Physical examination Lec:3
Techniques of physical examination:Inspection method: it involves the visual sense, such as looking to observe the color of skin.
Palpation method: involves the sense of touch or the examiner used his hand, fingers to feel or press on the body for tenderness or soft or masses.
Percussion method: tapping a particular area of the body, either with the finger or with percussion hummer.
Auscultation method: use the sense of hearing to interpret sounds made the body usually is performed with the aid of stethoscope to listens heart sound.
Commonly instruments used:
Ophthalmoscope: to see various structures in side of the eye.Otoscope: to see interior of the external ear.
Tuning fork: to test hearing.
Percussion hummer: to test reflexes and determine tissue density.
Vaginal speculum: to examine the vagina and cervix.
Other equipment:
Tongue depressor, skin pencil, tape measure, safety pins, light, cotton, test tubes, gloves, lubricant, paper towels, and waste container.
Preparing the patient to the examination:
Explain to the patient what we do.Undress the wear the patient gown.
Empty urinary bladder.
Provide privacy to the patient.
Draping the client.
Put the patient in good position.
Assessing the patient in his/ her position as well as his health status.
Abdominal paracentesis:
Definition: aspiration of fluid from the peritoneal cavity.
Purpose:To withdraw fluid from the peritoneal cavity for the purpose of diagnosis or laboratory analysis.
For therapeutic effect by aspirate the fluid from the abdominal cavity.
Preparation of the patient:
Take vital signs.
Explain the patient what you are going do.
Empty the bladder patient from urine.
Put the patient in position for the treatment.
Sitting up in the chair.
Fowler's position.
Put draw sheet over patient and exposed the abdomen.
Shave the area of operation.
Disinfect the area of operation.
Site of paracentesis:
Midway between the umbilicus and symphysis pubis in center of abdomen.* Determined the site of injection of abdominal paracentesis .
Important point:
Aseptic technique is used in process.Prevent patient from moving during procedure.
Sterile drapes are applied around the puncture site.
Skin should be prepared by cleansing with antiseptic solution.
Give attention to patient's appearance, skin color like pallor and T.P.R.
Record the amount, color, and adore of fluid.
Thoracentesis:
Definition: aspiration of fluid from the pleural cavity.Purpose:
Aid in diagnosis.Remove accumulation of fluid in the pleural cavity.
May be done for therapeutic reasons.
Relieve symptoms.
Important point:
Assist doctor as needed.Observe the patient during procedure for pallor, dyspnea, and chest pulse rate.
Measuring fluid and record amount and appearance on intake and out put sheet.
THE MODULAR UNIT -5-
Body Mechanics
A/ Over view--------------------:-
1- Central ideas.: -
3.1- Definition of body mechanics .
3.2- The purpose of it .
3.3- The principles of body mechanics .
3.4 – Factors that influence body mechanics & posture .
3.5- The immobility of& its danger .
3.6- Body position for comfort .
2/ Performance objective :- After this studding this modular unit you should be able to :
Define body mechanics & its purpose .
2-Enumerate the principles of body mechanics .3-Explain the factors that influence body mechanics .
4-Enumerate the common danger immobility .
5- Enumerate the type of changing patient position .
Enumerate the body position for comfort .
Body mechanics
Definition: is the term used to describe the physical coordination of all parts of the body.
Purpose:
To keep important organs in their correct anatomical and physiological position.To facilitate good muscular control and the smoothness of movement.
To move and work with minimum muscular effort.
To make good impression on other and produce feeling of self confidence.
Body posture: is the relation of various parts of the body at rest or in any phase of activity.
Principles of body mechanics:
Use a wide base of support when moving object.Keep objects to be moved close to the body.
Push, pill, roll or slides objects rather than lifting.
Avoid twisting the spine by pushing or pilling the objects.
Use the body weight when pushing objects.
Factors that influence body mechanics and posture:
General health.Nutrition.
Emotions.
Situation factors.
Life style.
The important of exercise:
Improve the strength and flexibility of all body muscle.
Improve blood circulation.
Promote good respiratory function.
Relieve depression.
Common danger immobility:
Respiratory system: like atelectasis, collapse of lung tissue.Circulatory system: like thrombosis, bed sores.
Urinary system: like urinary tract infection or stone.
Gastro intestinal system: happened disturbance in appetite, poor digestion, constipation.
Psychological effects.
Type of changing patient position:
Helping the patient move to the side of the bed.Raising the shoulder of helpless patient.
Raising the shoulder of semi helpless patient.
Moving the helpless patient up in the bed (two nurses).
Using a draw sheet pill to move a helpless patient up in bed.
Assisting the patient to get out of bed and into a chair.
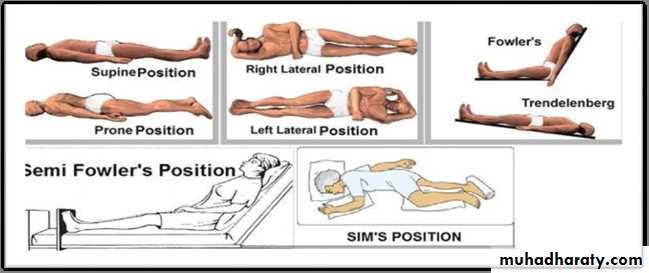
Body position for comfort
Standing position (anatomical position).
Dorsal position.
Dorsal recumbent position.
Sitting position.
Prone position.
Fowler's position.
Lateral position.
Sim's position.
Lithotomy position
10. Trendelenburgs position.
11. Knee-chest position.
The purpose of changing position:
For diagnosis.To prevent bed sores.
To help out of drainage.
For rest.
For therapeutic.