
Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 1 of 16
Conditions affecting the vulva and vagina:
The vulva
Is a common symptom which is an irritation of vulva sufficient to lead to
scratching
:
1. Infections.
o trichomonas vaginalis or candidasis
o Parasites such as scabies and lice.
o Threadworms
2.Skin conditions may affect vulval skin.
eczema, psoriasis, lichen simplex, lichen planus, and lichen
sclerosus.
3.Sensitization of the vulval skin to drugs or chemicals as soap
and disinfectant , chemical spermicide,
ointments.
4. Medical disorders:
o Diabetes, chronic renal failure, polycythemia, liver
cirrhosis, Hodgkin's disease.
o Urinary incontinence.
5. Non neoplastic epithelial disorder as lichen sclrosus,
squamous hyperplasia
6. Neoplasia: VIN, carcinoma, lymphoma, Paget's disease
7. Excess or inappropriate hygiene.
8. Psychogenic causes.
:العدد
8
91
/
2
/
4
209

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 2 of 16
:
History: Carful history, including the use of any substance which
might lead to allergy.
o General examination of the patient including inspection for
dermatological lesion of face, mucous membrane, hands,
wrist, elbows, trunk, and knees
o Any evidence of systemic disease
o Gynaecological examination including inspection of cervix
and vagina and vulva urethral meatus and anal area
o Colposcopic examination of cervix and vagina and vulva
o Palpation of inguinal lymph nodes.
o Bacteriological examination of vaginal secretions and scraping
from the skin.
o Full blood count.
o Blood sugar
o Biopsy of the skin of vulva.
Successful treatment depends on two cardinal principles:
1. To remove any underlying cause.
2. To stop further damage to the skin by scratching.
The help of dermatologist may be sought in difficult cases.
Great care should be taken in prescribing any of anti-pruritics
Corticosteroid applications sometimes used.
o Aphthous ulcer
o Herpes gentalis.

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 3 of 16
o Primary syphilis.
o Crohn's disease.
o Behcet's disease.
o Lymphgranuloma venereum.
o Chancroid.
o Tuberculosis.
o Malignant ulcer.
o Most vulval lumps are benign and can be treated
conservatively.
o Excisional biopsy is indicated in solid lesions or when the
diagnosis is uncertain.
Bartholin's glands lies on each side of the vagina and it's duct
opens into the posterior part of the vestibule.
o Is the most common vagial vulvar tumour. Cyst may arise
from the duct of the Bartholin's gland that lies in
subcutaneous tissue below the lower third of labium
majorum. Cysts can develop if the opening of bartholin duct
becomes blocked and distended with mucoid secretion.
o It present as painless swellings or some time present with
discomfort posterolaterally in the introitus and usually
unilaterally. It may become infected, to form an bartholin's
abscess.
:
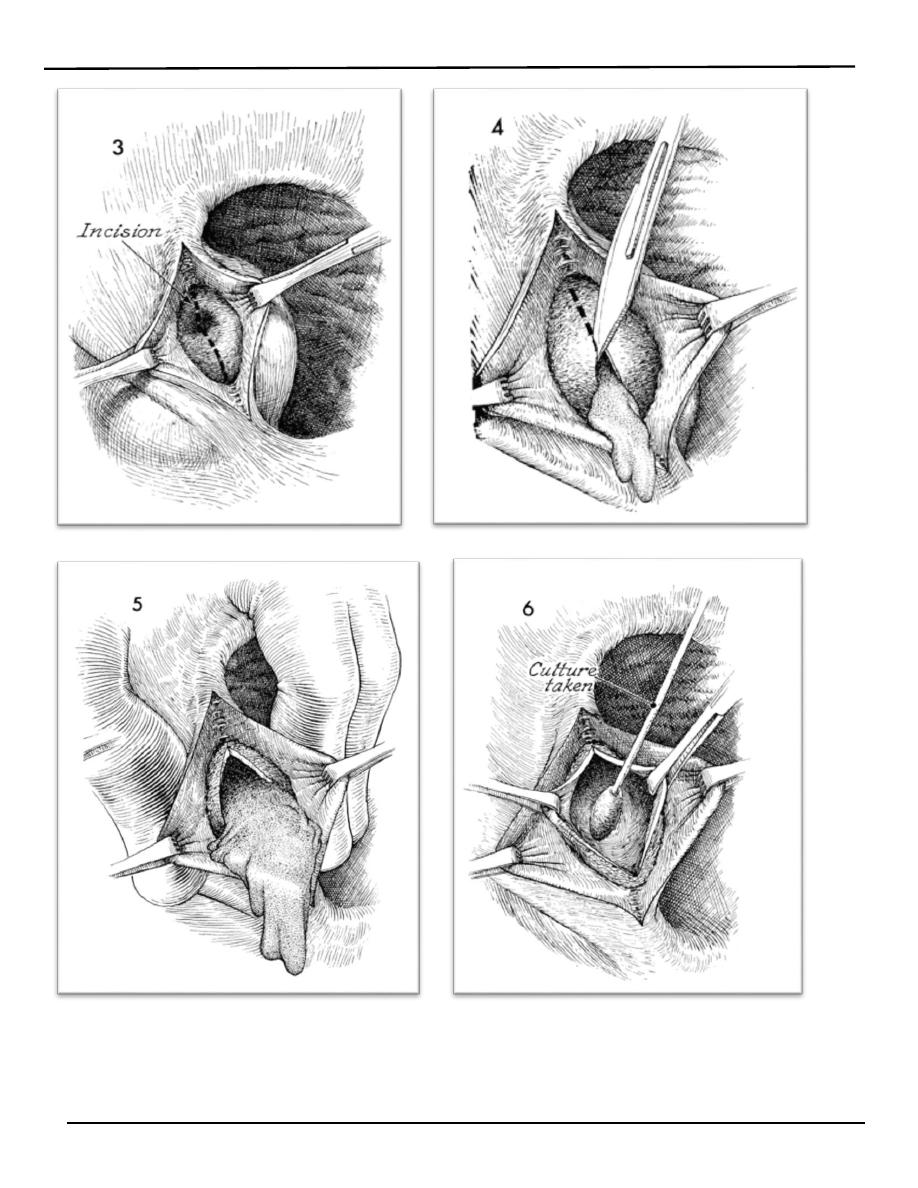
o Marsupilizeation the cyst (permit adequate drainage and
mostly the function of the gland is retained).

