
Fifth stage
Surgery-Ortho
Lec-6
د.هشام القطان
19/10/2015
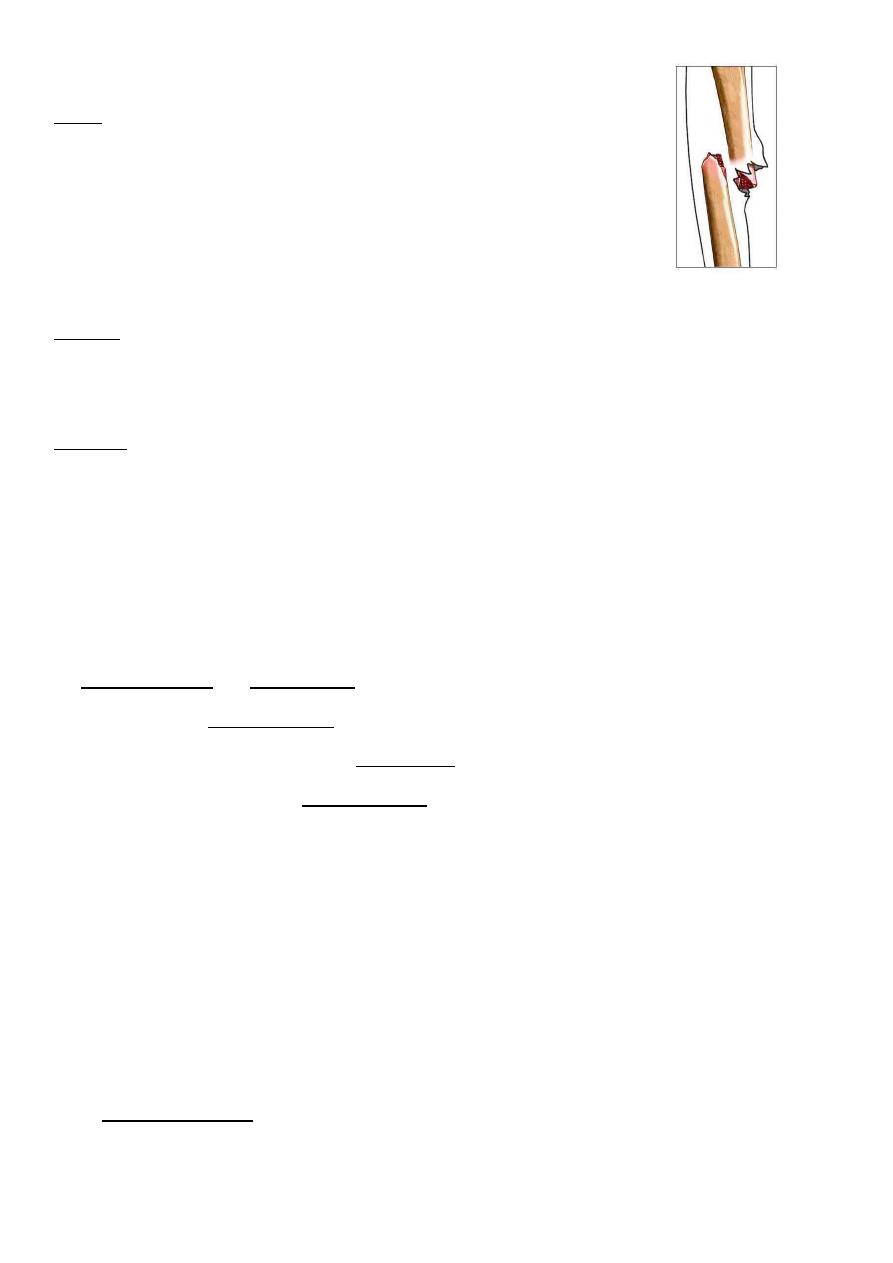
Treatment of open fractures (compound)
Initial managements
Patient with open fractures have multiple injuries and severe shock.
At the site accident
the wound should be covered with sterile dressing or clean material and left
undisturbed until the patient reach the accident department.
Tetanus prophylaxis is administered.
In hospital
a rapid general assessment is the first step (clinical examinations).
We should study the nature of the wound.
State the skin around .
State of circulation.
Neurological statement.
Antibiotic cover
Classification of compound fractures by Gustilo :
I
Typ
Small wound
clean ,little soft tissue
damage, fracture not comminuted
(low –energy
fracture)
Type II
Wound more than 1 cm no much soft tissue damage, moderate comminuted fracture.(low
–energy fracture)
Type III
Extensive damage to skin ,Soft tissue &neurovascular structure, with considerable
contamination of the wound.it is divided in to A,B,C. (High energy force )
Principles of treatment :
1.Antibiotic should be given as soon as possible
Benzylpencillin and flucloxacillin
2
nd
generation cephalosporin 6 hourly.
Gram negative coverage by add gentamycin.
And anaerobes by adding metronidazole.
