
D R . M O H A N A D A L - J A N A B I
PATHOLOGY OF
IMMUNE SYSTEM
Lec.
01

BLOCK OUTLINE
I.
Immune system
II.
Hypersensitivity
III.
Autoimmune Disease
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

INTRODUCTION
•
Components
•
Lymph is the fluid
•
Vessels – lymphatics
•
Structures & organs
•
Functions
•
Return tissue fluid to the bloodstream
•
Transport fats from the digestive tract to the
bloodstream
•
Surveillance & defense
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
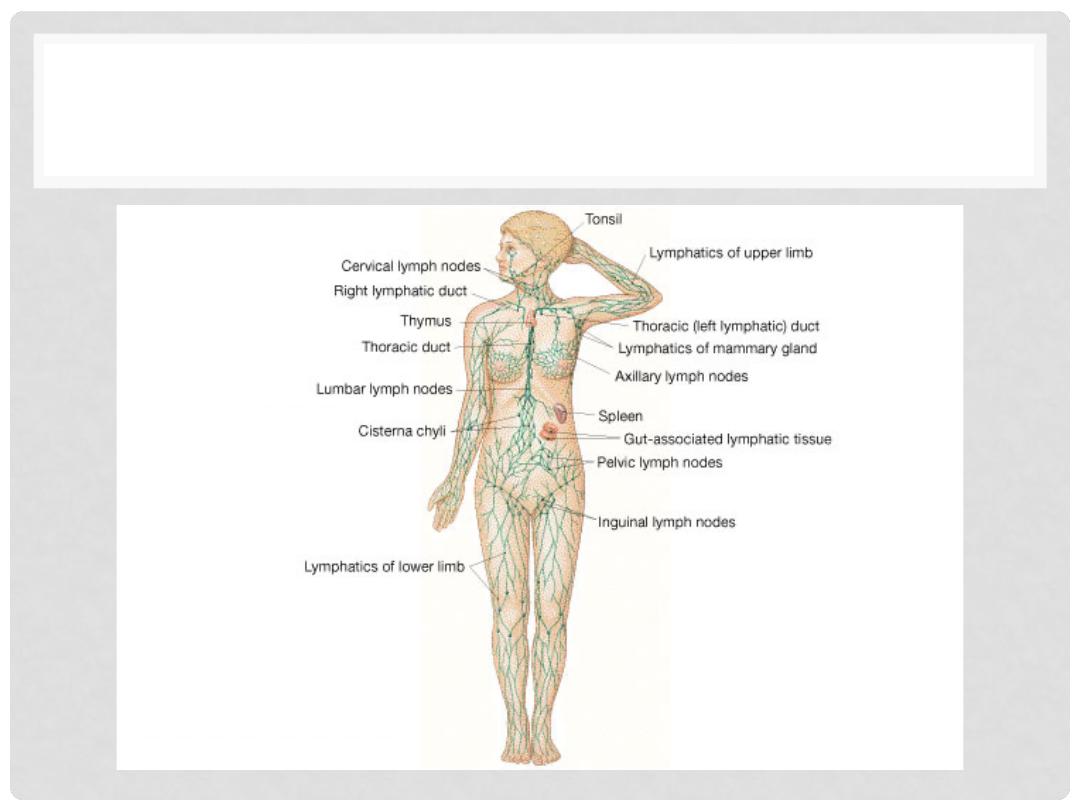
ANATOMY OF LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

LYMPHATIC DUCTS
Lymphatics ultimately deliver lymph into 2 main
channels
•
Right lymphatic duct
•
Drains right side of head & neck, right arm, right thorax
•
Empties into the right subclavian vein
•
Thoracic duct
•
Drains the rest of the body
•
Empties into the left subclavian vein
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

