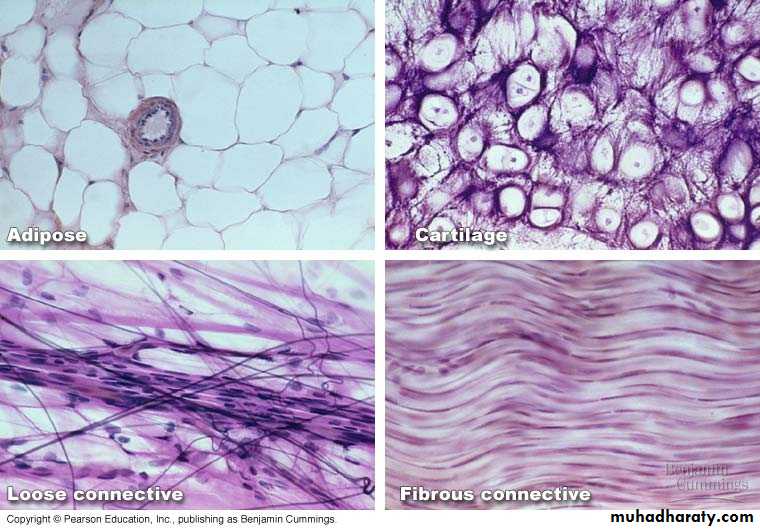
Connective tissue
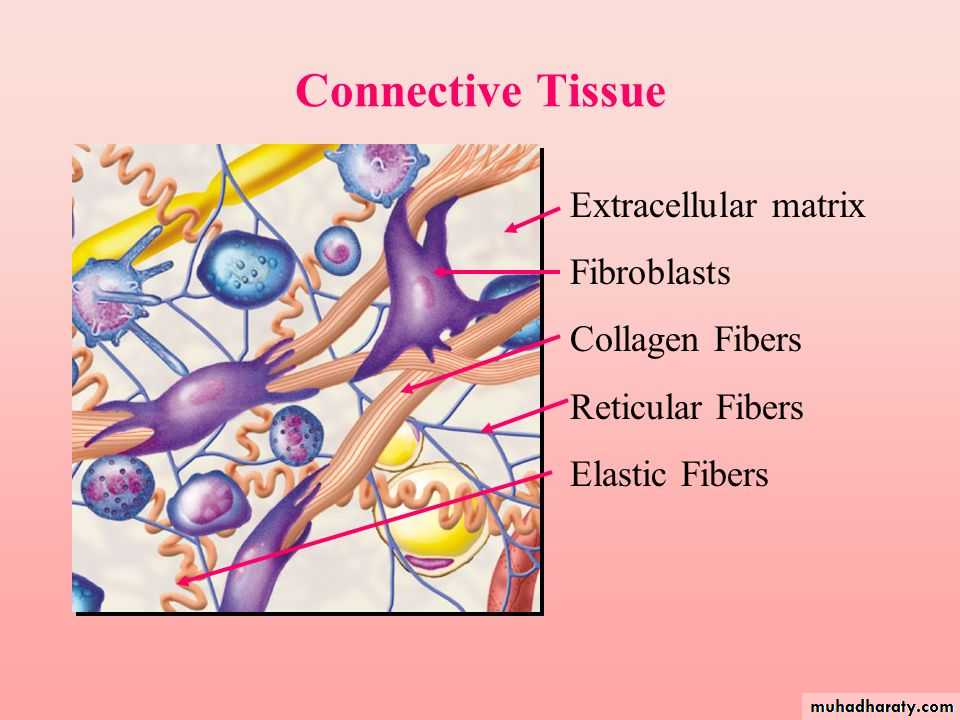
With the exception of blood and lymph, the connective tissue consists of cells and extracellular material called matrix.The matrix consists of fibers, ground substance, and tissue fluid.
Connective tissue bind, anchor and supports various tissue organs and body parts.
Functions
1- Hold together structures like skin , muscle, blood vessels etc . also it form a framework that support the cellular elements of various organs like spleen, lymph node and glands .2- The looseness of areolar tissue facilitate movement between structure connected by it .
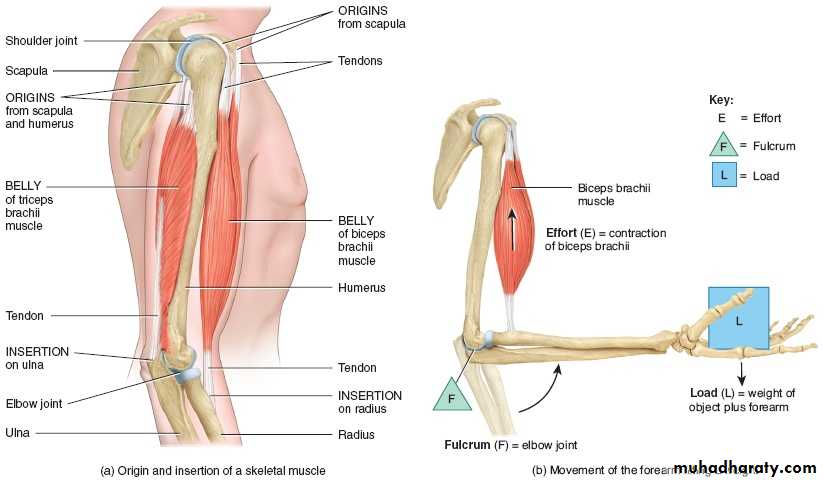
3- Tendon transmits the pull of muscle to their insertion
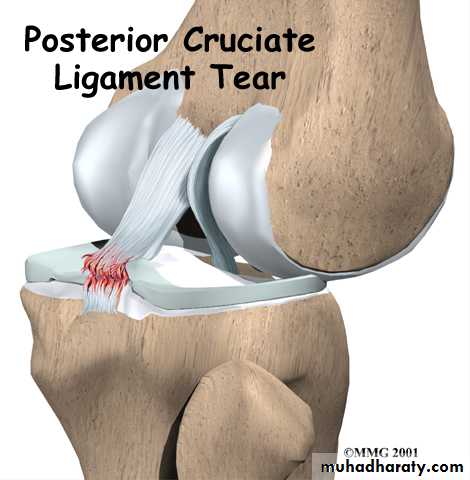
4- Ligament it hold the bone ends together as joints.
