
Sample
Collection and
Laboratory
Errors
O m eed A k b ar A l i
B i o c h e m i s t r y L a b .
1

Types of biological samples
1.
Blood
: (venous, arterial, and capillary) plasma, serum: 5 mL (-20 C)
2.
Urine
: 5-10 mL (-20 C)
3. Faeces: 1-5 g (-20 C)
4. Saliva : 1 mL (-20 C)
5. Amniotic fluid
6.
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
7. Synovial fluid
2

Reasons for sample collection
1. Diagnostic
2. Researches
3. Preventive measures
4. Screening (
Sample blood for screening test for HIV test)
3
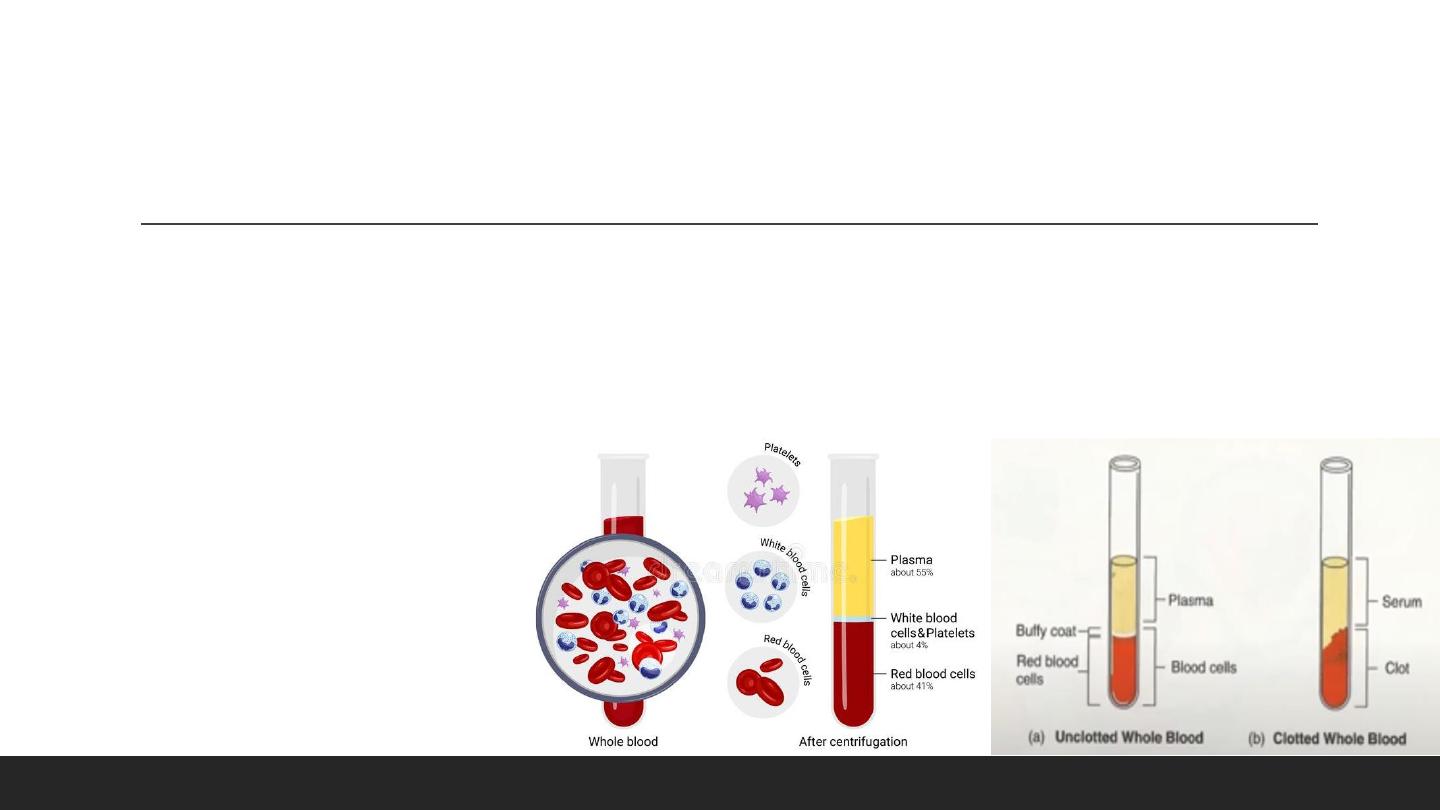
Blood Sample
Serum
- The undiluted extracellular portion of blood AFTER coagulation
Plasma
– The fluid component of whole blood containing anticoagulants post-centrifugation
4

