Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic CellsProkaryote : Greek word for “pre-nucleus”.
Size: 0.2 -1.0 µm 2 - 8 µm
Shape:Morphological characteristics
Basic shapes
Spherical(cocci)Rod- shaped
(bacilli)
Spiral
Spirochete
Vibrio (comma-shaped)
Unusual shapes
Star-shaped
Square or rectangular
• Most bacteria are monomorphic
• A few are pleomorphic. Arrangements
Pairs: diplococci, diplobacilliClusters: staphylococci
Chains: streptococci, streptobacilli
Structure of prokaryotic cells
Outer cell layers
GlycocalyxCell wall
Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm
Nuclear materialFlagella
Fimbreae
Ribosomes
Glycocalyx
Outside cell wallUsually sticky
Either
neatly organized called a capsule
Or unorganized & loose called a slime layer
Extracellular polysaccharide allows cell to attach
Protect bacteria from phagocytosis
Cell Wall
Prevents osmotic lysisMade of peptidoglycan (in bacteria)
Peptidoglycan
Polymer of disaccharideN-acetylglucosamine (NAG) & N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM)Linked by polypeptides
Gram positive Vs. Gram negative cell walls
• Thick peptidoglycan
• Teichoic acids• Lack outer membrane
• No periplasmic space
• Thin peptidoglycan
• No teichoic acids
• Outer membrane
• Periplasmic space
Gram-Positive cell walls
Teichoic acids:Lipoteichoic acid links to plasma membrane
Wall teichoic acid links to peptidoglycan
May regulate movement of cations
Polysaccharides provide antigenic variation
Gram-Negative Outer Membrane
Lipopolysaccharides, lipoproteins, phospholipids.Lipopolysaccharide consists of two parts
Lipid A is an endotoxin.
O polysaccharide antigen, e.g., E. coli O157:H7.
Protection from phagocytes, complement, antibiotics
Plasma Membrane
Phospholipid bilayerPeripheral proteins
Integral proteins
Transmembrane proteins
Plasma Membrane
Selective permeability allows passage of some moleculesEnzymes for ATP production
Photosynthetic pigments on foldings called chromatophores or thylakoids
Damage to the membrane by alcohols, quaternary ammonium (detergents) and polymyxin antibiotics causes leakage of cell contents.
Movement Across Membranes
Simple diffusion: Movement of a solute from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.Facilitative diffusion: Solute combines with a transporter protein in the membrane.
Osmosis
Active transport
Osmosis and osmotic pressure
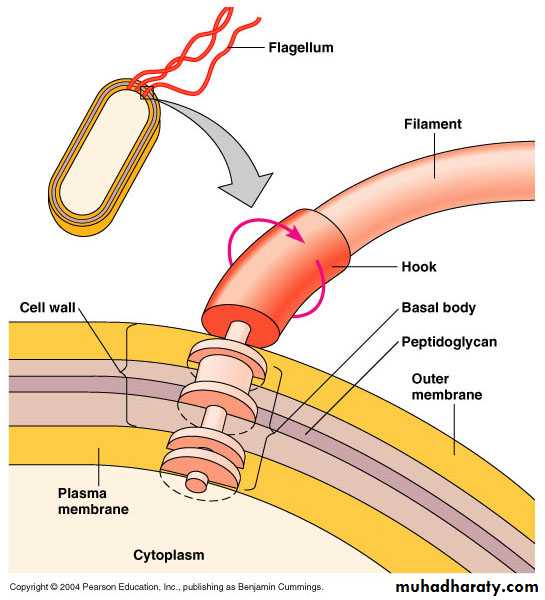
Flagella
Outside cell wallMade of chains of flagellin
Attached to a protein hook
Anchored to the wall and membrane by the basal body
Motile Cells
Move toward or away from stimuli (taxis)Flagella proteins are H antigens (e.g., E. coli O157:H7)
Axial Filaments
EndoflagellaIn spirochetes
Anchored at one end of a cell
Rotation causes cell to move
Fimbriae allow attachment
Pili are used to transfer DNA from one cell to another
• Fimbriae and Pili
CytoplasmCytoplasm is the substance inside the plasma membrane
Ribosomes
Prokaryotic ribosome consists of two subunits:
• Small 30S subunit• Large 50 S subunit.
Complete 70S ribosome
Nuclear Area
Nuclear area (nucleoid)
An area containing the genetic information. Unlike the eukaryotic cells, it is not surrounded by a membrane.
Eukaryotic Cells
Eukaryote : Greek word for “true nucleus”.Cell Wall
Cell wallPlants, algae, fungi.
Animal cells do not have a cell wall.
Plant and algae cells : mainly made of cellulose
Fungal cells: mainly made of chitin.
Flagella and Cilia
• Structure of flagellum
• Microtubules
• Tubulin
• 9 pairs + 2 arrangements
Plasma Membrane
Phospholipid bilayerPeripheral proteins
Integral proteins
Transmembrane proteins
Sterols
Glycocalyx
• Carbohydrates extending from animal plasma membrane
• Bonded to proteins and lipids in membrane
Plasma Membrane: Functions
Selective permeability allows passage of some moleculesSimple diffusion
Facilitative diffusion
Osmosis
Active transport
Endocytosis
Phagocytosis: Pseudopods extend and engulf particles
Pinocytosis: Membrane folds inward bringing in fluid and dissolved substances
Eukaryotic Cell: Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm Inside to plasma membrane
membrane
Cytosol Fluid portion of cytoplasm
Cytoskeleton Microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules
Cytoplasmic streaming Movement of cytoplasm throughout cell
Organelles
Membrane - bound structures within the cytoplasm
OrganellesMembrane-bound:
Nucleus Contains chromosomes
ER Transport network
Golgi complex Membrane formation and secretion
Lysosome Digestive enzymes
Vacuole Brings food into cells and provides support
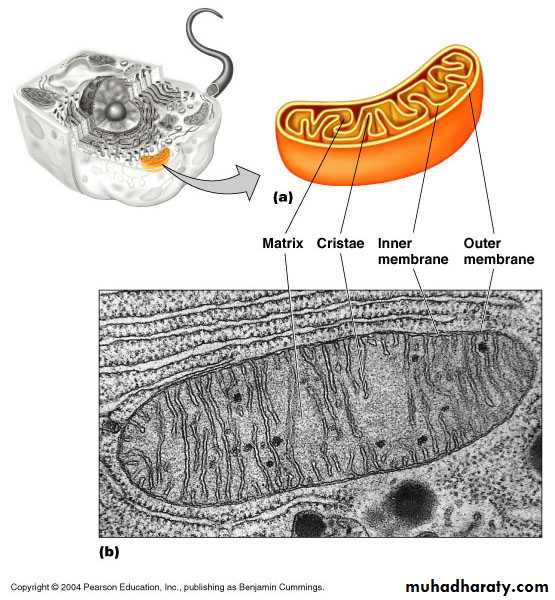
Mitochondrion Cellular respiration
Chloroplast Photosynthesis
Peroxisome Oxidation of fatty acids; destroys H2O2
Nucleus
Figure 4.24
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Ribosomes
80SMembrane-bound Attached to ER
Free In cytoplasm
70S
In chloroplasts and mitochondria
Golgi Complex
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Mitochondrion
Chloroplast
Prokaryote Eukaryote
One circular chromosome, not in a membraneNo histones
No organelles
Peptidoglycan cell walls
Binary fission
• Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane
• Histones
• Organelles
• Polysaccharide cell walls
• Mitotic spindle