Childhood Gynecological Disorders
Gynecological disorders are not common during childhood but this doesn't mean they are not importantExamination and investigations are more difficult
Emotional and psychological upset of patients and parents.
Neonatal period
Due to high estrogen during the intrauterine life, there is passive estrogenic stimulation when estrogen crosses the placenta , this disappear in neonatal periodThe uterus is relatively large Cx/body= 1/1
The vaginal lining is stratified squamous epithelium of many layers rich in glycogen .
Neonatal gynecological disorders:
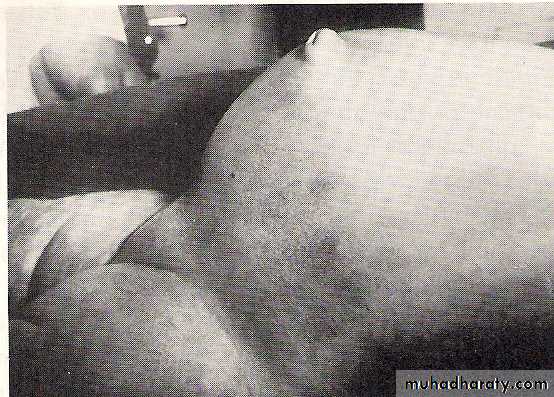
1-Breast enlargement and discharge : Variable amount of breast enlargement affect most neonates,Some times associated with nipple discharge (witches’ milk )
It is transient , no treatment needed avoid squeezing the nipples .
2- Vaginal discharge: Due to estrogen there is cervical mucous discharge and the vulva appear wet in the neonatal period ( not seen in childhood).
It is transient , need no treatment.PH=5(acidic due to glycogen).
3 -Vaginal bleeding: It is a sort of withdrawal bleeding (decrease of estrogen and progesterone from the placenta), the endometrium may shed off and a blood stained discharge may be noticed.
Affect 10 – 15 % of neonates in first week of life
It may cause a great deal of concern to the parentsNo treatment required.
4-Hydrocolpus: It occurs when the vaginal end is occluded by a membrane (misnomer :- imperforated hymen) .
There is accumulation of mucus inside the vagina (few cc –quite considerable amount ).Few cc completely asymptomatic and diagnosed at puberty when there is amenorrhea + hematocolpus. Large volume which distend the vagina , press on the bladder neck , rectum .
Symptoms and signs
There is abdominal pain ,
suprapubic mass,
retention of urine,
constipation,
bulging membrane at the site of hymen,
if the membrane is thick it may not be able to see the bulging and diagnosis is more difficult.
Investigations
U/S , MRI.
Treatment
Catheterization + surgical incision of the membrane for drainage .
If it is a thick septum , the treatment is more difficult .
Childhood period:
Very low E2 &P.Very low FSH, LH
Hypotrophic uterus Cx/body = 2/1
No uterine secretions
No Cervical secretions
Thin vaginal lining with few layers without glycogen
pH 7 ( loss of protective acidity ).
Childhood disorders:
1-Non specific vulvovaginitis: The commonest gynecological disorder in childhood .Causes usually low virulence micro-organisms
loss of protective acidity
Vaginal opening is less protected by fat
Anus is anatomically close to the vagina
Child slides on the floor
Pinworms (Entrobius vermicularis )
Foreign bodies *(severe persistent discharge usually blood stained or frank bleeding)
Sexual abuse*(specific STD as gonorrhoea ).
Symptoms of vulvovaginitis
Vulvar itching (pruritis vulvae).
Vulvar soreness (pain).
Discharge.
Blood stained discharge of variable severity.
Examination
Inspection: reveal red swollen vulva
Gentle separation of labia show discharge.
-Culture to identify causative organisms.
-Urine analysis.
-Perianal exam to test for pinworms.
Treatment
Vulvar hygiene
Avoid antiseptics
Cleaning after defecation
Drying after baths
Change underwear
Antibiotics ????
Usually improves as puberty approached .
2-lichen sclerosis: Atrophic changes of the vulvar skin .
(hyperkeratosis + hyaline degeneration of collagen ).
Signs and symptoms:
vulvar itching, A white, papular lesion may cover the vulva and perianal regions .