Factors Affecting Samples
Exogenous
▪
Patient Preparation
▪
Sample Collection
▪
Sample Handling
▪
Sample Transport
▪
Medication
▪
Timing
▪
Temperature
Endogenous
▪
Age
▪
Body Mass
▪
Sex
▪
Allergies
▪
Fitness
▪
Stress
▪
Pregnancy
▪
Genetics
▪
Stage of Menstrual Cycle
▪
Hunger Status
▪
Diet
5

There are four steps involved in obtaining
a good quality specimen for testing:
•
Preparation of the patient.
•
Collection of the specimen.
•
Processing the specimen.
•
Storing and/or transporting the specimen.
6

Preparation
Preparing the Patient
.
Provide the patient, in advance, with appropriate collection instructions and information on
fasting, diet, and medication restrictions when indicated for the specific test.
Preparing the Specimen
.
Verify the patient's identification. Proper identification of specimens is extremely important.
All primary specimen containers must be labeled with at least two identifiers at the time of
collection.
7
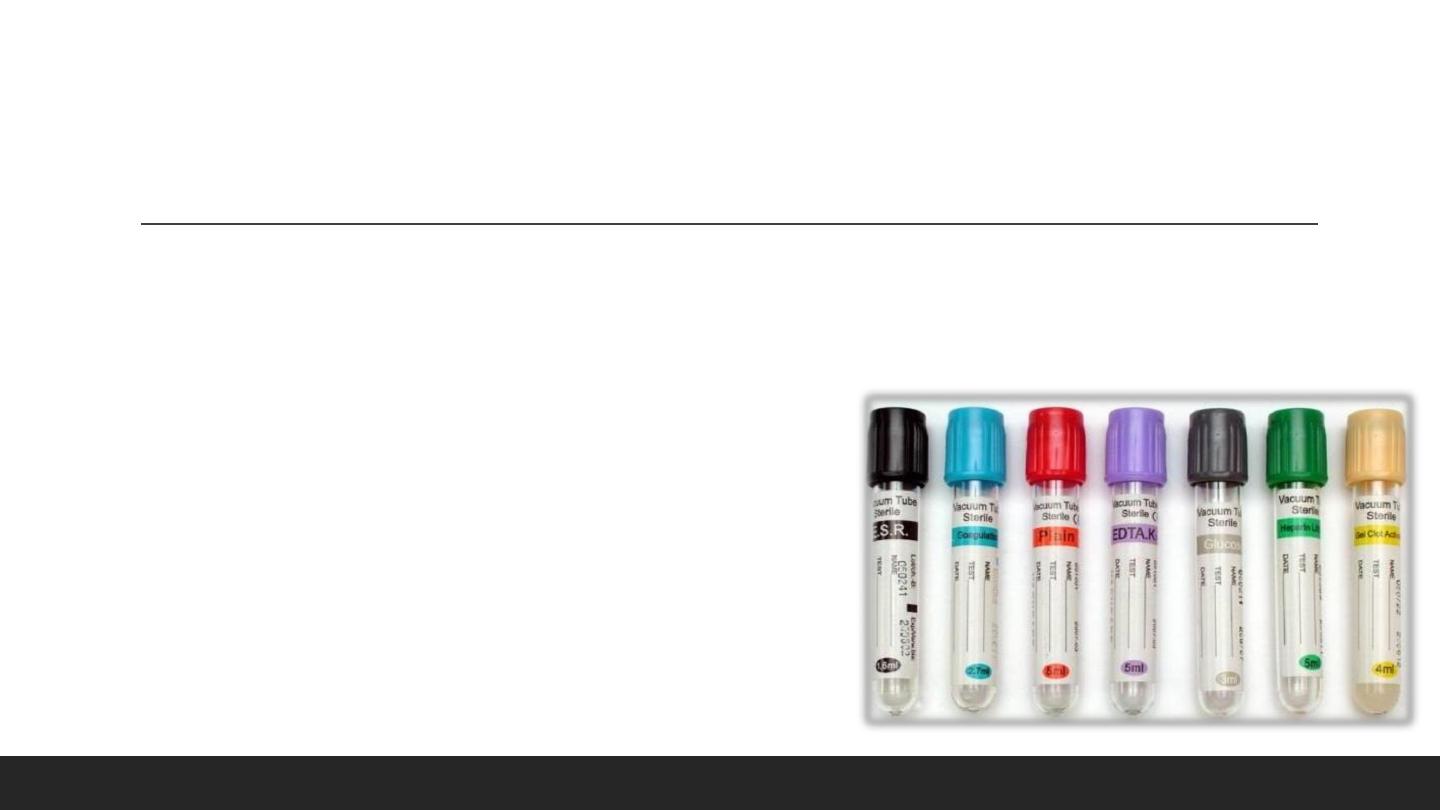

