Menstruation with clinical considerations
Menstruation is defined as monthly shedding of endometrial dead tissue which herald failure to achieve pregnancy.Menstrual blood is a mixture of dead endometrial tissue, blood components and pus cells.
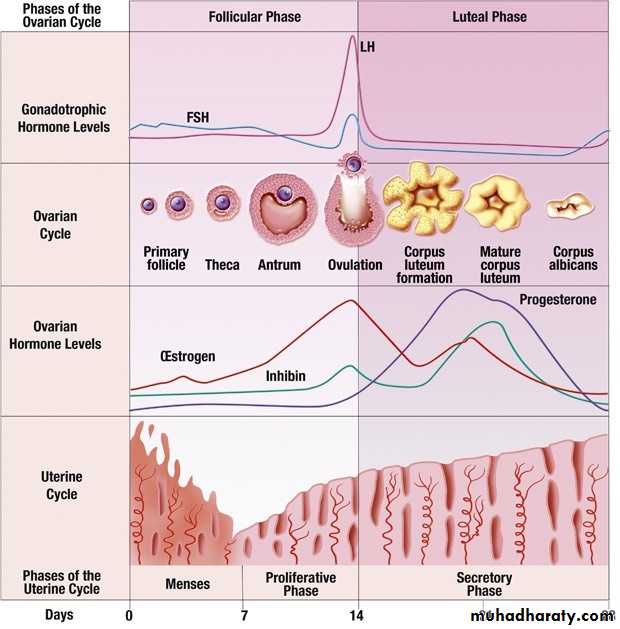
The normal limits of human cycle are 3-7 days in duration, with frequency 21- 35 days with average 28 days
The total blood loss should not exceed 70- 80 ml and usually above 30- 40 ml.
Anatomical overview of the limbic system, hypothalamus and pituitary as related to menstruation
Introduction
main parts are the singulate gyrus, mammillary bodies, hypocampus, Amon horn,
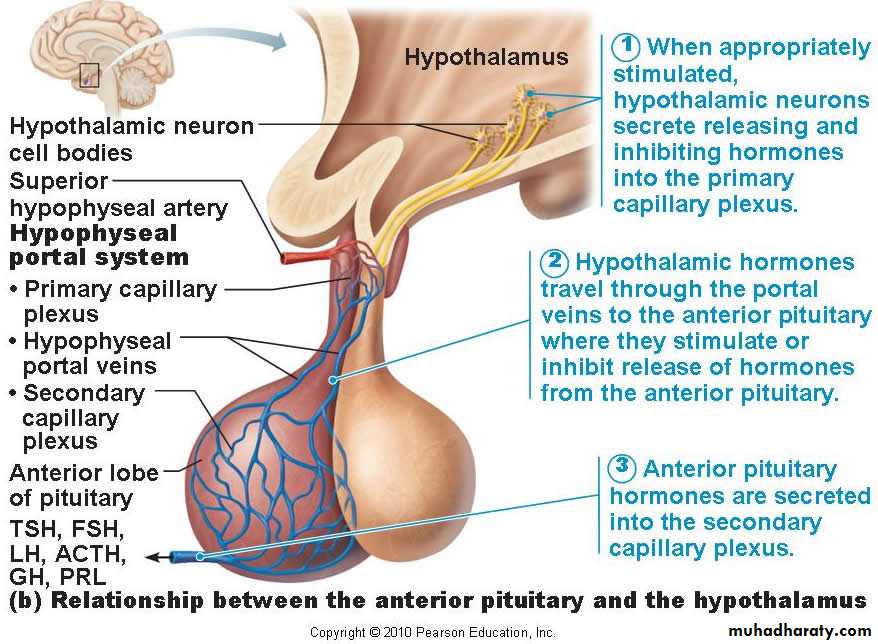
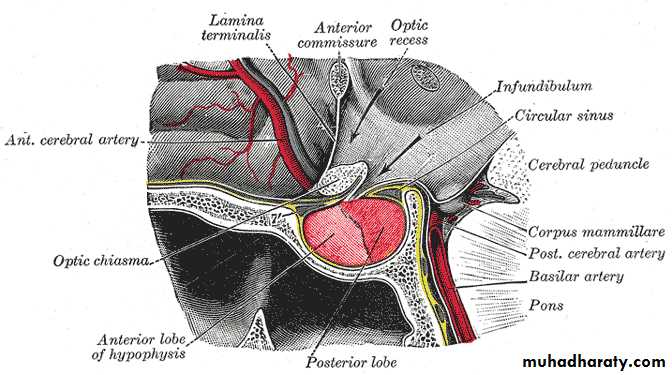
Pituitary gland receives its stimuli from the hypothalamus by a unique portal system which ensures the correct stimulus is delivered.’.
