1
Chicken pox
2
Instructional Objectives:At the end of the lecture the student would be able to:1-Demonstrate the main clinical characteristics of Chicken pox, Small pox, and Mumps.2-Point out the occurrence of the diseases.3-List the causative agent, mode of transmission, incubation period, and period of communicability of Chicken pox, Small pox, and Mumps.4-List the main preventive measures of Chicken pox, and Mumps.5-Describe the control measures of Chicken pox, and Mumps.
3
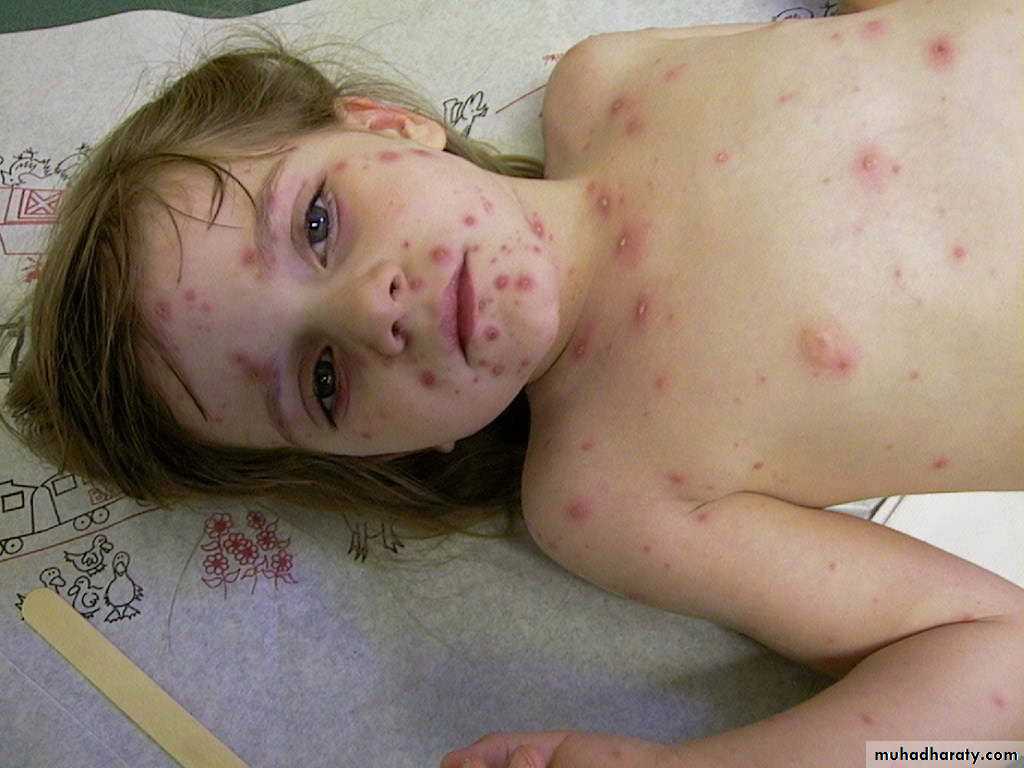
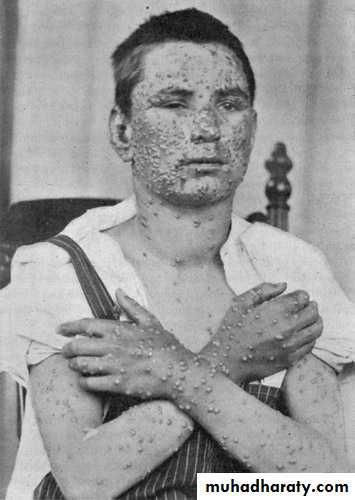
Acute generalized viral disease characterized by:
Sudden onset of fever, mild constitutional symptoms, &skin rash
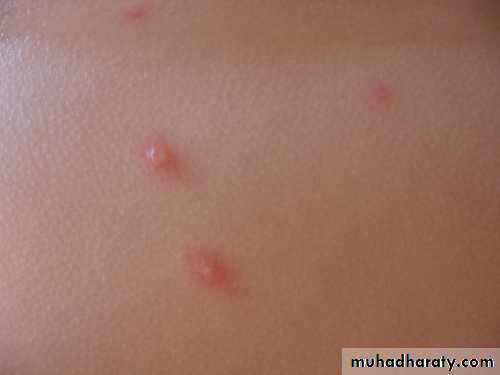
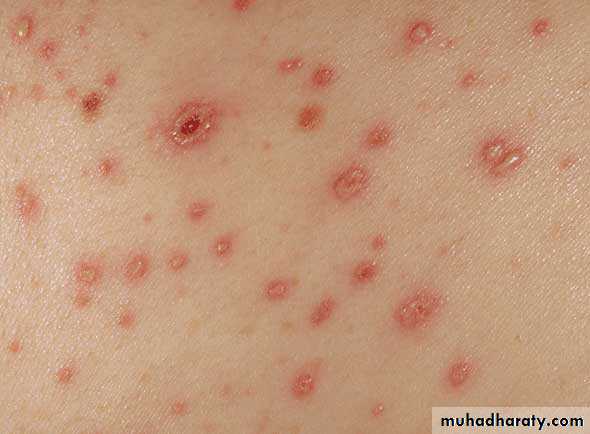
Maculo-papular rash.. few hours.. vesicles…. 3-4days.. granular crusts
Lesion commonly occur in successive groups with several stage of maturity present at the same time.
