
© 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved.
Infant
Reflexes and
Stereotypies

Infant vs. Lifespan Reflexes
Most
“infant” reflexes
do not last beyond the
first year
.
Infant reflexes
may not completely disappear.
• May be inhibited by maturing CNS.
• May be integrated into new movements.
Infant reflexes and stereotypies are very important in
the process of development
.

Why is the study of infant reflexes important?
• Dominant form of movement
for last 4 months prenatally
and first 4 months postnatally.
• Primitive reflexes
critical for human survival
.
• Postural reflexes believed to be
foundation for later
voluntary movements
.
• Appearance and disappearance helpful in
diagnosing
neurological disorders
.
Infant Reflex
Future Voluntary Movement
Crawling
Crawling
Palmar grasp
Grasping
Stepping
Walking
Role of Reflexes in Developing Future Movement
Postural reflexes
are related to the development of
later
voluntary movement
.
Reflexes can determine
level of neurological maturation
.

Primitive Reflexes
• Palmar Grasp
• Sucking
• Rooting
• Moro reflex(Startle reaction)
• Asymmetric Tonic Neck
• Symmetric Tonic Neck
• Plantar Grasp
• Babinski reflex
• Parachute reflex
• Landau reflex
• Glabellar reflex

Reflex
Concern
Moro reflex
if lacking or asymmetric
1. brachial plexus paralysis (Erb's palsy)
2. clavicle injury.
3. fractured arms.
4. cerebral paralysis.
Asymmetric tonic
reflex
May indicate cerebral palsy if persists past
normal time.
Reflexes as Diagnostic Tools

Stimulus /
Response
S: Palm stimulated
R: 4 fingers (not thumb) close
Duration
4 or 6 months postpartum
Concerns
No palmer grasp may indicate(spasticity).
Other
Grasping may predict handedness in
adulthood
Voluntary reaching to the objects
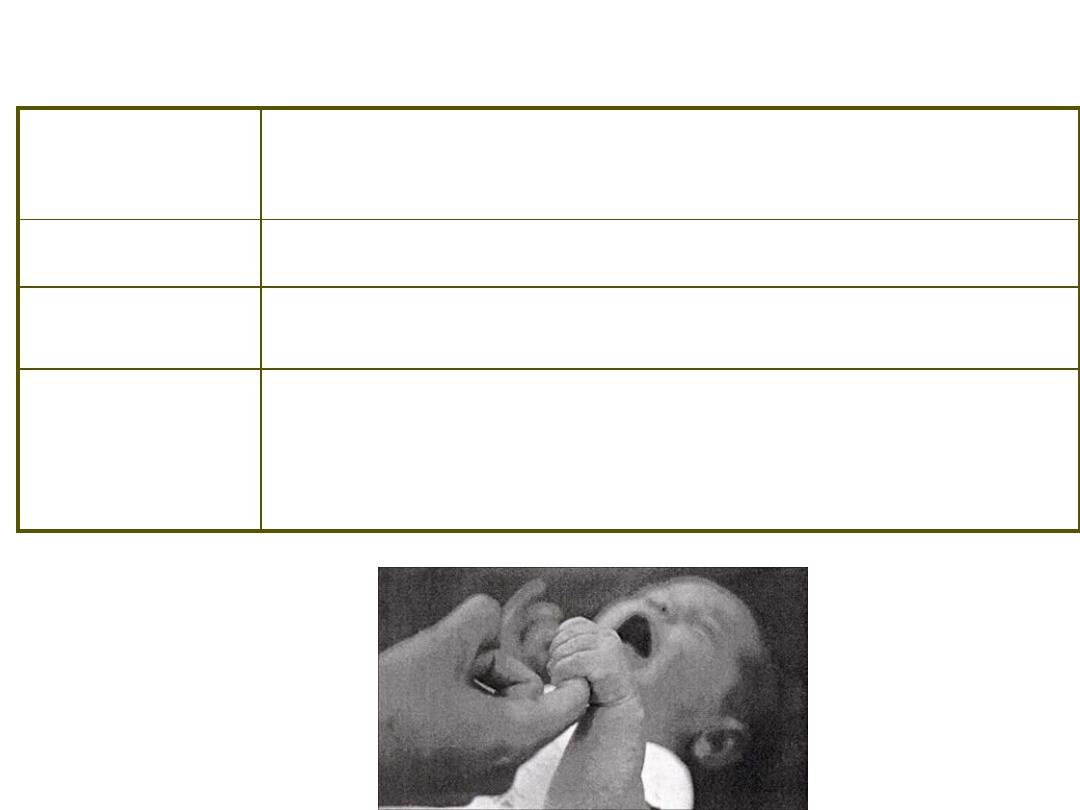
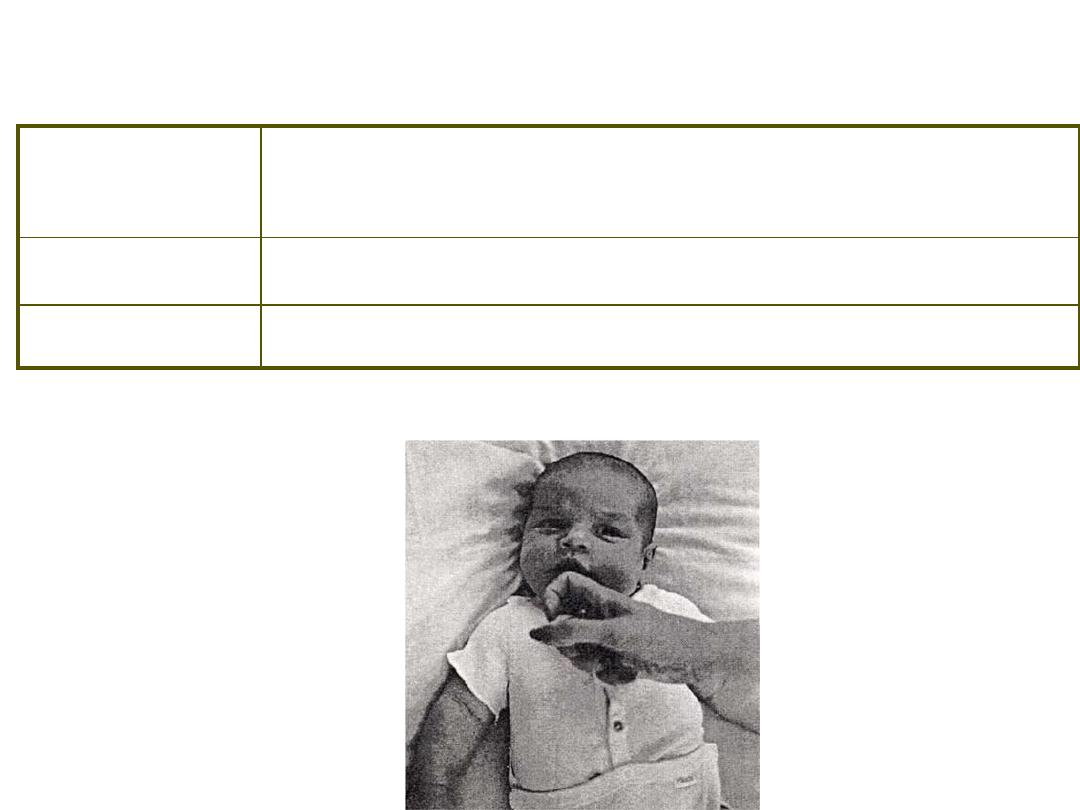
Primitive Reflexes ~ Palmar Grasp
Stimulus /
Response
S: touch of lips
R: sucking action
Duration
3 to 4 months postpartum
Other
Often in conjunction with searching reflex
Primitive Reflexes ~ Sucking