5- Forming a site for storage of fat.
6- Defense and protection against invading foreign substances (ex: bacteria)
7- Helping in wound repair.
Connective tissue cells
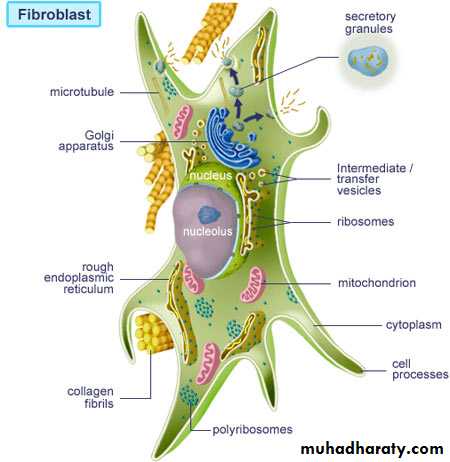
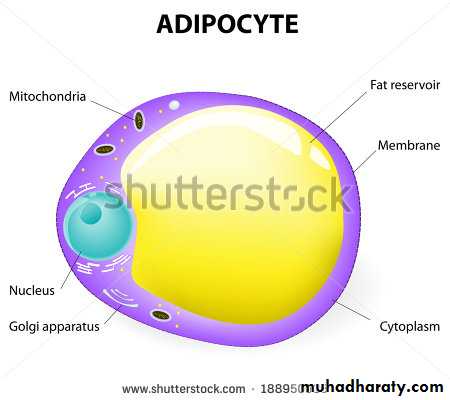
1-Fibroblasts are the most common connective tissue cells; it is synthesize connective tissue fibers and the surrounding ground substance.2-Adipose (fat) cells store fat and may occur singly or in groups. When adipose cell predominate, it is called adipose tissue.
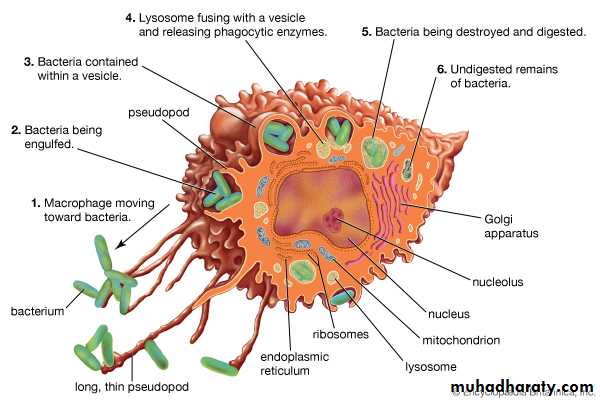
3-Macrophages or histocytes are phagocytic and are most numerous in the loose connective tissue regions.
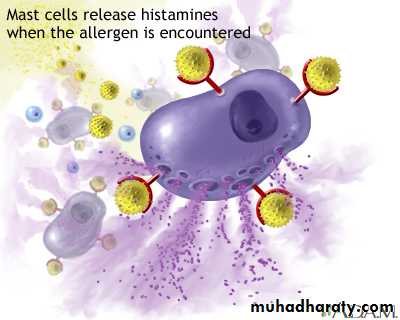
4-Mast cells usually closed associated with blood vessels are widely distributed in connective tissue of the skin and in digestive and respiratory organs. And it is spherical cell filled with fine, dark- staining granules, that contains mediators such as histamine & heparin .
