
Lec. : 6 Physiology
Urinary System
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The
system produces urine by a process of filtration, reabsorption, and tubular secretion. The
kidneys extract the soluble wastes from the bloodstream, as well as excess water, sugars, and
a variety of other compounds. The resulting urine contains high concentrations of urea and
other substances, including toxins. Urine flows from the kidney through the ureter, bladder,
and finally the urethra before passing from the body.
Renal physiology is the study of kidney function, while nephrology is the medical
specialty concerned with kidney diseases. Diseases of the kidney are diverse. Common of
these diseases are : nephrotic syndromes, renal cysts, acute kidney injury, chronic kidney
disease, urinary tract infection (UTI), nephrolithiasis, urinary tract obstruction and renal
cell carcinoma. Although they are not severely harmful, kidney stones can be painful and a
nuisance.
The kidneys: are organs that serve several essential regulatory roles in most animals,
including vertebrates and some invertebrates. They are essential in the urinary system.
The kidneys functions are:
1- Filtration of blood plasma.
2- Regulation of electrolytes to maintenance of acid–base balance . (Serve
homeostatic functions).
3- Regulation of blood pressure (via maintaining salt and water balance).
4- Remove wastes such as urea and ammonium.
6- Produce hormones such as erythropoietin, and the enzyme renin.
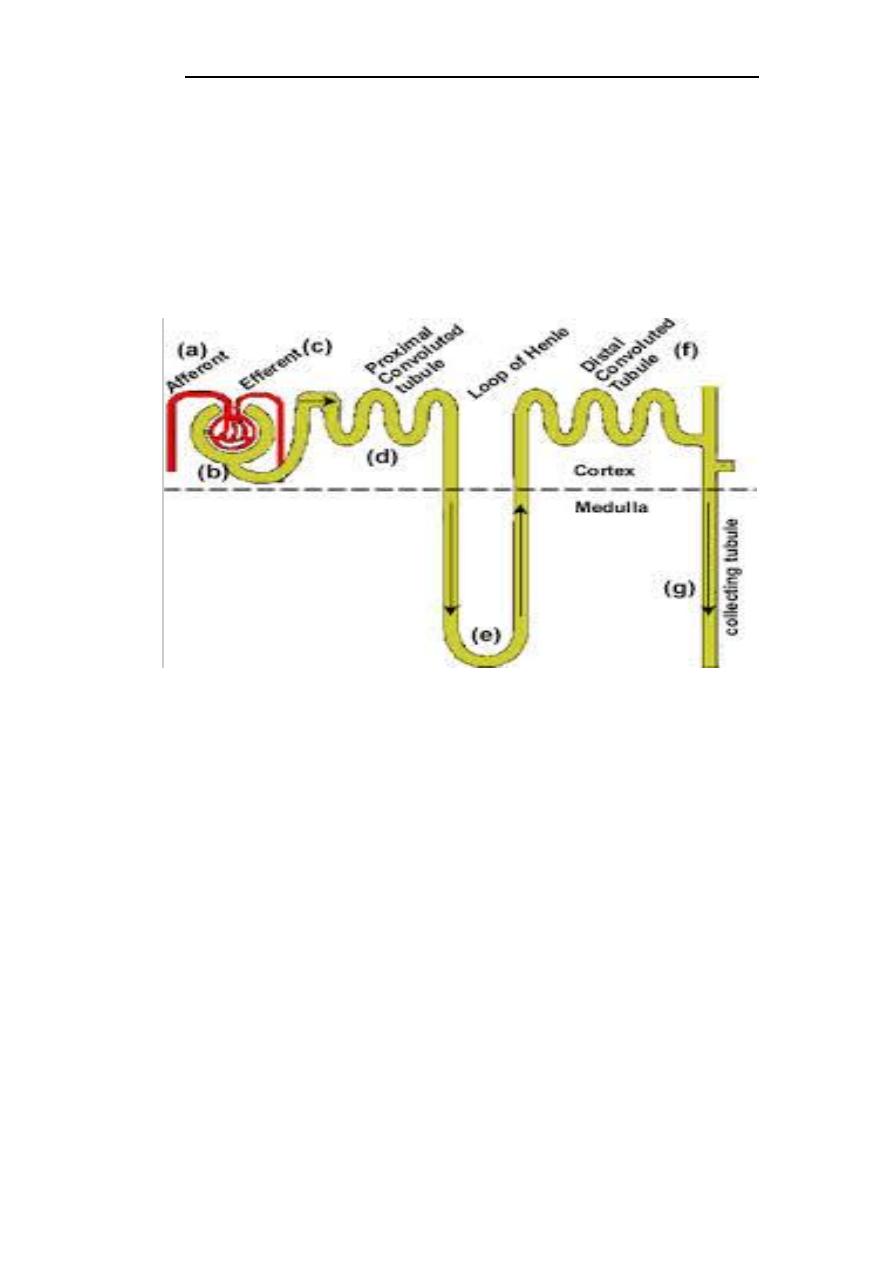
Nephron: it is functional unit of kidney, it is primal a tiny coiled tube with a bulb at one end
called bowman’s capsule, each kidney contain more than one million nephron.