4
More abundant on covered than exposed parts of the body
Lesions may appear high in the axilla &on the scalp ,MM of the mouth and R.T., &on the conjunctivae
5
They may be so few as to escape attention
Mild, atypical, & inapparent infection can occur6
Sever form can occur in adults.
Children with acute leukemia are at high risk of severe disseminated form with CFR of 5-10 %
Neonates (5-10days)have a CFR of up to 30%
Infection early in pregnancy may be associated with (CVS) in 0.7 % &if infection occurs at 13-20 weeks in may be associated with CVS in 2%Herpes zoster is a local manifestation or reactivation of varicella infection in dorsal root ganglia.
7
8
Infectious agent:
Human (alpha) herpes virus 3
(V-Z virus)
Occurrence:
World wide, in temperate climates at least 90% of the population has had chicken pox by the age of 15 years &at least 95% by young adulthood.Zoster occurs more commonly in older groups.
In temperate zones occurs most frequently in winter &spring
Reservoir : Human
9Mode of transmission:
Direct contact person-to –person
* Droplet
* airborne spread
vesicle fluid or secretion of the URT of chicken pox case or vesicle fluid of patient with HZ can transmit infection.
Indirect
* Soiled articles
Scabs are not infectious
Incubation period:
2-3 weeks , commonly 14-16 days
10
Period of communicability
1-2 days before the Rash
and 5 days after.
11
Susceptibility &resistance:
general
More sever from occur among adults
Infection gives life long immunity
Second attacks are raresub clinical re-infection is common
Viral infection remain latent &disease may occur later as HZ in about 15%of older adults &some times in children12
• Prevention:
• Live attenuated Variclla vaccine (Varivax). A single dose of 0.5 ml sc is recommended for children age 12m-12 yrs who have not had chicken pox . This vaccine had cumulative efficacy at 70-90 % in preventing varicella in children. It is protective if it is given within 3 days of exposure
• Protect high risk individuals from exposure
• VZIG is effective in preventing or modifying the disease .if given within 96 hours of exposure
13
• Control :
• Reporting is not necessary
• Isolation :Exclude children from school for 5 days after appearance of rash
• Disinfection of articles soiled by discharge from nose & throat
• Protection of contact:
• VZIG within 96 hrs of exposure
• Varivax vaccine within3 days of exposure
• Newborns of mothers exposed who develops varicella 5 days before or 2 days after delivery.
14
• VZIG given to pregnant does not prevent CVS
• Acyclovir week of exposure 80mg/kg/day/qds
• Specific Rx :
• Antiviral drag
• Zovirax( Acyclovir), Vidarabine
15
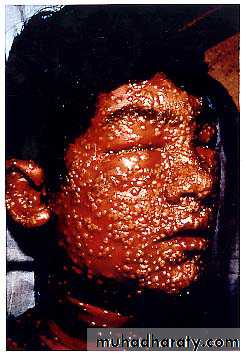
Smallpox (Variola)
Last naturally acquired case in word occur in October 1977 in Somalai
Global eradication
was certified two years
later by WHO
16
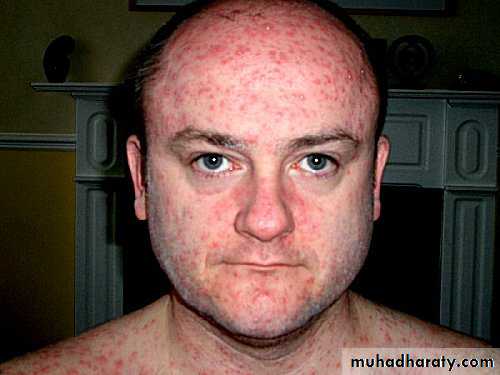
It is systemic viral disease
Onset sudden fever,malaise, prostration,
severe backache,
&occasional abdominal
pain &vomiting
within (2-4 days).