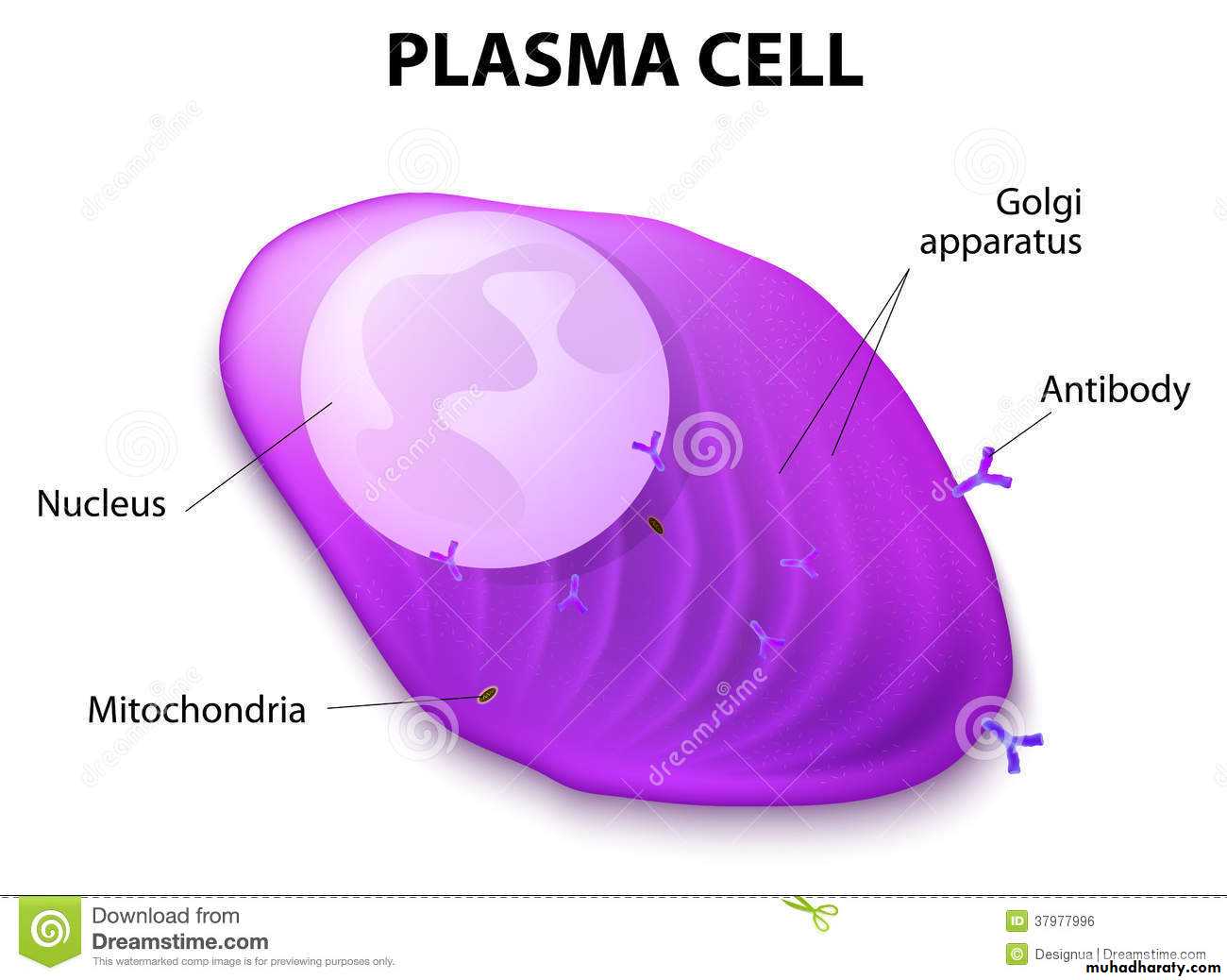
5-Plasma cells are large cells arise from B lymphocytes that migrate into the connective tissue. These cells are found in great abundance in the loose connective tissue and lymphatic tissue of the respiratory and digestive tracts respectively.
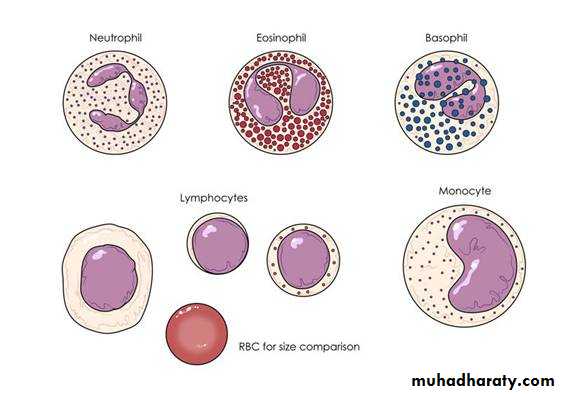
6-Leukocytes are migrate into the connective tissue from the blood vessels their main function is to defend the organism against bacterial invasion of foreign matter.
Fibers in connective tissue
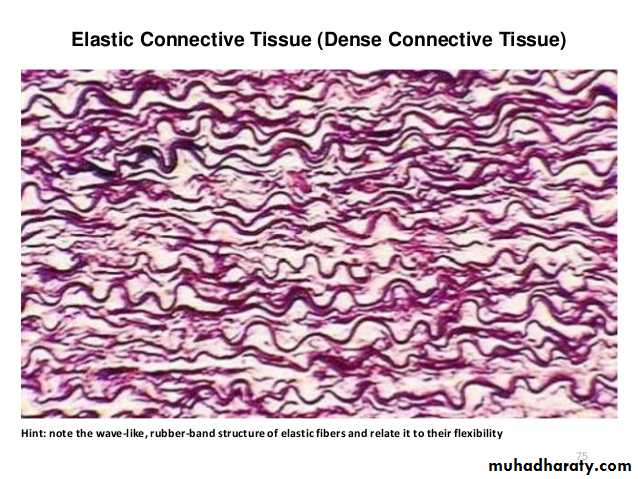
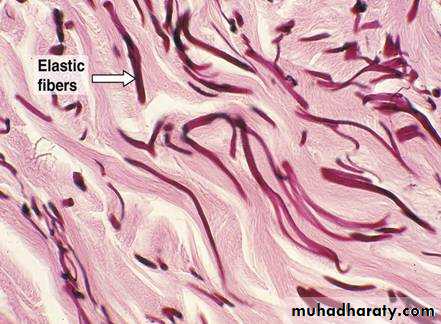
1- Collagen fibers are tough , fibrous protein that are thick and that do not branch . they are the most abundant fibers of most connective tissue of all organs.2-The elastic fibers are thin and small that branch, they have less tensile strength than collagen fibers. the elastic fibers found in the lungs , bladder and skin. in the wall of aorta.
