• Methods of tonometry:
1+3=goldmans applanation tonometry: used to
measure IOP.
2=schiotz tonometry : used to measure IOP
Normal IOP : 16 +- 5
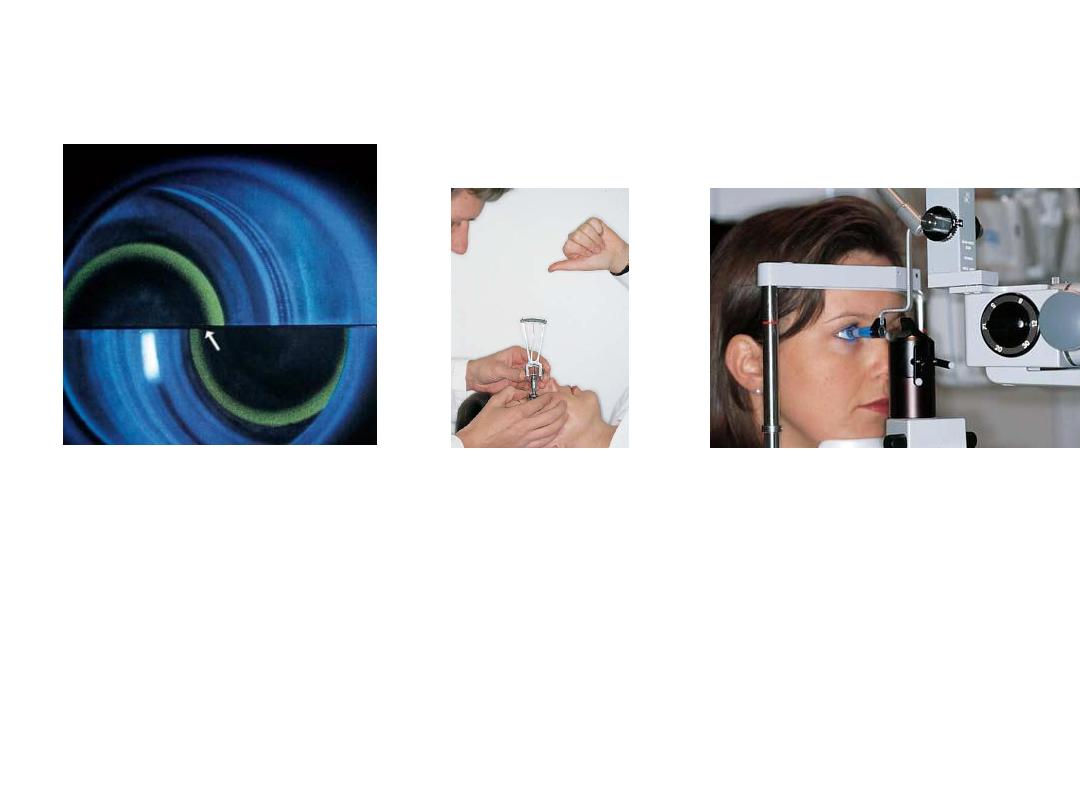
• By using which test we can
get this view?
