Cement
Dr. Samira J. Juhi TarfaCement
Reasons for use of Base and Lining materials:1. Insulation against temperature changes and electrical stimuli under metallic restorations such as amalgam.
2. Mechanical protection provides by distributing local stresses from restoration across the underlying dentin surface.
3. Reduce the risk of microleakage.
4.Cementation of cast or ceramic restoration.
5. Pulp capping.6. Some have bactericidal or bacteriostatic properties.
7. Prevention of the risk of a long term damage to the pulp dentin organ from operative treatment.
8. Cementation of orthodontic bands.
Properties of ideal lining material
Compatible with restorative materials.Not irritant to the pulp.
Prevent injuries of the pulp dentin from restorative materials.
Insoluble in the oral fluids.
Possess sufficient physical strength during insertion of the restoration.
Prevent heat/ cold conduction from metallic restorations.
It should have a bacteriostatic effect e g: zinc oxide eugenol . Material
It should improve the marginal seal and have sealing ability e g: zinc oxid eugenol , so we used it as a temporary restorative material.
It should be easy to manipulation and apply.
It should be radiopaque in the x-ray.
Pulp Protection materials
• Liners• Cement bases.
• The materials may be used alone or in combination, depend on :
1.The extent and location of the preparation.
2. The restoration material to be used.
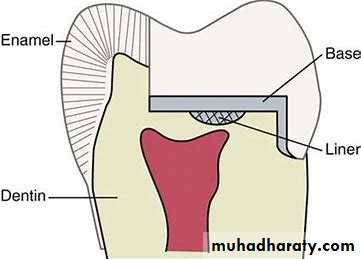
Liners
Materials that are placed as thin coating or layer to :1.Provide a barrier against chemical irritation. (They do not function as thermal isolators)
2.Reduce marginal leakage around most filling materials so reduce inflammatory reaction and post operative sensitivity caused by leakage.
3. Electrical insulation ( treatment of galvanic shock)
The need for liners is greatest with metallic restorations that are not well bonded to tooth structure.
1. Varnish.
2. Ca(OH)2.
3. Resin bond.
Bases
Deep part in dentin should be covered by a base or a sub-base or combination.The thickness of the base depends on its physical properties, but always allowing adequate thickness for the final restorative material.
Function
1. Provide thermal insulation.2.Mechanical protection by resist forces applied during condensation of the restorative materials.
3. A barrier against chemical irritation.
The Cement materials include:
It is Hard and Strong, but irritating to the pulp.Powder-liquid system.
The powder consists mainly of zinc oxide with the addition of magnesium oxide and silicon.
The liquid consist of ortho-phosphoric acid 40% with metallic salts that serve to slow down the setting reaction, and water.
Advantages
Easy to manipulate.High strength necessary for a base.
Withstand mechanical trauma.
Provide good protection against thermal shock.
Uses
As a base material when high compressive strength is required.
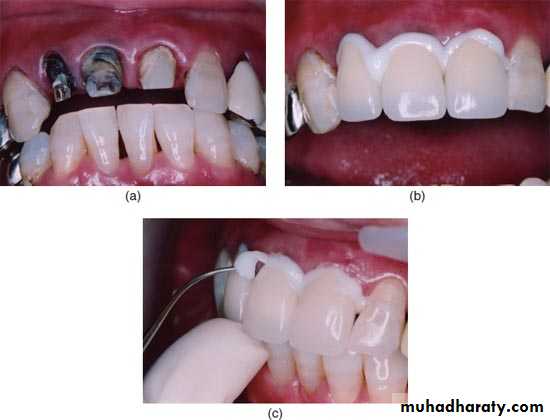
To lute cast restoration to the teeth.
Cementation of orthodontic bands.
Rarely may be used as temporary cement dressing.
Characteristic properties of zinc phosphate
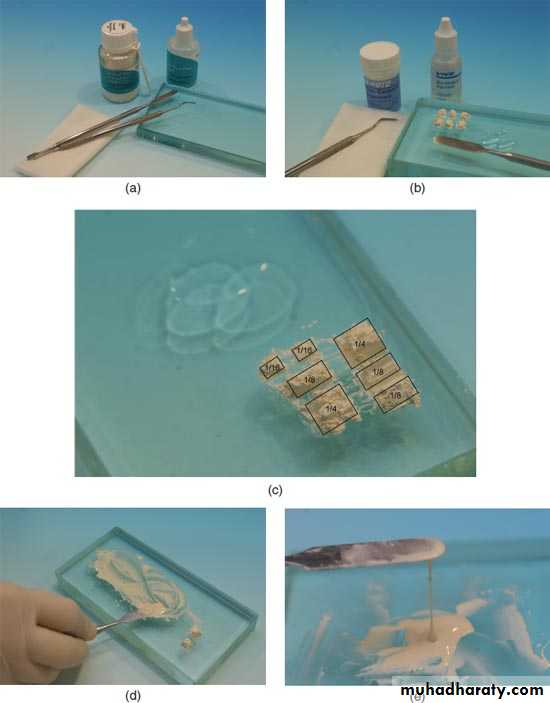
I. Consistency : Two consistencies1.Luting consistency: less powder/liquid ratio is used in order to have creamy mix which is used for cementation of crown and inlays.
• 2.Cement base consistency: more powder/ liquid ratio is used to have putty mix of zinc phosphate cement which may be used as thermal insulator over thin dentin.
