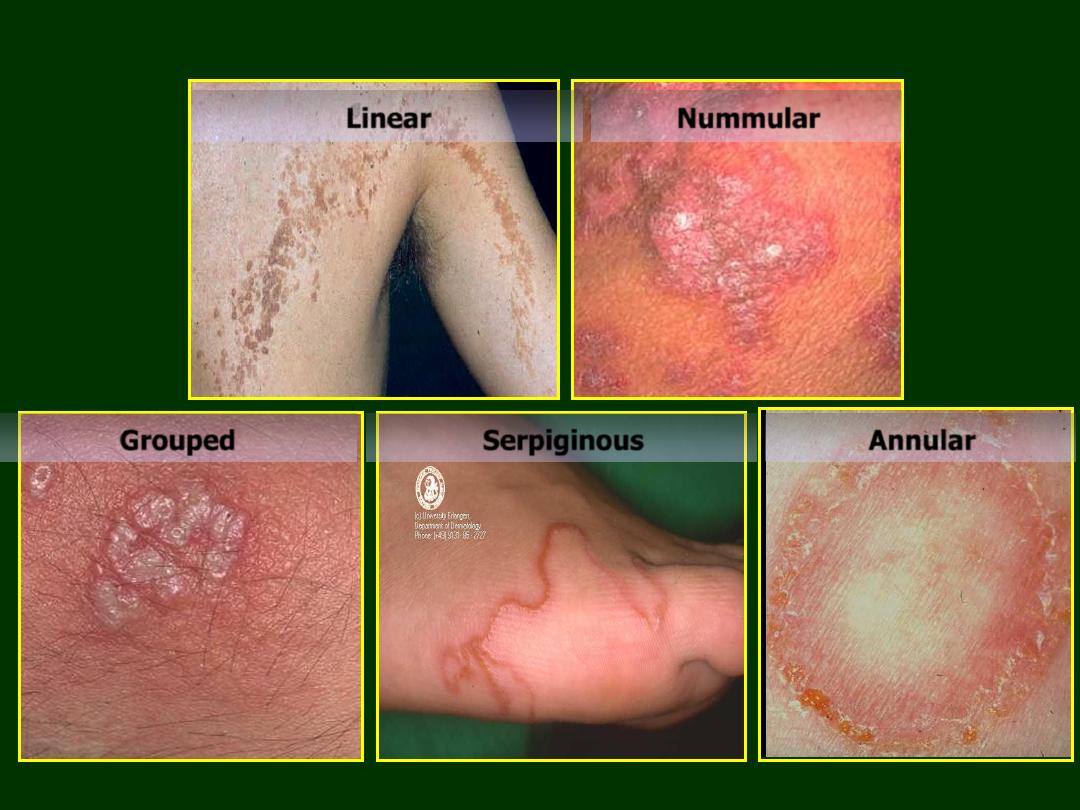
Linear
Nummular
Grouped
Serpiginous
Annular
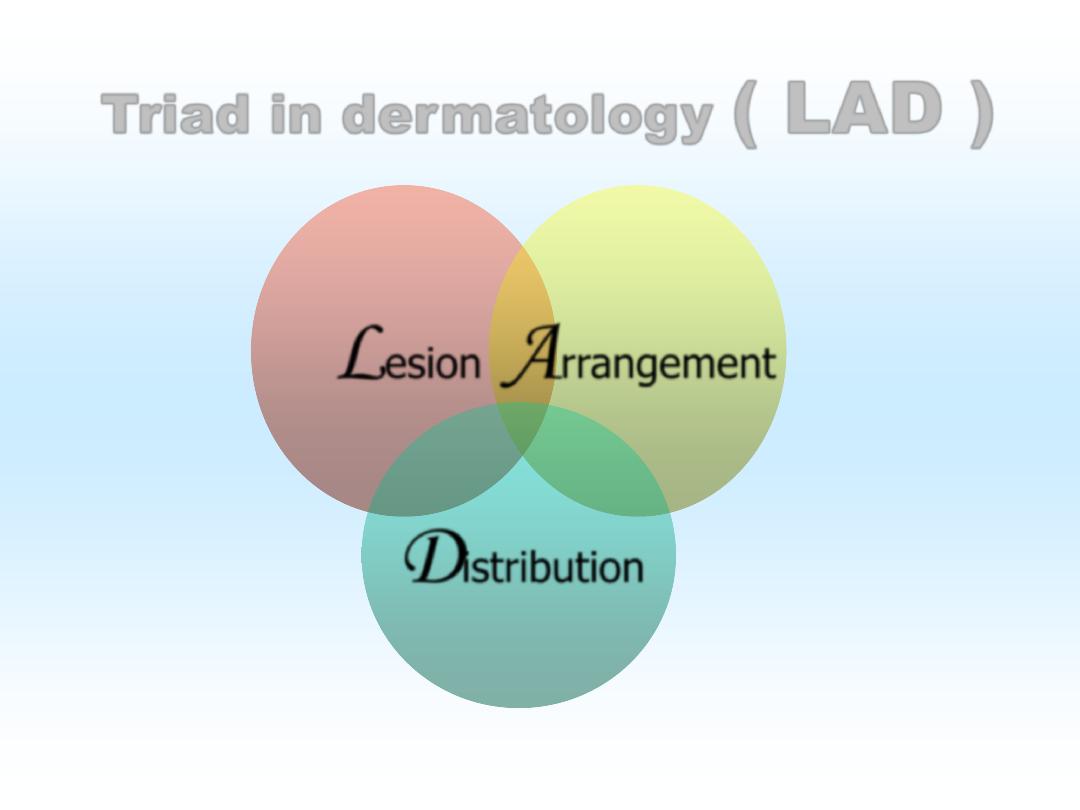
Triad in dermatology
