
1
Fifth stage
Radiology
Lec-5
.د
محمد ميسر
28/10/2015
Nuclear medicine
Nuclear medicine is a medical specialty involving the application of radioactive substances
in the diagnosis and treatment of disease.
Diagnostic
In nuclear medicine imaging, radiopharmaceuticals are taken internally, for example,
intravenously or orally. Then, external detectors (
) capture and form
images from the radiation emitted by the radiopharmaceuticals. This process is unlike a
diagnostic X-ray, where external radiation is passed through the body to form an
image.
There are several techniques of diagnostic nuclear medicine.
There are a number of different types of scintigraphy, including bone, pulmonary,
cardiac, thyroid , parathyroid & renal .
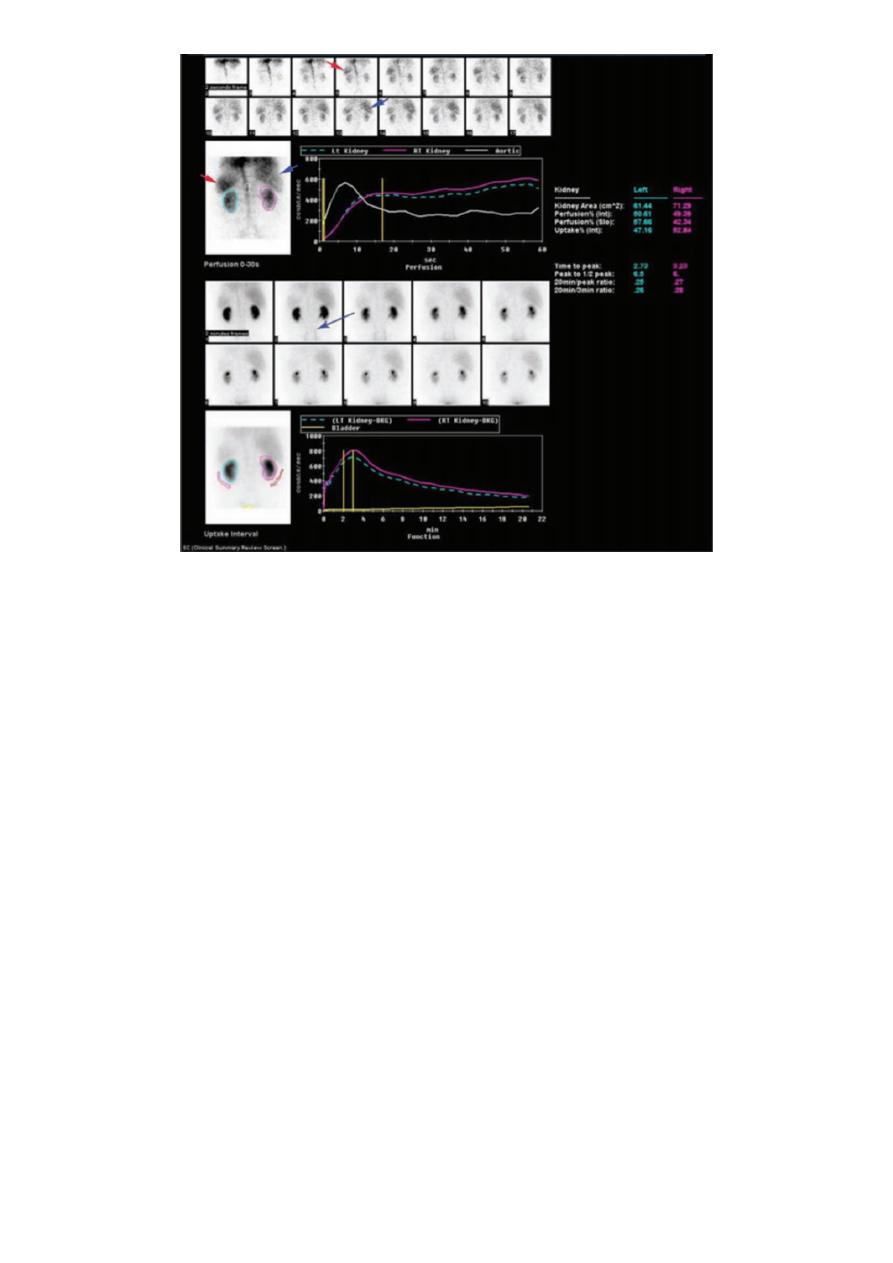
Renal scintigraphy
Despite advances in US, CT, and MRI, there remain many areas where scintigraphy remains
the easiest, least expensive, and most accurate test. Radiopharmaceuticals are well suited
for evaluating renal function including blood flow, glomerular filtration rate (GFR); effective
renal plasma flow (ERPF); nephron uptake and clearance; renovascular hypertension/
Renal artery stenosis (RAS); acute and chronic renal failure, ischemic nephropathy;
pyelonephritis, trauma or surgical complications; renal transplant function, obstruction, and
acute or chronic rejection; and ureteral obstruction and vesicoureteral reflux.
Radionuclide renal studies are safe, minimally invasive and expose the patients to radiation
doses comparable or less than competing radiologic procedures
pictures of the kidneys are taken with a special camera following the injection of a
weak radioactive solution (radioisotope), known as Tc DMSA or DTPA
2
Risks
Because the doses of radiotracer administered are small, diagnostic nuclear medicine
procedures result in relatively low radiation exposure to the patient, acceptable for
diagnostic exams. Thus, the radiation risk is very low compared with the potential
benefits.
Allergic reactions to radiopharmaceuticals may occur but are extremely rare and are
usually mild. Nevertheless, you should inform the nuclear medicine personnel of any
allergies you may have or other problems that may have occurred during a previous
nuclear medicine exam.
Injection of the radiotracer may cause slight pain and redness which should rapidly
resolve.
limitations
Nuclear renal images cannot reliably differentiate between cysts and tumors.
Nuclear medicine procedures can be time-consuming. You will be informed as to how
often and when you will need to return to the nuclear medicine department for further
procedures.
The resolution of structures of the body with nuclear medicine may not be as clear as
with other imaging techniques, such as CT or MRI. However, nuclear medicine scans
are more sensitive than other techniques for a variety of indications, and the functional
information gained from nuclear medicine exams is often unobtainable by any other
imaging techniques.