2.Debridment
Under general anaesthesia.
The wound all around should be cleaned and shaved.
The wound should be irrigated thourghly with copious amounts of physiological saline.
Tourniquet should not be used.
Wound exscion only enough to leave healthy skin.
Wound cleansing from all debris and foreign materials with copious saline.
(a common mistake is to inject syringefuls of fluid through small aperture so push
contaminants further in).
Removal of devitalized tissue (no bleeding , not contractile, no change in color ).
All doubtfully viable tissue ,whether soft or bony should be removed.
Nerves and tendons is best to leave them by marking .
3.Wound closure
Either primary sutured.
Delayed primary sutured.
Split skin graft.
Flap graft.
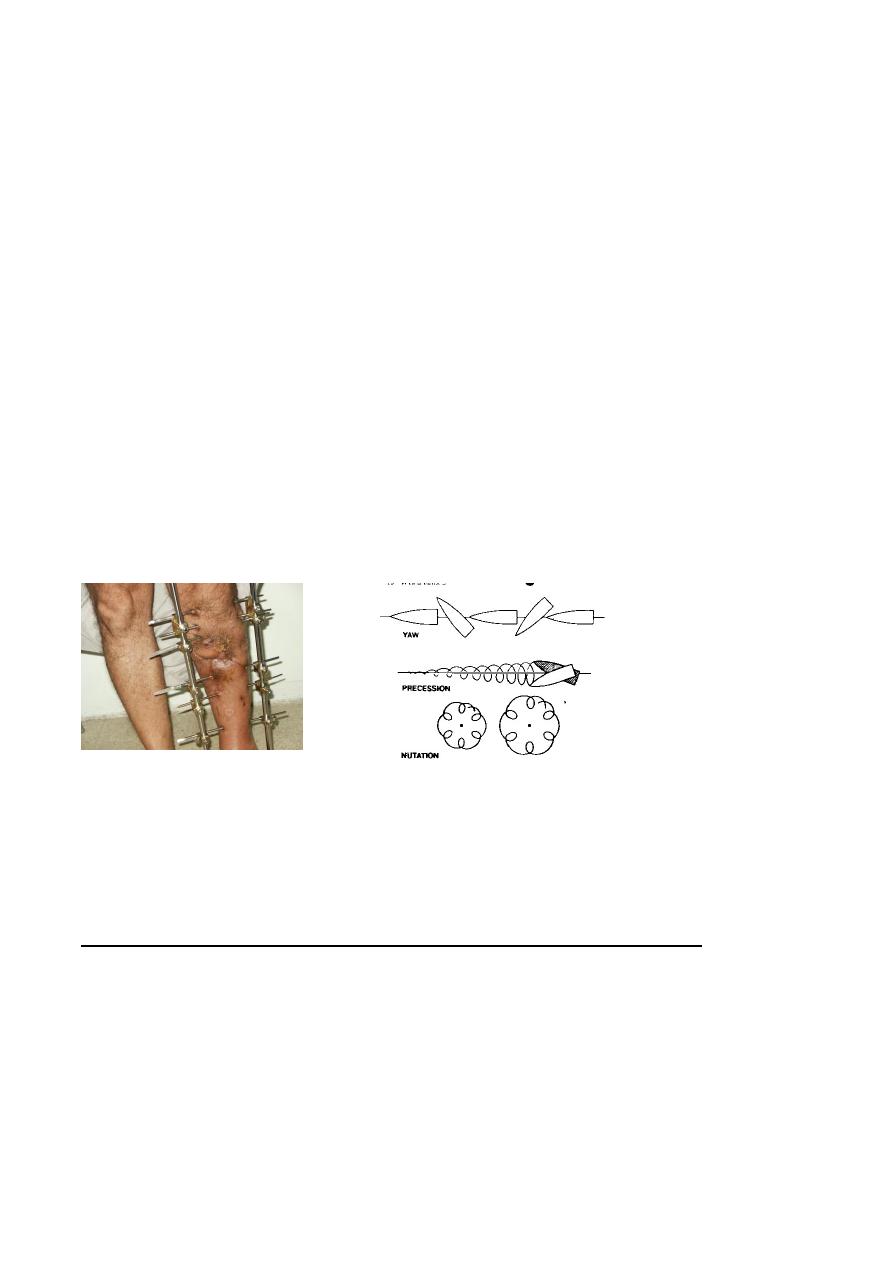
4.Stabilization of fractures
The stability of the fracture is important in reducing infection and assist recovery of soft
tissue.
If no obvious contamination and the time less than 8 hours open fracture up to grade 3
A could be treated with as for closed .
Or better in not expertise surgeons to do External fixations
The patient should be followed till healing developed .
And physiotherapy.
Gunshot injuries:
Missile wounds are special type of injuries. Tissue damage produced by
direct through immediate path of the missile
contusion of muscles around the track.
contusion and congestion away from the track.
Either high velocity
missiles as rifles
(>600m/s).