Stimulus /
Response
S: touch cheek or side of mouth by the edge
of finger .
R: head moves toward stimuli
Duration
3 to 4 months postpartum
Concerns
No reflex problematic for nutrition
No reflex or lack of persistence may be sign of
CNS or sensorimotor dysfunction.
Other
Often in conjunction with sucking reflex.
Primitive Reflexes ~ Search or rooting reflux

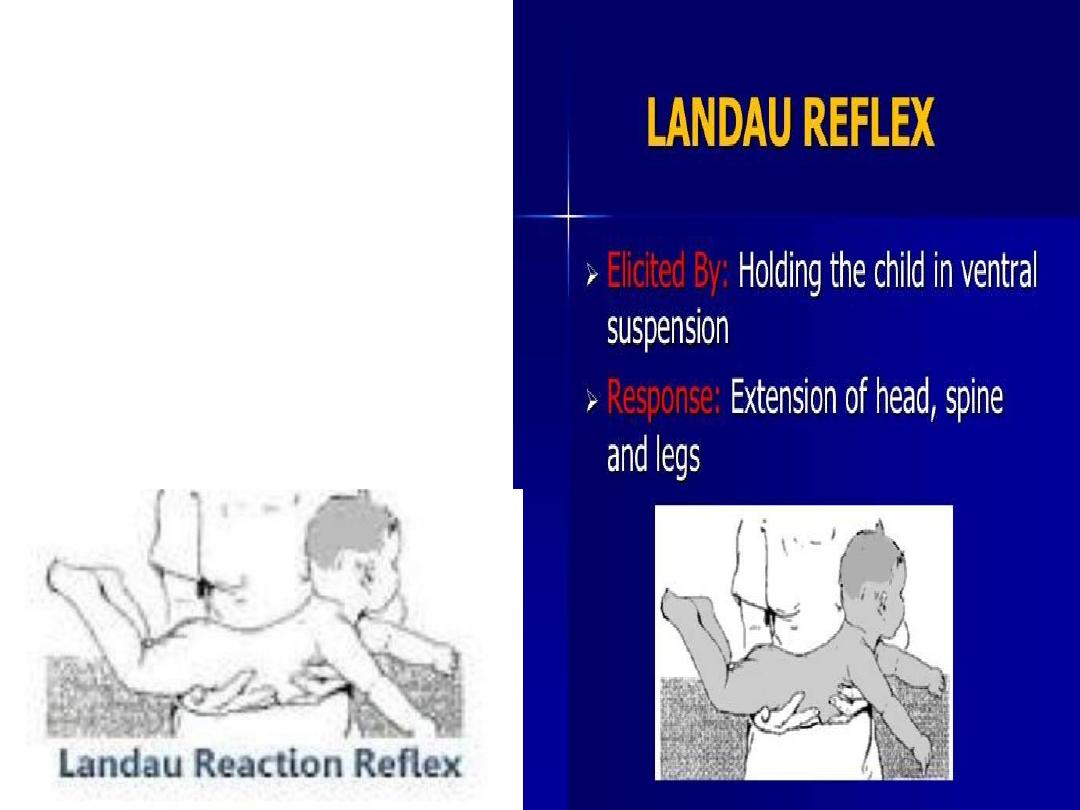
Primitive Reflexes ~ Landau reflex
S:- position of the infant when held
horizontally in the air in prone
position.
R:- maintain a convex arc with the
head raised and the legs slightly
flexed
Landau reflex
Appears at 3 months after birth and
lasts until up to 12 months to 24 months
of age
Duration
An abnormal Landau reflex may
indicate hypotonia or hypertonia and
may indicate a motor development
issue
