
General approach :
History
Inspection
Range of Motion (ROM)
Palpation
History
“Have you any pain or stiffness in your muscles, joints or back?”
“Do you have any trouble getting up or down stairs?”
“Do you have any difficulty getting dressed?”
How symptoms started (mechanism of injury)?
Duration of complaint?
Location, nature of pain, or symptoms?
Exacerbating or relieving maneuvers?
Inspection
n
Observe how the patient moves as they go into the room or move from chair to table
n
Look for asymmetry between sides
n
Swelling
n
Deformities
n
Atrophy
n
Erythema
n
Bruises , scarring , psoriatic lesions
Range of motion
Active
n
Have patient range the joints
n
Watch for decreased or increased movement of the joint compared to the other side
as well as the norm
n
Watch for pain with movement
n
Listen for crepitus or “popping”
n
Watch for abnormal movements

Passive
n
Next range the joints passively, comparing the end points to the active
n
Again note any decreased or increased movement
n
Pain with the movement
n
Crepitus or “popping”
Palpation
n
Palpate for swelling
n
Palpate for warmth
n
Palpate each area of the structure in turn evaluating for pain, and abnormalities as
compared to the other side
#Note
every joint has 4 segments
every movement has two segments
wrist
- Flexion ( F )
- Extension ( E )
Elbow
- F → c5 , c6
- E → c7 , c8
Shoulder
- F → c4 , c5
- E → c6 , c7
Pronation and supination
Abduction and adduction
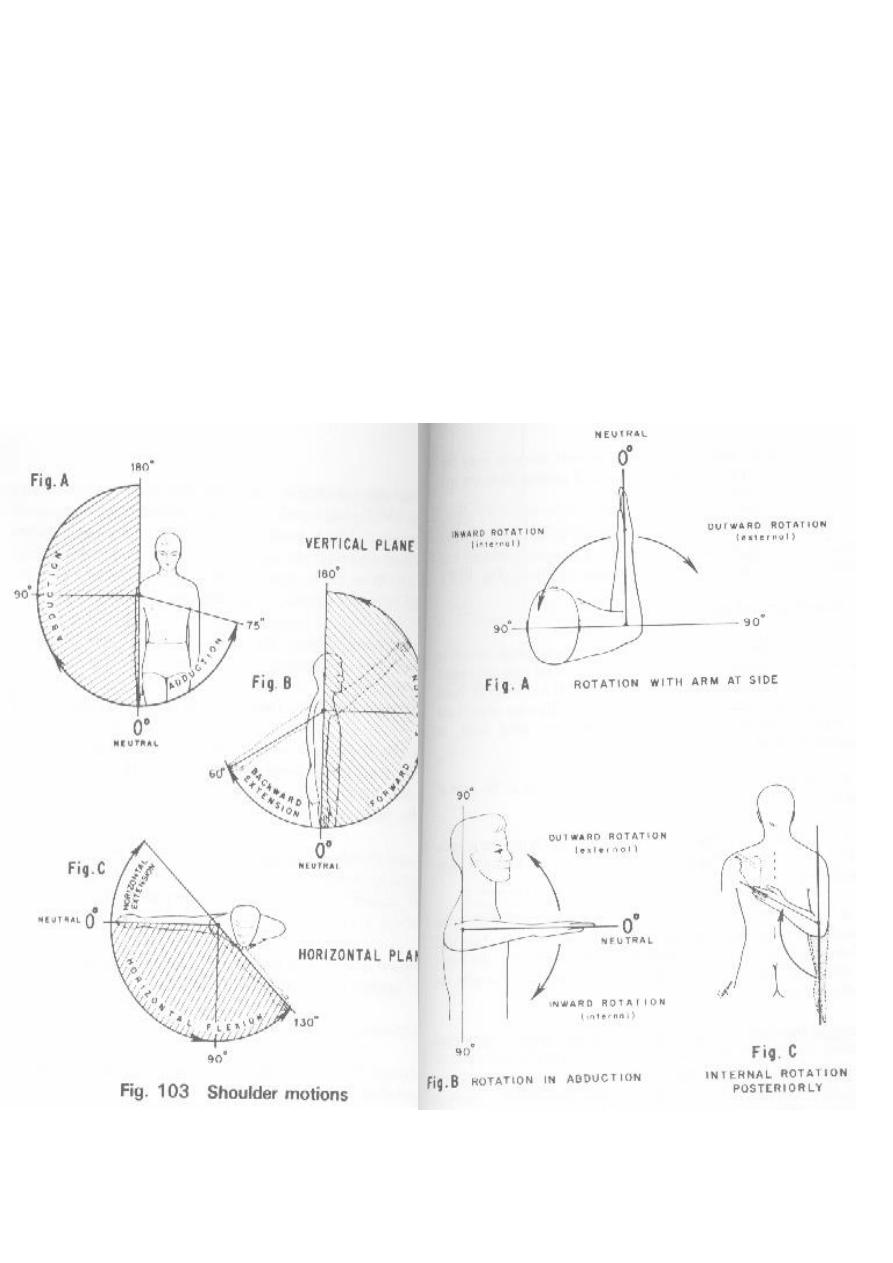
# Shoulder Exam
Joints of the shoulder
– Glenohumeral
– Sternoclavicular
– Acromioclavicular
– Scapular thoracic (not a true joint)
# Have patient place each hand:
Behind head (external rotation and abduction)
Up the small of the back (internal rotation)
sholder motions ::
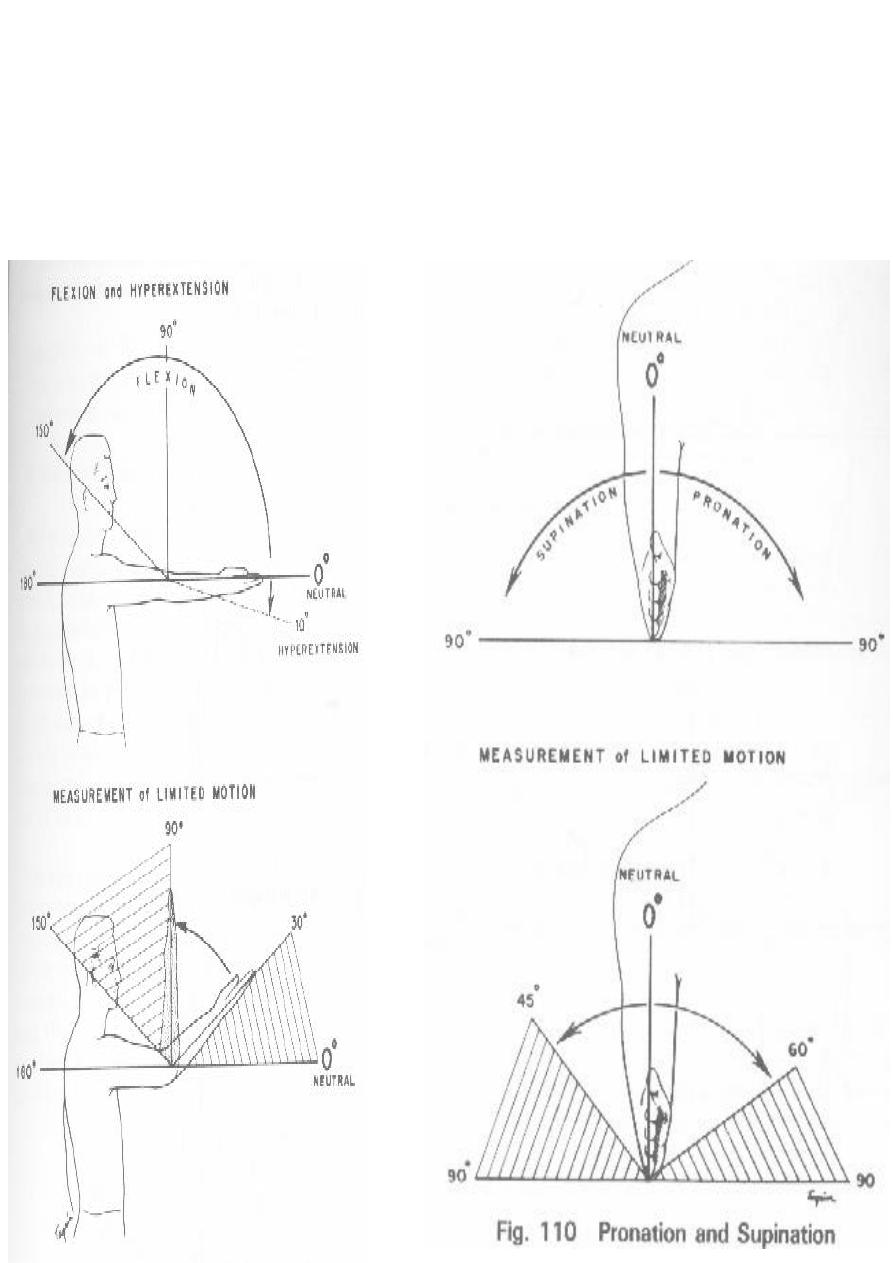
# The Elbow
n
Palpation: lateral and medial epicondyles, olecranon, radial head, groove
on either side of the olecranon
n
Inspect the carrying angle, and any nodules or swelling
Elbow motions ::
n
Varus test: Tests for ligamentous stability of the lateral collateral ligament
n
Valgus test: Tests the medial collateral ligament
n
Golfer’s elbow test: While palpating the medial epicondyle, the forearm is
supinated and the elbow and wrist are extended. Positive if pain over the
medial epicondyle.
n
Tinel’s of the elbow: Percussion of the ulnar nerve in the grove. Positive if
radiating sensation down arm into hand.
