Manual WBC Count
Ms,c NOOR. S. DALIS
Definition:
White blood cells or leukocytes
are cells of
the immune system which defend the body
against both infectious disease and foreign
materials
The WBC number is kept remarkably
constant in health, but it increases or
decreases in many diseases,
particularly acute and chronic
infections.

The normal count
in adults ranges between 4000/mm
3
and
11,000/mm
3
, with an average of 7000/mm
3
.
•
2-after birth may be as high as 18,000 to
20,000/mm
3
, the normal levels being reached
in a few years.
•
In the adults, about 55 to 75% of the WBCs
are
granulocytes
, while in young children,
lymphocytes
dominate.
•
The count may be high in some physiological
conditions such as
heavy exercise, stress,
etc.
This fact should be kept in mind while
interpreting the results of cell counts.

Leukocytosis
is a condition
characterized by an elevated number of
white cells in the blood, which is usually
due to:
Bacterial infection such as appendicitis, tonsillitis,
ulcers
and urinary tract infection
Leukemia.
Pregnancy.
Hemolytic disease of new born.
Following exercise.
Emotional stress.
Food intake.

Leukopenia
is a condition characterized by a
decreased number of white cells in the blood,
which
is usually due to:
Viral disease such as measles and infectious
hepatitis.
Some bacterial infections such as typhoid fever,
brucellosis, and typhus fever.
Rheumatoid arthritis.
Systemic Lupus Erythematosis.
Certain drugs such as radio therapy and
chemotherap
y
PRINCIPLE
A sample of
blood is diluted with a
diluting fluid
which destroys the red cells
and stains the nuclei of the leukocytes.
The cells are then counted in a counting
chamber.

APPARATUS AND MATERIALS
1.Microscope
•Counting chamber with a heavy coverslip.
•Blood lancet/pricking needle.
•Sterile cotton/gauze swabs.
•70% alcohol
2.WBC pipettes
white bead in bulb, and markings 0.5, 1.0,
and 11. Two such, clean and dry pipettes, with free-rolling beads
are required.

3. Turk’s fluid. This fluid is used for diluting the
blood.
-Glacial acetic acid = 1.5 ml (hemolyzes RBCs
without affecting WBCs).
-Gentian violet (1% solution) =1.5 ml (it stains
the nuclei of leukocytes).
-Distilled water to 100 ml.

PROCEDURES
1-
Draw the blood up to 0.5 mark in the thoma pipette.
Wipe the outside of the capillary pipette to remove
excess blood that would interfere with the dilution
factor.
2-Holding the pipette almost vertical place into the fluid.
3-Draw the diluting fluid into the pipette slowly until the
mixture reaches the 11 mark, while gently rotating the
pipette to ensure a proper amount of mixing.
4-Place the pipette in a horizontal position and firmly
hold the index finger of either hand over the opening in
the tip of the pipette, detach the aspirator from the
other end of the pipette now the dilution of the blood
is completed

