
1
Fifth stage
Surgery-Ortho
Lec-6
د. يقضان
29/11/2015
TUBERCULOUS INFECTION OF BONE AND JOINT
The incidence of TB. Infection is decrease in the developed countries during 1960 s and
1970 s of the last century due to improvement in the general health programs, and the
improvement in the chemotherapy .
There is increase in incidence of extrapulmonary TB.infection in the last 2 decades due to
i.v. drug abuse , AIDS .
The predisposing factors: all the conditions that decrease the defense mechanism of the
body like ch. Debilitating diseases , drug abuse , prolong corticosteroid medication , AIDS .
Pathology
TB. M.O. either human type or bovine type ,
Enter the human body through :
1- droplet inhalation to the lung .
2- to the G.I.T. by infected milk .
3- through a wound in the skin .
This type of M.O. not cause pyogenic infection like other bacteria , but it cause
Granulmatous reaction which associated with tissue necrosis and caseation .
Primary complex :initial small lesion in the lung , pharynx or gut with lymphatic spread to
regional lymph node (primary complex) .
Secondary spread :in case of decrease resistance to original infection ; wide spread via the
blood lead to miliary TB.or meningitis or pulmonary TB. .
Tertiary TB. : bone and joint are affected in 5% of patient with TB. ; skeletal TB. Affect
mainly synovium of the larg joint and the vertebral body .
The infection either started in the bone and spread to the joint or vice versa .
Bone lesion spread quit rapidly ; epiphyseal plate is not act as a barrier .
At the beginning the synonvium will be involved by the infection , this lead to effusion ;
then panus of granulation tissue extend across the joint and destroy the articular cartilage
slowly .
2
The increase vascularity cause local osteoporosis .
If the condition not treated , the infection may extend into the surrounding tissue to
produce cold abscess and it is cold only in comparison to a pyogenic abscess and this may
burst through the skin cause chronic discharging sinus .
If this condition treated early , there will be no residual injury to the joint .
If the articular cartilage is damaged then the healing will be by fibrosis .
Clinically
The patient is usually a child or young adult , complain from pain and in the superficial joint
there is marked swelling .
In the advanced cases there may be fever , lassitude and loss of weight .