#
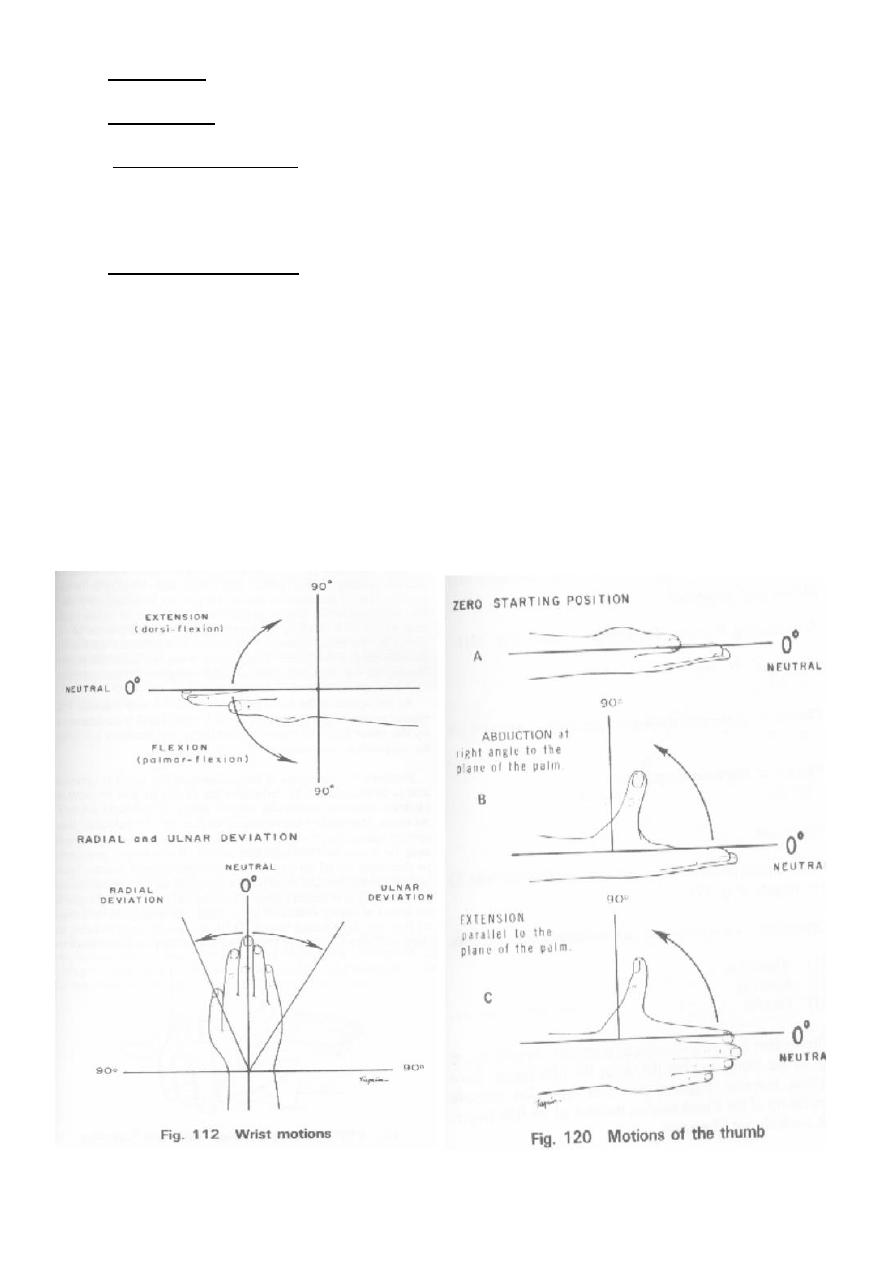
Wrist and Hand
n
Inspect for swelling or deformities
n
Palpate: anatomic snuff box, volar and dorsal aspects of the wrist, all joints of the
fingers
n
Flexion, extension, ulnar and radial deviation of the wrist
n
Have patient make a fist and extend and spread the fingers.
Pes planus
:-flat foot