Concern
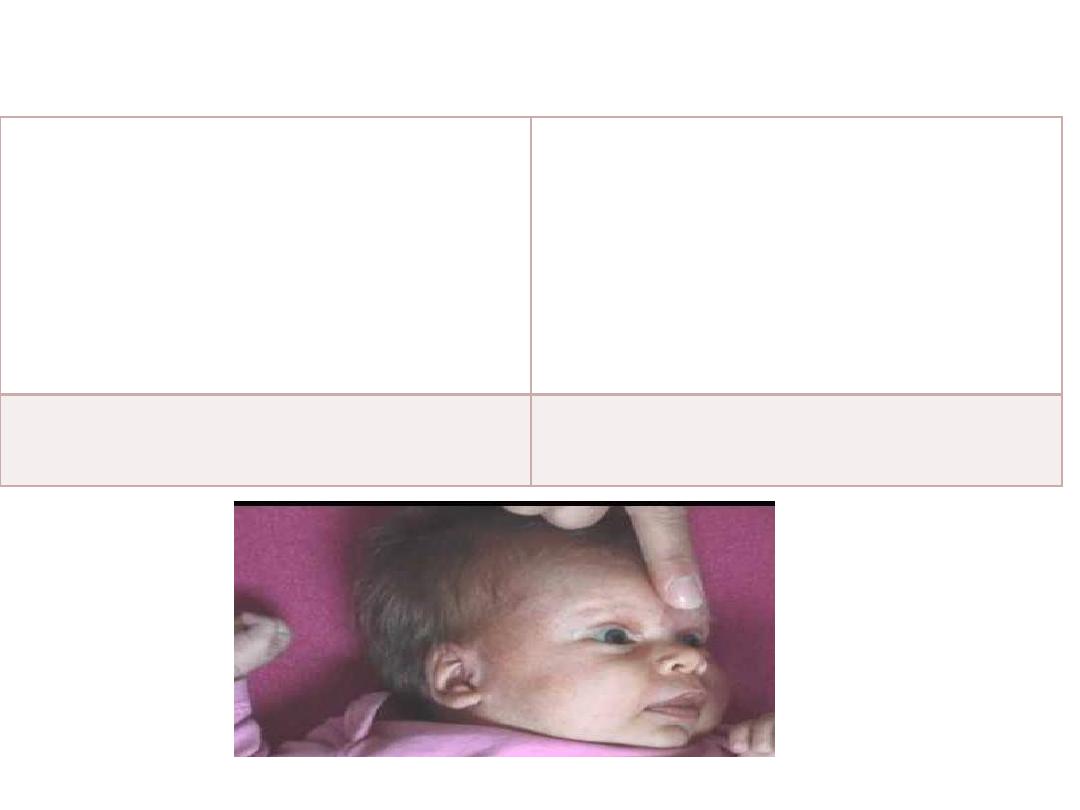

Primitive Reflexes ~ glabbellar reflex
S:-repetitive tapping on the
forehead.
,near the eyes.
R:Subjects blink in response to the
first several taps.
Glabbellar reflex
4-6
months
Duration
Stimulus /
Response
S:head is supported by the palm (2cm above the table)&
then suddenly released (the other palm will receive the
dropping head)
R:Normal response of baby will be (
).
he/she spreads his/her arms (abduction & extension of
arms);he will open his hands.
he pulls his arms in but his legs are extended .
sometimes he cries
Duration
4-6 months postpartum
Concerns
An asymmetrical response indicate
1-brachial plexus paralysis (
2-clavicle injury.
3-fractured arms.
4-cerebral paralysis.
Primitive Reflexes ~ Moro
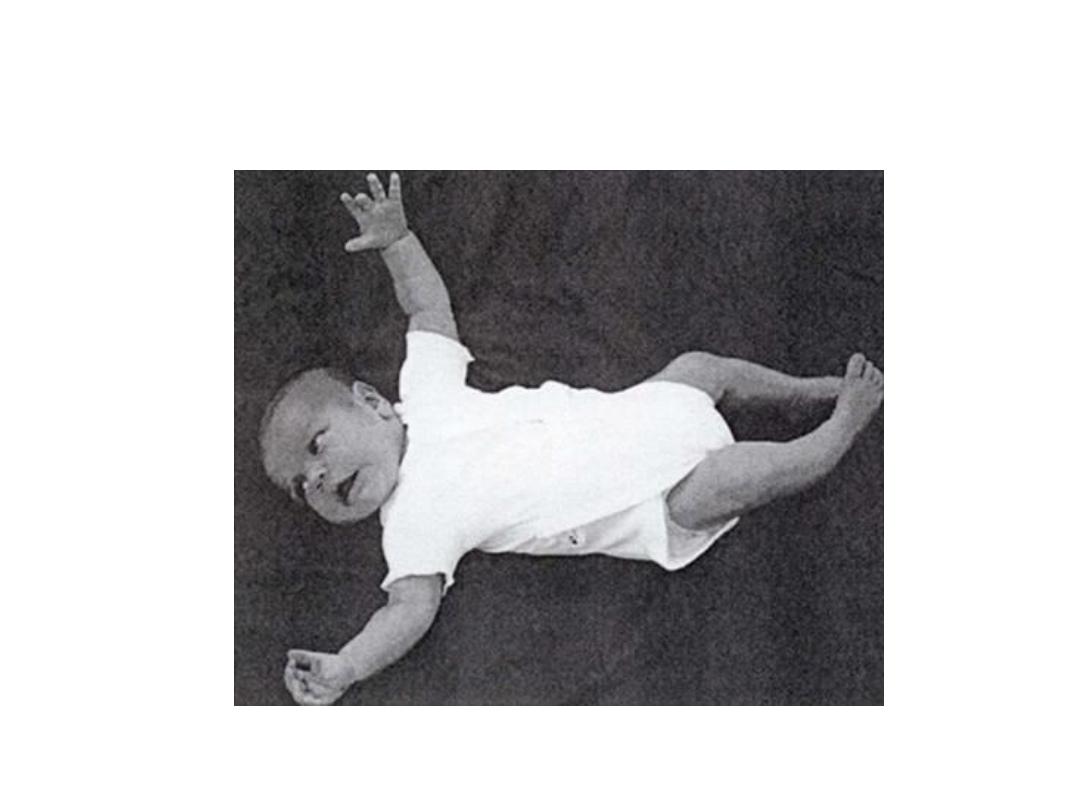