• Gonoscopy(visualization of the angle
of the anterior chamber)
•
Describe the aqueous
circulation:
It is produced by the
ciliary process of ciliary body
>posterior chamber >pupil> anterior
chamber >trabecular meshwork>
•
Canal of Schlemm>extraocular veins
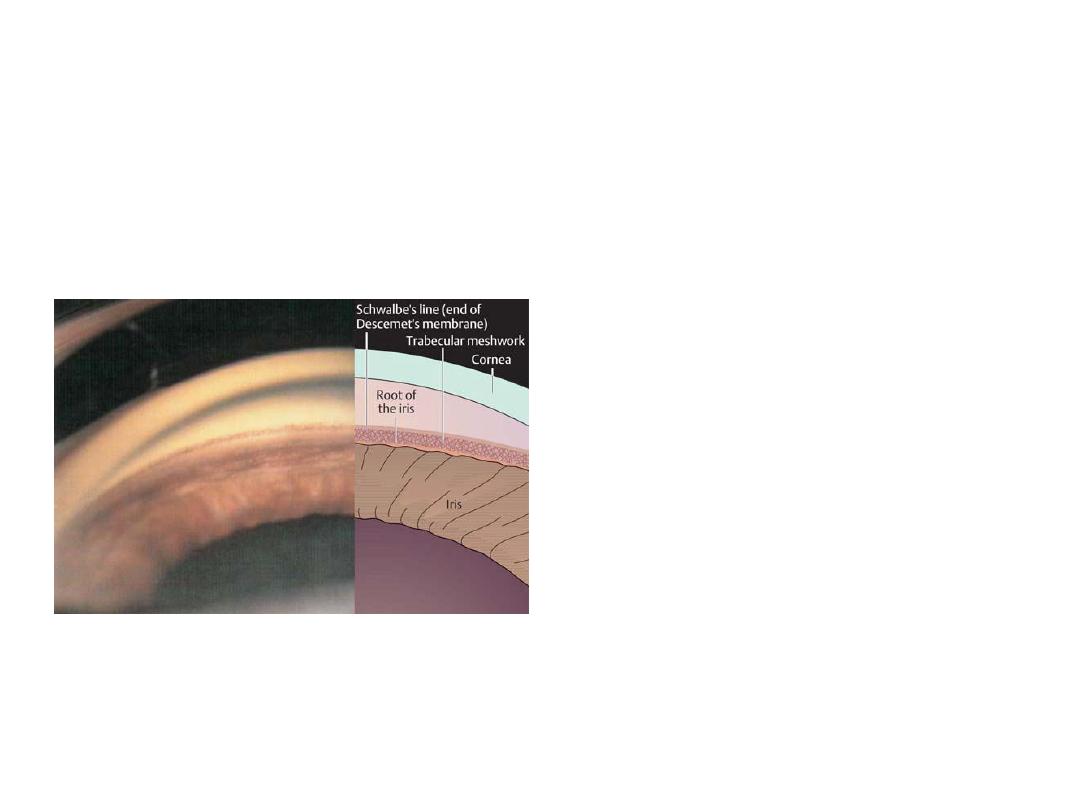
• Comment on the AC
depth.
• Shallow anterior chamber depth
• If this patient is