5-Mix the sample for at least 3 minutes to facilitate
hemolysis of RBCs.
6-Clean the hemacytometer and its coverslip with an
alcohol pad and then dry with a wipe.
7-Before filling the chamber, discard the first four to
five drops of the mixture on apiece of gauze to expel
the diluent from the stem.
8-Carefully charge hemacytometer with
diluted blood by gently squeezing sides of
reservoir to expel contents until chamber is
properly filled.
Under low magnification 10X
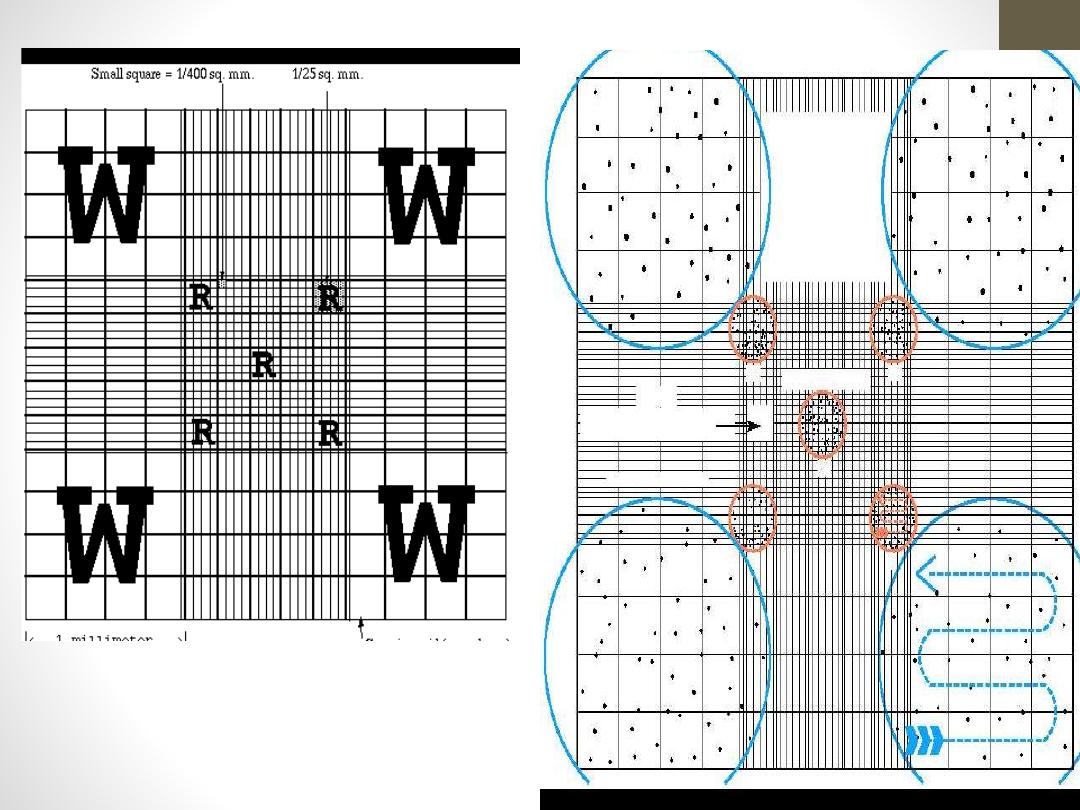
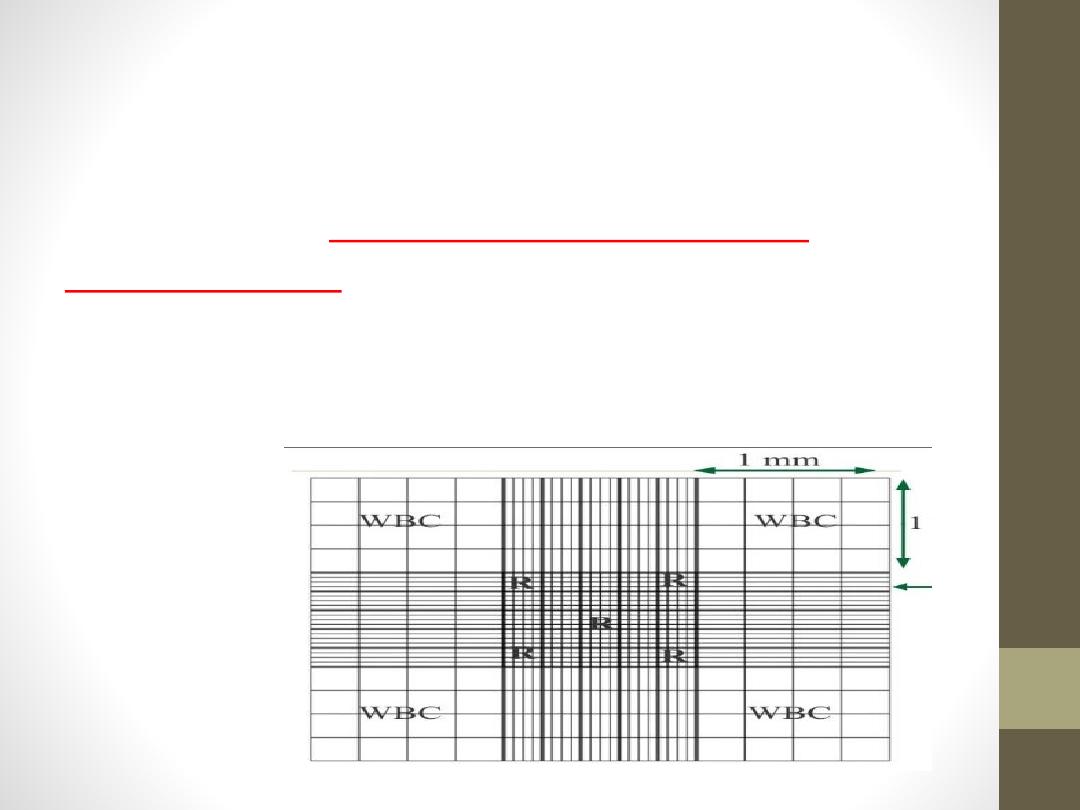
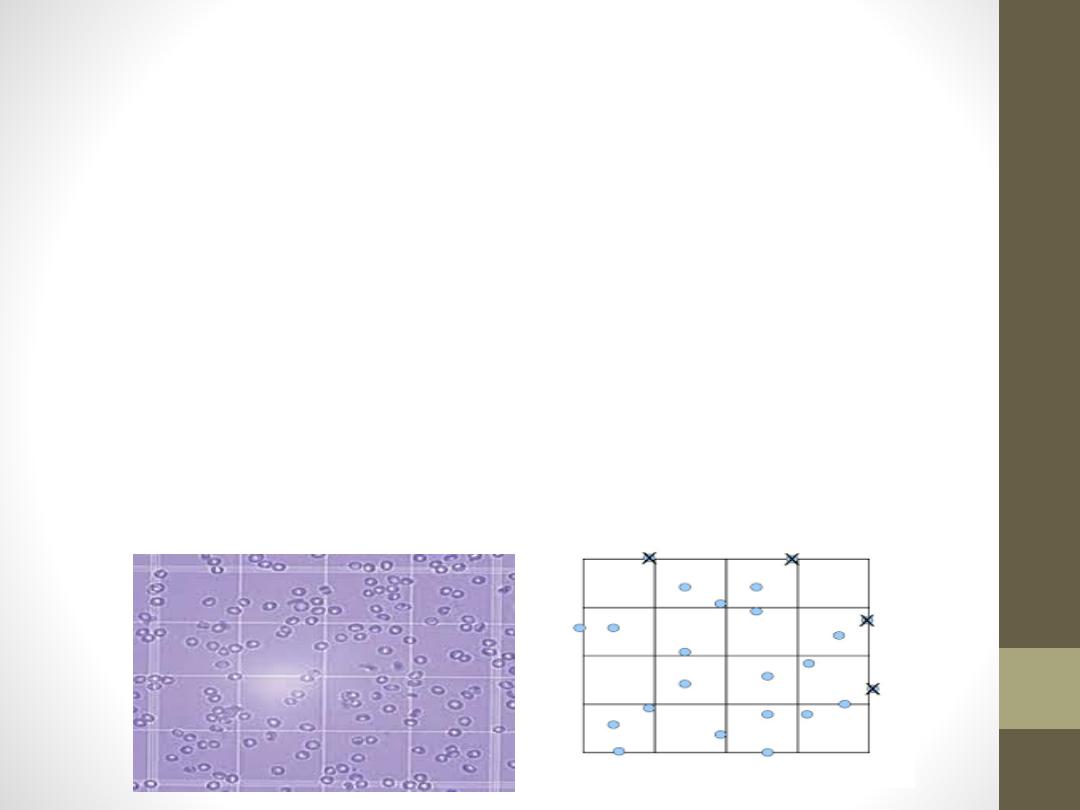
1-Under 10 x magnifications, scan to ensure even
distribution. Leukocytes are counted in all nine large
squares of counting chamber.
2-Count cells starting in the upper left large corner
square. Move to the upper right corner square,
bottom right corner square, bottom left corner square
and end in the middle square.
3-Count all cells that touch any of the upper and left
lines, do not count any cell that touches a lower or
right line.

Correction for dilution
:
The thoma pipette is 1:20
Dilution factor 20
Correction of volume:
Depth= 0.1
Volume of 1small square = 1x1x0.1= 0.1mm3
Volume of 4 large squares = 4x0.1= 0.4 mm3 or
μL
Suppose that you count 50 cells in 4 squares
(0.4mm3), found the count in 1mm3?
50 o.4 mm3
X 1mm3
X = 50 x 1\ 0.4
Volume correction =
1\ 0.4
Total count \ 1mm3 =
No. of cells x volume correction x dilution =
no. of cells x ( 1\0.4 ) x 20 =
No. of cell x 50 =