Types of blood tubes
8
• Red Tube : No additive. (Immunology, Serology, Biochemical Test).
• Yellow Tube: Gel Separator. (Immunology, Serology, Biochemical Test).
• Blue Tube : Sodium Citrate. (Coagulation Tests).
• Green Tube : Heparin, sodium, lithium. (Biochemical Tests)
• Lavender Tube : (EDTA) . (Blood routine Examination, hemogram)
• Black Tube : Sodium Citrate. (Sedimentation (ESR))
• Grey Tube : Potassium Oxalate, Sodium Fluoride (Glucose / Lactic)

Blue Tube : Sodium Citrate. (Coagulation Tests)
9
▪ Drawbacks
-This is not a good anticoagulant for a complete blood
examination.
-This is not good for the estimation of calcium.
-It inhibits aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase.
-This will stimulate acid phosphatase when phenyl phosphate
is used as the substrate.
▪ Indications:
- Contain sodium citrate ,which chelates calcium and inhibits, used for coagulation Tests. For PT and PTT.
▪ Mechanism of action:
• This will chelate calcium. Inactivates Ca++ ions.
• This will prevent the rapid deterioration of labile coagulation factors like factor V and factor VII.
- In blood, its ratio is 1:9, where 9 parts are blood, and 1 part is sodium citrate.

