
Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 1 of 10
FERTILITY CONTROL
Men and women have used contraception, in one form or another, for
Thousands of years. There is no one method that will suit everyone, and
individuals will use different types of contraception at different stages in their
lives
The characteristics of the ideal contraceptive method are:
1. highly effective
2. no side effects
3. cheap
4. rapidly reversible
5. widespread availability
6. acceptable to all cultures and religions
7. easily distributed
8. can be administrated by non- health care personnel
o Virtually all methods of contraception occasionally fail and some are much
more effective than others.
o Failure rates are traditionally expressed as the number of failures per 100
woman-years (HwY ), i.e. the number of pregnancies if 100 women were
to use the method for 1 year.
o Failure rates for some methods vary considerably, largely because of the
potential for failure caused by imperfect use (user failure) rather than an
intrinsic
:العدد
5
31
/
1
/
4132

Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 2 of 10
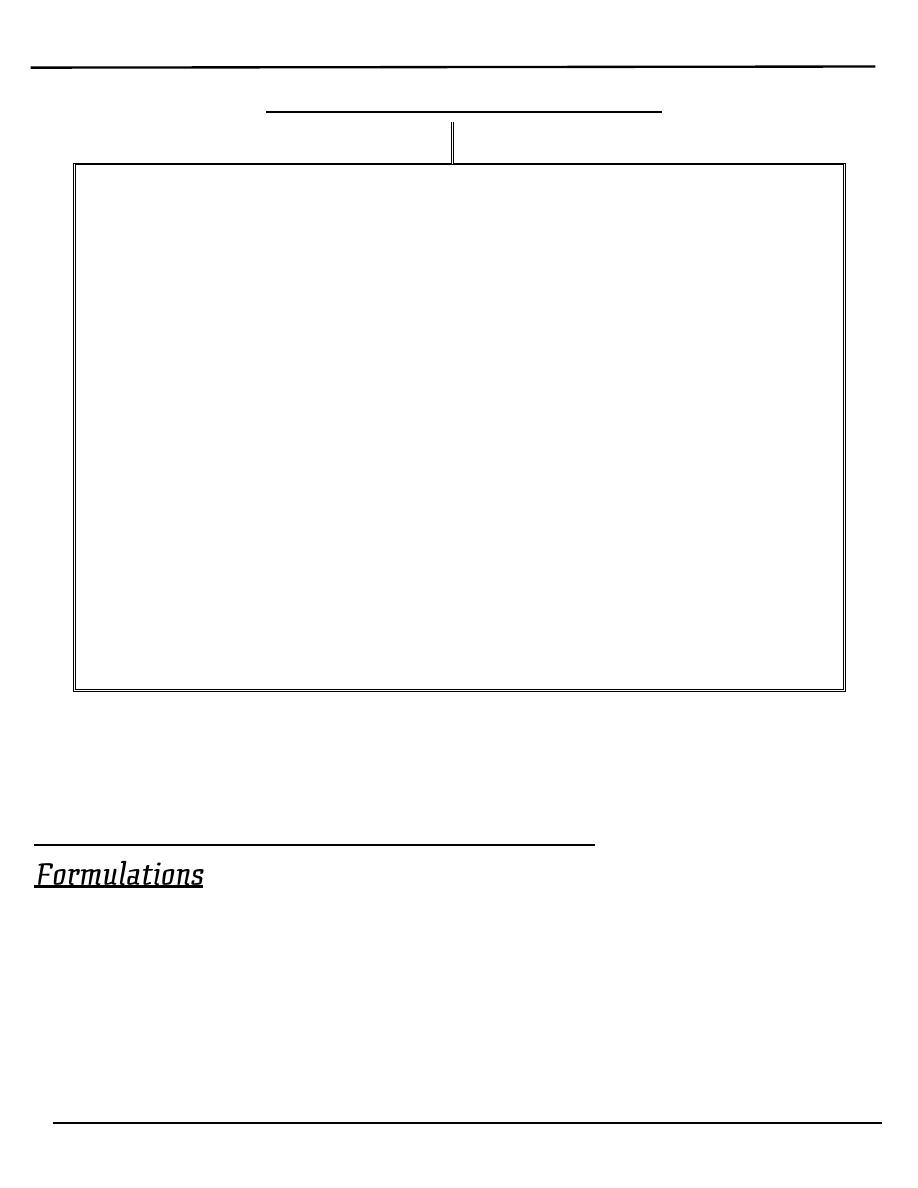
Classification
A. Methods not requiring medical cosultation:
1- coitus interruptus
2- safe period [Natural family planning]
3- vaginal spermicides
4- barrier methods include:
• Male condom
• Female barriers
B. Methods requring medical supervision
1- Hormonal contraception:
• Combined oral contraceptive methods
• Progesterone-only preparations include:
A-progesterone only pills
B-injectables
C-Subdermal implants
D-Hormone-releasing intauterine system
2- Intauterine device
3- Post-coital emergency contraception
4- occlusive diaphragms&caps
C. Perminant methods[sterilization]
• Female tubal occlusion
• Male vasectomy
Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 3 of 10
Failre rate for contraception
Contraceptive method
Failure rate /100 women year
Combined oral contraceptivepill
Progestogen -only pill
Depo-Provera
Implanon
Copper-bearing IUD
Levonorgestrel-releasing IUD
Male condom
Female diaphragm
Persona
Natural family planning
Vasectomy
Female sterilization
1.1
-
1
1
-
3
1.1
-
2
o
1
-
2
1.0
2
-
0
1
-
10
6
2
-
3
1.12
1.13
Hormonal contraception
Combined oral contraceptive pills
Combined oral contraceptive pills contains both:
1-Synthetic Estrogen (Ethinyl estradiol mostly): The dose of oestrogen varies
from 50 to 15 μg (microgram).
2-Synthetic progestogens Either one of these:
First generation (e.g. norethindrone).
Second generation progestins (e.g. levonorgestrel) .

Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 4 of 10
Third generation series including gestodene, desogestrel and
norgestimate.
o Monophasic pills contain standard daily dosages of oestrogen and
progestogen.
o Biphasic or triphasic preparations have two or three incremental variations
in hormone dose.
o Current thinking is that biphasic and triphasic preparations are more
complicated for women to use and have few real advantages.
o Most brands contain 21 pills; one pill to be taken daily, followed by a 7-
day pill-free interval. There are also some every-day (ED) preparations that
include seven placebo pills that are taken instead of having a pill-free
interval. For maximum effectiveness, COC should always be taken
regularly at roughly the same time each day.
1. low-dose pills containing 30μg of ethinyl estradiol
2. high-dose pills contain 50 μg estrogen. Higher dosages of oestrogen are
strongly linked to increased risks of both arterial and venous thrombosis
3. Yasmin contains ethinyl estradiol and drospirenone.
Drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid activity. It can help prevent
bloating, weight gain, and hypertension, but it can increase serum
potassium.
Yasmin is contraindicated in patients at risk for hyperkalemia and
should not be combined with other drugs that can increase potassium
Combined oral contraception acts both centrally and peripherally.
A. Centrally: Inhibition of ovulation is by far the most important effect.
Both oestrogen and progestogensuppress the release of pituitary follicle
stimulatinghormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which

Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 5 of 10
prevents follicular development within the ovary and therefore
ovulation.
B. Peripheral effects include: making the endometrium atrophic and
hostile to an implanting embryo altering cervical mucus to prevent
sperm ascending into the uterine cavity.
A. Absolute contraindications
I. Circulatory diseases:
1- iscihaemic heart disease- cerebrovascular accident
2- significant hypertension
3- arterial or venous thrombosis
4- any acquired or inherited pro-thrombotic tendency
5- any Significant risk factors for cardiovascularpisease
II. Acute or severe liver disease
III. Oestrogen-dependent neoplasms, particularly breast cancer
- Breastfeeding <6 weeks post-partum
- Smoking ≥15 cigarettes/day and age ≥35
IV. Focal migraine
B. Relative contra indications
1. Generalized migraine
2. Long-term immobilization
3. Irregular vagli.nal bleedillg (until a diagnosis has been made)
4. Less severe risk factors for cardiovascular disease, e.g. obesity, heavy
smoking, diabetes

Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 6 of 10
Major side effects:
1-Venous thromboembolism
o Oestrogens alter blood clotting and coagulation in a way that induces a
pro-thrombotic tendency, although the exact mechanism of this is poorly
understood.
o The higher the dose of oestrogen within COc, the greater the risk of
venous thromboembolism (VTE).
o Type of progestogen also affects the risk of VTE, with users of COC
containing third-generation progestogens being twice as likely to sustain
a VTE.
.
The risks of VTE are:
5 per 100 000 for normal population,
15 per 100 000 for users of second-generation COC,
30 per 100 000 for users of third-generation COC,
60 per 100 000 for pregnant women
2-Arterial disease
o 1 per cent of women taking coc will become significantly hypertensive
and they should be advised to stop taking COC
o The risk of myocardial infarction and thrombotic stroke in young,
healthy women using low-dose cac is extremely small.
o Cigarette smoking will, however, increase the risk, and any woman who
smokes must be advised to stop COC at the age of 35 years. Around
.
3-Mortality
o There is increased mortality in women using the pills over women not
using it.this is related to age&smoking habits.Death is most often the
result of pulmonary embolism,cerebral or coronary thrombosis.

Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 7 of 10
o Women who are under 35 years,do not smoke or have hypertention or
diabetes have no exess mortality In women over 35 years who are on pill
the exess mortality rises&rises more in women who smoke or have
hypertention
4-Carcinogenic effect
A. Breast cancer
Advising women about the association between breast cancer and COC is
very difficult. Most data do show a slight increase in the risk of developing
breast cancer among current COC users (relative risk around l. 24). This is
not of great significance to young women, as the background rate of breast
cancer is very low at their age. However, for a woman in her forties, these are
more relevant data, as the background rate of breast cancer is higher. The
same data also showed that beyond 10 years after stopping coc there was no
increase in breast cancer risk for former coc users
B. Cervical cancer
More than five years of pill use may be associated with small increase risk
of cervical carcinoma.
C. Liver cancer
Benign hepatic adenoma is a rare consequence of COC use.
Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 8 of 10
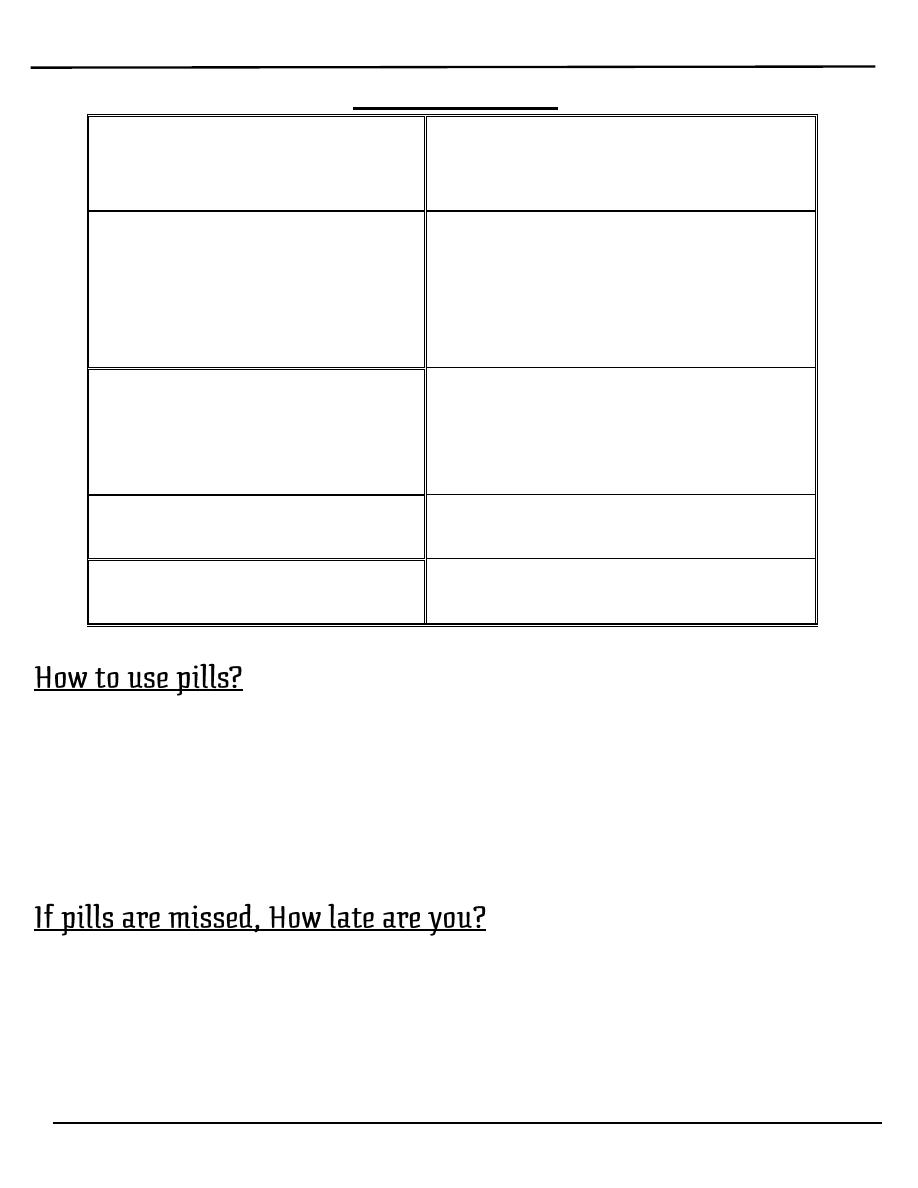
Minor side effects
Central nervous system
Depression
Headaches
Loss of libido
Gastrointestinal
Nausea and vomiting
Weight gain
Bloatedness
Gall-stones
Cholestatic jaundice
Genitourinary system
Cystitis
Irregular bleeding
Vaginal discharge
Growth of fibroids
Breast
Breast pain
Increased risk of breast cancer
miscellaneous
Chloasma (facial pigmentation)
Leg cramps
The patient begins taking the pills on the first day of menstrual cycle then in
the next cycles they are administered in fifth day of the cycle and continue for
21 days, each day at the same time, then discontinued for 7 days to allow for
withdrawal bleeding that mimics the normal menstrual cycle which occur
after 3-5 days from stopping pills
o Less than 12 hours late Don't worry. Just take the delayed pill at
once, and further pills as usual
o More than 12 hours late 1- Take the most recently delayed pill now
2- Use extra precautions
(condom, for instance) for the next 7d.

Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 9 of 10
This can occur with enzyme-inducing agents such as some anti-epileptic
drugs increase activity of hepatic enzyme so reduce efficacy of COC. Higher
dose oestrogen coc containing 50 Mg ethinyl oestradiol may need to be
prescribed some:
Broad-spectrum antibiotics Ampicillin, Amoxicillin, Tetracycline,
Neomycin can alter intestinal absorption of COC and reduce its efficacy.
Additional contraceptive measures should therefore be recommended
during antibiotic therapy and for 1 week thereafter
Steroids ,Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) and acetaminophen may elevate
plasma ethinyl estradiol so increse its efficacy
1. COC users generally have light, pain -free, regular bleed and therefore
COC can be used to treat heavy or painful periods i .e menorrhagia &
dysmenorrhea
2. It will also improve premenstrual syndrome (PMS)
3. Reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease (PID).
4. decreased incidence of benign breast lump
5. decrease number of functional ovarian cyst
6. less endometriosis
7. COC offers long-term protection against both ovarian and endometrial
cancers.
8. It can also be used as a treatment for acne.
o A contraceptive transdermal patch containing oestrogen and progestogen
has been developed and releases norelgestromin 150 Mg and thinly
estradiol 20 Mg per 24 hours.

Lecture 1
النسائية
د
.
سجى
FERTILITY CONTROL
Page 10 of 10
o Patches are applied weekly for 3 weeks, after which there is a patch-free
week.
o Contraceptive patches have the same risks and benefits as COC and,
although they are relatively more expensive, may have better
compliance.