( LAD )
L
esion
A
rrangement
D
istribution

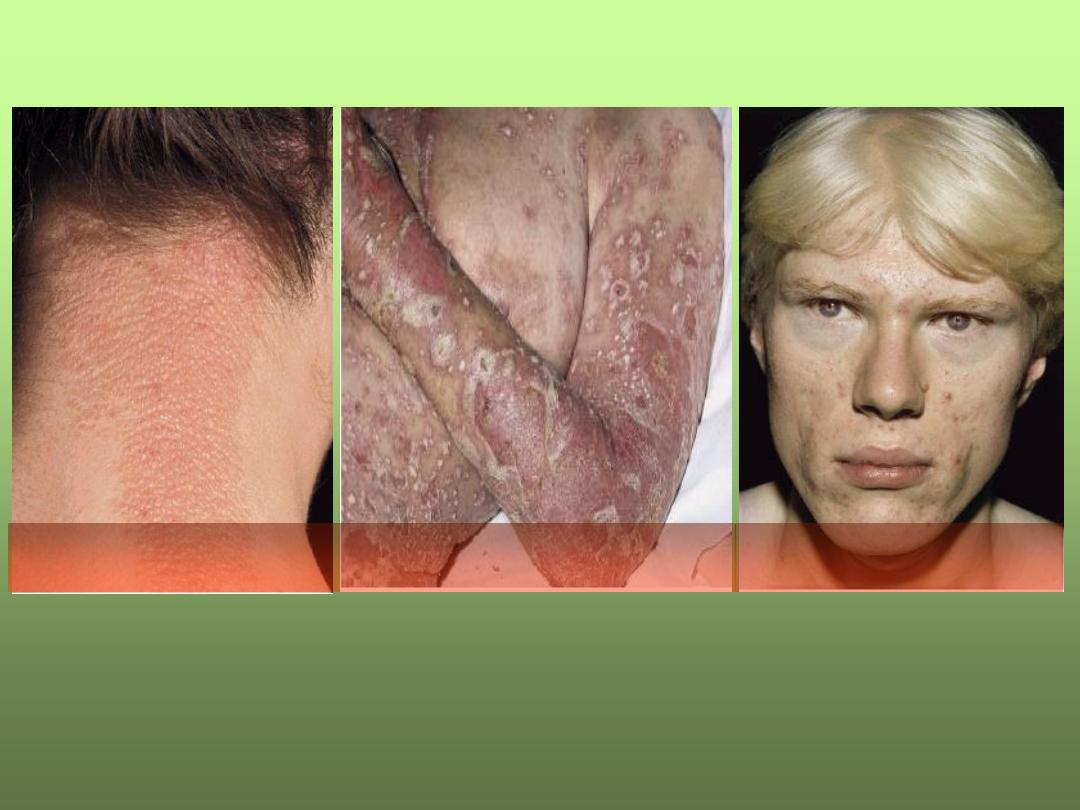
Distribution
Localized
Generalized
Universal
Unilateral
