Class V Amalgam cavity preparation
Dr. Samira J. Juhi TarfaClass V Caries
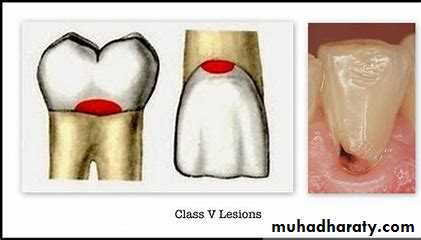
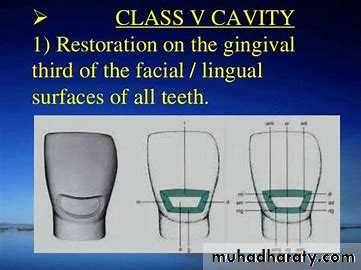
1.Smooth surface carious lesions located on the gingival / cervical third of labial / buccal and more rarely the lingual surfaces of all teeth.2.Simple lesions as it mostly involves one surface of a tooth.
Causes of Class V Cavitation
• Caries is the main reason of this type of cavitation.• 2.Erosion: tooth loss at the cervical area due to non bacterial acid attack.
• 3.Abrasion: tooth loss at the cervical area of the tooth due to abrasive slurry between two surfaces (mechanical - action) e.g : tooth brush dentifrice abrasion.
Restorative Materials for Class V cavity
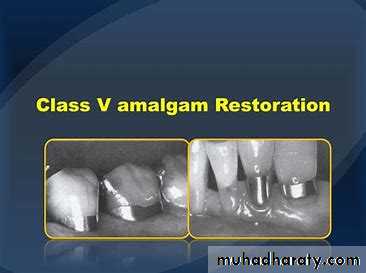
• Amalgam.
• Composite.
• Resin Modified GIC.
• Co mpomers.
•
Indication for Amalgam as Restorative Material
• Non-esthetic areas.• Areas where access and visibility are limited.
• Areas where moisture control is difficult.
• Areas those are significantly deep gingivally.
Contraindication
• Esthetically important areas.
Advantages of amalgam
• Stronger than other direct restoration.
• Easier to place.
• Less expensive.
• Easier to finish and polish.
Disadvantages of amalgam
• They are metallic and non esthetic.• The preparation for an amalgam restoration typically required 90° cavosurface margins specific and uniform axial depths, and incorporation of secondary retentive features.
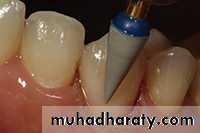
Clinical technique for class v amalgam preparation
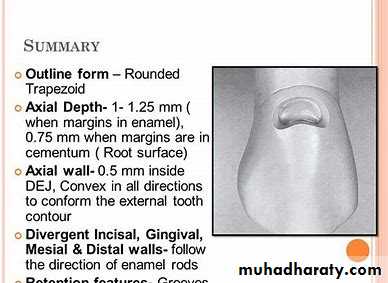
Outline Form:• Rounded trapezoid in gingival 1/3.
• Conforms to the tooth shape, typical caries location, and site of plaque accumulation.
• Primarily determined by the location and size of the caries /defect or old restorative material.
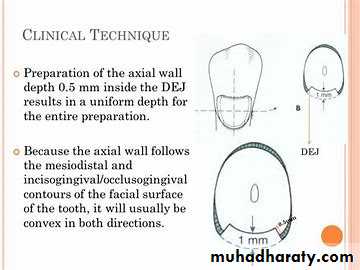
• Cavosurface margins should be extended to sound tooth structure while maintaining a limited axial depth of 0.5 mm inside the DEJ and 0.75 mm inside the cementum.
• Round bur is used to entry to the cavity, the direction of the bur should be perpendicular to the buccal or palatal surface of the tooth, then using a tapered fissure bur of suitable size, enter the lesion to a limited initial axial, depth of 0.5mm inside the DEJ.
• The depth of axial wall is usually 1-1.25mm in the crown, while in the root 0.75mm.
• Extent the preparation , until the margins are positioned in sound tooth structure .
• The axial wall follows the mesiodistal and inciso-gingival contours of the facial surface of the tooth, it will usually be convex in both directions.
• The mesial, distal, gingival, and incisal walls of the tooth preparation are perpendicular to the external tooth surface to keep the cavosurface angle 90° and follow the direction of enamel rods, they diverge facially.
• Consequently, this form provides no inherent retention form must be provided.
Resistance form
• Depth of the cavity is 1.5 mm : the axial wall of the cavity should not be flat, if we do so will not have even depth of the cavity because of the convexity of the tooth structure, so the axial wall should be slightly convex.• Cavo-surface line angle ( 90-110°).
• Rounded internal line angles.
• Removal of unsupported enamel.
• Mesial and distal walls should be slightly diverge.
• Occlusal and gingival walls should be perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth and parallel to each other, any convergence of these walls will create unsupported enamel.
Retention Form
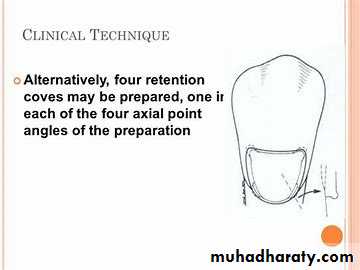
• Use a No. ¼ bur to prepare two retention grooves, one along the inciso-axial line angle and the other along the gingiva-axial line angle 0.2-0.3mm inside the DEJ.•
• The hand-piece is positioned so that No.1/4 bur is directed generally to bisect angle formed at the junction of the axial wall and the incisal/ occlusal or gingival wall.
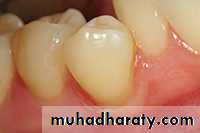
Final preparation
• Removal of any infected dentin.• Pulp protection.
• Finishing external walls.
• Cleaning and inspecting.