The olafactor nerve in all vertebrates arise also from the limbic system.
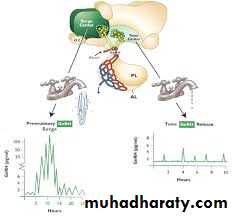
It is stimulated by pheromones pheromnes secreted usually from the female which stimulate GnRH secretion
The hypothalamus hormones inducing menstruation
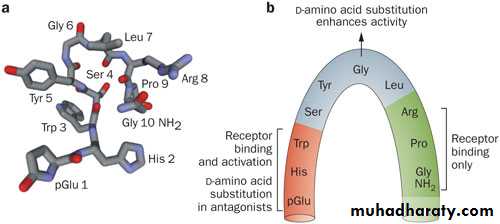
Gonadotophin Rleasing Hormone or GnRH. This Decapeptide amino acid short polypeptide is secreted from the hypothalamus and precisely translated to the basophil cells in the pituitary gland
The frequency and the amplitude of the GnRH secreting cells determine accurately which cell in the pituitary should be stimulated.
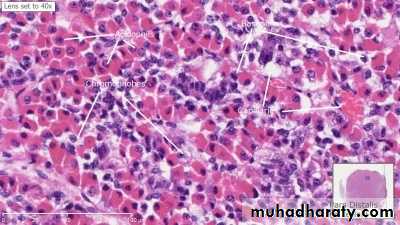
Dopamin which is an adrenergic agent yet a neurotransmitter has strong inhibitory effect of the acidophil pituitary prolactin secreting cells which appears as red staining cells under the microscope.
The dose of dopamine should adequate and prompt to ensure no prolactin is secreted
Hypothalamic specific causes which inhibits GnRH only
Heavy jobs which involves severe stress like female pilots, astronauts and exercise in athletes .Anorexia nervosa severe reluctance for feeding usually following heavy dieting.
Ballet’s dancers and similar slim woman requiring jobs.
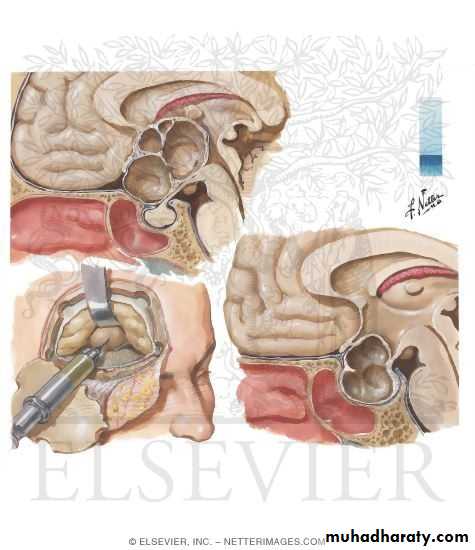
Craniophapharyngioma
It is in inclusion cyst from the posterior Rathke’s pouch.Once separated from the primitive mouth cavity it becomes impacted somewhere in front the hypothalamus.
As gradually increase in size with age it compresses the pituitary stack preventing all hormones from hypothalamus reaching the pituitary including the posterior part.
Diabetes insipidus commonly is the most common presentation. Amenorrhea is a secondary problem in this condition which should be removed surgically.
Pituitary gland
. The pituitary gland rest in an intracranial fossa called Sella Turcia.The posterior pituitary glands are bundles of especially elongated neurons with ability to store hormones accordingly.
The anterior are group of specialized cells which receive their stimulators from the hypothalamus via the portal system in the form of hormone..
Hormones of reproductions
follicle stimulating hormone and corpusluteum luteum secreting cells.
Both of those 2 cells stain blue under the microscope while cells which secretes
prolactin are red under or acidophil styled cells.
Various clinical conditions which suppress FSH and LH at the level of pituitar
ProlactinomaHyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism
Acromegally
Both Cushing disease and addison’s disease
Hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism
Chronic active hepatitiis
Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases
SLE, rheumatoid arthritis
Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a disease in which endometrial tissue present anywhere outside the endometrial cavity.Inhibition of the menstruation for 6 months by GnRH analogues is used to induce amenorrhea.