17
Then Fever began to fall deep seated rash developing in which individual lesions containing infectious virus macules papules vesicles pustules crusted scrabs
Which fell off after 3-4 weeks
Appeared on the successive stages of maturity
Abundant on the exposed parts (centrifugal distribution).
18
Two types of smallpox were recognized during the 20th century :
Variola minor (alastrim) CFR <1%
Variola major (ordinary) CFR 20-40%
(among unvaccinated )
In the previously vaccinated the rash stage was significantly modified.
Infectious agent:
Variola virus a species of orthopox virus.19
Occurrence :
Formerly a world wide disease. it is eradicated.
Reservoir :
Naturally human, officially, only in designated freezers.Mode of transmission :
Air borneSecondary attack rate among unvaccinated population was about 50%.
20
Incubation period:
7 to 19days
Communicability From the first day of the development of the earliest lesion to the disappearance of all scabs (about 3 weeks).
Susceptibility & resistance:
Among unvaccinated is universal.Method of control:
Immunization with vaccinia virus vaccine.21
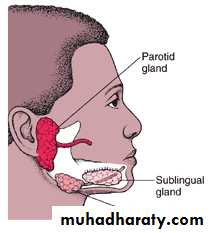
Mumps
Infectious parotistis
22
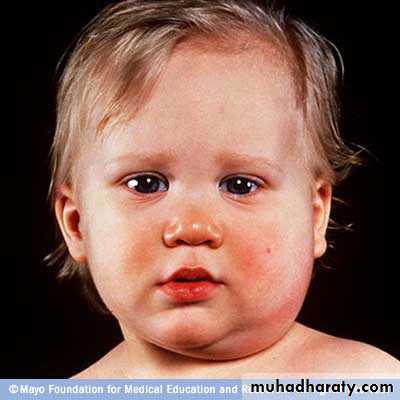
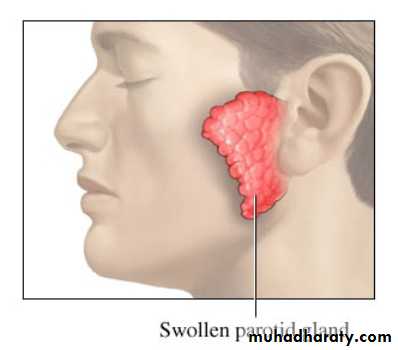
An acute viral disease characterized by: Fever, swelling &tenderness of one or more salivary glands (usually the parotid &some times the sublingual or sub maxillary glands).
23
Complications:
Orchitis, most commonly unilateral (20-30%) of post pubertal malesOOpheritis and or mastitis can occur in females >15 years of age
Sterility is extremely rare
Sensoneural hearing loss in children(5:100.000
cases).
Encephalitis (1-2 :10,000 cases)
Pancereatitis usually mild (4% of cases )
24
Infection during first trimester increase the rate of spontaneous abortion
No firm evidence of congenital anomalies
Permanent sequelae & deaths are rare
Infectious agent:
Mumps virus: a member of the ParamyxoviradaeAntigenically relates to the parainflunza virus
25
Occurrence:
Less regularly recognized than other common communicable childhood diseases
1/3 of the exposed susceptible may have inapparent infection
Winter &spring are seasons of greatest incidence
By the use of effective vaccination program (MMR) the incidence has dramatically decline &the greater risk of infection has shifted toward older children, adolescence &young adults
26
Reservoir: Human.
Mode of transmission:
Direct contact with saliva
Airborne
Droplet
Incubation period:
15-18 days
period of communicability :
Before Onset of illness After
6-7 days parotitis 9 days
2days Maximum 4days
before infectiousness after27
• Susceptibility &resistance:
• Immunity is life long after clinical or inapparent infection
• Inapparent infection is communicable
• Prevention:
• Public education
• Vaccination (Jerky Lynn strain) live attenuated vaccine (MMR). more than 95%develop long-lasting or probably life long immunity. Administered at any time after 12 months .
• Special efforts to vaccinate before puberty all persons with no definite history of mumps or mumps immunization.
28
• Contra-indication of the vaccine:
• Immune suppression.
• Pregnancy &planning of pregnancy in the next 3 months
29
• Control:
• Reporting: It is reportable disease.
• Isolation: respiratory isolation &private room for 9 days from onset of swelling. Also school exclusion for the same period
• Disinfection of all articles soiled with throat secretion.
• Protection of contact
• * Active not effective
• * Passive not effective
• No specific Rx.
30
Thank you all