II. Viscosity: It depends on time and temperature of mixing. So mixing should be made on a cool glass slab to reduce viscosity of mixing.
III. Setting time : It is time elapsed between the end of mixing and the beginning of setting. (2-8) minutes.
IV. Strength: Influenced by the initial powder/ liquid ratio , the manner of mixing, and the handling of the cement during its placement.
V. Solubility: Greater resistance to solubility is obtained by increasing the powder/ liquid ratio.
VI. Dimensional stability: Z.PH.C. exhibits shrinkage on hardening. This shrinkage can be reduced by increasing the powder/ liquid ratio and with proper incorporating of powder with liquid during mixing.
VII. Acidity: In early manipulation stage the cement is highly acidic, and this acidity reduced with the time, and become nearly neutral at 48 hours.
VIII. Thermal and electrical conductivity: Z.PH.C. is desirable to protect against thermal and electrical trauma to the pulp.
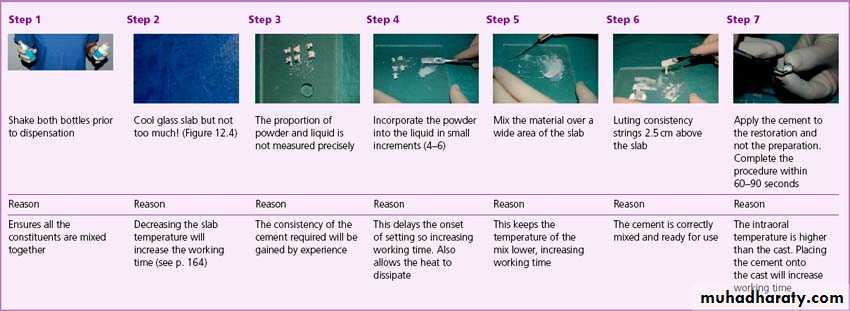
Manipulation of Z.PH.C.
1-Mixing slab: It should be:Thick.
Cool.( 21 C°)
Clean.
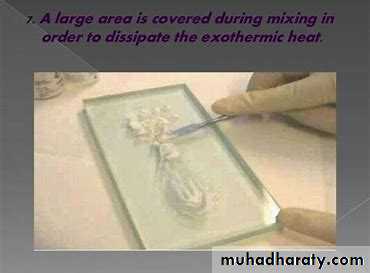
Because the reaction between zinc oxide and phosphoric acid is exothermic reaction. This will dissipate the heat.
2. Powder/ Liquid ratio: Because an increase in the ratio of powder/ liquid provide more desirable properties, incorporation as much powder as possible to obtain a particular consistency.
3. Care of the liquid:
Expose the liquid to a humid atmosphere, it will absorb water which will cause more rapid reaction result in shorting setting timeExposed to dry air will lose water from liquid which will lengthened the setting time.
4. Mixing procedure
a. Powder divided into several small amounts.b. Mixing over a large area to dissipated the heat of reaction.
c. The Z.PH. Should be mixed to: thinner consistency for inlays or crowns, a thick mix is used when basing material is required ( a putty-like mixture) .This will cause lowered initial acidity of the base material, less post-operative pain, and ease of placement.
d. Mixing time not more than 60-90 Sec. for each increment..
5. Frozen slab method:
The glass slab is cooled in a refrigerator at 6°C or a freeze -10°C.A mix of cement is made on the cold slab by adding the powder until the correct consistency is reached.
The advantages of this method are increase in working time and shorter the setting time.
This method has been advocated for cementation of bridges with multiple retainers.
6. Insertion
A. The tooth structure should be dry ,this will insure better adhesion and a harder set.
B. Small quantity of cement is rolled lightly into a ball between the thumb and the four finger then picked up on the point of a probe and carried into the cavity.
C. Then the cement shaped with appropriate instrument, either Ash 49 on the pulpal floor of the cavity.
D. Small excavator is used to remove any excess from the retention grooves or pits and from the cavity walls.
Any trimming by burs should be delayed for at least 10 minute after insertion to avoid dislodgment.
When there is one or two spots of caries on the pulpal floor they should be removed by round bur, but without removing the sound dentin around these spots to gain flat pulpal floor, because this may cause pulp exposure. In this case a base material is used in these deep parts to have flat pulpal floor.
Zinc Oxide –Eugenol cement (ZOE)
PowderZinc oxide with the addition of white rosin to reduce the brittleness of the set cement, and zinc acetate to improve the strength of the cement.
Liquid:
Eugenol with olive oil as a plasticizer.
Two compositional changes have been used to increase the strength of the cement for luting purposes:
1. Methyle methacrylate polymer is added to the powder.
2. Alumina (AL2O3) is added to the powder and ethoxy benzoic acid to the liquid.
Zinc oxide + eugenol Zinc eugenolate +Zinc oxide
This reaction is not exothermic so a cooled mixing slab is not needed, and the presence of moisture is essential for setting to occur.
There is no need to incorporate the powder in small increments. The bulk of powder is incorporated in the initial step, and then a series of smaller amounts is added until the mix is complete.
The average setting time is around 8 minutes.
Properties
1. Neutral in PH (7) can be safely used in moderately deep cavities without danger to pulp.2. Has a sedative effect on the pulp so that we use it without varnish or liner.
3. Radio-opaque.
4. Excellent seal against leakage, so used as temporary restoration.
Uses
1. As temporary restorations.2.The modified type used as a crown and bridge cementation and as a cement base.
3. As an endodontic sealer.