
LAB- 2 2
ND
CLASS
-
:
route of drug adminstration
d
an
forms
Drug
11- Parenteral therapy:-
This route of drug administration used in:
1- Treatment of actually ill patient and unconscious.
2- Drug that are poorly absorbed from GIT tract or unstable in the GIT.
Drugs given by injections act more rapidly & reliably, thus more useful for
-
Injections:
-
emergency situations. They require some technical skills, aseptic technique & suitable
equipments.
-
There are 2 types of injections preparation:
1- Ampoule:- which contains sterile drug solution & used once when opened.
2- Vial:- which is designed to contain one or multiple doses & having a rubber cover to
avoid contamination.
-
Parenteral therapy:
-
11
- Injection: Include the following routes:
1- Intravenous bolus injection and infusion.
- Advantages:
a- Can have immediate effects.
b- Ideal if dosed in large volumes.
c- In emergency situation.
d- Avoid first pass metabolism.
- Disadvantages:
a- Extravasations inflammation and necrosis. b- Infection and phlebitis.
c- Unsuitable for oily or poorly absorbed substance.
2- Intramuscular injection:
- Advantages:
a- Suitable for irritant substance and depot preparation.
b- Suitable if drug volume is moderate.
c- Safe, easy, effective, and convenient in most situation.
- Disadvantage:
a- Painful, infection. b- Local tissue necrosis.
c- Sterile abscess formation and hematoma.
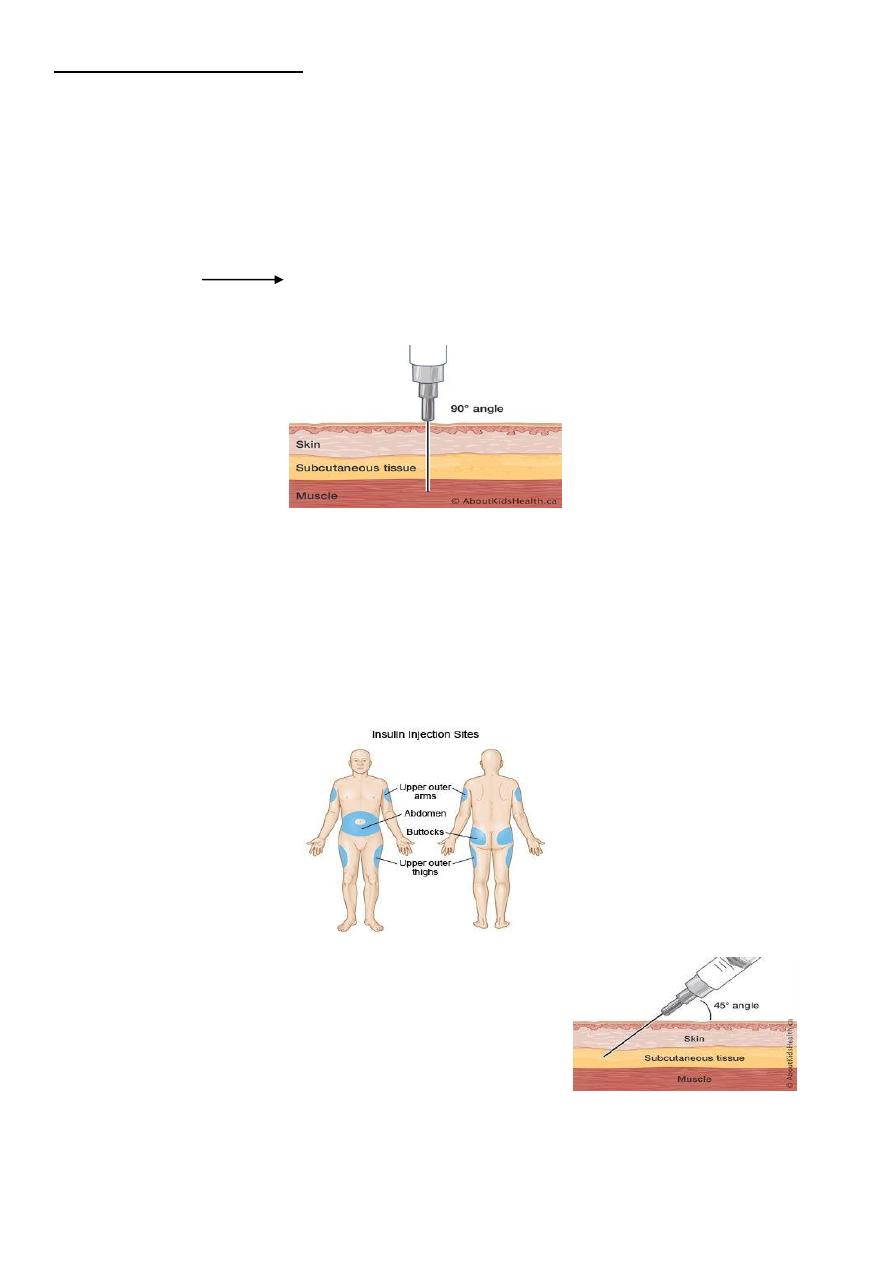
3- Subcutaneous injection:
- Advantage:
a- Suitable only if a small volume of drug is to be given:
b- Suitable for slow release drugs. c- Ideal for some poorly soluble suspensions.
d- Easy and safe. e- Acceptable for self administration.
- Disadvantage;
a- Irritable, infection and necrosis can occur. b- Lipodystrophy.
-
:
other
.
1
II
It is used a local effect of drug is desired.