Green Tube : Heparin with sodium, lithium. (Biochemical Tests)
10
Properties of Heparin:
• This is theoretically the best anticoagulant because it is a normal blood component
and does not introduce any foreign contaminants to the blood specimen.
• It is dissolves rapidly in sodium, potassium, lithium, and ammonium salts.
• This is the best anticoagulant used to estimate pH, blood gases, electrolytes, and
ionized calcium.
• It is not used for coagulation and hematology studies.
Ammonium heparin affects the
RBCs volume.
Mechanism of action of heparin:
- Heparin accelerates antithrombin III action, which neutralizes thrombin, thus
preventing the formation of fibrin from fibrinogen.
- It forms the complex of thrombin + antithrombin cofactor + heparin and prevents fibrin
clot formation.
- It prevents coagulation for
24 hours
by neutralizing the thrombin, thus preventing fibrin
clots’ formation from the fibrinogen.
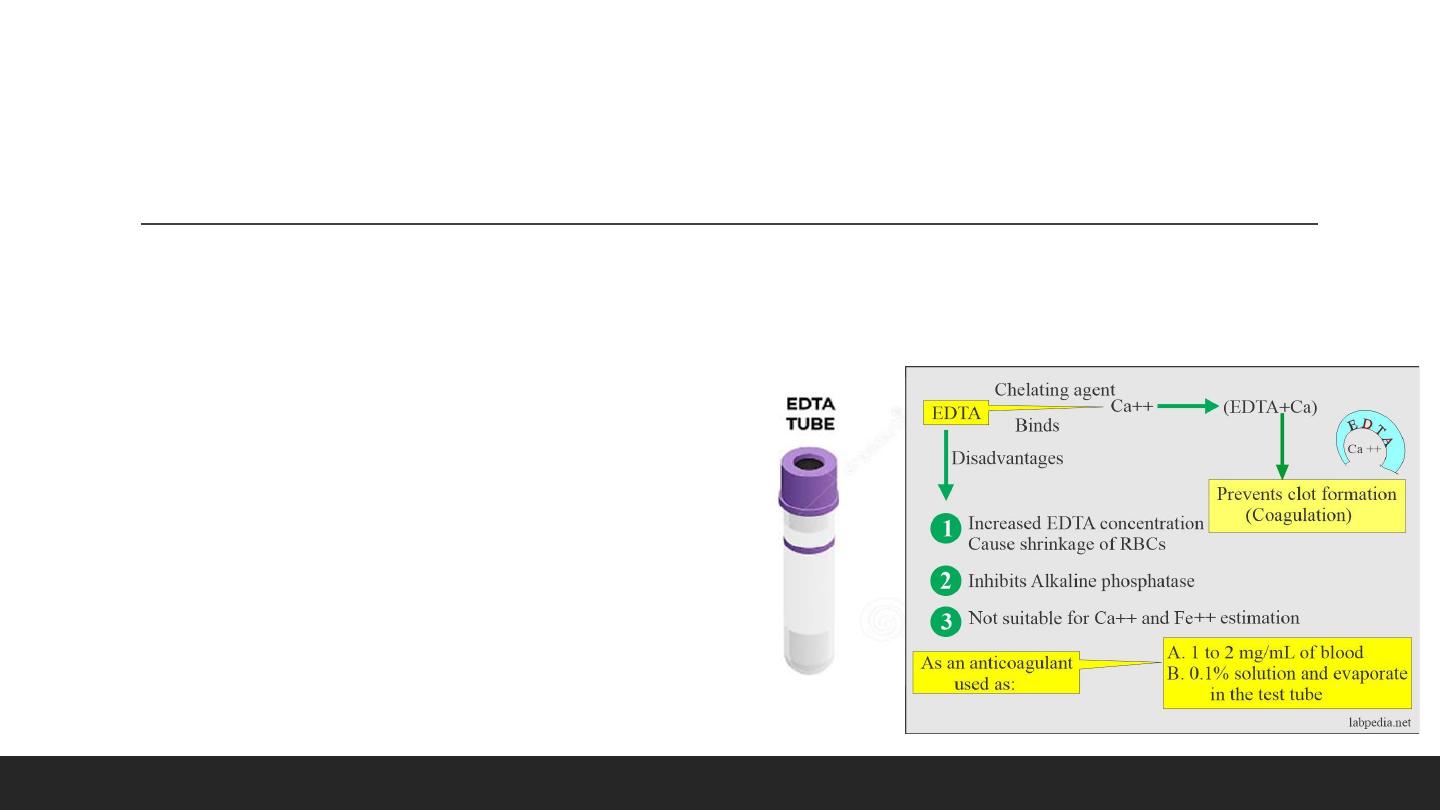