Contraceptive pills
Combined contraceptive pills are used for family control or contraception’s contains estrogen and synthetic progesterone.They act by complete inhibition of FSH- LH secretion
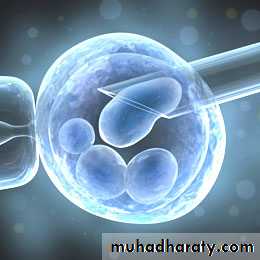
IVF
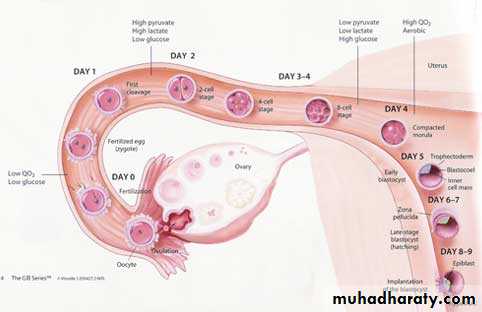
In vitro fertilization FSH and LH which can be mixed or FSH alone can be given in various protocols to induce maturation of the ovarian follicleand then extracted under U/S guidance so the ova is fertilized under the microscope.
Usually 3-5 morula stage embryos are returned to the uterus.
Down regulation of the pituitary is essential to give exogenous gonadotrophins
Enometrial carcinom
In endometrial carcinoma since the famous reports by Novak’s in USA that cannon balls in the lung have disappeared by progesterone;progestational agents may be part of the treatment of advanced endometrial carcinoma
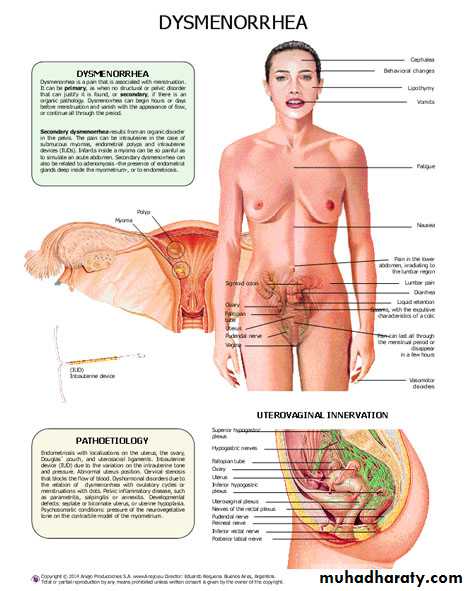
Primary dysmenorrhea
Primary dysmenorrheal a disease associated with menstruation with severe colicky abdominal pain.Contraceptive pills may be used as a second line.
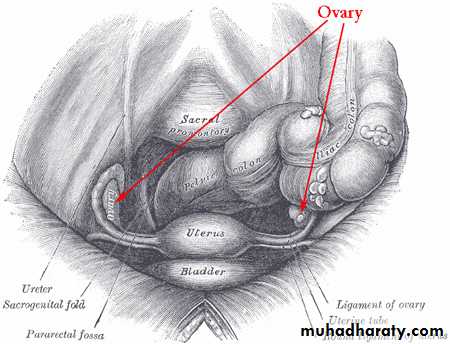
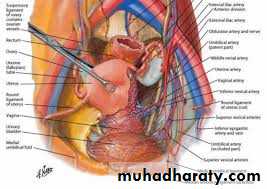
Anatomical overview of the ovary related to menstruation
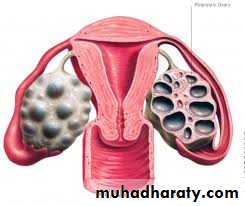
The human ovary is a highly intricate organ egg shaped with volume average 3,2, and 1 cm.it is freely mobile white to gray in color, lying on the posterior abdominal wall suspended by the strong suspensory ligament of the ovary.