asymptomatic, how
would you treat him ?
1-Medical Tx:mitotic agents ,alpha
agonist , b-blocker,carbone
anhydrase inhibitor, prostaglandine
analogs
2-peripheral iridotomy(YAG laser)
*it consider pre-glucoma so it is
ergent.
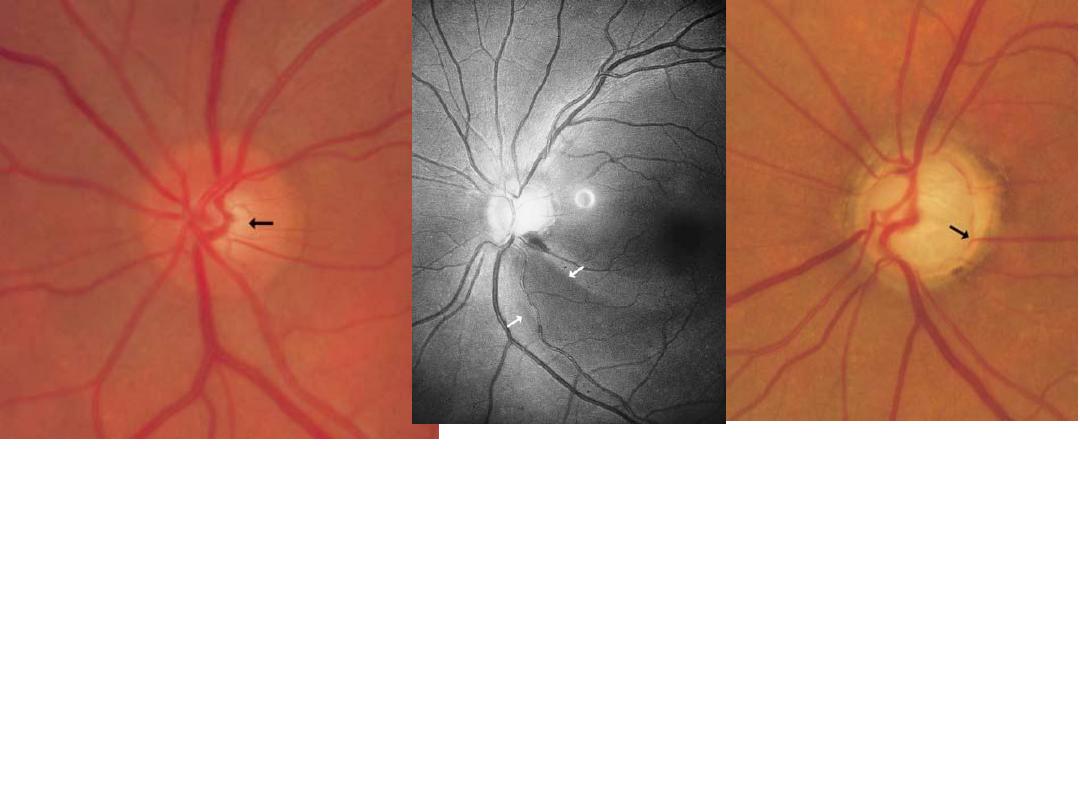
dx : abnormal cupping of the optic disk(normal cup:disk ratio 0.3)
Cause : primary open angle glucoma
اطالع