IMMUNE TISSUES
•
Three types of immune tissue
•
Diffuse lymphatic tissue
•
No capsule present
•
Found in connective tissue of almost all organs
•
Lymphatic nodules
•
No capsule present
•
Oval-shaped masses
•
Found singly or in clusters
•
Lymphatic organs
•
Capsule present
•
Lymph nodes, spleen, thymus gland
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
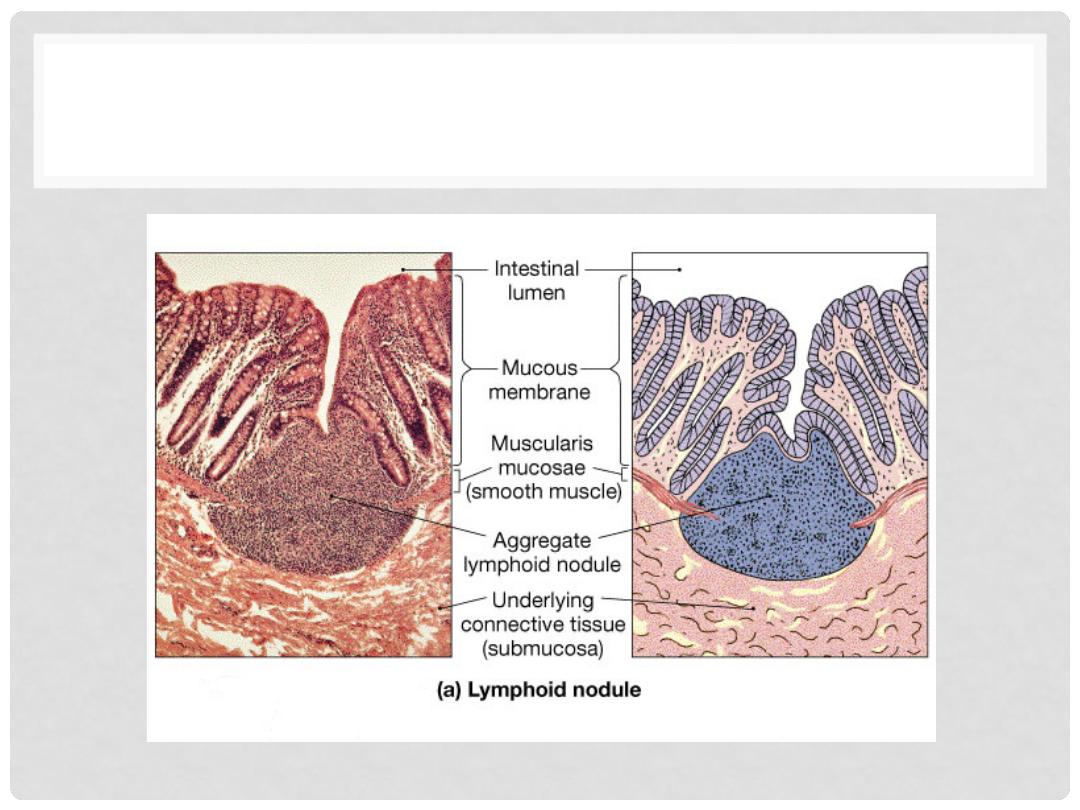
LYMPH NODULE
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
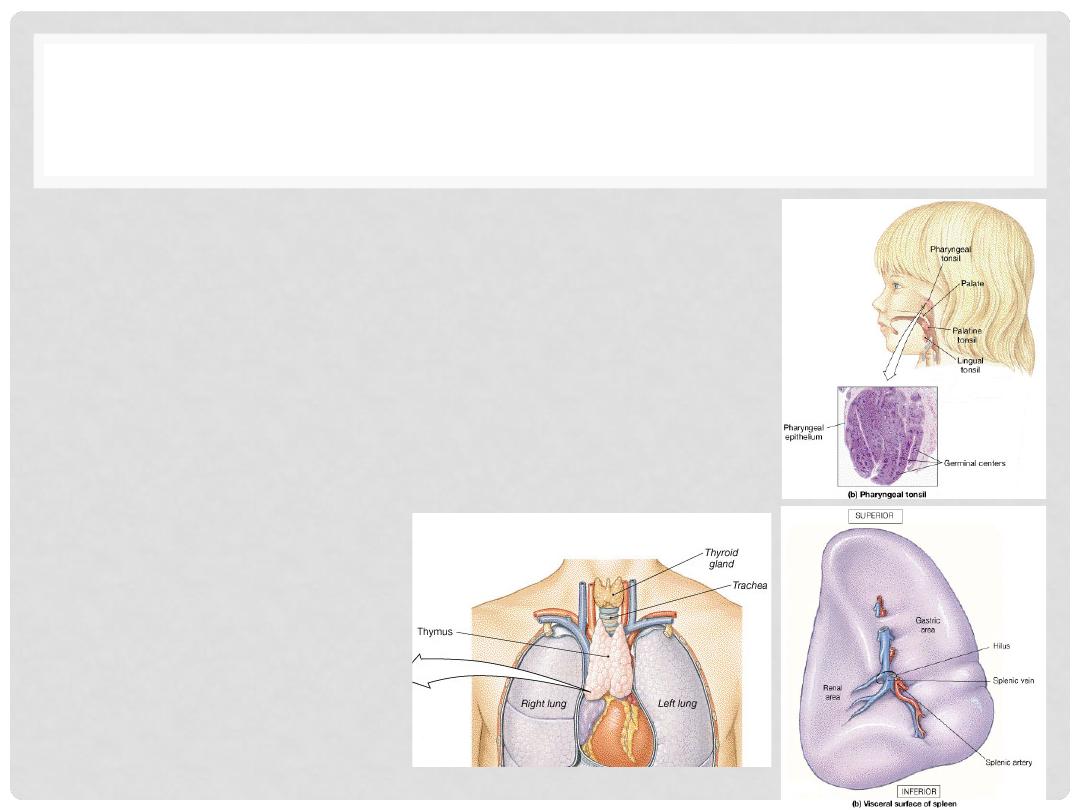
LYMPHOID ORGANS
•
Tonsil
•
Multiple groups of large lymphatic nodules
•
Splee
n
•
Largest lymphatic organ
•
Filters and store blood
•
Thymus Gland
•
Two lobes
•
Maturation of T cells
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

LYMPH NODES
•
Oval structures located along lymphatics
•
Enclosed by a fibrous capsule
•
Cortex = outer portion
•
Germinal centers produce lymphocytes
•
Medulla = inner portion
•
Medullary cords
•
Lymph enters nodes through afferent lymphatics,
flows through sinuses, exits through efferent
lymhpatic
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
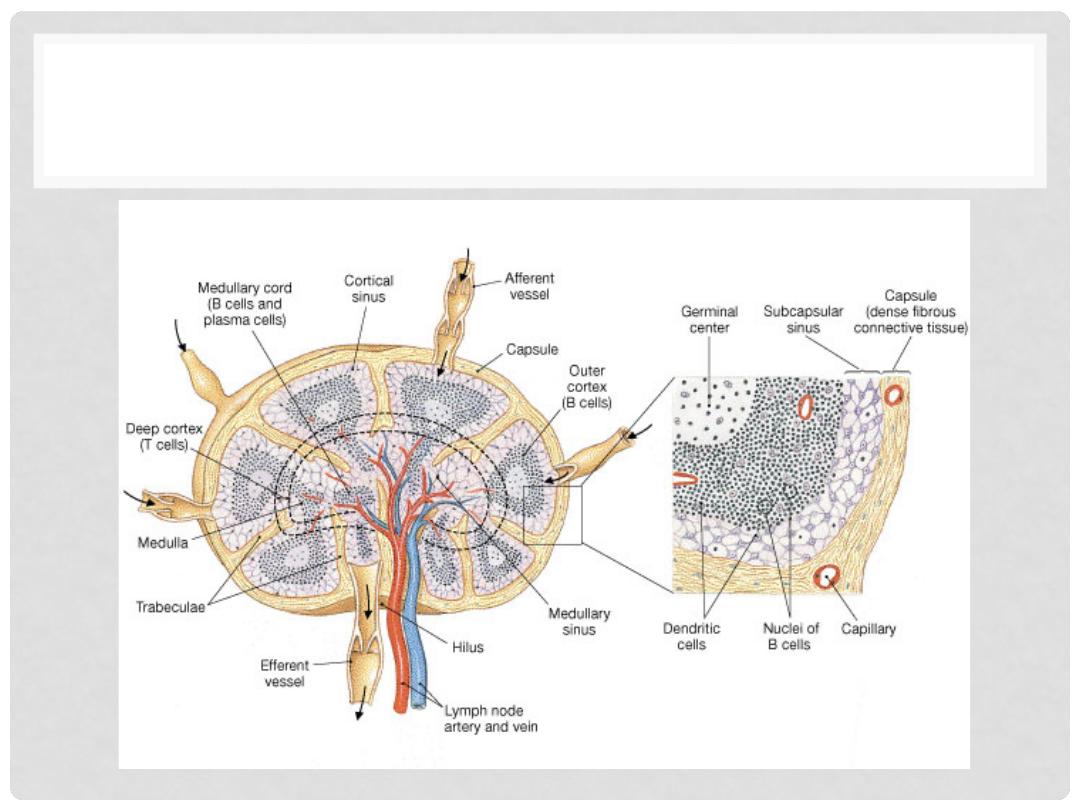
LYMPH NODE
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