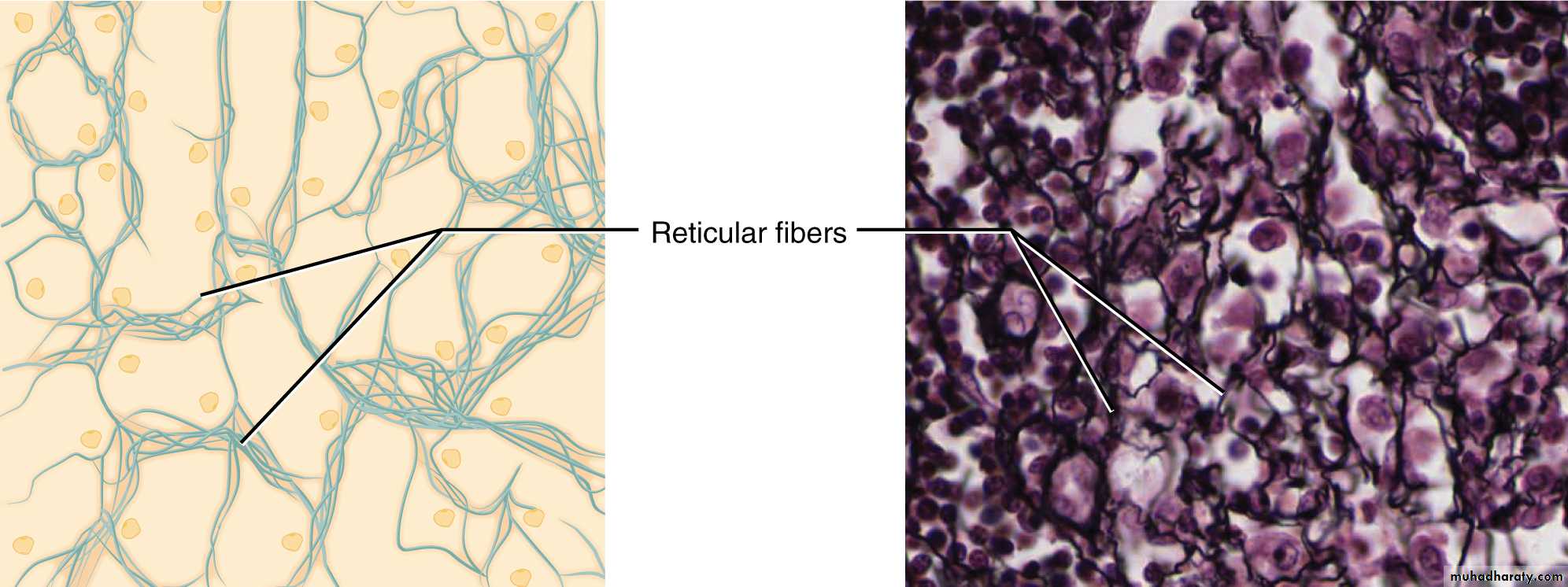
3-The reticular fibers are thin and form a delicate netlike framework in the liver , lymph node , spleen and other where the filter blood and lymph .
Ground substance
• The intercellular ground substance, a complex mixture of glucoproteins and proteoglycans, that participate in binding cells to the fibers of connective tissue, is colorless and transparent.• it fills the space between cells and fibers of the connective tissue;
• it is viscous as acts as both a lubricant and a barrier to the penetration of invaders .
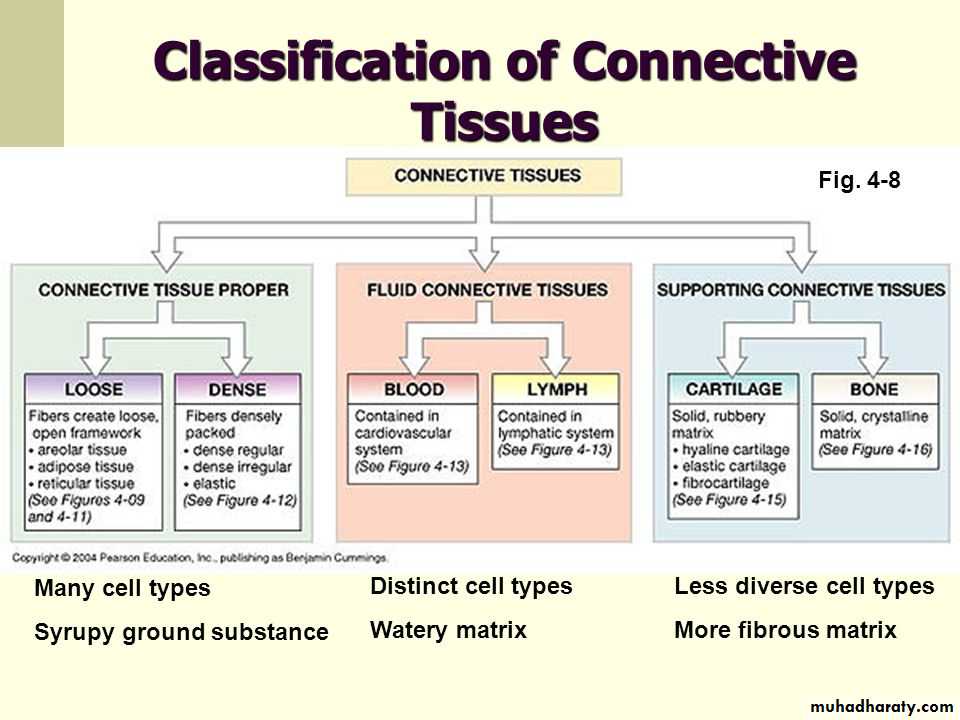
Classification of
Connective tissuesThe connective tissue depending on the amount, type, and arrangement of ,cells, fibers and ground substance.
