
1
Fifth stage
Psychiatry
Lec-5
د.الهام الجماس
6/10/2015
Psychiatric disorders specific to women
Psychiatric Aspect of Pregnancy
Psychiatric disorder is more common in the first and third trimesters of pregnancy, in the
1st trimester. Unwanted pregnancy is associated with anxiety and depression. In the 3rd
trimester there may be fear of delivery or doubts about the normality of the fetus. Minor
affective symptoms are common in pregnancy with those who has diabetes.
Pseudocyesis
Is a rare condition in which a woman believes that she is pregnant who she is not and
develops amenorrhoea, abdominal distention and other changes similar to those of early
pregnancy.The condition is more common in younger women, usually resolves quickly once
diagnosed.
Convade Syndrome
In this syndrome, the husband of the pregnant women report that he is himself
experiencing some of the symptoms of pregnancy, this occur in the early pregnancy the
man complain of nausea and morning sickness, these
complaints resolve after few weeks.
Termination of unwanted pregnancy
In the past psychiatrists were asked to see pregnant women seeking therapeutic abortion
on the grounds of mental illness. Most of the evidence suggests that the psychological
consequences of termination are usually mild.
Spontaneous abortion
After spontaneous abortion found that half of the women showed depression, many
women showed features of grief, improvement takes place with time.
Antenatal death
antenatal death ( still birth) causes an acute bereavement reaction and long term psychotic
problem and concern about further pregnancy, the parent may need further support and
the next pregnancy may be worrying time to them.
Psychiatric aspect of gynecology

2
Premenstrual syndrome:
A group of psychological and physical symptoms starting a few days before and ending
shortly after the onset of menstrual period.
The psychological symptoms include :
Anxiety, irritability and depression.
The physical symptoms include breast tenderness, abdominal discomfort and
feeling of distention.
Etiology
The cause is uncertain ovarian hormones , pituitary hormones, disturbed fluid and
electrolytes balance non of these theories has been proved.
Treatment
Psychological support and medication the effectiveness of SSRI antidepressants during the
acute state.
The menopause
In addition to the physical symptoms of flushing, sweating, and vaginal dryness,
menopausal women after complain of headache, dizziness and depression, depression and
anxiety at the time of menopause have several causes:
1. Hormonal changes have been suggested.
2. Changes in the women role, her children leave home.
3. Her relationship with her husband change.
4. Her own parents become ill or die. The treatment – antidepressant drugs + minor T.
Hysterectomy
An increased frequency of depressive disorder after hysterectomy, several studies
showed that women who are free from psychiatric symptoms before hysterectomy
suddenly developed them after hysterectomy
Sterilization
Sterilization leads to psychiatric disorder and sexual dysfunction , although some studies
showed sexual relationship, improve after sterilization.
Psychotropic drugs in pregnancy and post- partum
-SSRI there is no evidence of harm cause drugs. lithium should not be prescribe in
pregnancy and during breast feeding it causes cardiac malformation.
- lithium should not be prescribe in pregnancy and during breast feeding it
causes cardiac malformation.
-Tricyclic –antidepressant, these drugs secreted in the milk, breast feeding should be
avoided.
-Neuroleptics does not causes teratogenic effect but should be given if there is strong
indications
- Benzodiazepines- taken it late pregnancy causes flappy infant syndrome or withdrawal
3
symptoms in the neonate.
-The pregnant drug addict opiates cross the placenta and the fetus become depended
upon them and suffers withdrawal symptom. If the mother stop taking them the
withdrawal symptoms may precipitate fatal distress.
Premenstrual Disorders:
Etiology:
• Endocrine models
• Neurotransmitter models
• Psychosocial state.
• PMS as a variant effective disorder.
•
PMS as an autonomous mood disorder.
Management
Mild symptoms-education, diet & stress management, bromocriptine for breast
tenderness. Moderate to severe symptoms include Benzodiazepine + Antidepressants
Other Disorders
• Miscarriage & abortion.
• Hyperemesis gravidarum.
• Pseudocyesis
Mental disorder associated with puerperal
This divided into 3 categories
1. Maternity blues.
2. Postnatal depression.
3. Postpartum psychosis.
4.