IMMUNE CELLS
1.
LYMPHOCYTES
•
T cells
•
B cells
•
PLASMA CELLS (MODIFIED B CELLS)
2.
MACROPHAGES, aka “HISTIOCYTES”, (APCs, i.e.,
Antigen Presenting Cells)
•
“DENDRITIC” CELLS (APCs, i.e., Antigen Presenting Cells)
3.
NK (NATURAL KILLER) CELLS
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
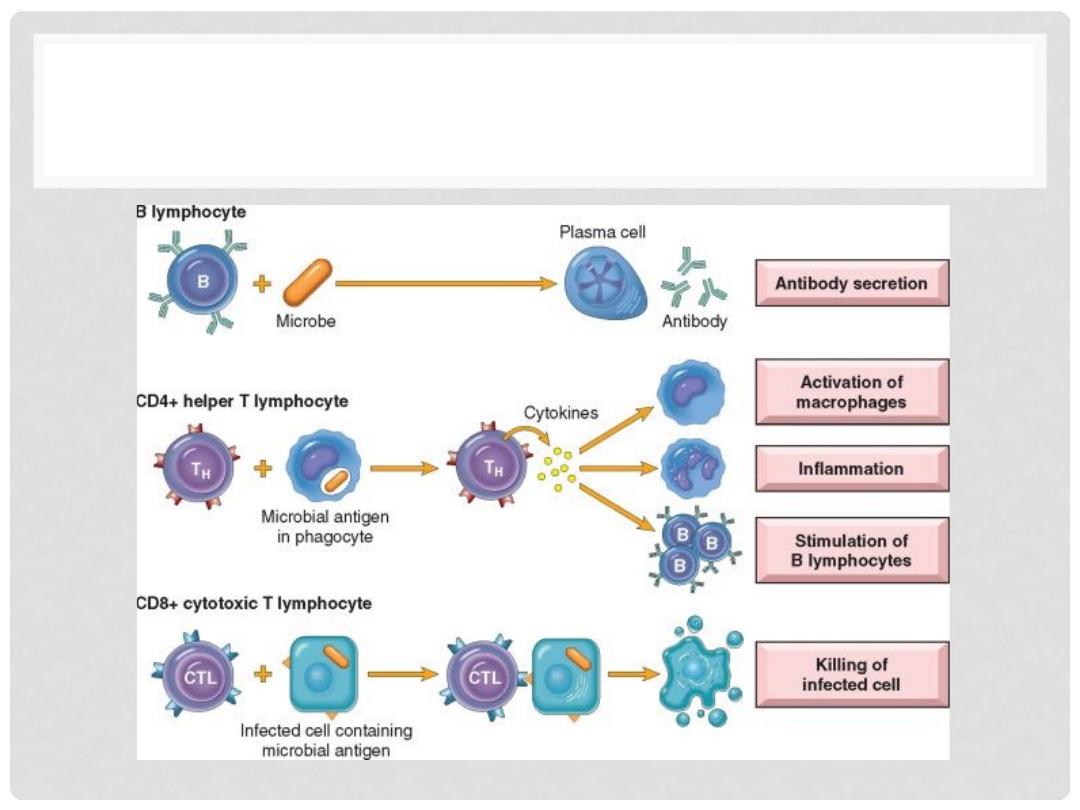
TYPES OF LYMPHOCYTES
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

CYTOKINES
•
CYTOKINES
are PROTEINS produced by MANY cells,
but usually LYMPHOCYTES and MACROPHAGES
•
Numerous roles in acute and chronic inflammation,
AND immunity
•
TNF, IL-1, by macrophages
•
CHEMOKINES
are small protein cytokines which are
attractants for PMNs
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