Lavender Tube : (EDTA) . (Blood routine Examination, hemogram (CBC))
11
• Drawbacks:
• It inhibits alkaline phosphatase, creatine kinase, and
leucine aminopeptidase activities.
• EDTA is not suitable for Calcium and iron estimation.
• It is effective at a final concentration of 1 to 2 mg / mL of
blood. More than 2 mg/mL causes shrinkage of the cells.
• Lavender Tube :
Additives :
E
thylene
D
i-amine
T
etra acetic
A
cid (EDTA)
• This is a chelating agent that binds the calcium, which is needed for coagulation. Chelation prevents coagulation.
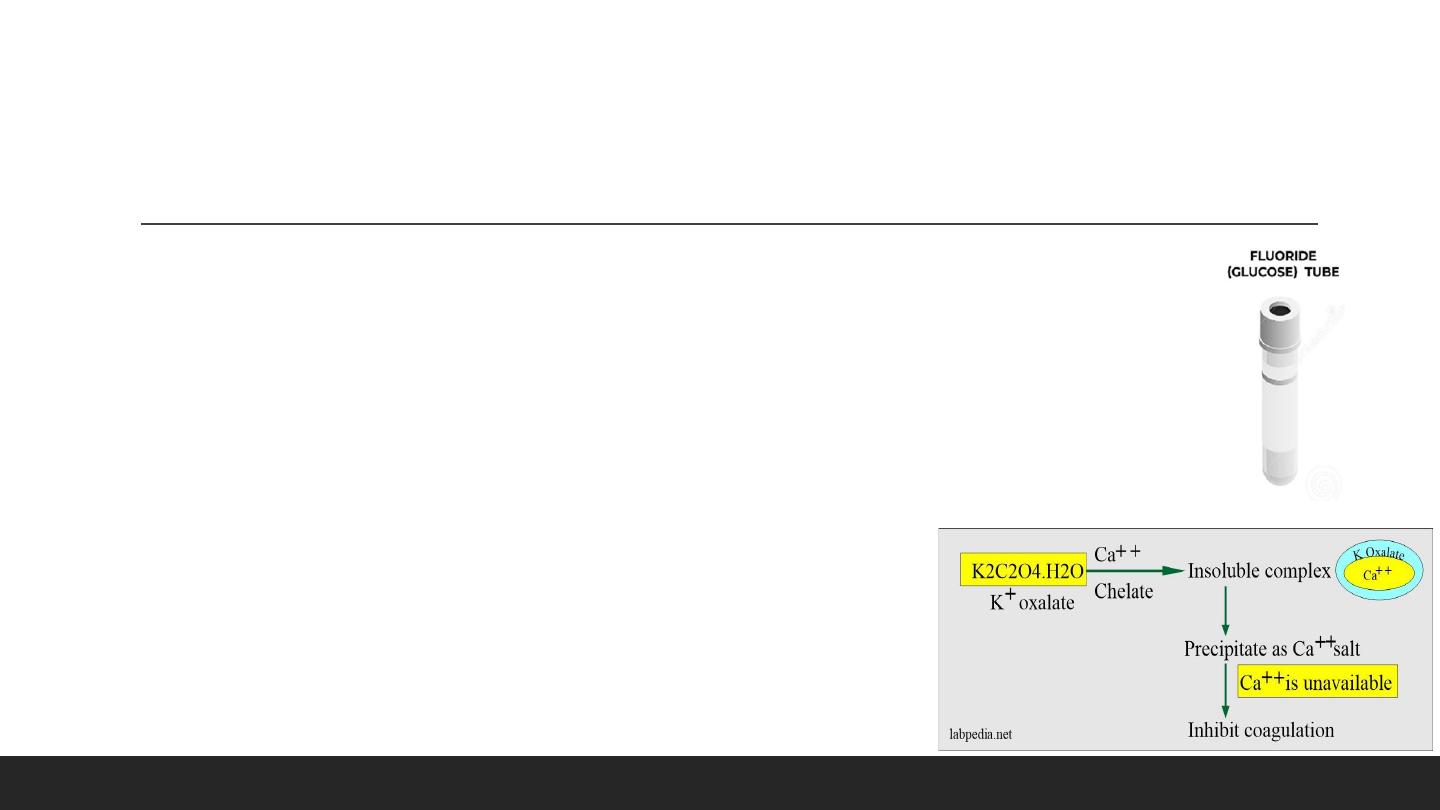
Grey Tube : Potassium Oxalate, Sodium Fluoride (Glucose / Lactic)
12
1- Potassium Oxalate
Mechanism:
- This may be sodium, potassium, ammonium, or lithium oxalic acid salt used as an anticoagulant.
- This forms an insoluble complex with calcium ions (precipitate with calcium as a salt).
- The combination of ammonium/potassium oxalate does not lead to shrinkage of the RBCs.
▪
Drawbacks