Primitive Reflexes ~ Moro
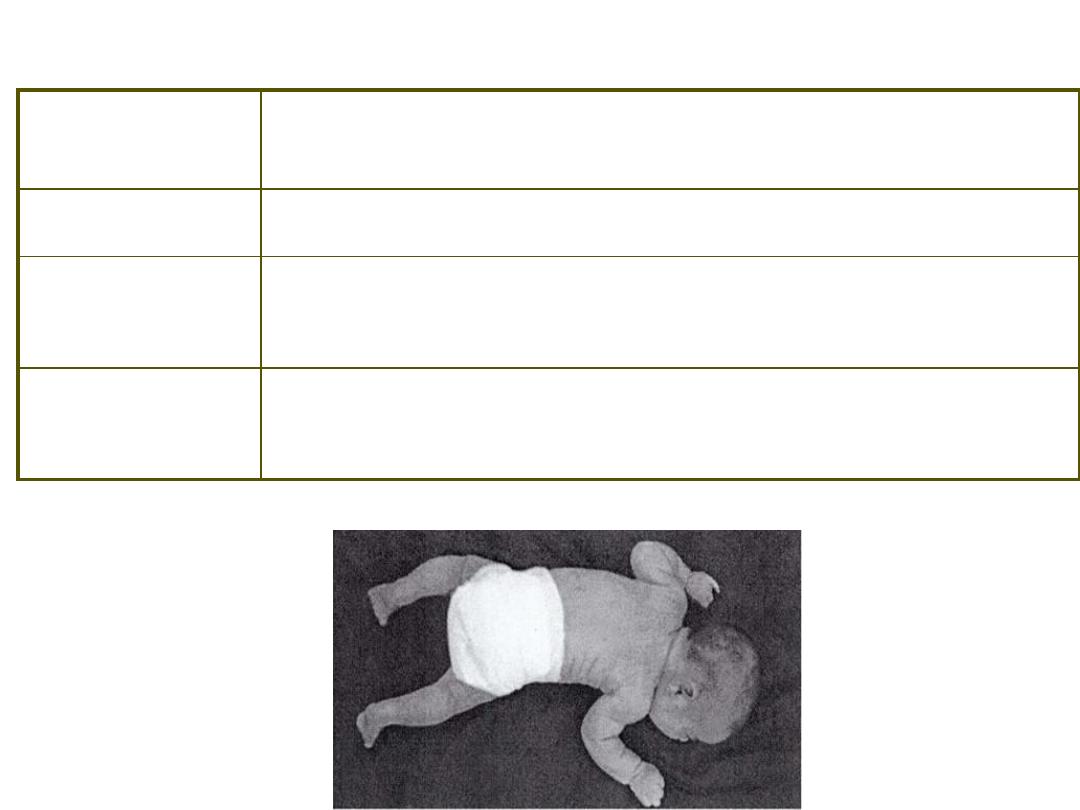
Stimulus /
Response
S: Prone/supine position, turn head to one side
R: Limbs flex on one side, extend on other side
Duration
3-4 months
Concerns
Facilitates bilateral body awareness
Facilitates hand-eye coordination
Other
Also called ‘fencer’s’ position
Primitive Reflexes ~ Asymmetric Tonic Neck