It is normally divided into:
Proper C. T:
Loose C.T• Adipose
• Areolar
• Reticular
• Mucous
• Mesecnchyma
Dense C.T
• Regular
• Irregular
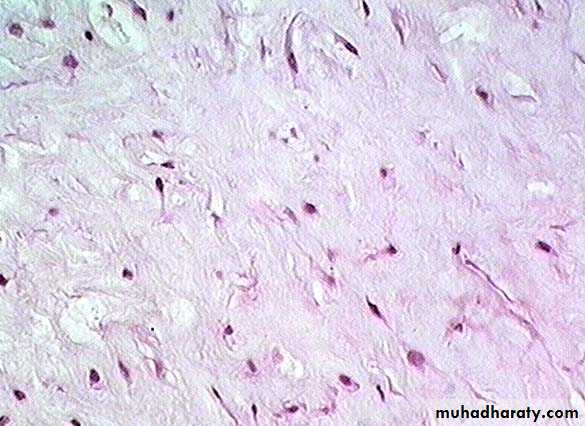
• Loose connective tissue: is more prevalent, it is characterized by a loose, irregular arrangement of its connective tissue fibers and abundant ground substance (numerous connective tissue cells in its matrix). Collagen fibers, fibroblast, and macrophages predominate.
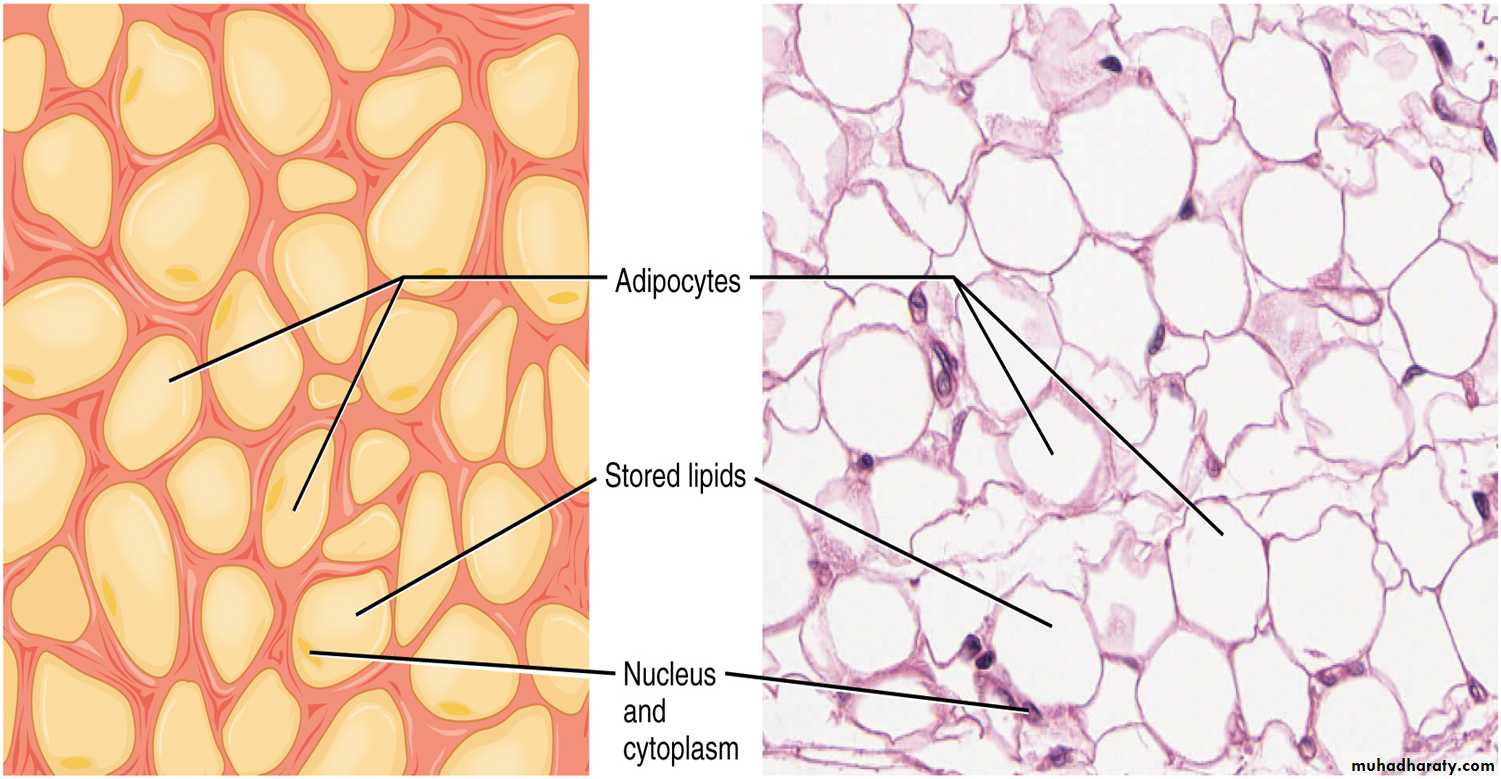
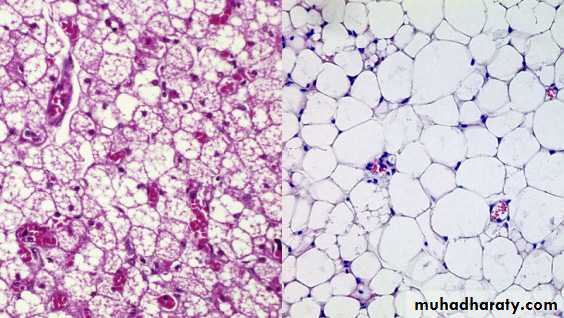
1- Adipose tissue
Most supporting tissues contain cells which are adapted for the storage of fat: these cells, called adipocytes. Adipocytes are found in isolation or in clumps throughout loose supporting tissues or may constitute the main cell type as in adipose tissue.Adipocytes tissue is often regarded as an in active energy store, acts as a temporary store of substrate for the energy–deriving processes of almost all tissues, therefore generally has a rich blood supply. (why)
The rate of fat deposition and utilization within adipose tissue is largely determined by dietary intake and energy expenditure, but a number of hormones and the sympathetic nervous system profoundly influence the fat metabolism of adipocytes.