FUNCTION OF CYTOKINES
•
MEDIATE INNATE (NATURAL) IMMUNITY, IL-1, TNF,
INTERFERONS
•
REGULATE LYMPHOCYTE GROWTH (many
interleukins, ILs)
•
ACTIVATE INFLAMMATORY CELLS
•
STIMULATE HEMATOPOESIS, (CSFs, or Colony
Stimulating Factors)
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
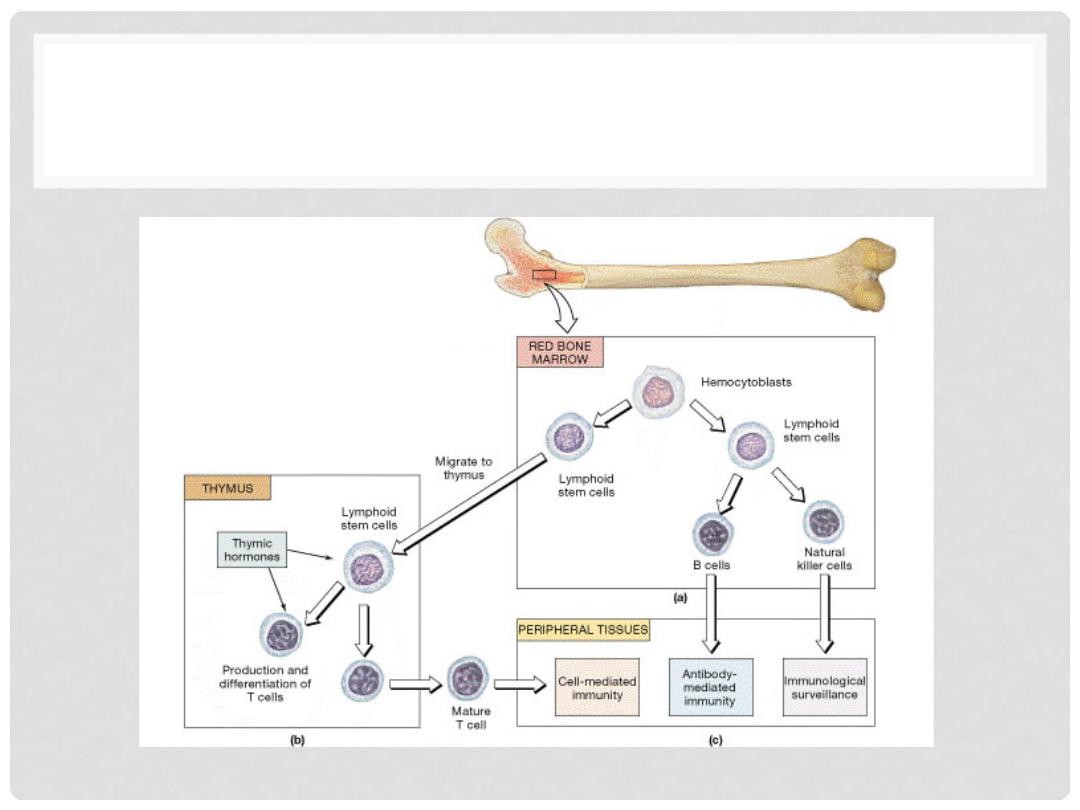
LYMPHOGENESIS
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

TYPES OF IMMUNE RESPONSE
•
INNATE (present before birth, “NATURAL”)
•
ADAPTIVE (developed by exposure to pathogens, or
in a broader sense, antigens not recognized by the
MHC)
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

INNATE RESPONSE
•
BARRIERS
•
CELLS: LYMPHOCYTES, MACROPHAGES, PLASMA
CELLS, NK CELLS
•
CYTOKINES/CHEMOKINES
•
PLASMA PROTEINS: Complement, Coagulation
Factors
•
Toll-Like Receptors, TLR’s (not adap)
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

MAJOR HISTOCOMPATIBILITY
MOLECULE (MHC)
•
A genetic “LOCUS” on Chromosome 6, p, which
codes for cell surface compatibility
•
Also called
HLA (Human Leukocyte Antigens)
in
humans and H-2 in mice
•
It’s major job is to make sure all self cell antigens are
recognized and “tolerated”, because the general
rule of the immune system is that all UN-recognized
antigens will NOT be tolerated
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

ADOPTIVE RESPONSE
•
CELLULAR, i.e., direct cellular reactions to antigens
•
HUMORAL (smarter), i.e., antibodies
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
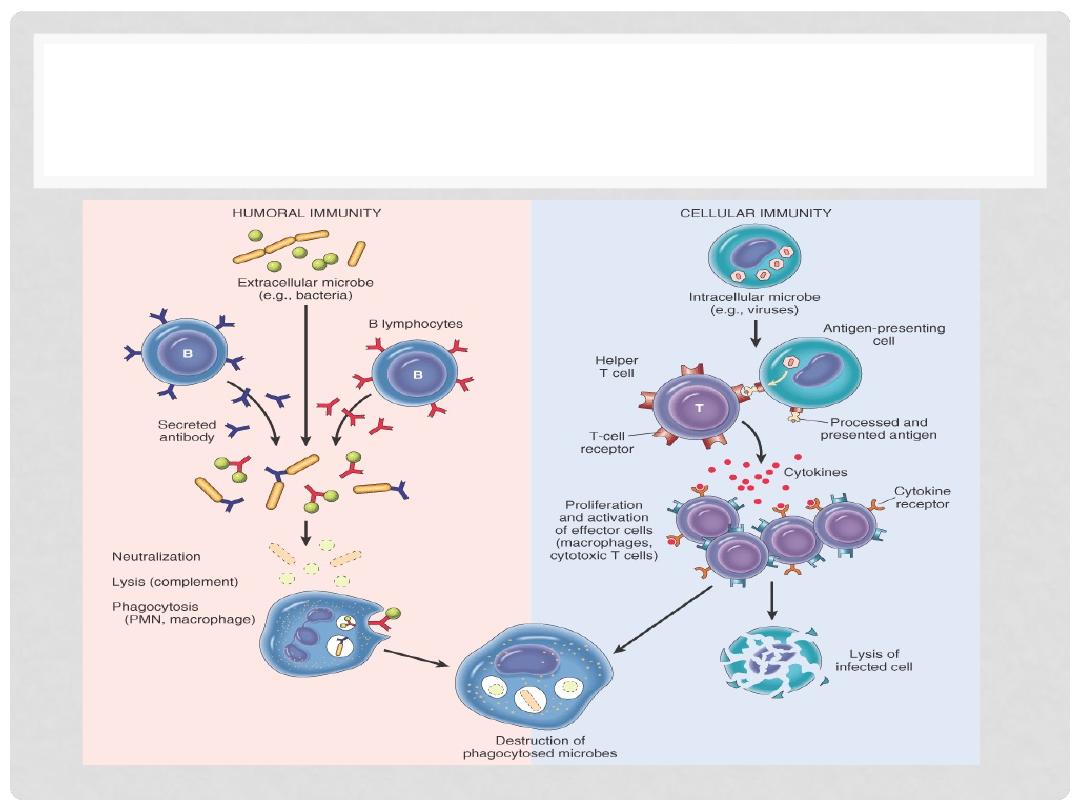
HUMERAL VS CELLULAR
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

