Introduction to Pharmacology
د. شامل هاشم ألنعيميبكالوريوس طب وجراحة
ماجستير سموم
دكتوراه أدوية
Objectives:
At the end of this lecture, the students will be able to:
1.Define some pharmacological terms
2. List the major factors that determine the properties of ideal drug3. Compare between potency and efficacy.
4.List the factors that determine the intensity of drug response
Drug: A drug is a chemical that affects physiological and biochemical functions in a specific way.
Pharmacology: can be defined as the study of drugs and their interactions with living systems.
Study the physical and chemical properties of drugs as well as their biochemical and physiological effects.
Clinical pharmacology: The use of drugs to diagnose, prevent or treat diseases. Or simply is the medical use of drugs.
Toxicology: It is part of pharmacology which deals with the undesired or toxic effect of drugs.
Pharmacy: It is the science that deals with preparing and dispensing drugs ( medicines)
Pharmacogenetic: It is the science that concern with drug response that are governed by heredity.
EffectivenessSafetySelectivityReversible action
Properties of an Ideal DrugEase of administrationFreedom from drug InteractionsLow costChemical Stability
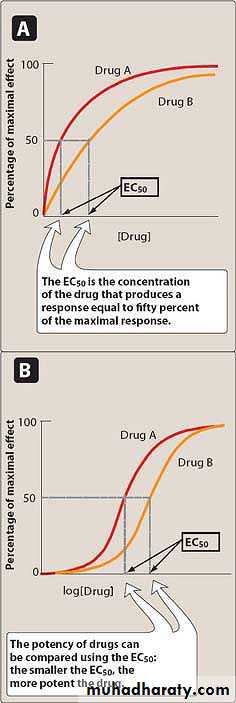
Efficacy: is the capacity of a drug to produce a specific effect.e.g.1 Meperidine vs pentazocine
e.g. 2 Amiloride vs Bendrofluazide
Potency: Refers to the amount of drug (in weight) that elicit an effect.
e.g. Morphine 10mg can relief severe pain , meperidine 100 mg can relief the same degree of pain relived by morphine, so morphine is more potent than meperidine.Prescribed doseAdministered doseConcentration at sites of action
Factors that determine the intensity of drug responsesAdministration: Medication Errors and Patient compliance
Pharmacokinetics processes.Individual Variations: Physiological variables, Pathological variables, genetic variables and drug interactions.
Pharmacodynamics: Drug receptor interaction and patient functional state.
Sources of Individual Variations:
Drug interaction
Physiologic variables: age, sex, weight, obesity