• There are two types of adipose tissue
• White adipose tissue: comprises up to 20% of total body weight in normal well-nourished male adults and up to 25% in females. It is distributed throughout the body particularly in the deep layer of the skin.• being an important energy store
• acts as a thermal insulator under the skin
• function as a cushion against mechanical shock in such sites as around kidneys.
2. Brown adipose tissue: this highly specialized type of adipose tissue is found in new born mammals and some hibernating animals where it plays an important part in body temperature regulation.
Only small amount of brown adipose tissue are found in human adults and although previously thought to contribute little to thermoregulation there is increasing evidence that brown adipose tissue may play a role in burning of excess energy thus preventing obesity.
2-Areolar tissue : is characterized by abundant ground substance housing the fixed connective tissue cells: fibroblasts, adipose cells, macrophages, and mast cells as well as some undifferentiated cells. Also scattered throughout the ground substance are loosely collagen, reticular and elastic fibers.
small nerve fibers as well as blood vessels that supply the cells with oxygen and nutrients.
It fills the space between groups of muscle cells , supports the epithelial tissue , and forms a layer that sheathes the lymphatic and blood vessels Fig .
3-Mucous tissue : it have abundant of ground substances. It is a jelly – like tissue containing very few fibers .
The cell in this tissue are mainly fibroblast . mucous tissue is the principle component of the umbilical cord.
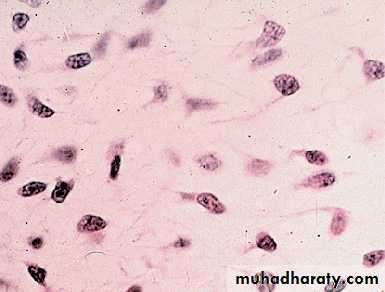
4-Mesenchyme tissue : it is made up of smalls cells with slender branching process that join to form a fine network. It is embryonic connective which is consist the tissue of embryo Fig(3).
Fig (3)
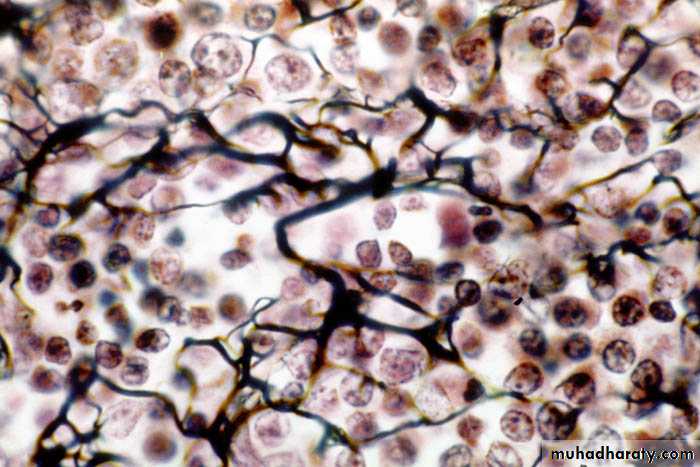
5-Reticular tissue: is a specialized loose connective that provides the architectural framework of bone marrow, liver, spleen, lymph node, smooth muscle and gland and the islets of Langerhans.
It is made up of reticular fibers and fiber form supporting network for the cells.