Dermatomal
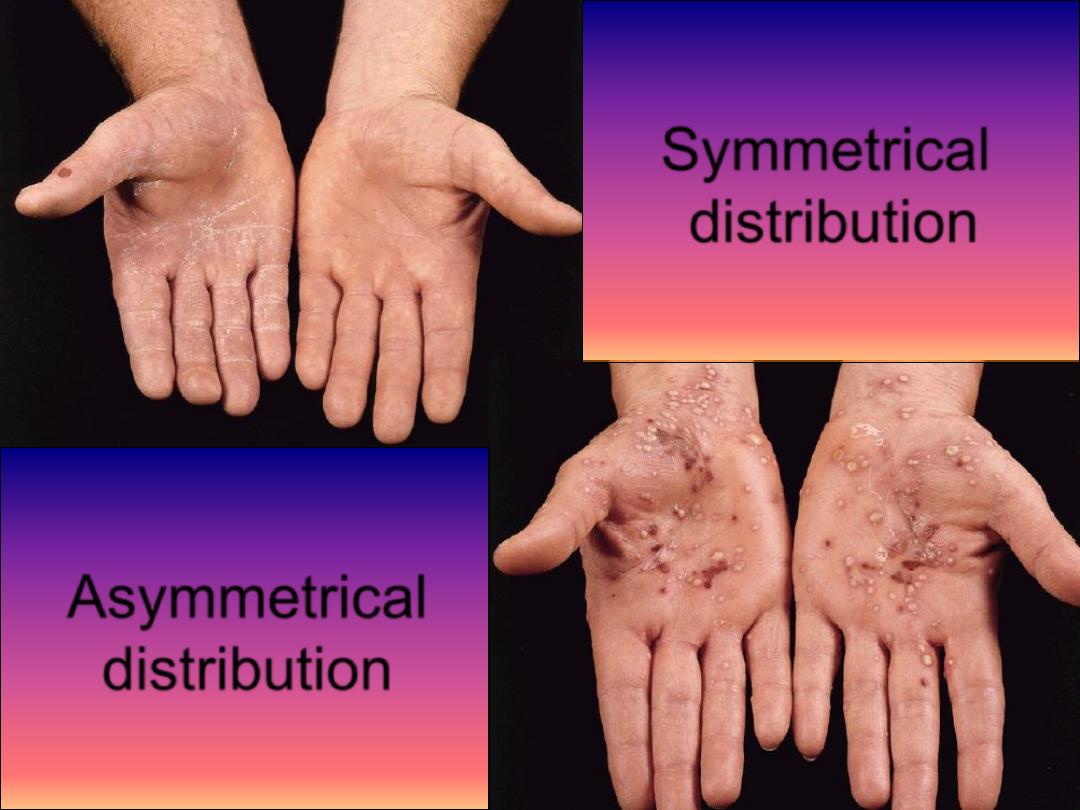
Symmetrical
Asymmetrical
Extensor
Flextrual
Sun-exposed
Centerpetal
Centerfugal
Seborrhoic