- If the concentration is >3 mg/mL, then there are chances for hemolysis.
- There is a reduction of 10% hematocrit.
- Oxalates inhibit several enzymes like acid phosphatase, amylase, ALP, LDH.
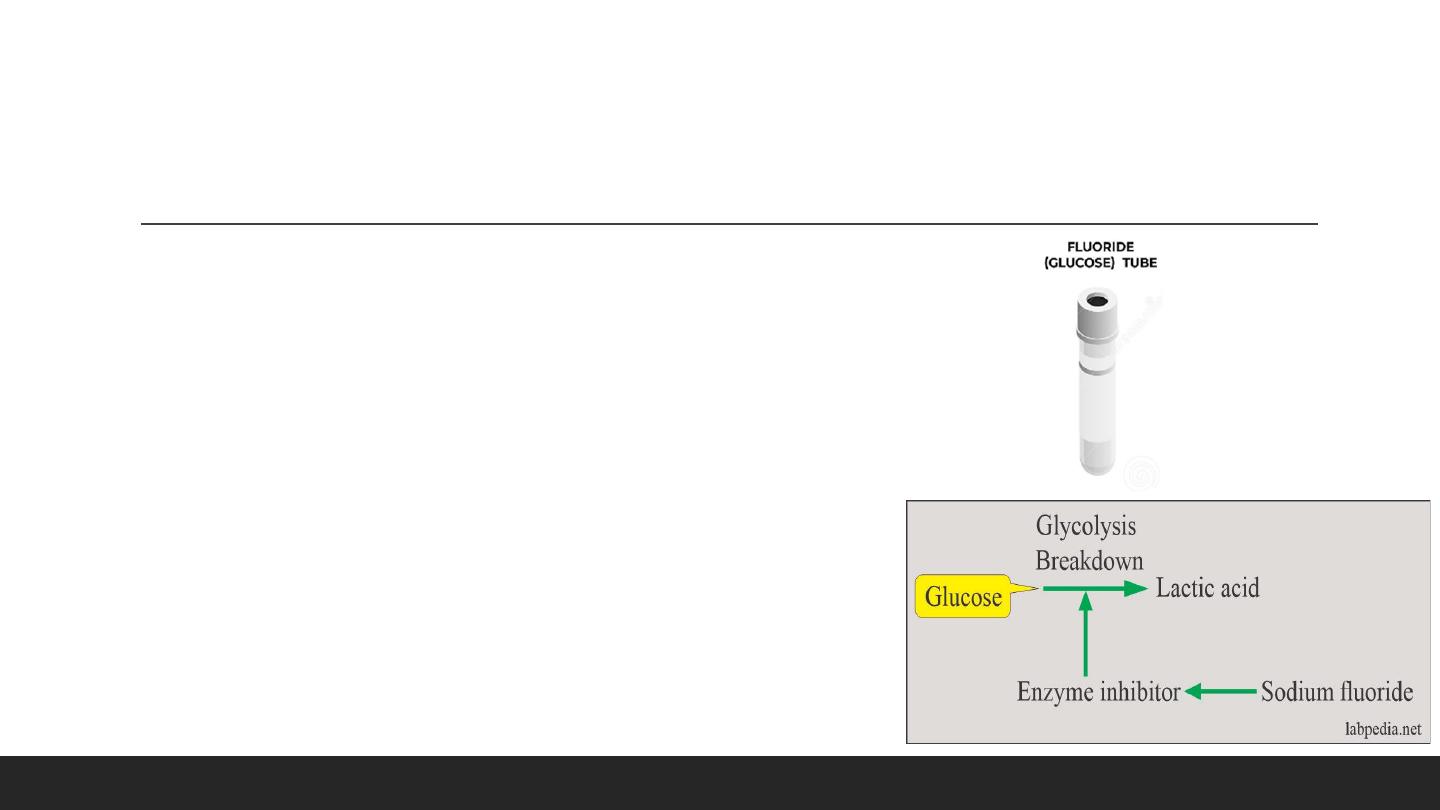
Grey Tube : Potassium Oxalate, Sodium Fluoride (Glucose / Lactic)
13
2- Sodium Fluoride
This inhibits the system involved in glycolysis and preserves the glucose.
▪ Mechanism of action: It acts in :
- As an enzyme inhibitor that prevents the glycolytic enzyme from
destroying the glucose.
- Sodium fluoride acts after the enolase, so it will not be effective in the
first 1 to 2 hours
. It prevents glycolysis after this period.
- Glucose can fall during this period,
around 10 mg/dL
.
- Transport on ice and rapid separation of the serum within
30 minutes
can prevent glycolysis. There is no need for the addition of sodium
fluoride.
▪ Drawback
This is also an inhibitor of many enzymes.
Also, effect urease for the estimation of urea.