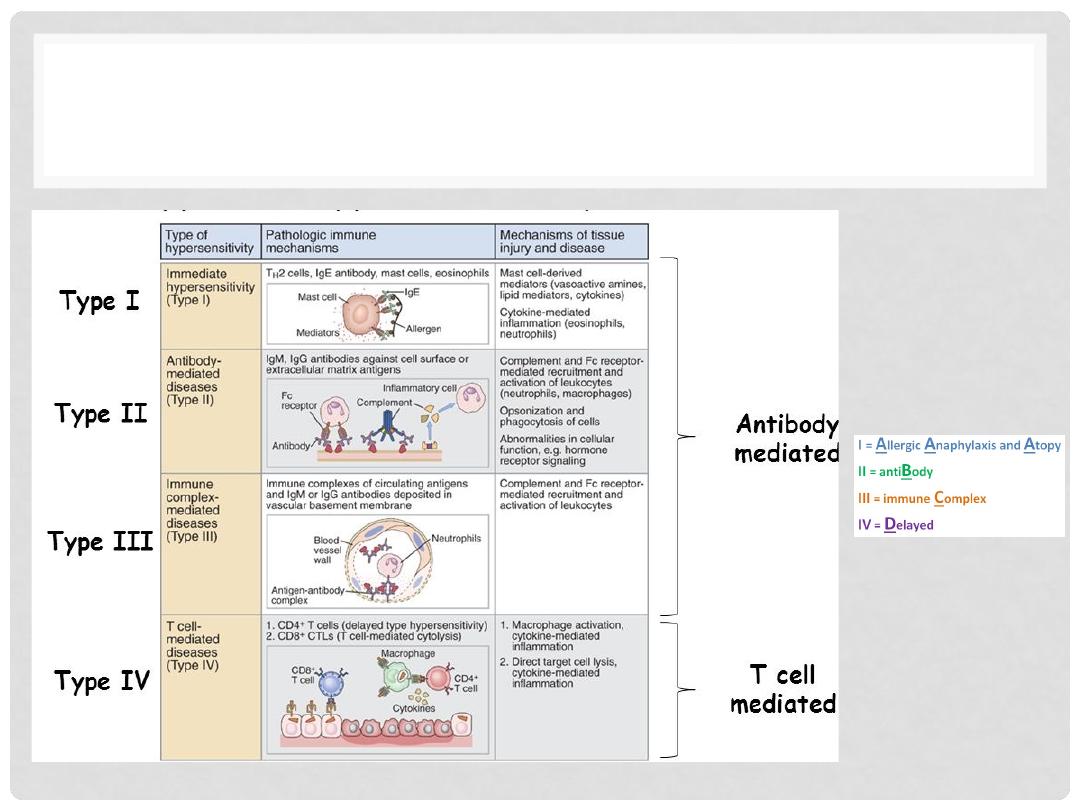
HYPERSENSITIVITY
•
Unwanted overreaction of immune system in response to
stimuli
•
There are four main types
•
Type I (Immediate Hypersensitivity)
•
Type II (Antibody Mediated Hypersensitivity)
•
Type III (Immune-Complex Mediated Hypersensitivity)
•
Type IV (Cell-Mediated Hypersensitivity)
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
TYPE I HYPERSENSITIVITY
(ANAPHYLAXIS)
•
“Immediate” means seconds to minutes
•
Involve IgE, Mast Cells or Eosinophils, Allergen
•
1) Allergen exposure
•
2) IMMEDIATE phase: MAST cell
Degranulation, vasodilatation, vascular
leakage, smooth muscle (broncho)-spasm
•
3) LATE phase (hours, days): Eosinophils,
PMNs, T-Cells, as expected with acute
inflammation
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
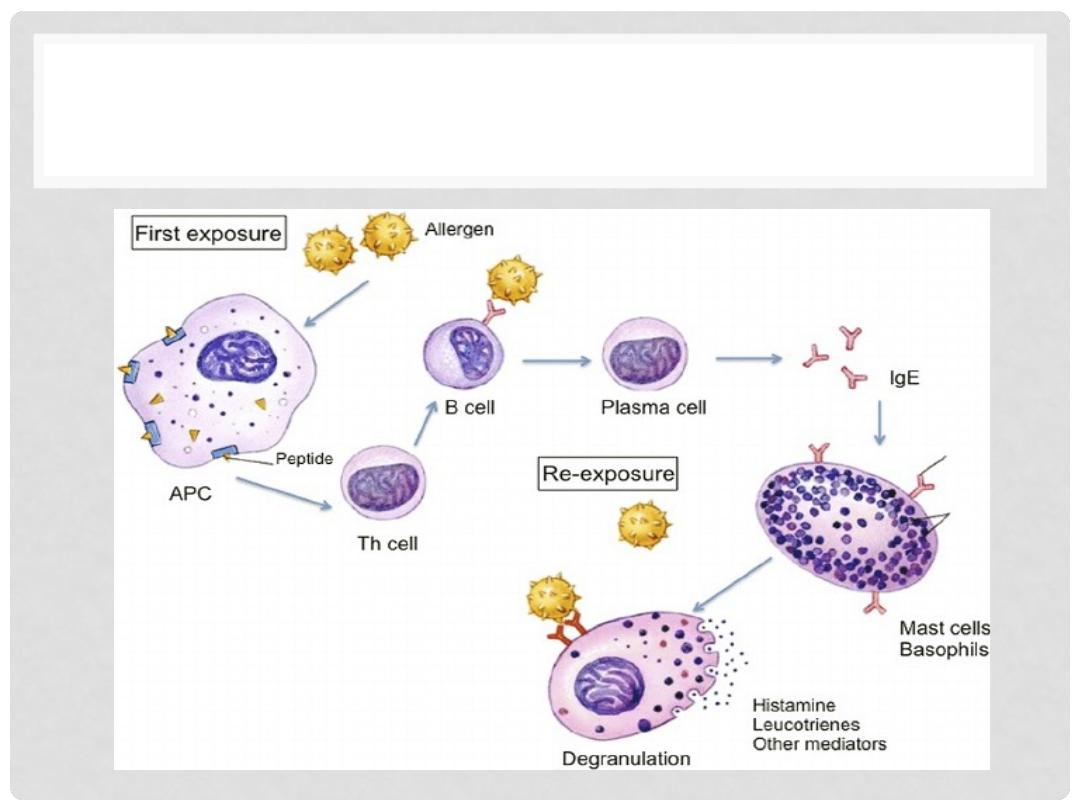
IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF TYPE I
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
TYPE I HYPERSENSITIVITY
•
Immunopathology
•
IgE production leads to release vasoactive
amine from mast cells
•
Two types:
•
Systematic anaphylaxis: acute asthma,
laryngeal edema, urticaria, drug allergy
•
Local anaphylaxis: food allergy and hay fever
•
Lab findings:
•
Increase in eosinophils, tryptase, and IgE
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