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 4 of 16
Or
o Cyst excision.
o Bartholin's abscess involves an accumulation of pus that
forms a lump (swelling) in Bartholin's glands
o The gland may be infected by gonococci, staphylococci,
streptococci or a mixture of organisms.
o It causes severe discomfort when walking or sitting.
:
o Symptom: it causes severe discomfort when walking or sitting.
o Physical examination:
o Diagnosis of a Bartholin abscess is made primarily upon the
following physical examination findings:
o The position of the labial swelling at the junction of anterior
two third (2/3) and posterior one third (1/3) of the labium
majorum is diagnostic
o Painful red swelling with reddens of the surrounding tissue
and odematous.
o The swelling is hot, tender and fluctuant
:
o drain the abscess by marsupilzation (pouch making).
o Antibiotic therapy.
o the drained pus should be sent for culture.
o biopsy may be recommended in older women to rule out an
underlying Bartholin's gland tumor.
Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 5 of 16
Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 6 of 16
o It may present at any age
o It dose not have the same malignant potential of that of CIN.
o It usually asymptomatic but it may present as Pruritus vulvae.
o colposcopic examination and biopsy are important.
o observation with regular follow up is required.
o there are three grades from mild to sever dysplasia as for CIN but
doesn’t have the same malignant potential
VIN III
o Itching is the most common symptom.
o Half of patients are asymptomatic.
o Most have visible or palpable abnormalities of the vulva (20% are
warty, and multicentric in about two third of cases).
o Most lesions are elevated ,of different color : may be white , red ,pink ,
or brown.

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 7 of 16
:
o inspection for abnormal areas.
o colposcopic examination of the entire vulva after 5 %
o acetic acid will highlight additional acetowhite areas.
o biopsy will confirm the diagnosis.
:
o regular follow up with multiple biopsy
o local superficial surgical excision with safe margin with primary
closure.
o for extensive lesions skinning vulvectomy with replacement by split-
thickness skin graft with the subcutaneous tissues are preserved.
o Laser ablation is used for multiple small lesions involving the clitoris,
labia minora and perineum.
It is uncommon (accounts 5% of genital cancer). It is a disease
primarily of the older age group with the majority of cases
presenting between the ages of 60 and 75.
:
o Ulcer or swelling on the vulva with soreness or irritation.
o Slight bleeding may occur.
o Offensive purulent discharge.
o Enlarged inguinal glands.
:
o Ulcer or hypertrophic growths in vulva .
o Lymph node examination