Stimulus /
Response
S: Baby sitting up and tip forward
R: Neck and arms flex, legs extend
S: Baby sitting up and tip backward
R: Neck and arms extend, legs flex
Duration
3-4 months
Concerns
Persistence may impede many motor skills and cause
spinal flexion deformities
Primitive Reflexes ~ Symmetric Tonic Neck
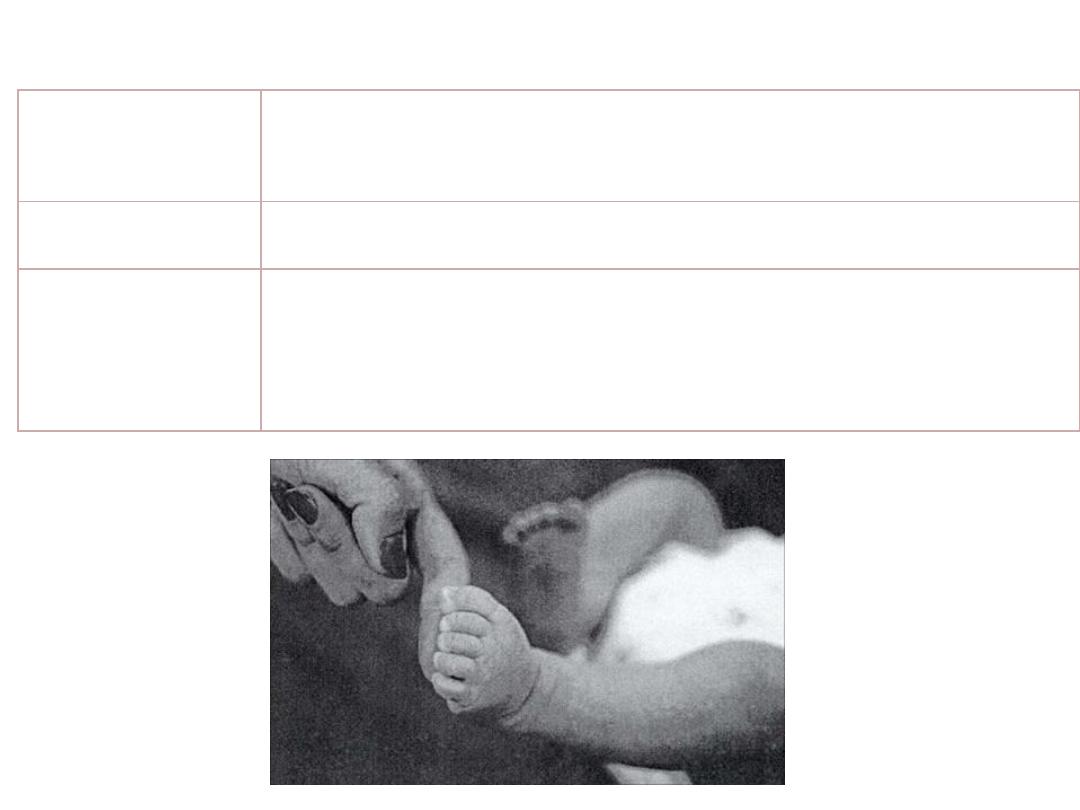
Stimulus /
Response
S: Touching the ball of foot
R: Toes grasp
Duration
Birth – 1 year
Other
Must disappear before the baby can stand or
walk.
Issue of shoes versus no shoes?
Primitive Reflexes ~ Plantar Grasp

Stimulus /
Response
S: Stroke bottom or lateral portion of foot
R: Great toe turns downward
Duration
Birth – 4 months
Concern
Test of the pyramidal tract (i.e. ability to perform
conscious / voluntary movement)
Primitive Reflexes ~ Babinski

Stimulus /
Response
S: Pressure to both palms or hair to hand
R: Eyes close, mouth opens, and/or neck flexes
(which tilts the head forward)
Duration
Birth – 3 months
Other
Also called the
Babkin reflex
Primitive Reflexes ~ Palmar Mandibular
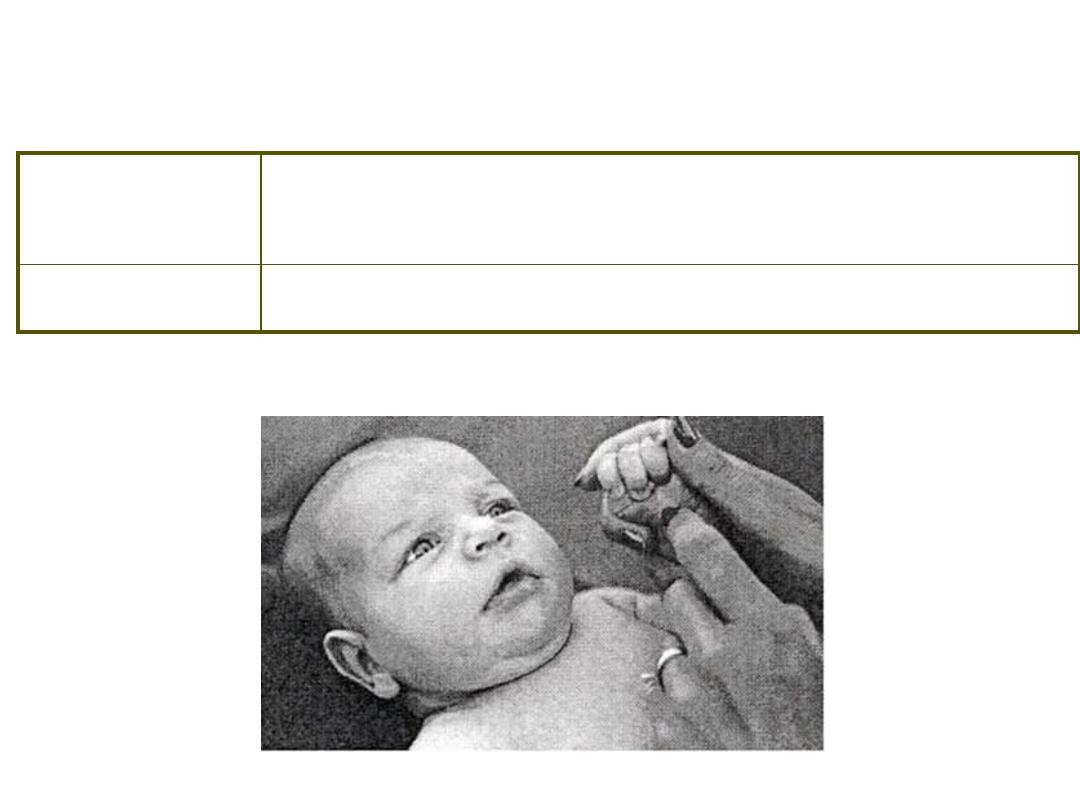

