
1
Fifth stage
Medicine
Lec-4
د.خالد نافع
17/11/2015
HEMOLYTIC DESORDERS
Red Cell Turnover and Life Span
2.5 million red cells are removed from the circulation every second.
BM produces 200 billion new red cells (reticulocytes) each day. These cell survived for 120
days before they are removed by the RES ( BM, liver, spleen).
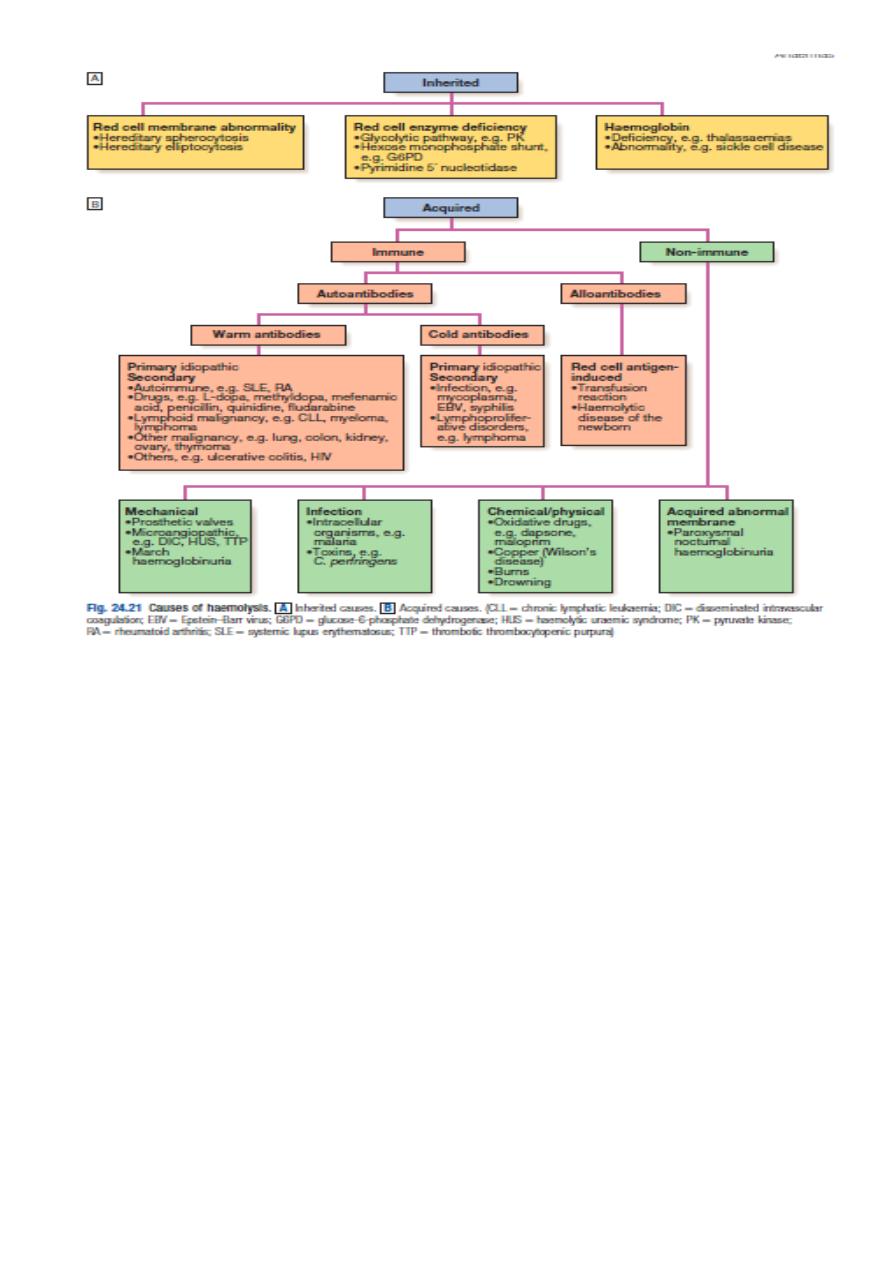
CLASSIFICATION
1.Acute versus chronic .
2.Acquired versus congenital.
3.Intra-vascular versus extra-vascular.
4.Intra-corpuscular versus extra-corpuscular.
HEMOLYTIC ANAEMIA
Definition
HA is a decrease in the total number of circulating erythrocytes that is caused by the
premature destruction or removal of red cells from the circulation.
Anaemia will result only if the rate of RBC destruction exceed the BM response (un
compensation).
Clinical features:
2
Laboratory manifestation:
I. signs of excessive RBC destruction:
• Decrease RBC life span
• Increase catabolism of heme.
• indirect hyperbilirubinaemia.
• increase rate of bilirubin production.