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 8 of 16
:
o The diagnosis is made by biopsy.
o As well as investigate patient as in other carcinoma
FIGO staging system is a surgical staging system revised in 1994:
Stage 0 carcinoma in situ ,intraepithelial carcinoma.
Stage I tumors confined to vulva or perineum ,lesion =or
<2 cm; no nodal metastasis.
Ia stromal invasion <or = 1 mm
Ib stromal invasion > 1 mm.
Stage II tumors confined to vulva or perineum ,
lesion >2 cm, no nodal metastasis.
Stage III any size tumors with adjacent spread and or unilateral
l.N.
metastasis.
Stage IV
IVa invades any or combinations of the following :
upper urethra,
bladder mucosa ,rectal mucosa ,pelvic bones or bilateral
regional L.N.
IVb any distant metastasis including pelvic L.N.
o radical excision of the vulva and inguinal lymph nodes on
both sides.
o radiotherapy in special situation.
:
o Overall 5 years survival is about 70%.
o Survival correlates significantly with the lymph node status
regardless the stage,

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 9 of 16
one L.N. involvement 50% 5 years survival
no L.N. involvement 90% 5 years survival
Vagina
The foreign bodies could be:
A. Therapeutic agents:
1. Packs and dressing of various kinds may be left in vagina
after operation.
2. Supporting pessaries.
3. Contraceptive device: (Sponges, occlusive caps, condoms
which have slipped out).
B. Articles inserted by the patient or entering accidentally.Mostly in
mentally retarded patient and children.
C. instruments for inducing abortion and labour as: laminaria tents,
chatheter.
D. menstrual tampone.
o it is varies from irritation to local vaginitis result in ulceration
of the vaginal walls and perforation and pressure necrosis and
this can involve neighboring structure to cause urinary and
faecal fistulae.
o infection may spread to produce salpingitis and peritonitis.
o carcinoma of vagina is a late squeal.
o The condition present as offensive vaginal discharge with
blood stained as the main symptoms.
: the foreign body must be removed.

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 10 of 16
o A vaginal secretion is normal in women in the reproductive
age group.
o It consists of transudate containing desquamated vaginal
epithelium, mucous secreated by cervical glands and
endometrial glands.
o The amount of discharge varies from woman to woman and
varies throughout the menstrual cycle(There is a cyclical
variation of the amount of secretion).
o Normal discharge is usually clear or white. Infections may
cause discharge of varying color, consistency, amount and
odor. A sudden change in discharge may signify pathological
condition.
:
o pregnancy.(due to increased estrogen production and greater blood
flow to the area around the vagina).
o in oral contraception users.
o At mid menstrual cycle
o During sexual intercourse.
o Exccesive vaginal discharge is a common gynaecological
complaint and can cause vulval symptoms. Comprehensive
clinical assessment is essential.
Excessive Vaginal discharge could be due to:
1. Physiological.
2. Infection:
(bacterial vaginosis, candidases, trichomonal vaginosis)
3. Foreign bodies as tampon, vaginal ring.
4. Malignant:
(endometrial ,cervical, vaginal cancer).
5. Fistula.
6. Atrophic vaginitis.

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 11 of 16
7. Large cervical ectropion
o It typically occurs in women of any age who experience a fall
in estrogenic stimulation to the urogenital tissues as in
o Menopausal women.
o Premenopausal women.
o Postpartum period.
o Lactation.
o During administration of antiestrogenic drugs (breast cancer
hormonal treatment).
o Prior to puberty.
:
o The patient may Present with vaginal bleeding, vaginal
discharge, or vaginal
o dryness and dyspareunia (pain during sexual intercourse).
o Superficial infection, with Gram-positive cocci or Gram-
negative bacilli, may be associated.
:
Shows pale, thin vaginal epithelium with loss of rugal folds
and prominent subepithelial vessels, sometimes with adjacent
petechial hemorrhage or ecchymoses.
:
o Requires oestrogen to restore the vaginal epithelium and pH.
o This is usually by topical oestrogen cream, but care must be
taken to avoid excessive absorption through the thinned
mucosa.Vaginal cream inserted nightly for a week and
repeated monthly to prevent atrophy.
o Alternatively in postmenopausal women, hormone