Stimulus /
Response
S: Scratch base of palm
R: Lower jaw opens and closes
Duration
Birth – 3 months
Primitive Reflexes ~ Palmar Mental

Postural Reflexes
o Stepping
o Crawling
o Swimming
o Head and Body Righting
o Parachuting
o Labyrinthine
o Pull Up
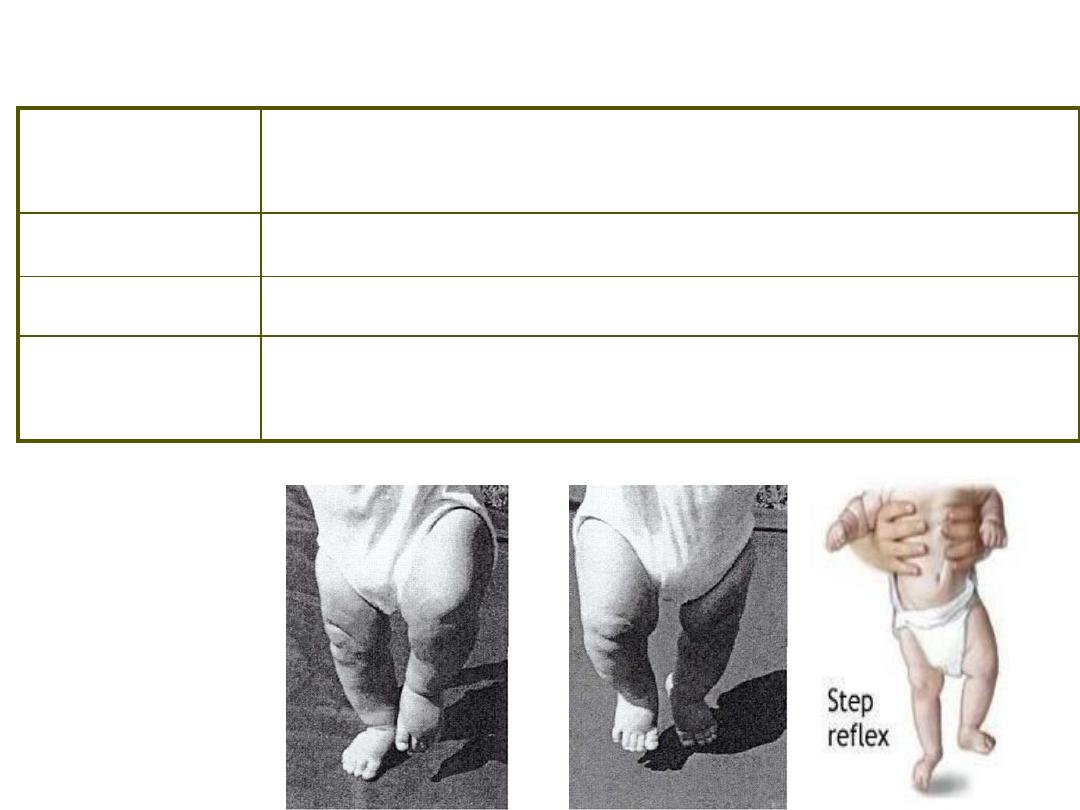
Stimulus /
Response
S: Infant upright with feet touching surface
R: Legs lift and descend
Duration
6months.
Concerns
Essential forerunner to walking