-
Topical:
-
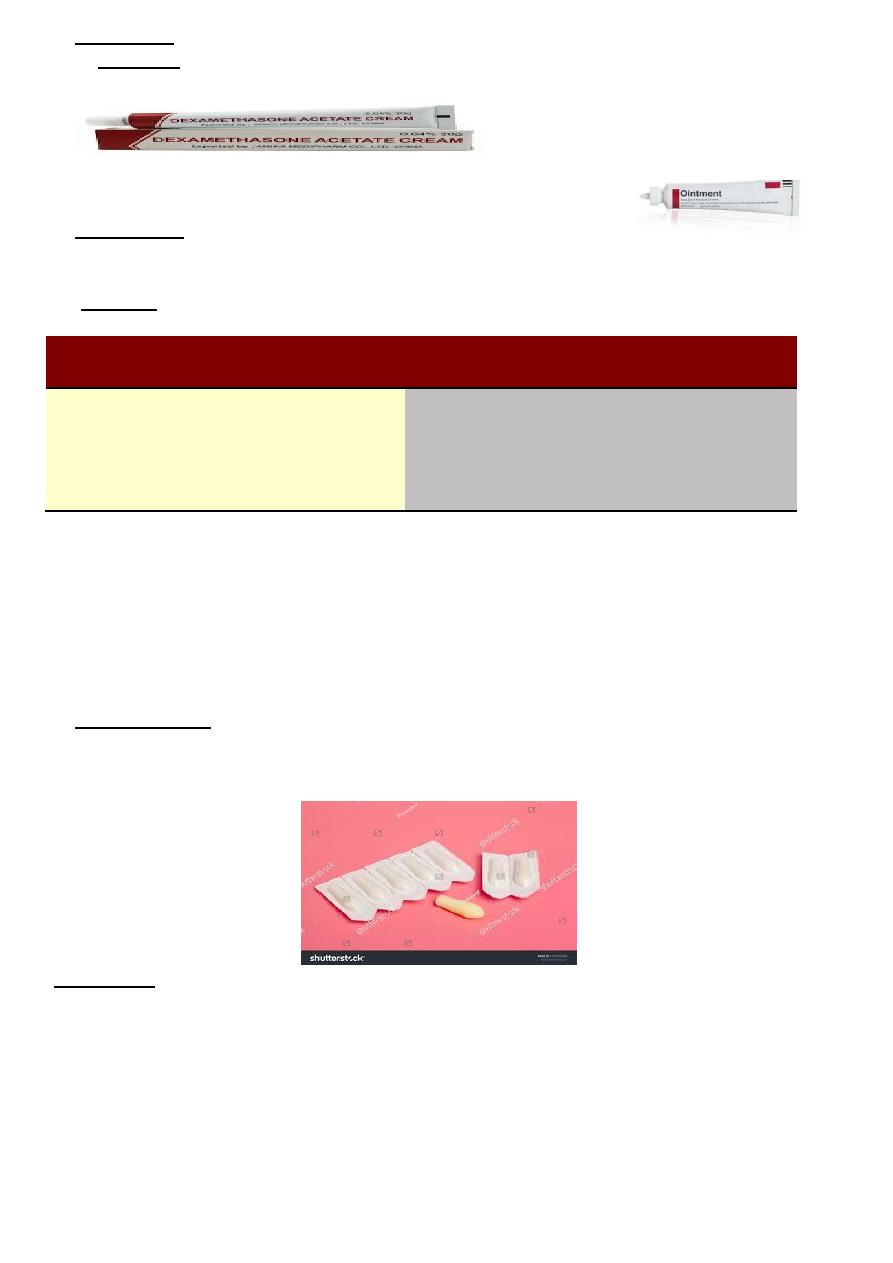
1
Are semisolid, greasy preparations for application to
-
Ointments:
.
a
the skin, rectum. The base is usually anhydrous & contains the medicament in solution or
suspension.
They are semisolid solution for external use.
-
Cream:
.
b
Ointment
Cream
1-greasy
1-relatively not greasy
2-semisolid anhydrous
2-semisoilid emulsion(oil + water)
3-less skin penetration
3-more skin penetration
4-used for dry, chronic skin lesion
4-used for wet lesions of skin
5-applid to skin & rectum
5- applied to skin only
= Topical administration of ointment or cream:
a- Advantages:
a- Easy, safe and effective with less systemic side effects.
b- Deliver a high concentration of drug at its site of action.
b- Disadvantages:
- Irritant, inflammation and sensitization.
for insertion into the rectum,
Are conical or ovoid solid preparations
-
Suppositories:
.
2
vagina or urethra, once its inside, its melts or dissolve and release its medication. Their
base is fat, wax or glycerol gelatin.
icated preparations for introduction into vagina where they melt
olid med
S
-
Pessaries:
or dissolve & exert a local action.
= Rectal therapy
- Advantage:
a- Partially bypasses first-pass effect.
b- Bypasses destruction by stomach acid.
c- Ideal if drug causes vomiting.
d- Ideal in patients who are vomiting, or comatose.
- Disadvantage:
a- Psychological upset, not a well accepted route.
b- Drugs may irritant the rectal mucosa.

-
Others:
-
111
used
They are suspensions of fine solid or liquid particles in a gas. They are
-
Aerosols:
3.
to the respiratory tract or skin.
.
at or prevent throat infections
They are aqueous solutions used to tre
-
Gargles:
4.
Could be to the eye, ear, nasal or oral drops.
-
Drops:
5.
Slow and sustained delivery of drugs.
-
Transdermal (patch):
6.
- Inhaled therapy:
a- Advantage:
- Effective and convenient for patient with respiratory trouble.
- Low systemic side effect.
- Ideal for gases.
- Lower doses used compared to that with oral or parenteral administration.
b- Disadvantage:
- Special apparatus is needed.
- Irritation cough.
Difficulty regulating dose.
–
- Difficulty using inhaler.