TYPE II HYPERSENSITIVITY
•
Two types of type II
•
Antibody-mediated reaction (Cytotoxic)
•
COMPLEMENT FIXATION (cascade of C1q, C1r, C1s, C2, C3,
C4, C5….. )
•
OPSONIZATION (basting the turkey)
•
PHAGOCYTOSIS
•
LYSIS (destruction of cells by rupturing or breaking of
the cell membrane)
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
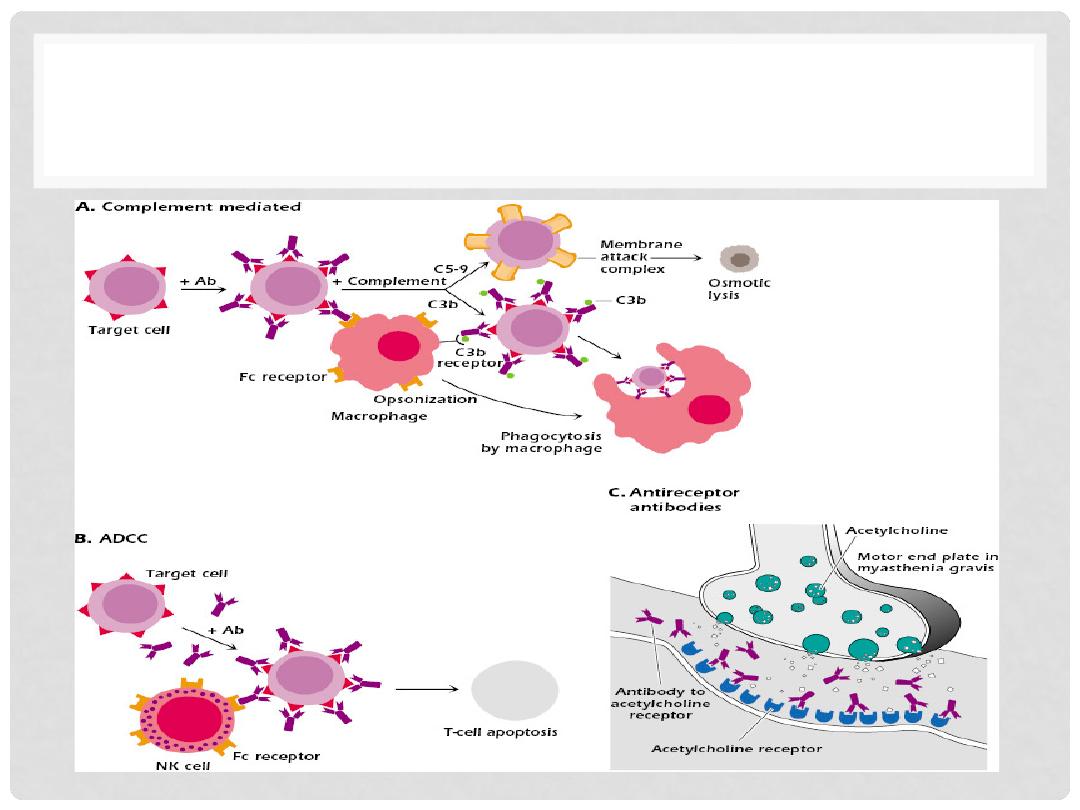
IMMUNOPATHOLOGY OF TYPE II
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

TYPE II HYPERSENSITIVITY
•
Immunopathology:
•
IgG or IgM binds to target cells to form anitgen-antibody
complex
•
Complement or Fc receptor activate phagocytosis and
recruit leukocytes
•
Histopathology:
•
Inflammation and functional derangment
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

EXAMPLES OF TYPE II
•
Complement-dependent type II
•
Transfusion Reactions, incompatible RBCs
•
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
•
Erythroblastosis fetalis ( IgG crosses to baby’s RBCs)
•
Goodpastyre’s syndrome (Abs against BM of glomerular)
•
Antibody-dependent type II
•
Graves Disease (anti-TSH receptor Abs)
•
Pernicious anemia
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

