ERYTHROCYTE
SEDIMENTATION RATE
OR ESR
MSC. Noor Salman Dalis

ERYTHROCYTE
SEDIMENTATION RATE
It is the rate of downward descent of RBCs in a vertical column of blood.
Principle:
If anti-coagulated blood is allowed to stand vertically in a narrow tube ,
the red cells will settle progressively to the bottom leaving clear
plasma above.
-The cells settle due to :
1-Density of RBCs is greater than that of plasma.
2-RBCs tend to aggregate to form Rouleaux.
(Rouleaux differs from agglutinatin that agglutinated cells are
irreversibly bound together and can not be separated )
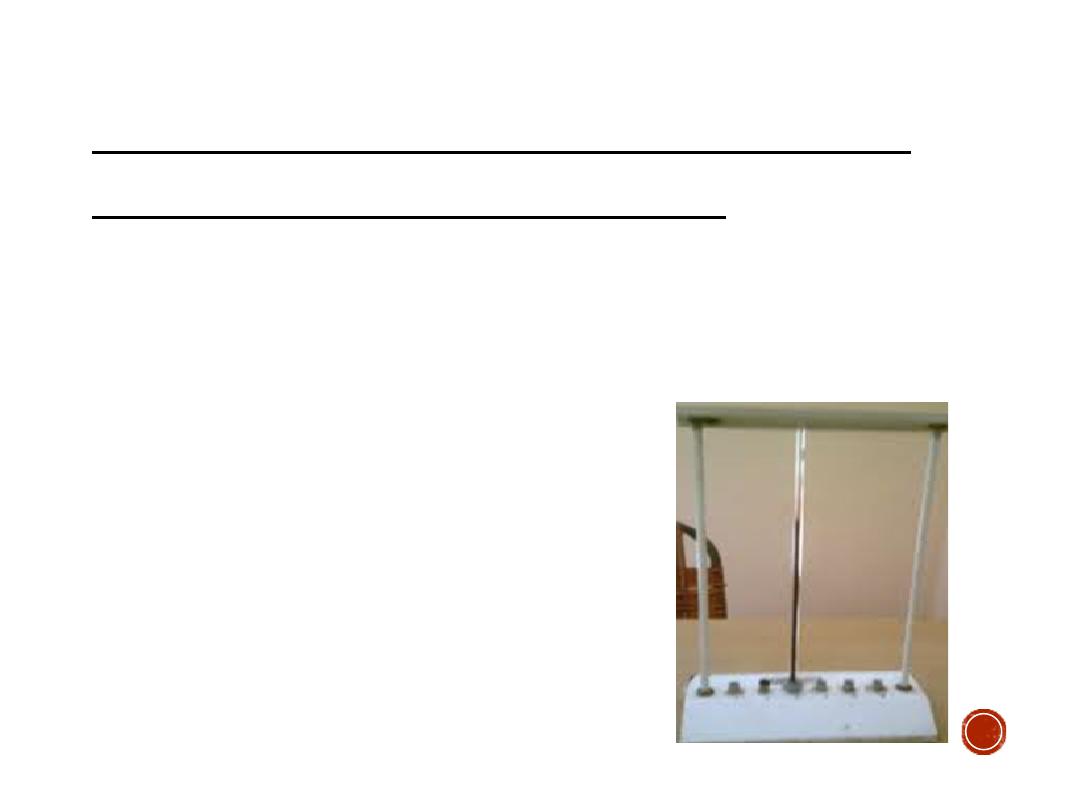
WESTERGREN METHOD FOR
ESTIMATION OF ESR :
Equipments:
-Westergren tube ( straight glass tube 30 cm in length , 2.5
mm in dimeter and graduated from 0 – 200 mm )
-Special stand.
-o.4 ml Sodium Citrate.
-5 ml disposable syringe.
Westergren tube for ESR
.

PROCEDURE :
1-Withdraw blood sample in a syringe and mix it
with 3.8% Na Citrate at a ratio 4 : 1 (e.g. 2ml
blood + 0.4 ml Na Citrate)
2-suck the citrated blood to Westergren tube up to
zero mark exactly and place your finger over its
openning.
3-Place the tube in a special stand that fix the
upper lip with a clip.
4-The height of clear plasma on the top of the
tube is measured after one and two hours.

NORMAL VALUES :
-In males : 1st hr : 3-5 mm
2nd hr : 6-10 mm
-In females : 1st hr : 8 -10 mm
2nd hr : 16 -20 mm

Clinical significance of ESR :
-Because the ESR is changed in a great variety of
conditions , Its alteration is not specific and not
diagnostic.
-It is a prognostic test :
1-It detects the presence and severity of disease.
2-It gives an idea about the activity of disease
3-Repeated ESR estimation helps in prognosis and
follow up of disease
Factors determining the rate of
sedimentation of RBCs :
1- plasma proteins :
a- Albumin : If plasma albumin level is
increased the ESR decreases.
b- Fibrinogen and globulins : If plasma
fibrinogen or globulins level is increased the
ESR increases.
2- Red cell count :
- If RBCs count is increased the ESR
decreases.
Factors affecting ESR :
A- Physiological factors :
1- ESR is increased in :
1-Old age. 2-Females.
3- Prgnancy. 4-Menestruation.
2- ESR is decreased in :
1- Newborn. 2- Males.
3- High altitude.
B- Pathological factors :
a- ESR is increased in :
1-Acute inflammation as
tonsillitis. 2- Malignancy.
3-Chronic inflammation as T.
B. 4- Fevers.
5-Rheumatic fever .
6-Tissue trauma.
b- ESR is decreased in :
1-polycythemia.
2-Hyperviscosity of plasma.