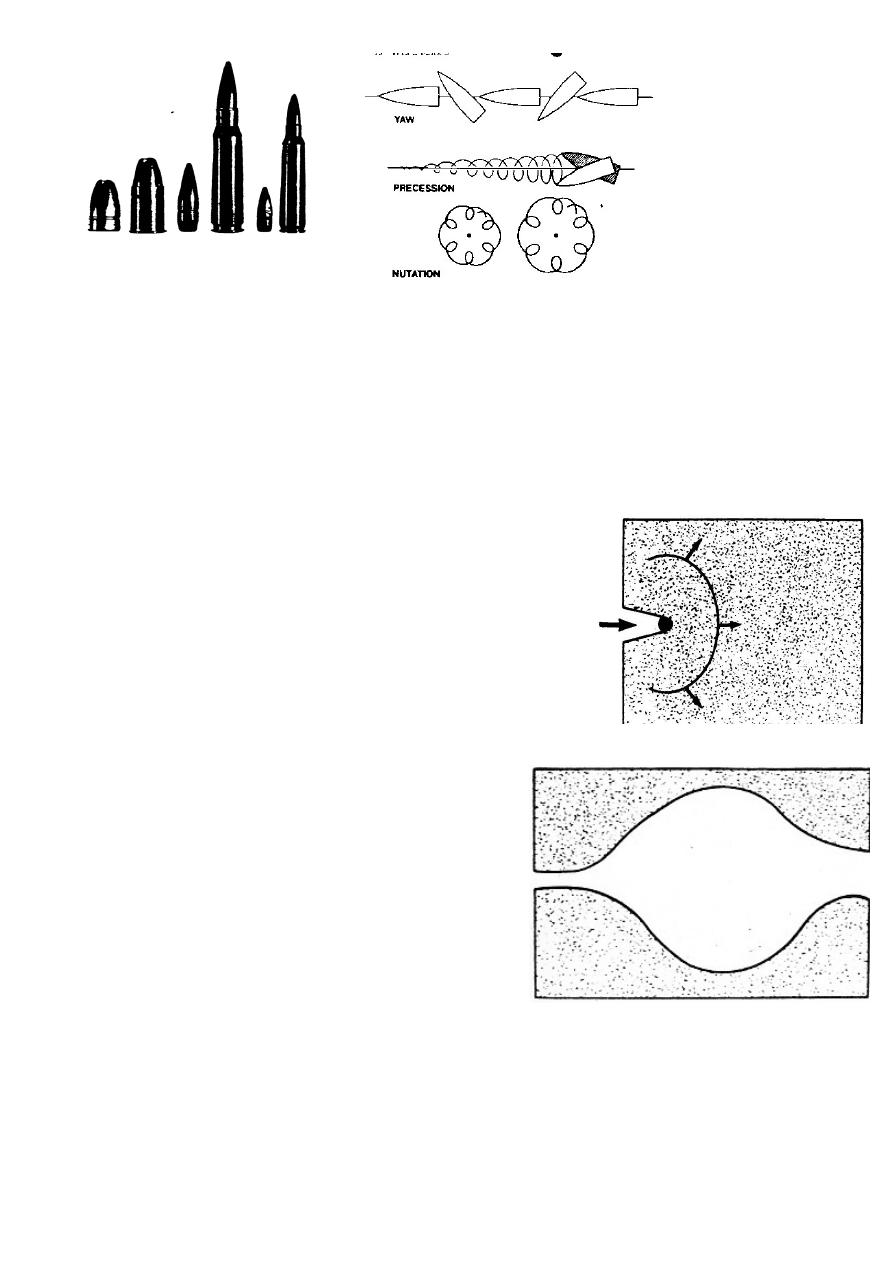
Mechanism of injury :
Wound results from absorption of energy imparted by the missile it strike and penetrate
tissue.
Kinetic energy is calculated by the formula
(KE=MV2/2 )
1. Laceration and crushing by bullet passage in the tissues.
2.Shock wave
through forcing atract in the solid tissue the missile
compresses the medium in front of it and this compression
moves away as a shock wave of spherical form.
3.Temporary cavitation only in high velocity
missiles .
4.This cavity has sub atmospheric pressure, so
bacteria and debris sucked into the depth of
the wound.
5.and tissue destruction over wide area.
6.greater bone damage.

Low velocity (300-600 m/s)
From civilian hand-guns .
Smaller tissue damage confined to the bullet tract.
In all gunshot injuries debris is sucked into the wound.
Treatment
Emergency treatment.
A B C.
Covering the wound with sterile dressing till general condition is well.
Antibiotic.
antitetenus…
Definitive treatment
Low velocity:
Debridment.
splintage .
antibiotic.
High velocity:
Thorough cleansing with exscion deep damage tissue.
Wound kept open for dressing.
Bone immobilization by external fixation.
Wound either Delayed primary suture , skin graft or skin flap.
Photos www.muhadharaty.com/lecture/2832