The ligament passes very closely to the bifurcation of the common iliac artery and ureter making it liable to injury during hysterectomy in few cases
Embryonic origin of the ovary
Ova from the yolc sacSurface epithelium from the coelimic epithelium
Stroma which is fibrous tissue and fbroblast from mesoderm
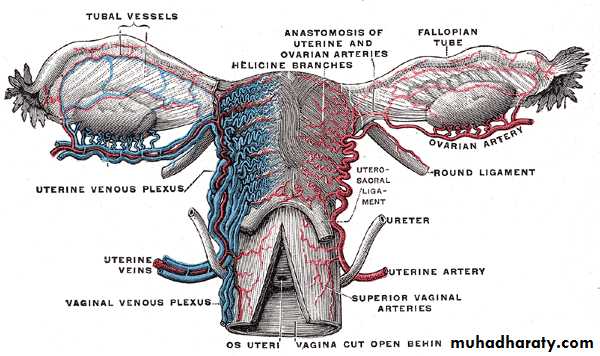
Ovarian blood supply
The ovarian artery comes from the aortaThe ovarian vein drains to IVC
Ureter is very close to the point of suspensory ligaments origin
This site is one at which the ureter is liable for injury
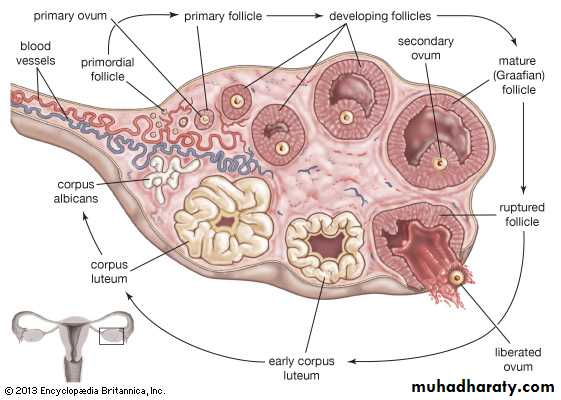
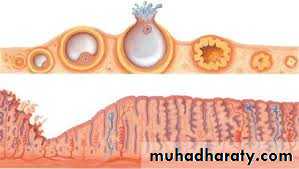
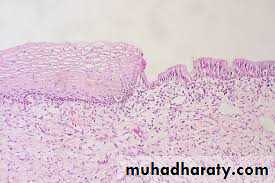
Ovary under microscop
Primordial ovarian follicleSeconday ovarian follicle
Tertiary ovarian follicle
Immature and mature ovarian foliicle
Corpus luteum
Corpus albicans
Mullerian inhibiting factor as predictor of menstrual age of woman
MIF has been long used to predict the age of menopause. ‘It is secreted by the follicular cells throughout the follicular phase making hypothalamus more sensitive to the increasing estrogen levels.
In addition it may play some role in converting mature ovarian follicles into corpus luteum after rupture.
Online free calculator of menopause is widely available and may be used by any woman.
Mittelschmerz
Mittleschmerz is a mild brief localized pelvic pain which is caused by rupture of the ovarian follicle with possible leak of few blood drops.It is mostly a minor disorder which requires nothing but assurance and explanation.
Unfortunately this condition enters in the differential diagnosis of appendicitis and some other surgical emergencies and laparotomy may be done for exploration.
Careful monitoring of the patient in high risk departments usually solves the issue whether it is a minor disorder or more serious condition.
Ovulation and fertilization
Polycystic ovarian syndrome
This syndrome was described as combination of obesity, hirsutism, menstrual abnormalities and infertility.In the last 20 years it was discovered to be a disease of insulin resistance group.
Associated with chronic un ovulation, high androgenic steroids, high insulin and LH in n addition to lipid abnormalities .
Both ovaries are covered with immature thecal follicles and ratio of LH/FSH more than 2.
Premature menopause
Menopause when occur at age less than 40 years.Auto immune diseases are significantly associated with.
Family associated sometime seen.
Such women are those with highest risk of ischemic heart disease, CVA and osteoporosis. Hormone replacement therapy is the available treatment.
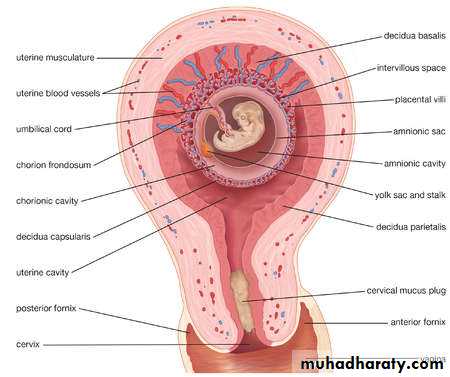
Anatomical overview of the uterus related to menstruation
Secretory phase and luteal
Anatomical overview of the fallopian tubes related to menstruation
Simple test to confirm ovulation
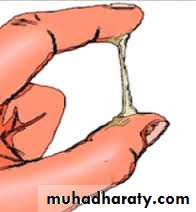
Body temperatureSpinbarkeit test
Vaginal cells aspiration and staining with eosin and hematoxylin.
Aspiration of the endometrial lining for histopathology.
Serum progesterone at day 21 or mid luteal phase above 20 ug/ ml is highly associated with ovulation.
Ultrasounds scan at day 14 and 21 of the cycle
The modern widely used kits which stains according to the instructions coming with those kits may be used.