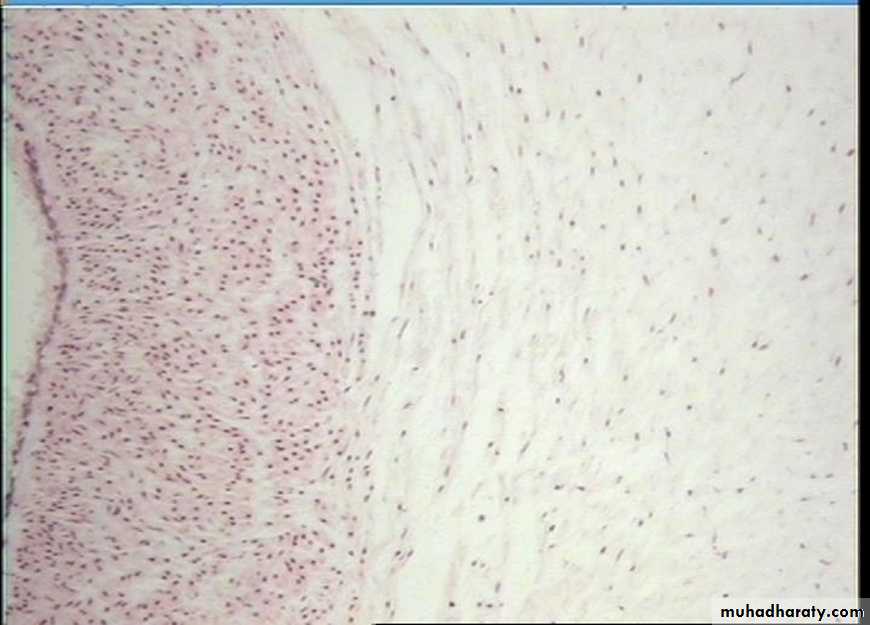
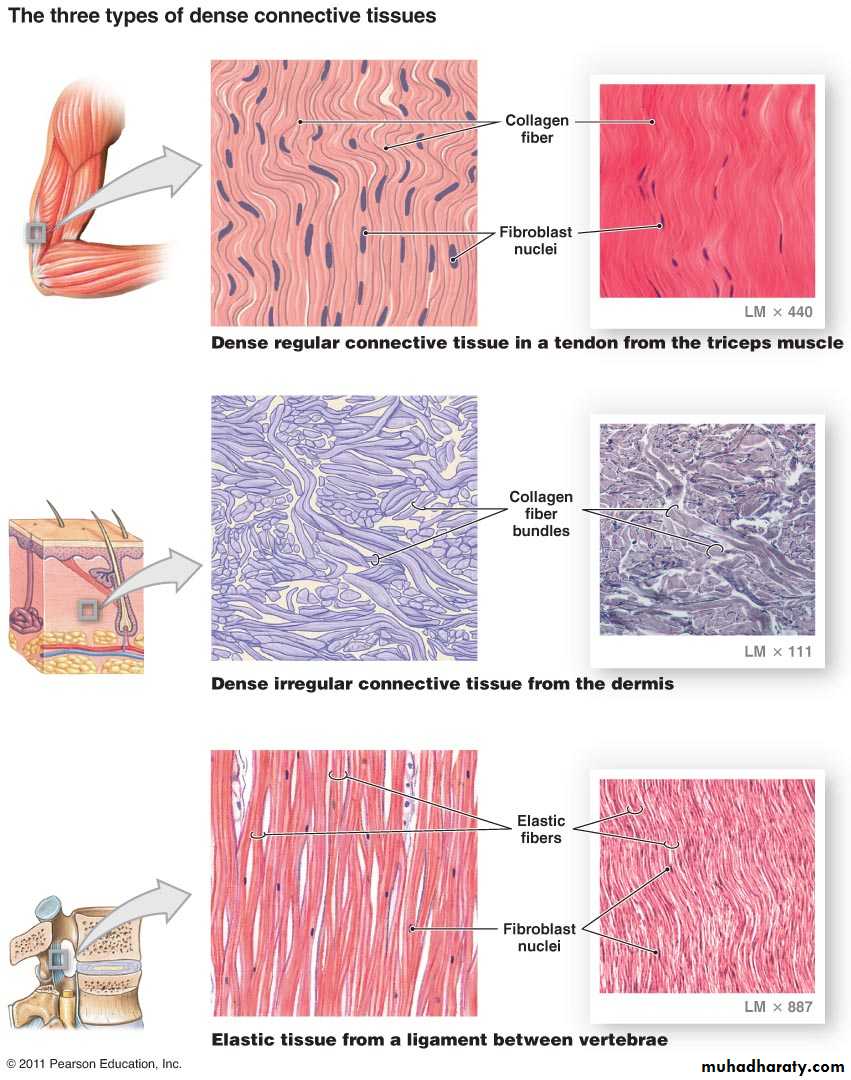
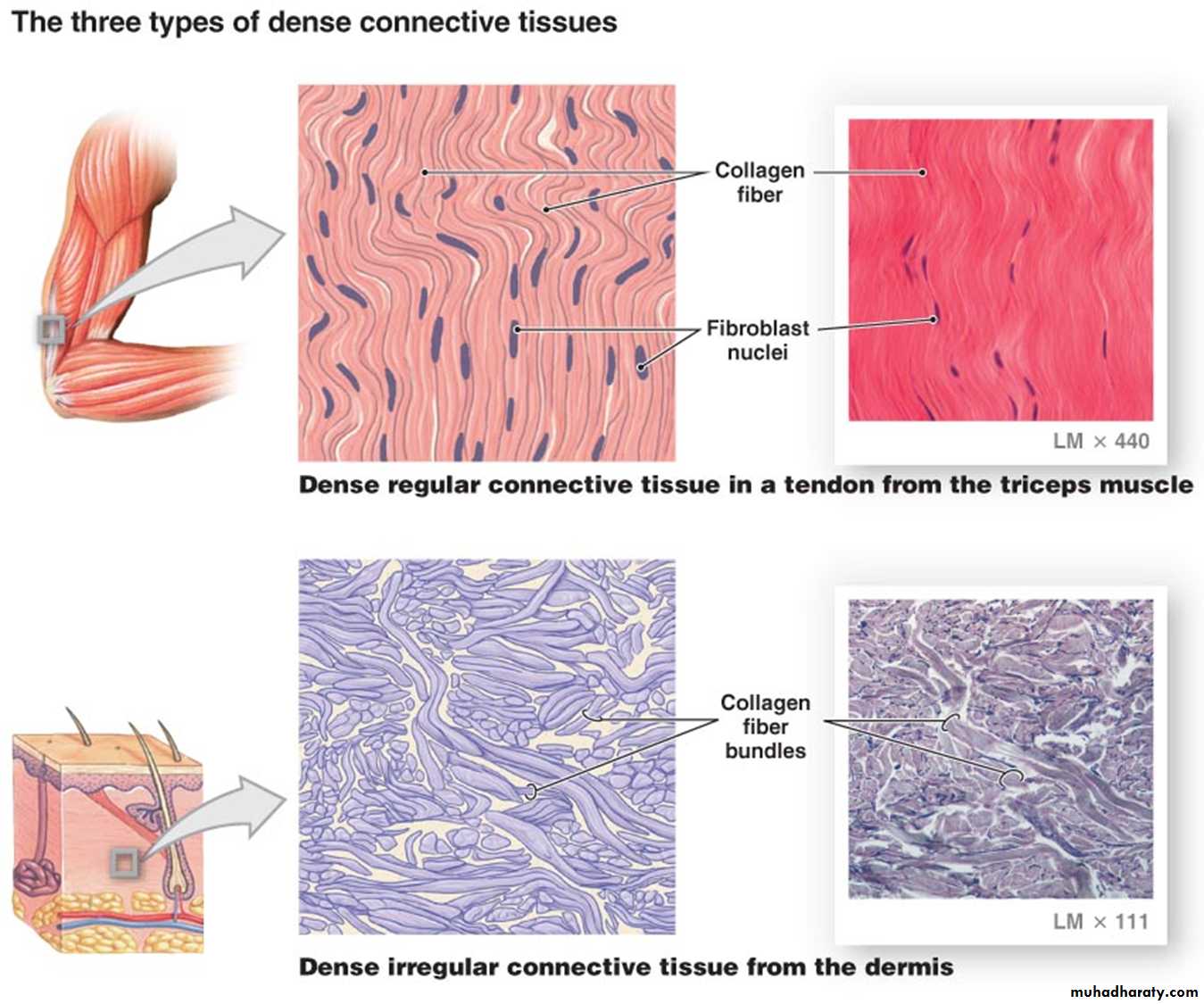
B. Dense connective tissue:
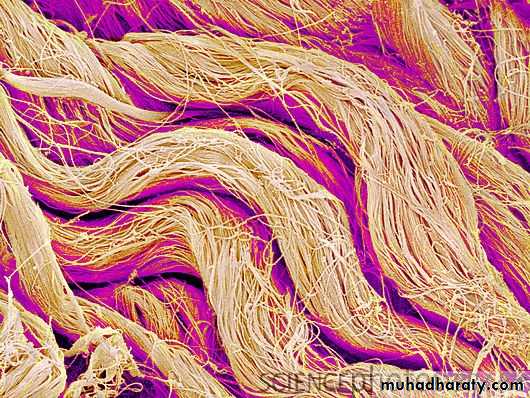
contains thicker and densely packed collagen fibers (fewer cells-types and less ground substance),• irregular dense connective tissue exhibits a random and irregular