Vital signs
Definition: further information about patient's health status is obtained by taking his vital signs; it includes temperature, pulse, respiration and blood pressure.Times assess vital signs:
Change in health status.Admission the patient to health care agency.
Nursing or medical order.
Before or after surgery or diagnostic procedure.
Before and after administration of medication.
Before and after any nursing intervention.
The purpose of checking vital signs:
1- For making diagnosis.2- Planning progressing of patient.
3- Seeing reactions of patient to the specific medications treatment and care.
Body temperature:
Definition: is a balance between heat production and heat loss, the normal degree of body temperature is 37Co (98.6 F).
Maintenance of Body Temperature
1.Thermoregulatory center in the hypothalamus regulates temperature.
Center receives messages from cold and warm thermal receptors in the body
2.Center initiates responses to produce or conserve body heat or increase heat loss
There are two kinds of body temperature:
1- core temperature: is the temperature of the deep tissues of the body, such as the abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity. It remains relatively constant. The normal is a range of temperature
2-Surface temperature :is the temperature of the skin, the subcutaneous tissues ,fat. It, by contrast, rises and falls in response to the environment.
Methods for measuring body temperature:
1- Orally method.2- Auxiliary method.
3. Rectal method.
4. Tympanic method
Foreheah method
Oral body temperature:
Measuring body temperature by putting thermometer under tongue for 3 -5 minute.Contraindication:
1- For unconscious patient.
2- Infant.
3- Patient who breathe from mouth.
4- Patient who has disease in the oral cavity or surgery of nose or mouth.
2. Auxiliary method: by putting thermometer in auxiliary place for 10 minute.
Be ensuring that thermometer is contact with skin surface.
Pluses 0.5 degree to the degree of checking temperature.
3.Rectal method: check temperature by rectal when you can not take temperature by mouth or auxiliary.
Put thermometer inside rectal by using especial thermometer with square bulb.
Putting thermometer inside the rectal for 2 minute and minus 0.5 degree from the degree of checking temperature.
Clinical thermometer: is the instrument that used to measure the body temperature it constructed of the bulb and stem.
Kind of thermometer:
Mercury thermometerElectric thermometer
Electronic thermometer
The normal degree of body temperature is 36 – 37.5 Co or 98.6 F
How you change one degree from one system to anther.To convert one degree from one system to another need to know the following formula:
- From Co to F [(Co x 9) + 32 = F]- From F to Co[ (F - 32 ) x 5 = Co]
9
Factors affecting body temperature:
1- Time of the day.
Physical exercise.
Sex
Age and growth hormone.
Fever (pyrexia):
The body temperature is above usual range (37.5 Co)TYPES of FEVER (pyrexia):
1.Intermittent :temperature fluctuates between periods of fever and periods of normal/subnormal temperature. An example is with the disease malaria.2.Remittent :temperature fluctuates within a wide range over the 24 hour period but remains above normal range
3.Relapsing : temperature is elevated for few days, alternated with 1 or 2 days of normal temperature
4.Constant: body temperature is consistently high
Signs and symptoms of fever:
High heart rate.High and depth of respiratory rate.
Flash face and sweating.
Back pain.
Fatigue.
Headache.
Nausea and vomiting.
Chilling and thirst.
Delirium.
10. Loss of appetite.
Nursing care:
Check body temperature every 10 minute.
compress with tape water made for patient.
Give good nutrition and fluid.
Change clothing if necessary.
Make bathing if necessary.
Reduced physical activity.
Giving anti pyrel drugs (paracetamol, asperin gtc,….).
If cold compress is unless used alcohol bath (70% alcohol with water).
Make oral hygiene.
Good ventilation and circulation.
Preparation of disinfecting solution:
To prepare (100cc) of disinfected solution you need to mixed (99cc) of alcohol 70% with (1cc) of iodine.
2.Pulse:
Definition: is the expansion of the arterial wall occurring with each ventricular contraction.
The normal range of pulse is (60 -100) beat /minute.
Notes when taking pulseA- Pulse rate:
Is the number of heart beat in minute it is (60 -100) beat /minute.
Factors affecting pulse rate:
Sleeping: pulse rate morning lowest than at afternoon.
Sex: female is faster about (7 -8) beat / minute than male.
Age: infant higher than adult.
Infant 120 - 130 beat /minute
Adult 60 - 100 beat /minute
Body build: body size and build may affect pulse rates.
Thin and long body ……… low pulse
Fat and small body…………high pulse
Other factors are emotion, medication, activity, digestion of food and hormones
-Tachy cardiac: pulse rate is over 100 beat /minute
- Brady cardiac: pulse rate is below 60 beat /minute- Arrhythmia: irregular pulse rhythm.
B- Rhythm of pulse: it means the time interval between heart beats is equal.
Arrhythmia: Irregularity of time interval between heart beats.C- Volume of pulse:
Is the degree of fullness of the artery and reflects the strength of the left ventricular contraction.Bounded pulse: when is not particularly easy to do.
Feeble or weak pulse: when the volume of blood is small and very easy to stop the feel of the pulse.D- Arterial wall condition:
The condition of wall artery and this become abnormal with old ageE. Bilateral equally : the pulse should be eqaual for two side( RT,LT)
Site of taking pulse:
Radial artery
Temporal artery.
Carotid artery.
Facial artery.
Femoral artery
Posterior tibia artery.
Dorsal pedis artery
Brachial artery.
Apical pulse rate.
POPLITEAL artery
3.Respiration:
Is the process by which oxygen and carbon dioxide are interchanged.
The normal adult breath is (14 – 24 breath/mint) time in minute.External respiration:
Is providing oxygen to the blood and removal carbon dioxide from the blood.Internal respiration:
Is providing oxygen that is in the blood to the cells in the body and removal of carbon dioxide from the tissue to the blood.
Two Types of Breathing:
Costal (thoracic)
Diaphragmatic (abdominal)
Notes in observed respiration:
Respiratory rate.Respiratory depth.
Nature of Respiration (ordinarily regular, or irregular).
`Eupnea: normal Respiration.
Tachypnea : increase rate of Respiration.
Hyperpnea: increase depth of Respiration.
Dyspnea: difficult breathing.
Orthopnea: Dyspnea at lying position.
Paroxysmal nacturnal dyspnea( PND): dyspnea that wake up the patient after 2 hours of sleeping.
Stertorous: breathing with sound.
Is the snoring sound resulting from secretion in trachea and large bronchi.
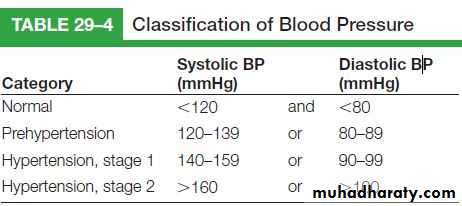
4.Blood pressure:
Definition: the pressure is exerted on the wall of the arteries when the left ventricles of the heart push blood into the aorta.
Systolic pressure: is the maximum of the pressure 100 – 140 mm /Hg.
Diastolic pressure: is the minimum of the pressure 60 - 90 mm /Hg.
The average of blood pressure 120 mm /Hg.
80
Factors maintaining normal arterial pressure:
Cardiac out put.
Peripheral resistance.
The quantity of blood.
The viscosity of blood.
The elasticity of vessel walls.
Hypertension: the pressure is above 140/100 mm /Hg.
Hypotension: the pressure is below 60-90 mm /Hg.Blood pressure checked by sphygmomanometer and stethoscope.
pulse pressure – difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures, normal is 30 – 40 mmHg.