The pain is mainly at night ; and this due to muscle relaxation at sleep ; also in advanced
cases there will be muscle wasting and joint stiffness .
In the back the patient develop low grade back ache ; and some time the patient presented
with visible swelling (abscess) in the groin or lumber spine( to one side of the mid line) .
Or the patient presented with localized kyphosis due to collapse of the body of the
vertebrae .
Lastly the patient may presented with weakness and loss of sensibility of the lower limb .
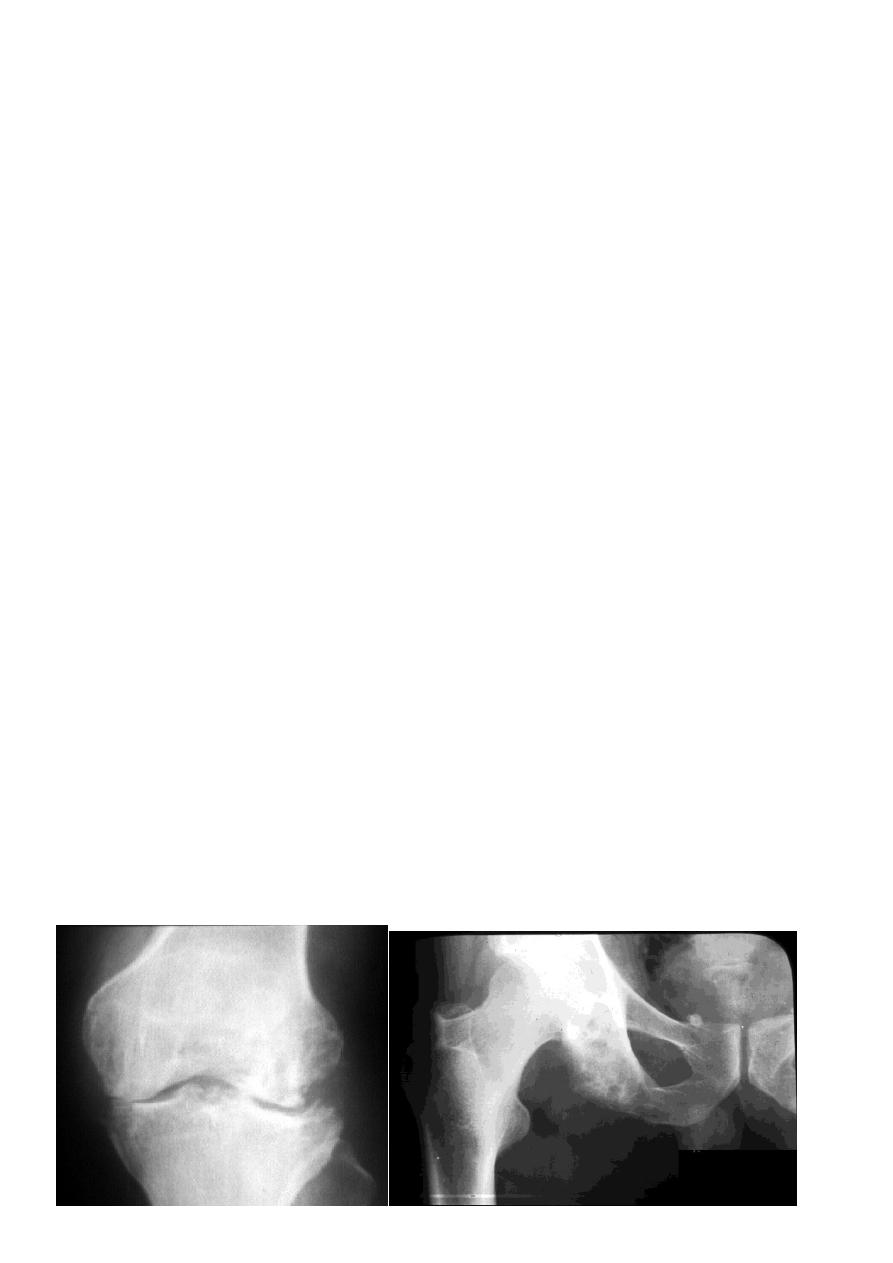
X-ray of TB.infection :
Soft tissue swelling and periarticular osteoporosis are characteristic ; the bone ends take on
a washed out appearance and narrow joint space .
In spine there is bone erosion and collapse ;
Soft tissue shadow may define a paravertebral abscess .
TB.arhritis(dec.joint space, periarticular osteoporosis)

3
Investigation
ESR increased .
Lymphocytosis .
Mantoux test +ve (sensitive not specific) .
Synovial fluid aspiration: cloudy, increase protein , acid fast bacilli identified in the synovial
fluid in 10 – 20% of the cases ; and culture is +ve in 50%of the cases .
Synovial biopsy show characteristic histological feature ; culture of the biopsy is +ve in 80%
of the cases .
Differential diagnosis
1- transient synovitis
2- pyogenic arthritis
3- monoarticular rheumatoid arthritis
4- hemorrhagic arthritis
Treatment
Rest : splintage of the joint or traction , the patient kept in bed .
The symptoms are subside especially if the disease diagnosed and treated early .
The changes take 6 months to subside completely , so returning to full activity not before
that time .
In neglected cases need prolong period of rest and immobilization to prevent ankylosis in
bad position .
Chemotherapy : combination of anti TB.
drugs usually contain refampicine , INH ,and ethambutol for eight weeks ; then refampicine
and INH for further 8-12 months .
Streptomycin and ethambutol are more toxic and they should not be used for long time .
surgical treatment
Operative drainage of TB. Arthritis is seldom necessary now a day .
A cold abscess need drainage .
If the joint is severely destroyed and still there is sever pain during the movement of the
joint after healing of TB. Infection , then arthroplasty (joint replacement) is indicated , and if
it is impossible for any cause , then arthrodesis (joint fusion) is indicated to relief the pain .