Acral
1
2
3
6
7
4
5
8
9
10
13
14
11
12
Localized
Generalized
Universal
Asymmetrical
distribution
Symmetrical
distribution
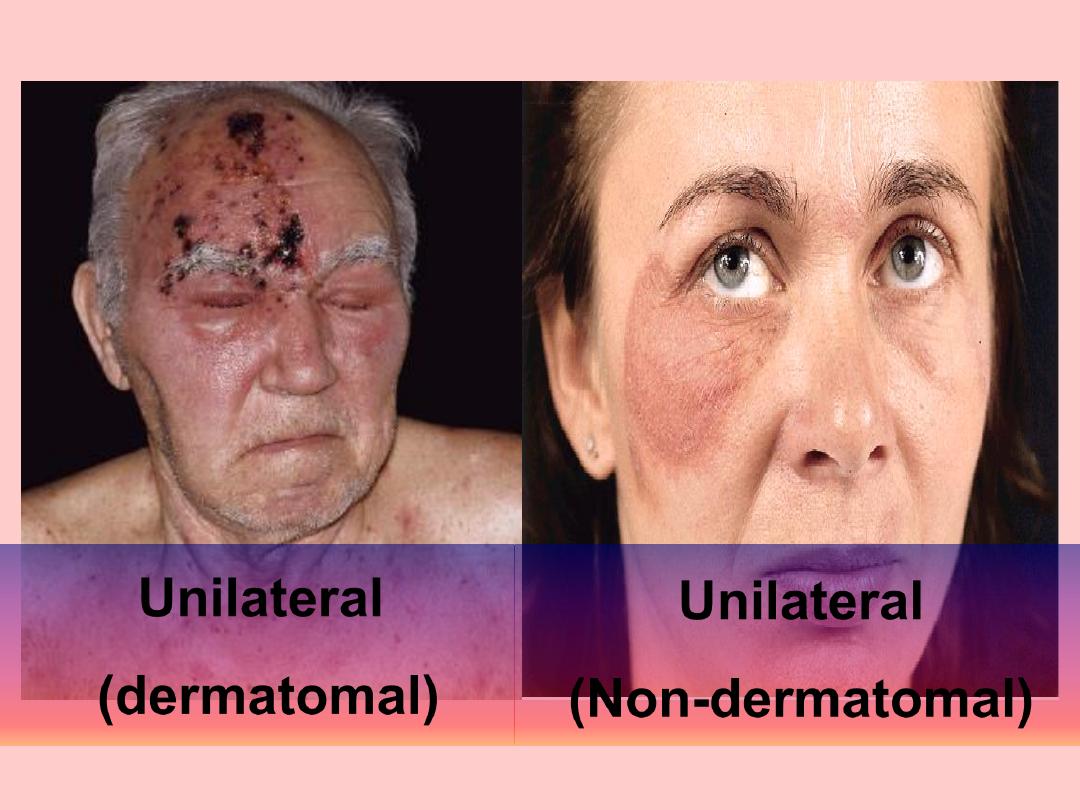
Unilateral
(dermatomal)
Unilateral
(Non-dermatomal)
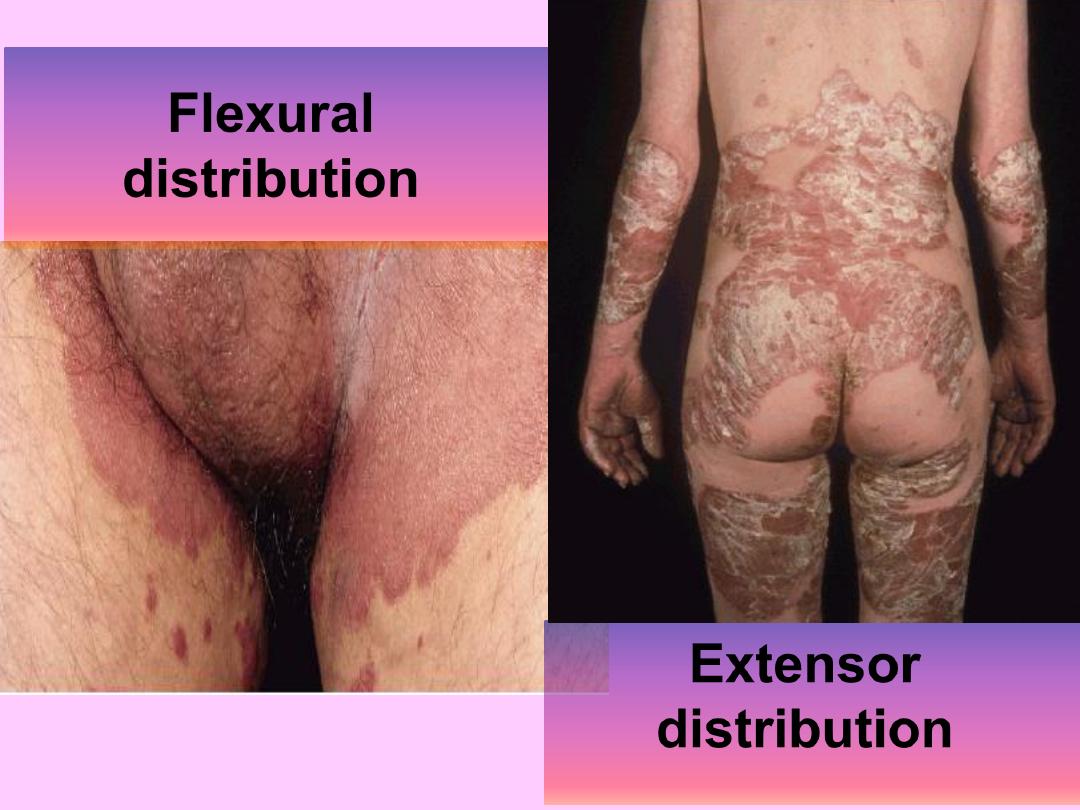
Extensor
distribution
Flexural