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 12 of 16
replacement therapy (HRT) can be used.
A fistula may be due to:
1. Trauma.
2. Carcinoma.
3. Crohn’s disease.
4. Childbirth : (Fistula of the anterior wall is now uncommon in
association with childbirth, but rectovaginal fistula may follow
an obstetric tear or extension of an episiotomy, and an
incomplete or inadequate repair).
5. Gynaecological surgery Fistulae involving ureter, bladder or
rectum may follow gynaecological surgery.
o It is seldom seen alone and is usually a vaginal extension of
CIN (Cervical Intra epithelial Neoplasia).
o Classification of intraepithelial neoplasias of the vagina
parallels that of the cervix VaIN 1, VaIN2, and VaIN 3.
o VaIN is usually asymptomatic and is diagnosed by abnormal
cytologic testing. Infrequently women complain of postcoital
staining or unusual vaginal discharge
o VaIN usually occurs in the upper third of the vagina on the
posterior wall
o VaIN lesions may be either single discrete or multifocal.
o Diagnosis is made by colposcopy.
o The usual treatment involves laser vaporization.
o It is rare gynaecological tumours accounting for 1-2% of all
gynaecological cancers.
o The peak incidence is between age 60 & 70 years.
o Vaginal carcinoma may be primary or secondary.

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 13 of 16
o Only 10-20% of vaginal carcinomas are primary.
o Squamous cell carcinoma is the most common malignant
tumor of the vagina
o Clear cell adenocarcinoma is found in women who had
exposure to diethylstilbesterol in utero (DES) and to a lesser
degree in post menopausal individuals.
o Metastatic tumors are the most common cancer found in the
vagina.
:
o direct extension from the cervical carcinoma.
o Endometrial cancer.
o Choriocarcinoma.
o From vulva.
o From rectum or anus.
o Distant metastasis may occur from primary carcinoma in the
breast or gastrointestinal tract.
:
o Usually occurs after the menopause and most commonly
affects the upper posterior wall.
o Vaginal bleeding mainly post coital.
o Offensive watery discharge.
o Fistula (rectum, bladder).
FIGO staging used of vaginal carcinoma staging.
Stage I invasive cancer confined to the
vaginal mucosa.
Stage II subvaginal extension not involving

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 14 of 16
the pelvic side wall.
Stage III extends to pelvic side walls.
Stage IVa extends to mucosa of bladder &rectum
Stage IVb spread beyond the pelvis.
:
o Surgery: removal of whole vagina, uterus, and pelvic lymph
nodes
o Radiotherapy in some cases.
Lesion of urethra:
o Small, fleshy bright red out-growths of the distal edge of the
urethra.
o It is always single lesion arises from the posterior wall of
urethrra
o Usually seen in post-menopausal women. there is high rate of
recurrence after treatment.
:
1.No symptoms
2.Symptomatic:
A. Very tender causing dysparunia or pain on micturition.
B. Slight bleeding may occur.
:
o Topical estrogen therapy.
o If no response biobsy should be done to exclude serious

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 15 of 16
morphology. Once malignancy ruled out, it can be treated by
surgery either by:
o Excision or destruction by diathermy.
It usually found in the distal third of posterior urethral wall
bulging towards the vagina. It's incidence is 3%.
:
o It is vary but usually include frequency, dysuria, dysparunia,
voiding difficulties and recurrent urinary tract infection. Post
micturition dribble is classical symptom.
o Vaginal examination can show:
o No physical sign.
Or
o suburethral mass.
o Tenderness can be palpated.
: Voiding cystourethrogram.
:-
o Surgical repair if patient affected by symptoms.
o Treatment by marsupilization and vaginal diverticulectomy.
o DES is a drug that was administered frequently to pregnant
women who were at high risk for early pregnancy loss during
the 1940’s through the 1960’s.
o it can be the cause of :
1. Vaginal Adenosis
Vaginal adenosis refers to the replacement of the
normal squamous epithelium of the vagina by
columnar epithelium. It is asymptomatic and presents

Lecture 1
النسائية
د. أحمد جاسم
Page 16 of 16
as red, granular patches on the vaginal mucosa.
Benign but rarely, may give rise to clear cell
adenocarcinoma.
2. Structural changes of the cervix and vagina and uterus.
These are in the form of:
Transverse vaginal septum.
Cervical hypoplasia.
T-shaped uterus.
others
3. Exposed individual have an increased risk of abortion,
preterm labour, ectopic pregnancy.
4. Clear cell adenocarcinoma
It affects young women, average 17 years old. Two
thirds of patients have history of in utero DES exposure.
The risk in exposed population is 1 in 1000.
By: Mu’taz Fathi