• increase rate of urobilinogen production
• increase LDH activity .
• Absence of serum haptoglobin
II. Signs of intra-vascular hemolysis
• Hemoglobinaenemia.
• Hemoglobinuria.
• Haemosiderinuria.
• Met-heme-albuminaemia.
• Decrease hemopexin
• Decrease Hb level.
3
III. Signs of accelerated erythropoiesis
• Blood
o Reticulocytosis (polychromasia in the blood film).
o Macrosytosis.
o Normoblastaemia .
o Leukocytosis and thrombocytosis
• Bone marrow.
o Erythroid hyperplasia.
o Ferrokinetics:
increase plasma iron turnover
increase erythrocyte iron turnover
IV. Lab tests useful in the differnitial diagnosis:
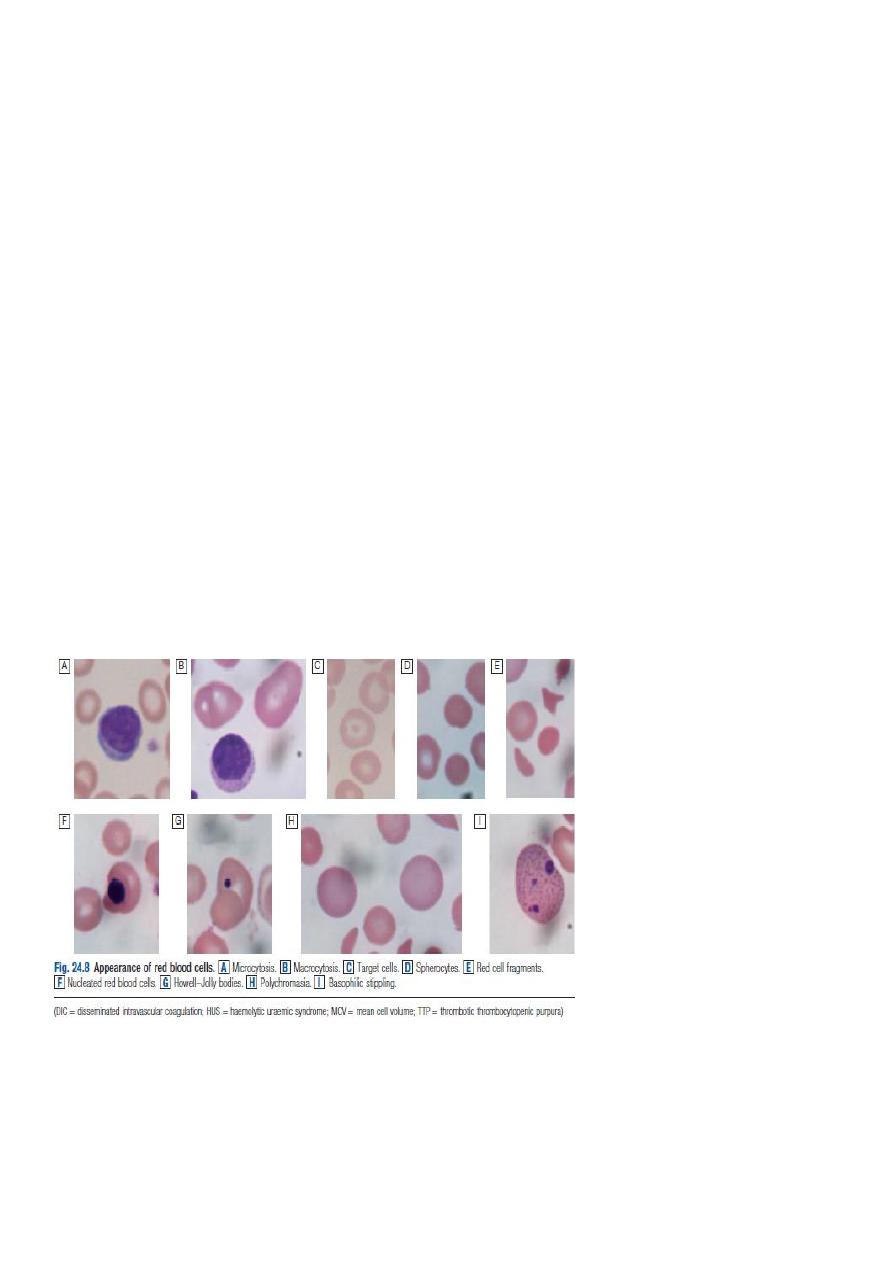
• Morphology (blood film findings) (spherocytes, elliptocytes, acanthocytes,
stomatocytes, target cells, fragmented RBCs, Autoagglutination)
• Direct coomb’s test (Direct anti-human globulin-DAT)
• Osmotic fragility test
• Auto-hemolysis test.