The Nephron consists of:
1- Bowman capsule or glomerular.
2- Proximal convoluted tubule.
Lec. : 6 Physiology
3- Loop of Henley.
4- Distal convoluted tubule.
A nephron eliminates wastes from the body, regulates blood volume and blood pressure,
controls levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulates blood pH. Its functions are vital
to life and are regulated by the endocrine system by hormones such as antidiuretic hormone,
aldosterone, and parathyroid hormone.
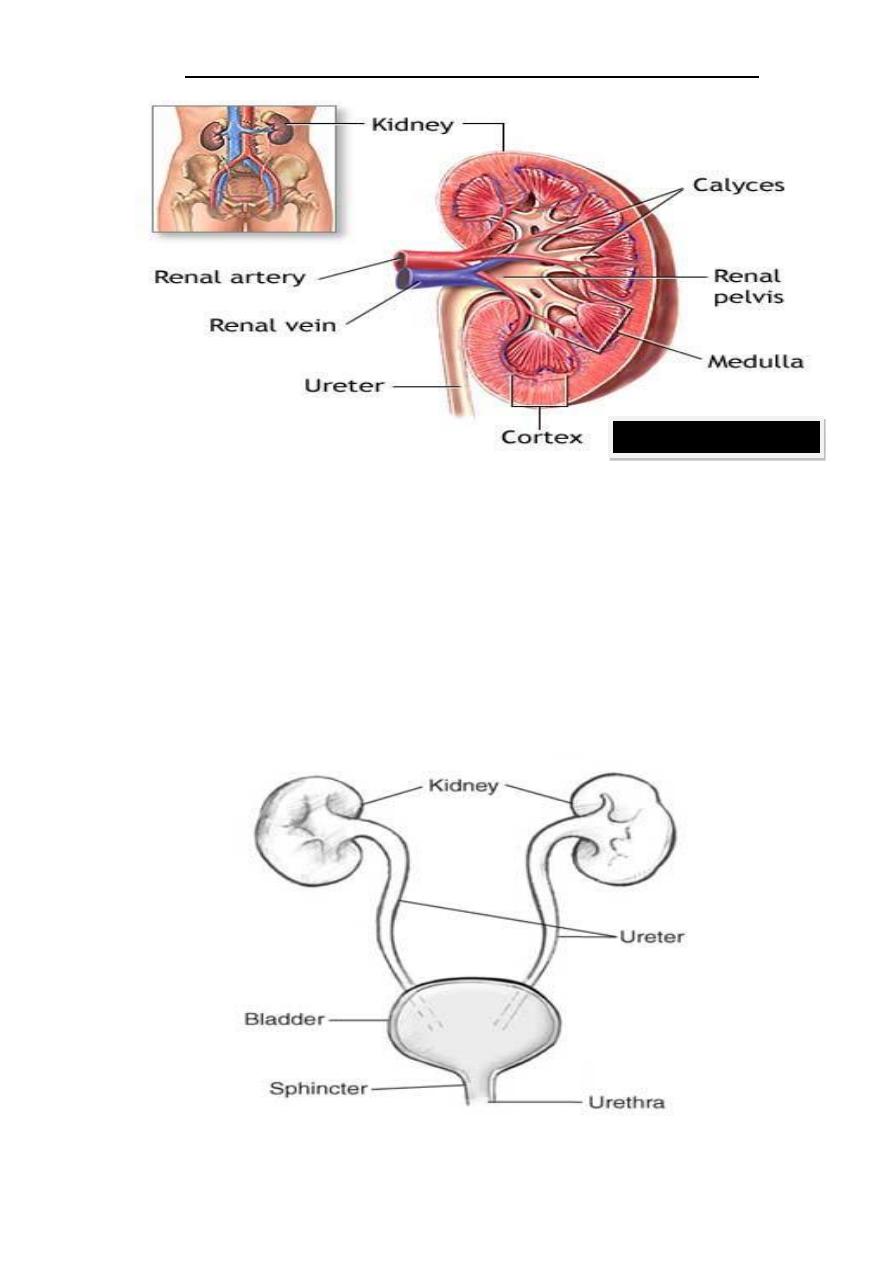
Structure of the kidney:
1-
Renal cortex.
2-
Renal medulla.
3-
Renal pelvi.
4-
Renal calyces.
5-
Renal artery.
6-
Renal vein.
Lec. : 6 Physiology
Structure of the urinary system:
1- Two kidneys.
2- Two ureters.
4- Urethra.
Each kidney excretes urine into a ureter, itself a paired structure that empties into the
STRUCTUR OF KIDNEY