TYPE III HYPERSENSITIVITY
•
Antigen/Antibody “Complexes” (circulating)
•
Immunopathology:
•
Immune complex deposited on various organs
•
Complement activation
•
Recruitment of leukocytes
•
Release toxin and enzymes to digest
•
Could impact several organs like Kidney
(Glomerular Basement Membrane), Blood Vessels,
Skin, Joints (synovium)
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
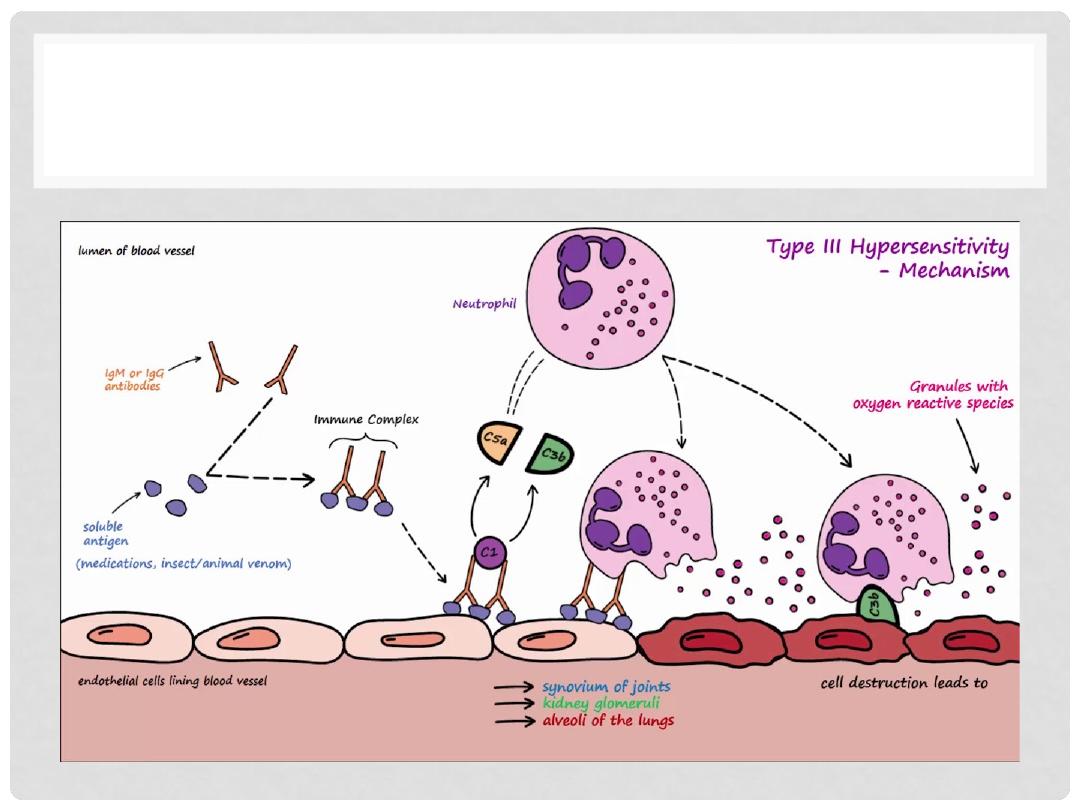
TYPE III ( IMMUNE-COMPLEX)
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