Acute organic confusional state ( Delirium)
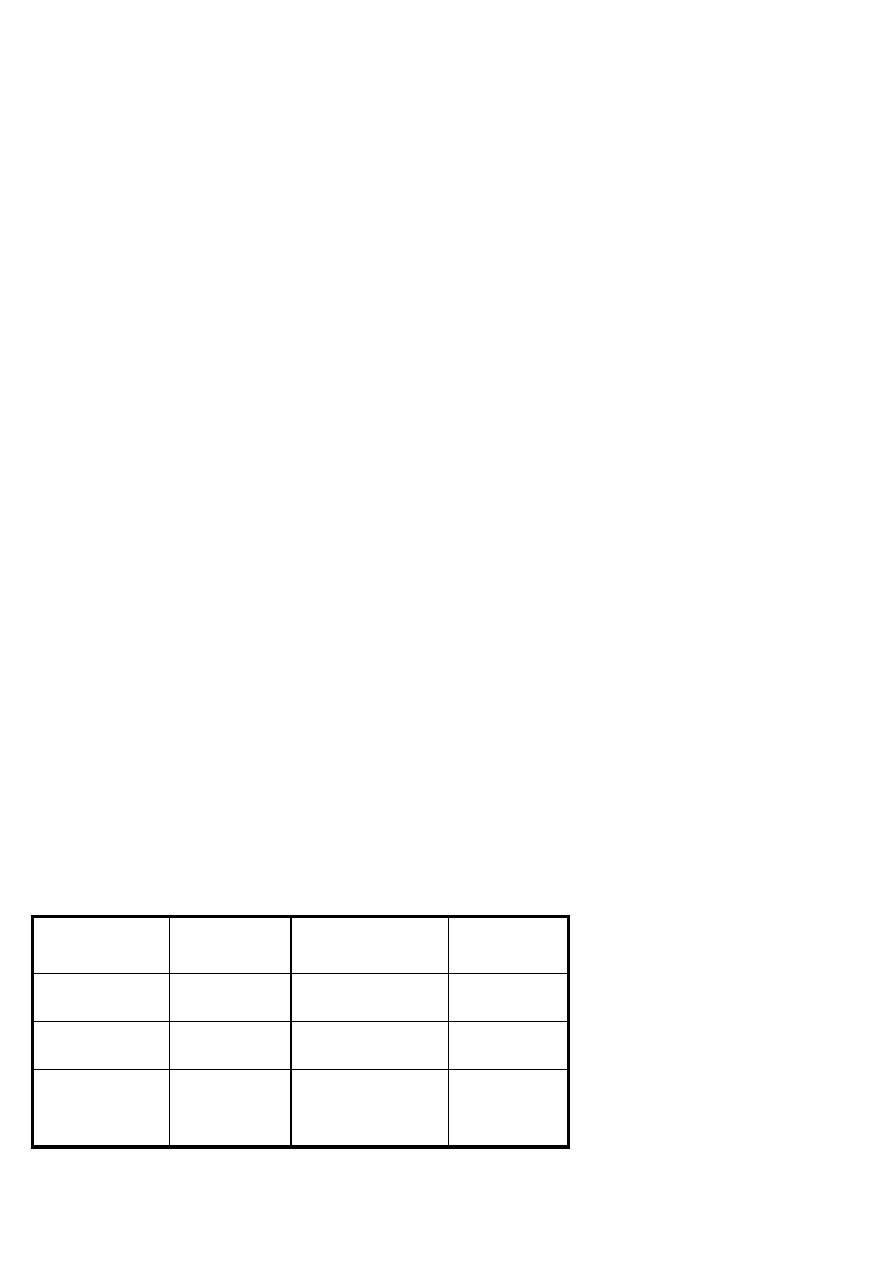
Table: Puerperal mood disorders
Maternity blue
Postnatal depression
Postpartum
psychosis
incidence
30-80%
10-15%
0.2%
Onset after child
birth
About 3-10 days
About 3 weeks
About 2 weeks
Management
Support &
education
Cognitive therapy +
antidepressant
Admission +
antipsychotics

4
Maternity blue
Maternity blue is the term used to describe a mild self-limiting.
Episode of psychological disturbance beginning 3-10 days after parturition ( peak onset day
5) and remitting by 12-14 days after parturition.
The reported prevalence varies from 30-80%.