Laboratory Testing
BIOCHEMISTRY TESTS
▪
- Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) test
▪
- Random plasma glucose (RPG) test
▪
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
▪
HBA1C
▪
Creatinine
▪
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
▪
Uric acid test
▪
Total cholesterol
▪
LDL cholesterol
▪
HDL cholesterol
▪
Triglyceride (TG)
▪
Alanine Aminotransferase (ALT)
▪
Aspartate Aminotransferase (AST)
▪
Gamma-glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
▪
Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP)
▪
Total Protein
▪
Total Bilirubin
▪
Direct Bilirubin
▪
Albumin
▪
Creatine Kinase (CK)
▪
Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH)
▪
Amylase
▪
Lipase
▪
Total Calcium
#-Electrolyte Panel
• Sodium
• Chloride
• Potassium
• Bicarbonate
IMMUNOLOGY AND
SEROLOGY TESTS
▪
- Antistreptolysin O (ASO)
▪
- C-reactive protein (CRP)
▪
- Rheumatoid Factor (RF)
▪
- Immunoglobulin A (IgA)
▪
- IgE
▪
- IgG
▪
- IgM
▪
- Anti-HCV
▪
- Anti-HIV
▪
- Anti-HBs
14

Laboratory Testing
#- HORMONES TEST
▪
B-HCG
▪
PROGESTERON
▪
Follicle-Stimulating Hormone(FSH)
▪
Luteinizing Hormone (LH)
▪
Estradiol (E2)
▪
prolactin (PRL)
▪
Testosterone
▪
Cortisol
▪
Thyroid-stimulating Hormone (TSH)
▪
Free triiodothyonine (FT3)
▪
Free Thyroxine (FT4)
▪
Thyroid Peroxidase (TPO)
▪
Anti-Thyroglobulin (Anti-Tg)
HEMATOLOGY TEST
•
Complete blood count (
CBC)
•
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
•
peripheral blood film (PBF)
•
Iron
•
Total iron-binding capacity (TIBC)
•
Ferritin
•
Folic Acid
•
Vit. B12
•
Indirekt Coombs
•
Direkt Coombs
ONCOLOGY TEST
▪
- CEA
▪
- AFP
▪
- Ca15-3
▪
- Ca72-4
▪
- Ca19-9
▪
- Ca125
Urine & Faeces test
Fecal Occult Blood(FOB)
H.Pylori antijen
Coagulation Tests
▪
Prothrombin time (PT or PT-INR)
▪
activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
▪
D-Dimer
15

Laboratory Errors
A . Errors That Occur During The Analysis:
•
Hardware programming error / Calibrations.
•
Use of expired solutions /
Hemolysis
.
•
Dilution of samples and not calculating the
percentage of dilution in the final result.
•
Inaccurate handling of pipettes and fluid dispensers.
•
Use of unclean tubes or instruments during the
analysis process.
B . Errors that occur after analysis
• Errors writing or entering numeric results.
• Error in writing the normal range for the analysis
(it may vary according to age and gender).
• switching data in place of each other.
Lab Error Stages
16

Interferences of hemolysis
17
1- Some constituents are present in High concentration in R.B.C which causes a high false reading as:
❖
Potassium(K
+
)
❖
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
❖
Acid phosphatase (ACP)
❖
Aspartate transaminase (AST)
2- Some constituents are present in Low concentration in R.B.C which causes low false reading as:
❖
Sodium (Na
+
)
❖
Chloride (Cl
-
)
3-Haem may directly interferes in chemical reactions, this interfere with colorimetric procedures.