distribution
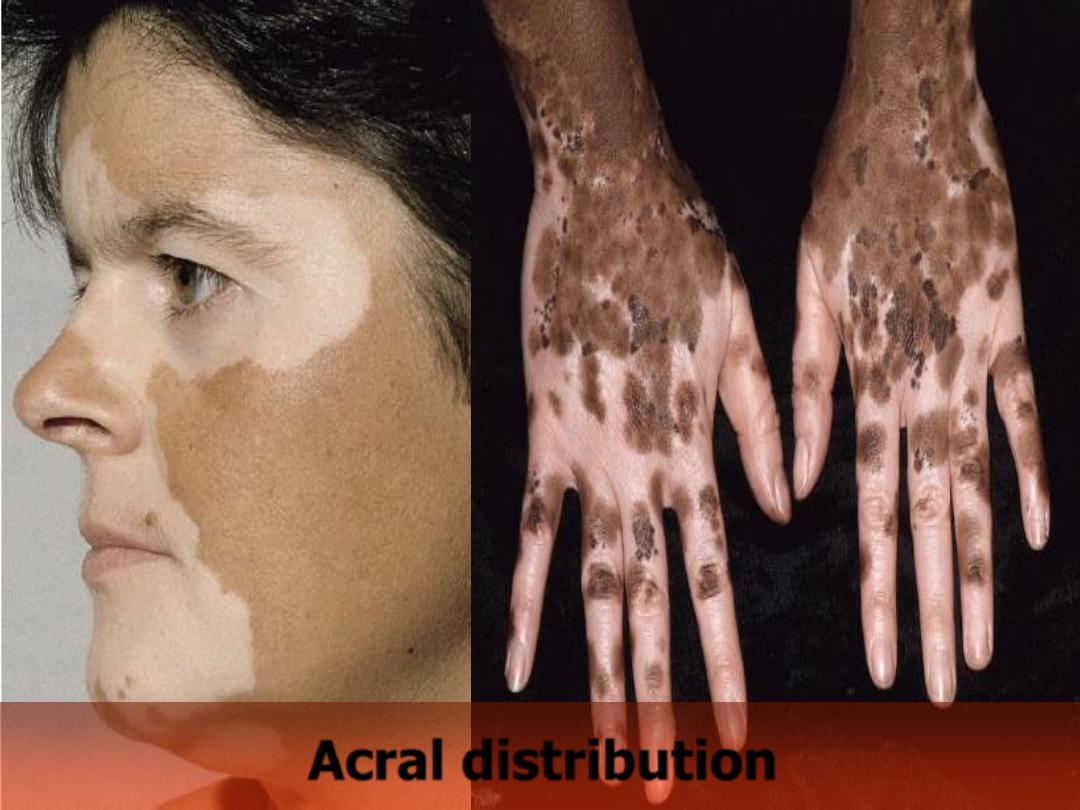
Acral distribution
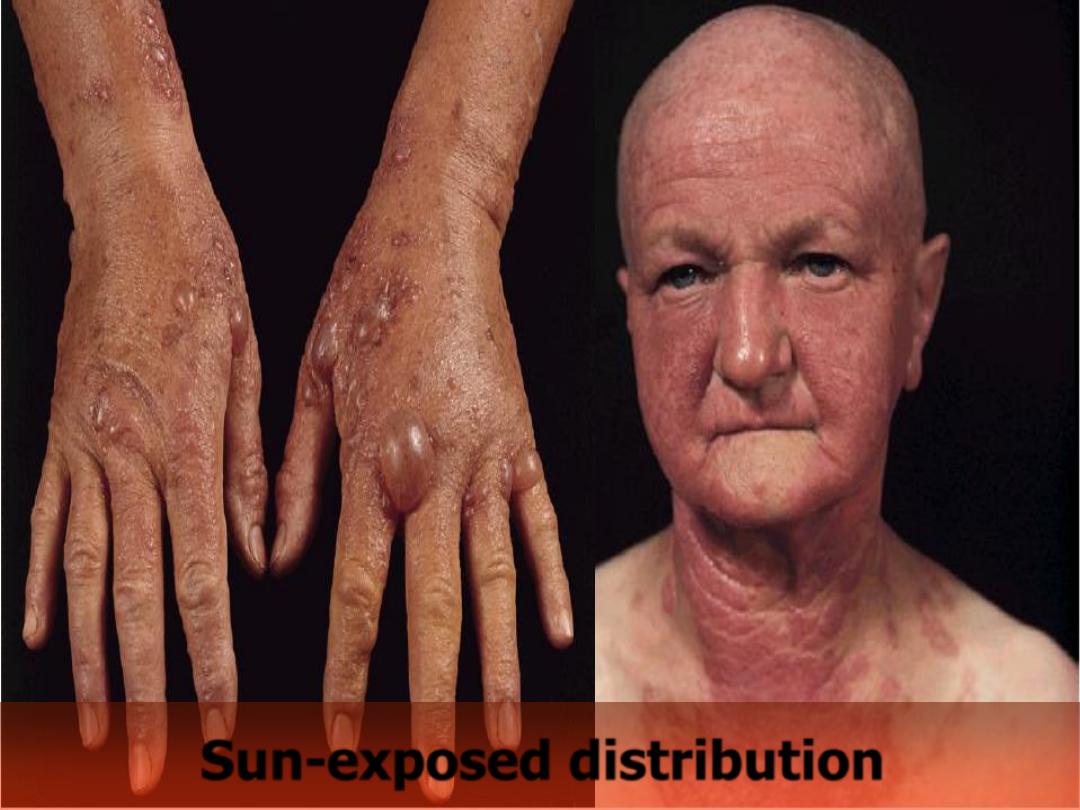
Sun-exposed distribution