The most frequent symptoms include depression, mood liability, insomnia, anorexia,
fatigue, irritability, anxiety and confusion, the syndrome is common and the clinicians
regard it as a normal part of childbirth.It appears to occur across all race and cultures and it
is the response to childbirth. The most casual theory fall in estrogen, progesterone and
prolactin level after childbirth.
The treatment of maternity blues- no active treatment are recommended. Education about
the nature of the condition with support.
Postnatal Depression
The diagnosis of postnatal depression is restricted to a non-
psychiatric depressive disorder that develops insidiously~ 3-4 weeks after childbirth.
The prevalence of depressive disorder is about 10-15% in the 6 months postpartum.
The symptoms of post-partum depression are similar to depressive disorder arising at other
stages of the life cycle.Weepiness, irritability, anxiety more prominent than depressive
affect, anxiety more focus on the well-being of the baby, thought of inadequacy or familiar
to care of baby.
Suicidal ideation and vegetative symptoms of depression including loss of libido, sleep
disturbance is common-fatigue and slow movement.
Etiology
I s not clear yet, a family or personal history of:
1. Affective disorder.
2. Poor marital relationship.
3. Inadequate social support..
4. Stressful life events during pregnancy.
5. Severe maternity blue may at risk of postnatal depression.
Management
Psychological and medical treatments is effective in treating postnatal depression.
Antidepressants medications all of them excreted in the breast milk, however this should
not be regarded as an absolute contraindication.
Antidepressant medications delivered in the breast milk is small and not risk to the infant.
SSRIs is effective antidepressant and does not affect the infant and can be augmented with
lithium or carbamazepine or Benzodiazepine.

5
Some time ECT is needed if the above treatment failed.
Postpartum Psychosis
Postpartum Psychosis usually has a rapid onset in the first 1-2 weeks after childbirth, but is
never reported within the first few days postpartum the incidence remain high for up to 2
years postpartum.
The cause is personal or family history of major mental disorder , also lack of social support
and single parenthood have also been reported.
Risk is higher in women with history of bipolar disorder as compared with unipolar disorder.
Women with previous history of postpartum psychosis are at greater risk.
Primaparons is the only risk factor for development of postpartum psychosis.
There is no clear evidence that obstetric complication during pregnancy or delivery is
associated with the development of psychosis.
Three clinical presentation of postpartum psychosis are described:
- Affective psychosis.
- Schizophrenic.
- Acute organic psychosis.
Insomnia is common , psychomotor agitation, liability of mood, behavior and psychotic
symptoms , paranoid delusion about the family and abnormal idea about the baby , suicidal
and infanticidal ideation may be a significant problem.
Management
There is a risk that woman with postpartum psychosis will experience the psychosis in a
subsequent pregnancy. Careful assessment is required.
Hospitalization should be considered in a special mother and baby unit, ECT may be an
effective treatment for postpartum psychosis.
Antipsychotic medication required lower than Non-puerperal psychosis, mood stabilizing
medication is required.
Education will help reduce the stress in adult, encourage the mother to take her
medications.
Acute organic (Delirium) confusional state
Symptoms:
➢ Acute onset.

6
➢ Decrease awareness of the surroundings and self .
➢ Poor attention.
➢ Memory impairment.
➢ illusion and Hallucinations.
➢ Fragmentary delusion.
➢ Worsening at night.
➢ Fluctuating course.
delirium is a common disorder in hospital practice affecting ladies after delivery.
Management
The management of acute organic involves skilled supportive nursing and treatment of
underlying cause.
▪ To identify and treat the underlying cause.
▪ Nurse in a constant and well environment.
▪ Use small consistent team of nursing staff.
▪ Reduce the possibilities of misinterpretation.
▪ Maintain fluid balance.
▪ Administer medication in cases of extreme disturbance like 5-10 mg tds Diazepam or 25-
50mg tdsThioridazine.
▪ At risk for post-partum schizophrenia
▪ Women with a personal or familial history of schizophrenia have an increased risk of
developing schizophrenia 20-50% more likely to experience psychosis in future
pregnancy.
▪
Risks for Post-Partum Depression
Having a personal or familial history of depression 30% a chance for developing post-
partum depression and having 50-80% more likely to suffer from depression in future
pregnancy.