• Hb-electorphoresis test
• Screening test for G6PD deficiency
• Sickling test
DIRECT ANTIHUMAN GLOBULIN (DAT):
Testing the patient RBC for their invivo sensitization. It is used in ;
1.Transfusion reaction,
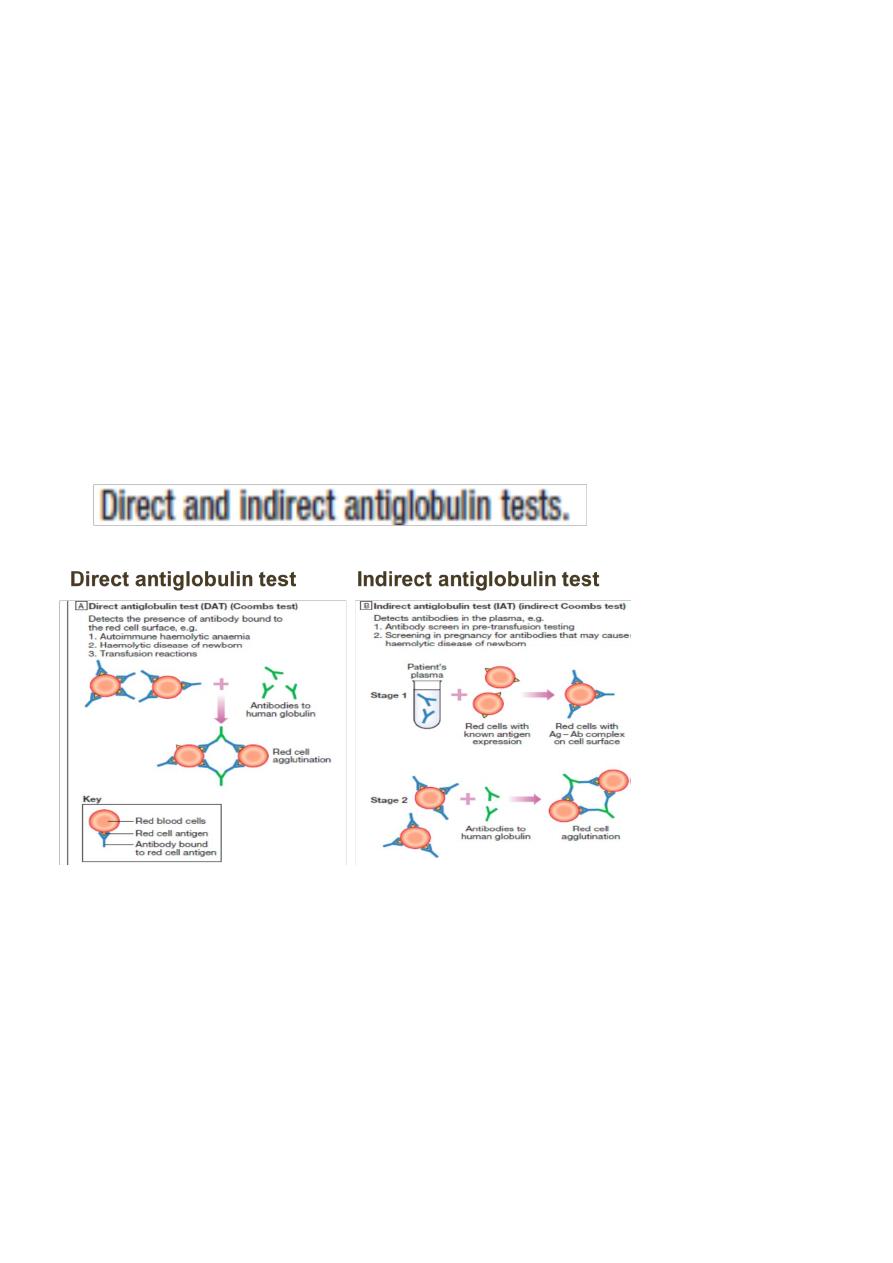
4
2. Hemolytic disease of the newborn.
3. Auto immune hemolytic anaemia(AIHA)
4.Drug-induced hemolytic anaemia.
INDIRECT ANTI-HUMAN GLOULIN TEST (IAT)
Testing the patient serum for the presence of irregular antibodies (Allo);
1.Part of cross matching.
2.Antibody screening & identification.
3.Titration of antibodies.
Differential Diagnosis Of Hemolytic Anaemia:
1.Anaemia with increase Reticulocytes:
a. Haemorrage
b. Recovery from deficiency of iron, B12, folate.
c. Recovery from marrow failure as in cessation of alcohol cosumption.
2.Anaemia with acholuric jaundice;
a.Ineffective erythropoiesis.
b.Loss of blood in to body cavity.
3.Acholuric jaundice without anaemia.
4.Marrow invasion.
5.myoglobulinuria.