EXAMPLES OF TYPE III
•
SLE (Lupus),
•
Poly(Peri)arteritis Nodosa,
•
Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis,
•
Arthus reaction (hrs),
•
Serum sickness (days)
•
SYSTEMIC? Autoimmune diseases
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
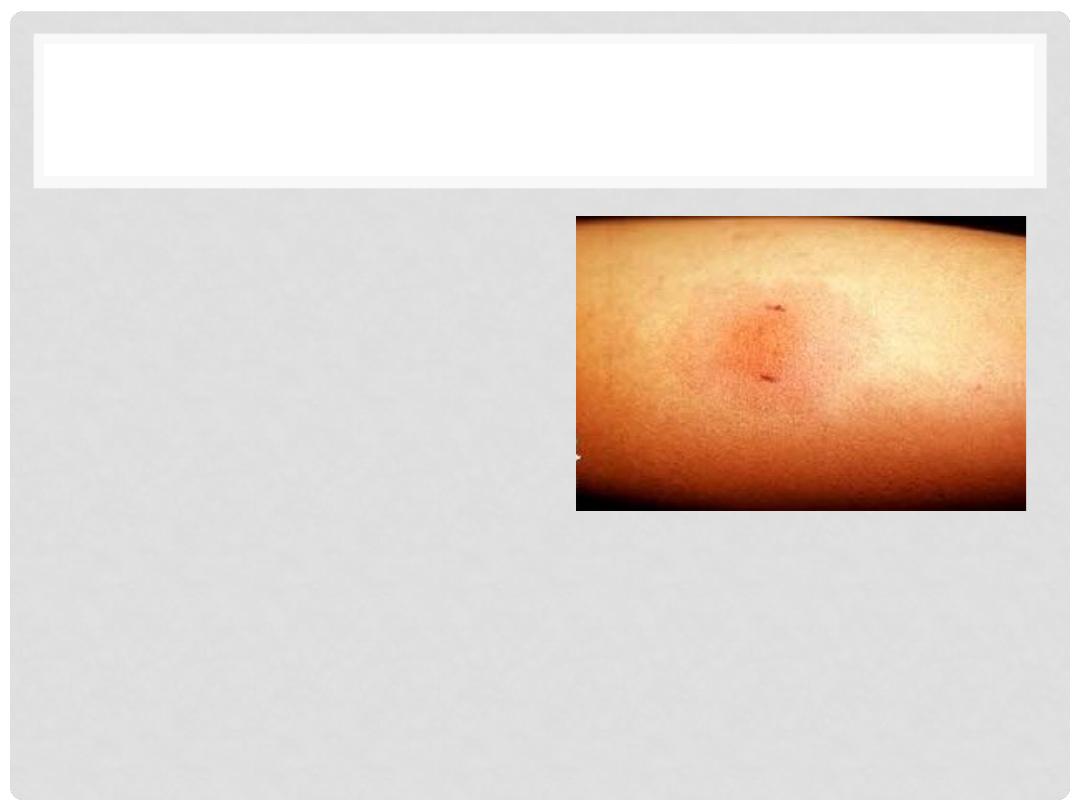
TYPE IV HYPERSENSITIVITY
•
CELL-MEDIATED (T-CELL)
DELAYED HYPERSENSITIVITY
•
CD4 mediated
•
Tuberculin Skin Reaction
•
DIRECT ANTIGEN CELL CONTACT
•
GRANULOMA FORMATION
•
CONTACT DERMATITIS
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
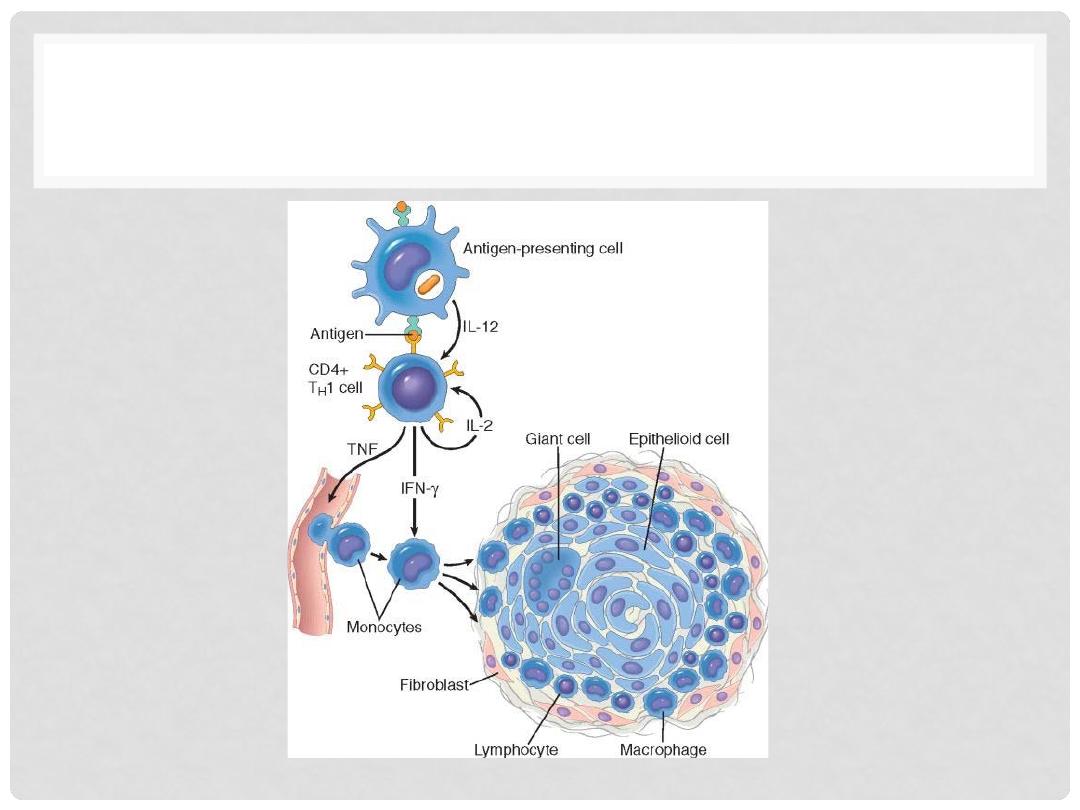
PATHOGENESIS OF TYPE IV
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
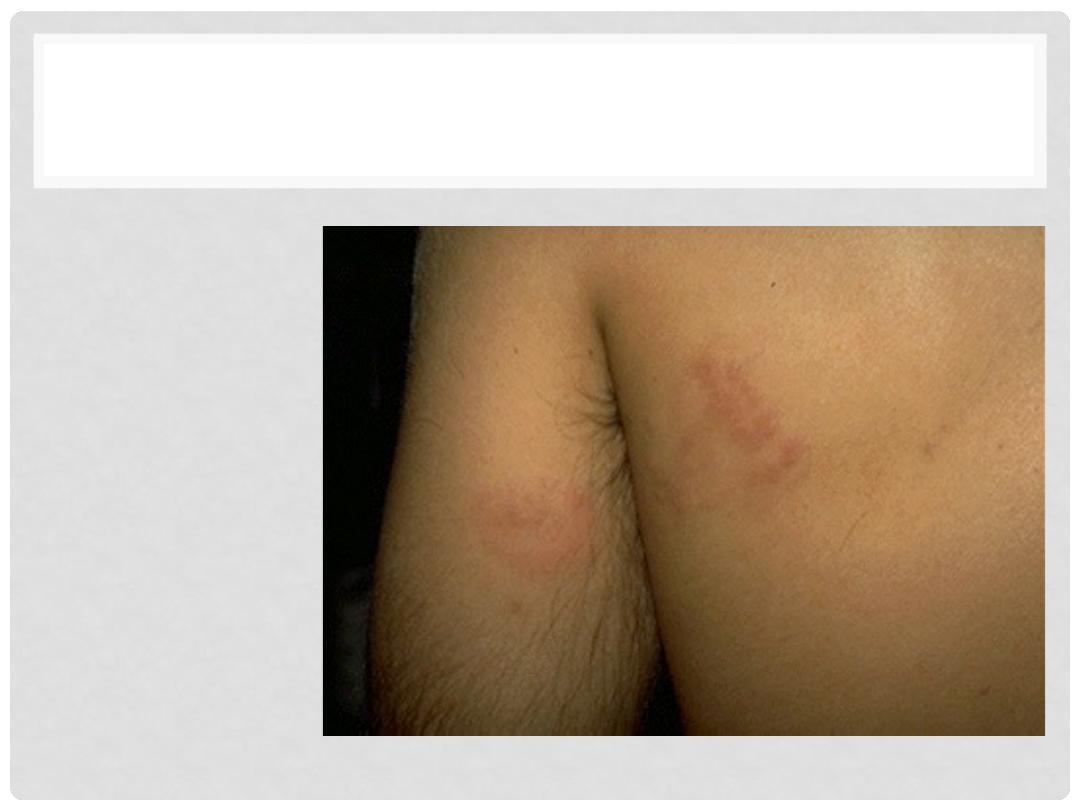
TYPE IV
CONTACT DERMATITIS
•
Pre-sensitized
CD4
•
Inflammatory
reaction
•
Coupe of days
after initial
contact
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

EXAMPLE OF TYPE IV
•
Granulomatous diseases
•
Tuberculin skin reaction
•
Transplant rejection
•
Contact dermatitis
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy
HYPERSENSITIVITY
Lectures of Dr. Mohanad Aljanabi /ImmunoPatholoy

Questions & Comments!