Etiology: Causes are unknown . Autoimmune disorder?? .
Diagnosis: Biopsy
Management:This condition is benign and can be self-limiting. Improved hygiene is the first line of therapy. +- topical steroids 2wks. Improves at puberty.
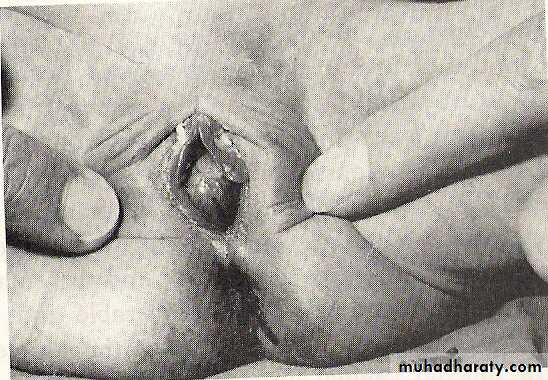
3-labial adhesion: Adhesion of the labia minora in the midline is the usual presentation. This vertical line of fusion distinguishes labial agglutination from imperforated hymen or vaginal atresia.
Seen in childhood ,It is not uncommon.Usually start posteriorly and moving anteriorly leaving small orifice through which urine passes
The line of adhesion is thin and translucent at the beginning but becomes firmer and thicker with time .The child is asymptomatic.
Causes of labial adhesion
Low oestrogen (E2)
Bad hygiene
Treatment
Vulvar hygiene
Separation of labia minor manually,or by surgery
E2 cream locally 2wks.→spontaneous separation
It may recur again
(( The primary reason of treatment is to reassure the parents ))
4-Vaginal Bleeding in Children:
Causes-Foreign body.
-Trauma.
-Genital tumors.
-Urethral prolapse.
-Vulvovaginitis.
-Condyloma acuminata.
-Precocious puberty.
-Exogenous hormone usage
5-Butryoid tumor: It is a rare sarcoma of the vagina and cervix
Affect children at their first decade of life,could be related to exposure to synthetic estrogen in utero (estrogen treatment during pregnancy ).Signs and symptoms
Polypoidal mass in the vagina , it may come out through the vaginal orifice .It causes vaginal discharge .It causes vaginal bleeding in childhood.
Treatment
Chemotherapy
Then hysterectomy + vaginectomy
Sometimes pelvic exenteration
Prognosis is bad.
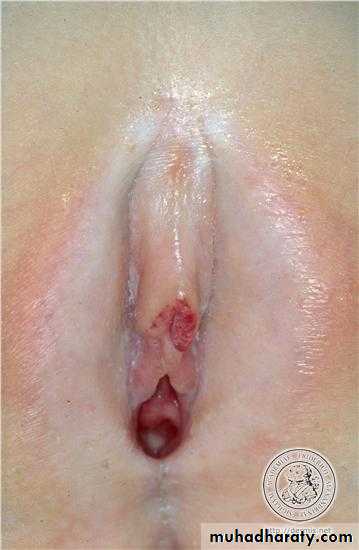
6-Urethral prolapse: It is a rare condition.It is a prolapse of urethral mucosa through the urethral orifice and form a congested mass which may bleeds easily.It may occur following dehydration or weight loss.It may be mistaken as botryoid tumor ( sarcoma botyroides of the vagina ).
Examination under anesthesia may reveal the condition.
7-Sexual abuse: May occur in childhood at any age.More common in low social class.Strict religious community doesn’t prevent it completely
Penetration of child genitalia cause tears of the hymen and often vulvo-vaginal tears and lacerations. It may be non penetration sexual abuse
Other injuries depends on many factors
Age of child and body size
Age of the abuser
Resistance by the child
Degree of violence and others.
Other findings: Perineal lacerations ,Contusions and bruises on other part of the body .Severe psychological trauma ( need special psychiatric care ).
Absence of physical trauma doesn’t exclude sexual abuse
Presence of STD without evidence of trauma may suggest non penetration sexual abuse .
Management: include
Notifying the authoritiesPhysical treatment of injuries
Prevention of STDs
Emergency contraception ( if the child at puberty age )
Psychiatric treatment and support
Social care
Care for the parents