orientation of its collagen fibers, it is present in the dermis of skin, in capsule of different organs, and in areas for strong support.
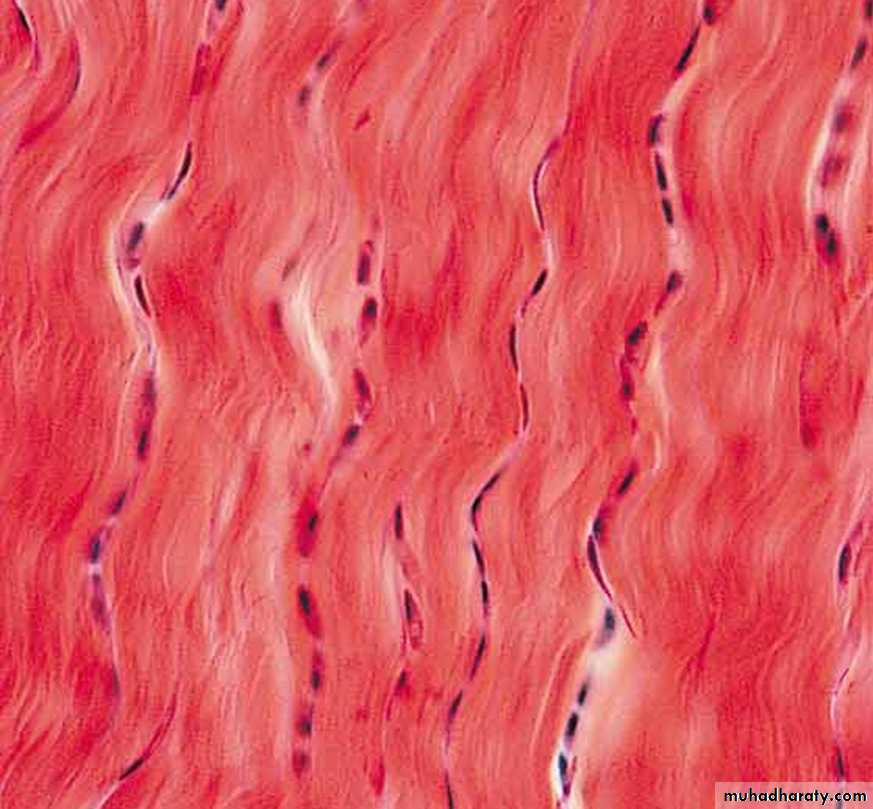
• Regular Dense connective tissue exhibits densely packed collagen fibers with regular and parallel arrangement. This type of tissue is found in the tendons and ligaments Fig (5).
Thank you