Spectrophotometer
Omeed Akbar Ali
Biochemistry Lab.

19
Spectrophotometer
Spectrophotometer - an instrument which can measure the amount of
the light absorbed by the sample at any selected wavelength.
The Assays is either:
1. Qualitative: Determined if the substance is there or not.
2. Quantitative: Determined the concentration of the substance.
The samples being measured:
Plasma
,
Urine
,
CSF
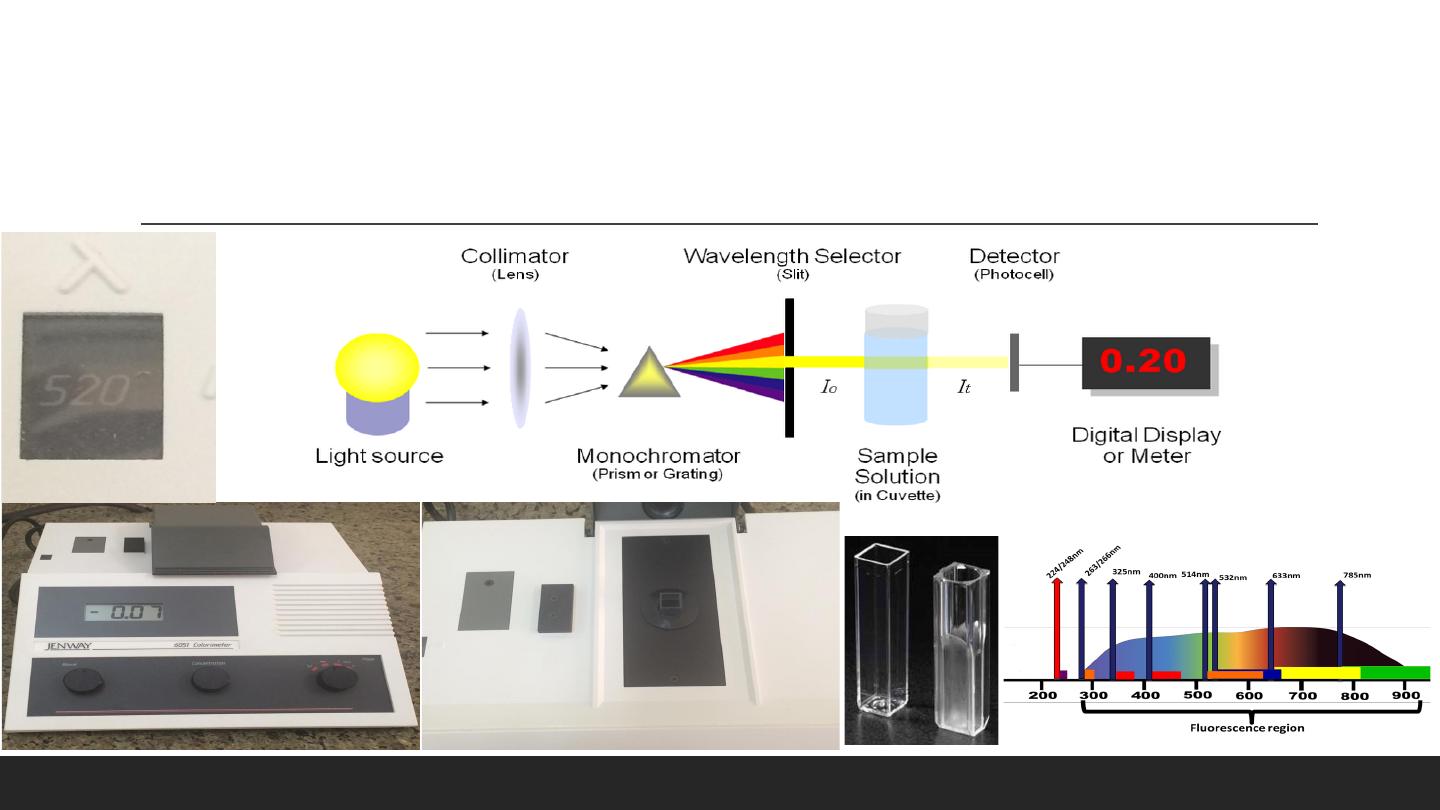
Basic structure of spectrophotometers
20
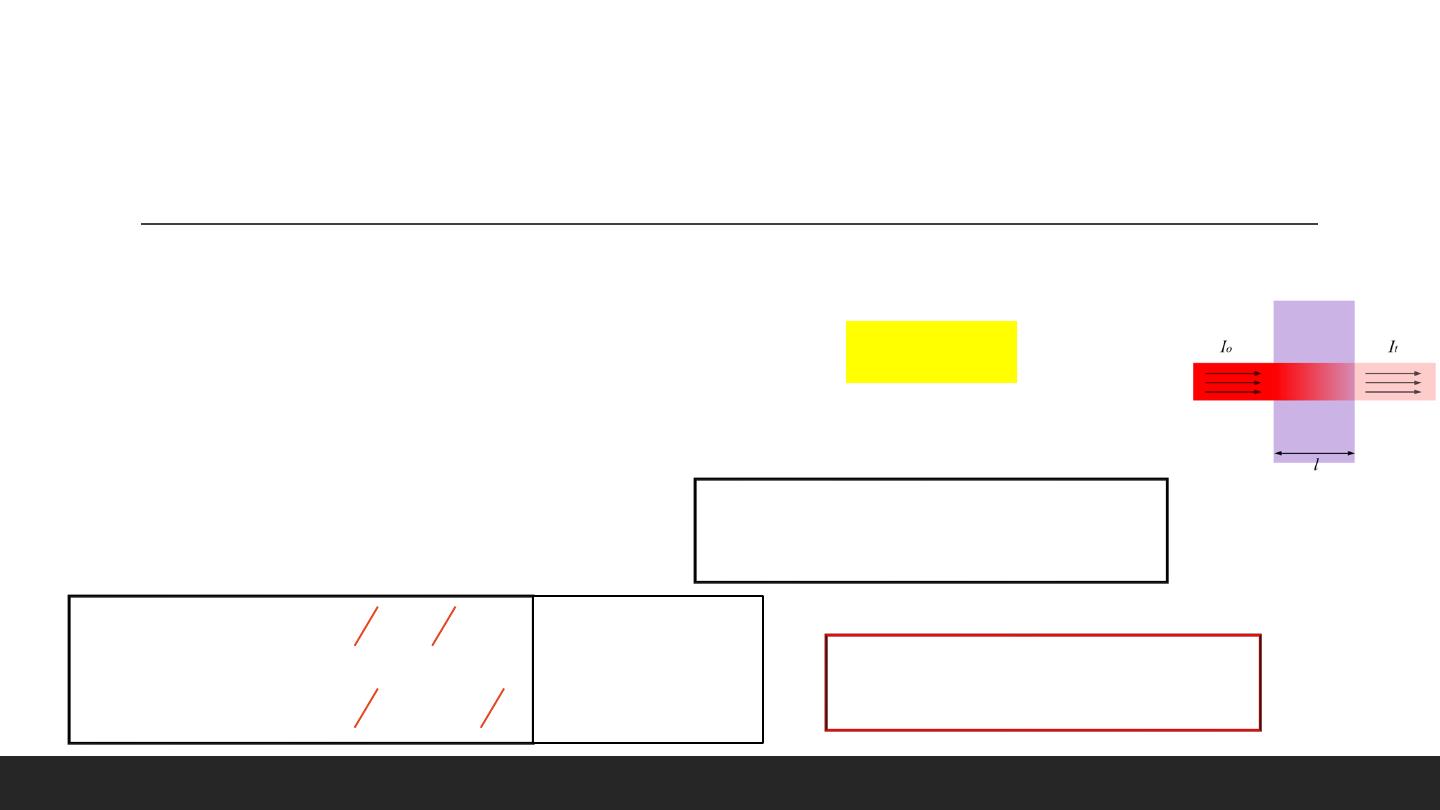
Beer-Lambert Law
21
A
test
= εC
test
L
A
Standar d
= εC
Standard
L
A
test
εC
test
L
______ = _______
A
Standard
εC
Standard
L
A
test
C
test
= ________ x
c
Standard
A
Standard
Lambert Beer's law is a mathematical means of expressing how light is
A
bsorbed (
A
=
A
bsorbance)
by matter. The law states that the amount of light emerging from a sample is diminished by three
physical phenomena:
1. The amount of absorbing material in its pathlength (
C
oncentration).
2. The distance the light must travel through the sample (optical pathlength OP
L
).
3. The probability that the photon of that particular wavelength will be absorbed by the material
(absorptivity or
E
xtinction coefficient).
A = εcL
C
test
= ______
C
Standard

Thanks For Listening …
22