Other
Developmental changes in reflex over time
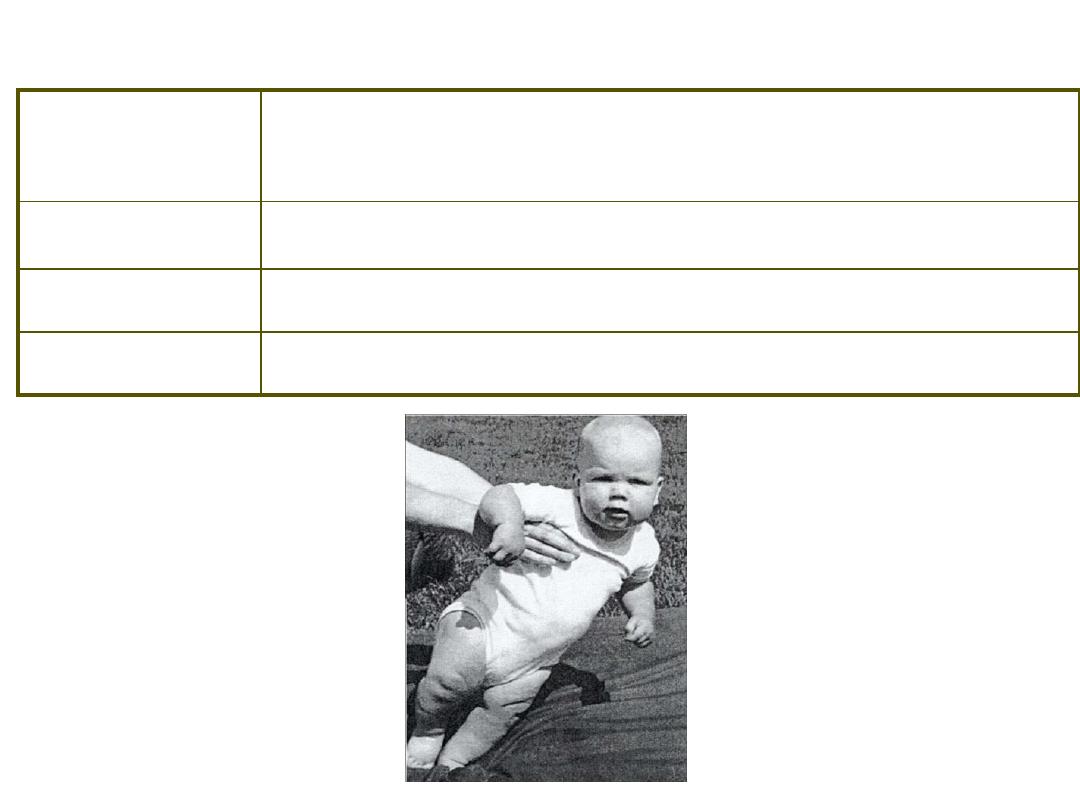
Postural Reflexes ~ stepping
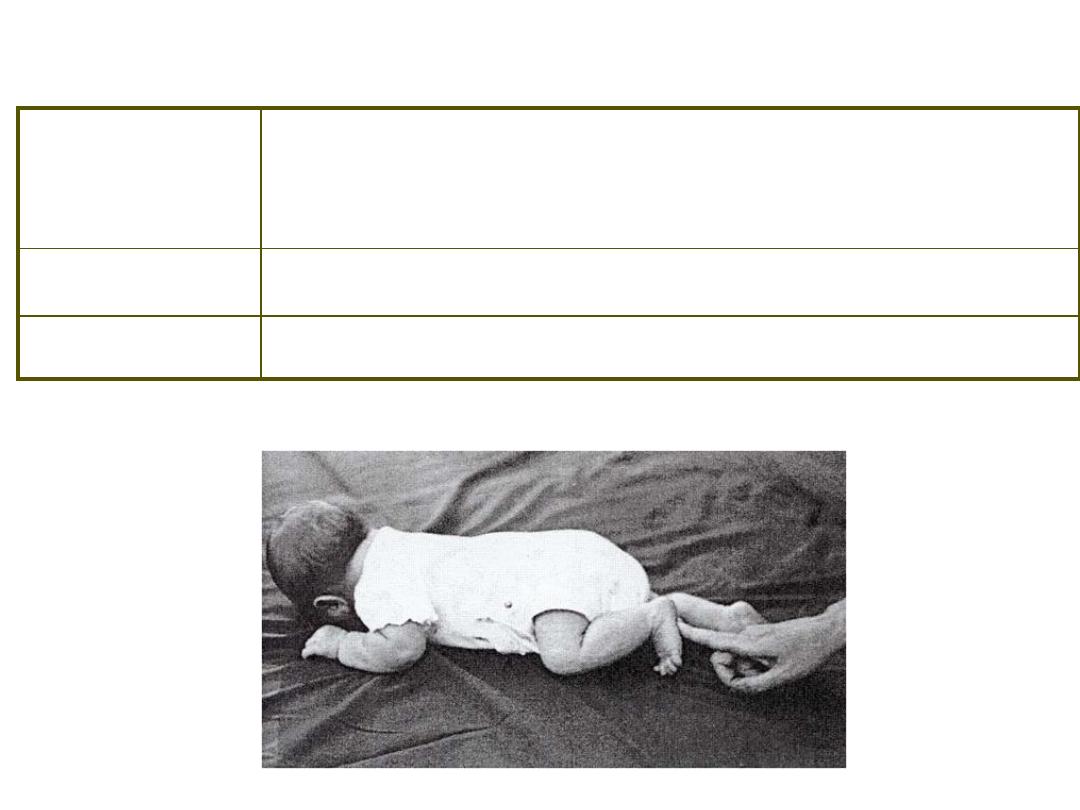
Stimulus /
Response
S: Prone position on surface, stroke alternate
feet R: Legs and
arms move in crawling action
Duration
Birth – 3-4 months
Concerns
Precursor to later voluntary creeping
Postural Reflexes ~ Crawling
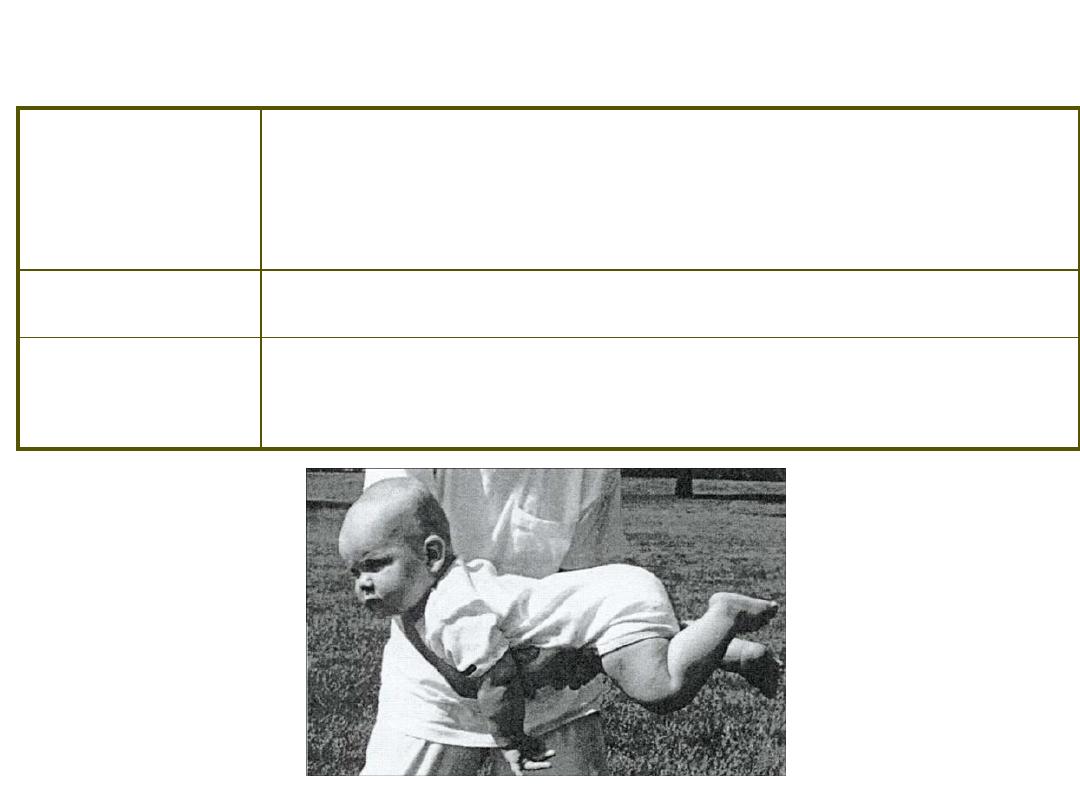

Stimulus /
Response
S: Infant held horizontally
R: Arms and legs move in coordinated
swimming type action
Duration
2 weeks after birth – 5 months
Other
Recognition of reflex led to popularity of
infant swim programs
Postural Reflexes ~ Swimming

Stimulus /
Response
S: Off balance in upright position R:
Protective movement in direction of fall
Duration
Appears at 9months & never disappear
Other
Also called
propping reflex
Occurs downward, sideways, & backward
Postural Reflexes ~ Parachuting
Stimulus /
Response
S: Baby held upright, tilted in one direction R:
Baby tilts head in opposite direction
Duration
2-3 months – 1 year
Concerns
Related to upright posture
Other
Also considered primitive reflex
Postural Reflexes ~ Labyrinthine
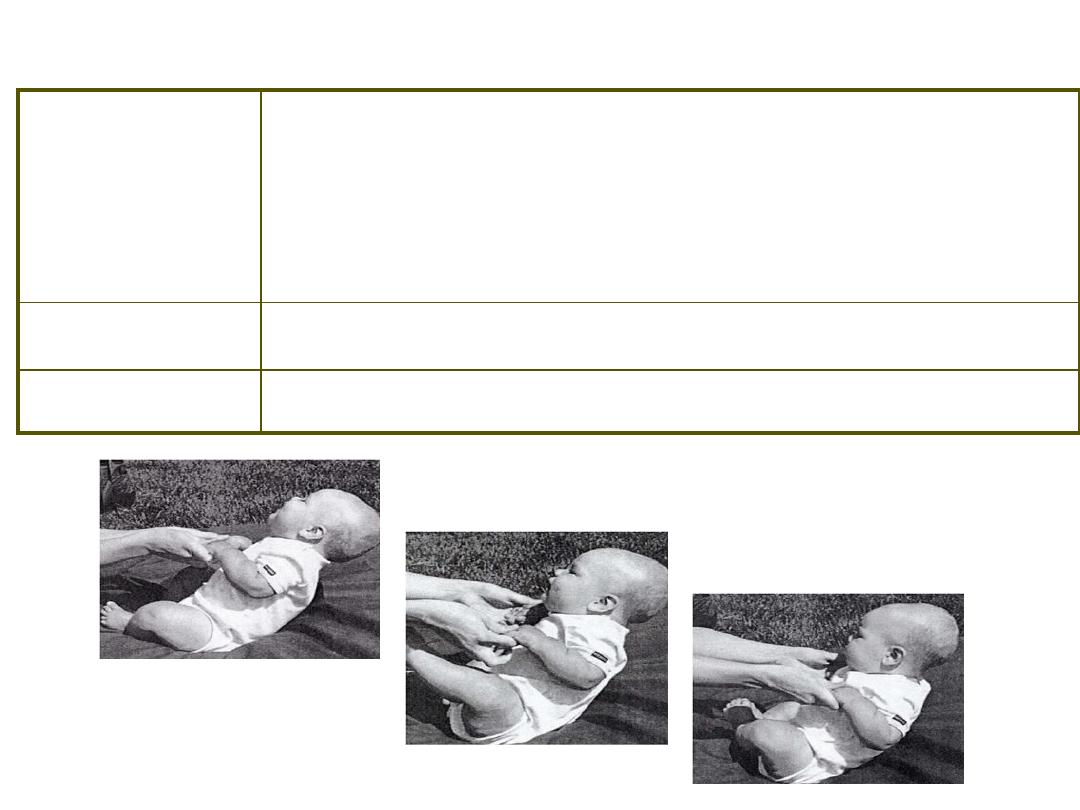

Stimulus /
Response
S: Sitting/standing, hold hands, tip in one
direction
R: Arms flex or extend in to maintain upright
position
Duration
3 months – 1 year
Concerns
Related to upright posture
Postural Reflexes ~ Pull Up