#Criteria of cupping :1-cup:disk ratio > 0.3. 2-progressive enlargment 3-
asymmetrical between the two eyes.
#dx of glucoma:1-increased IOP . 2-Abnormal cupping. 3-changes in visual
field
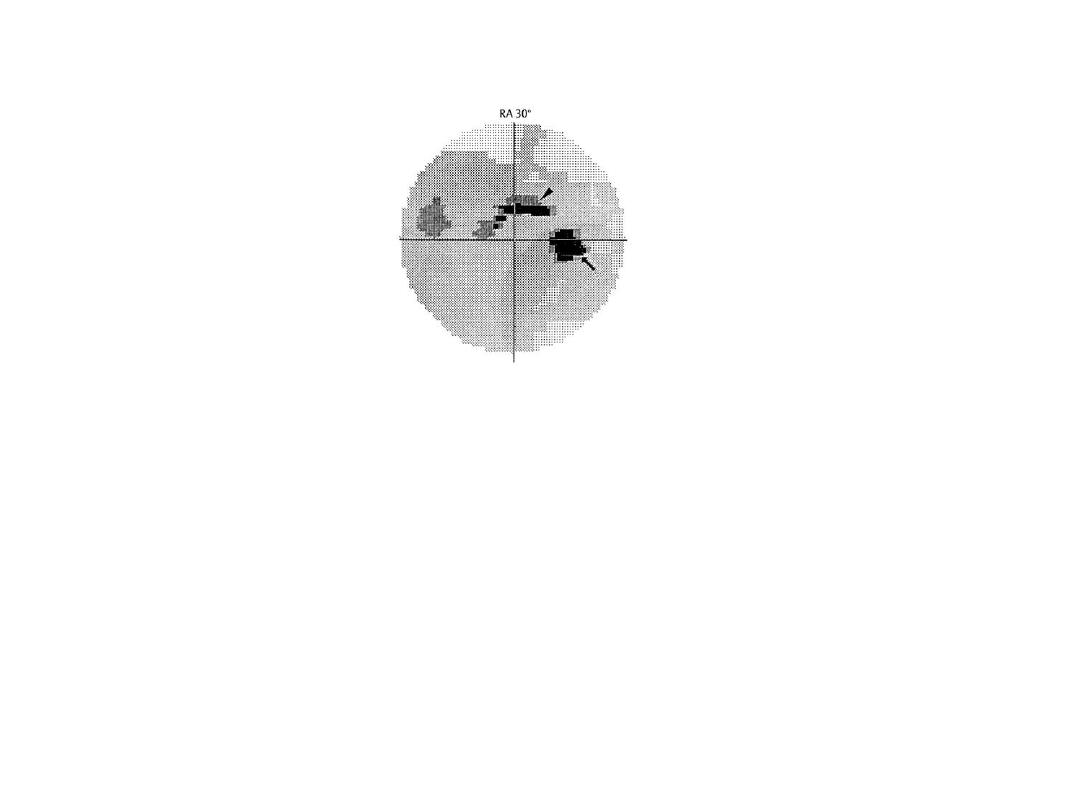
-Perimatery graph showing paracentral
scotoma in open angle glucoma
-No patient complain
-Diagnosed by chance
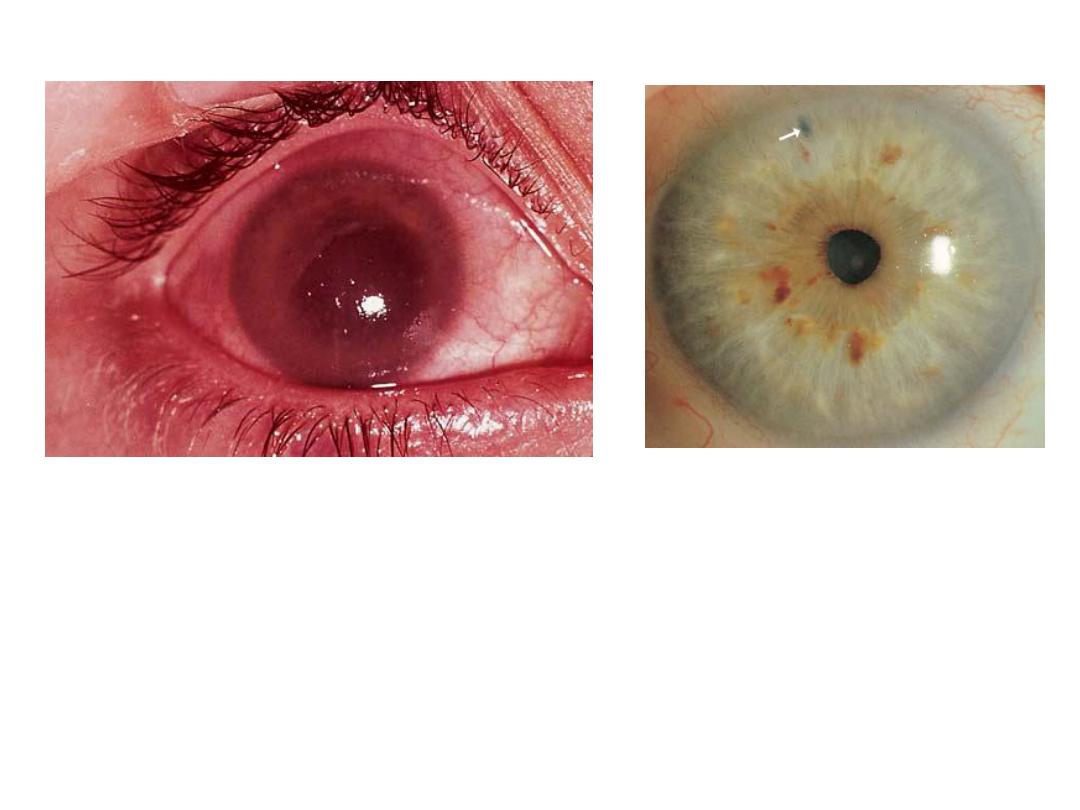
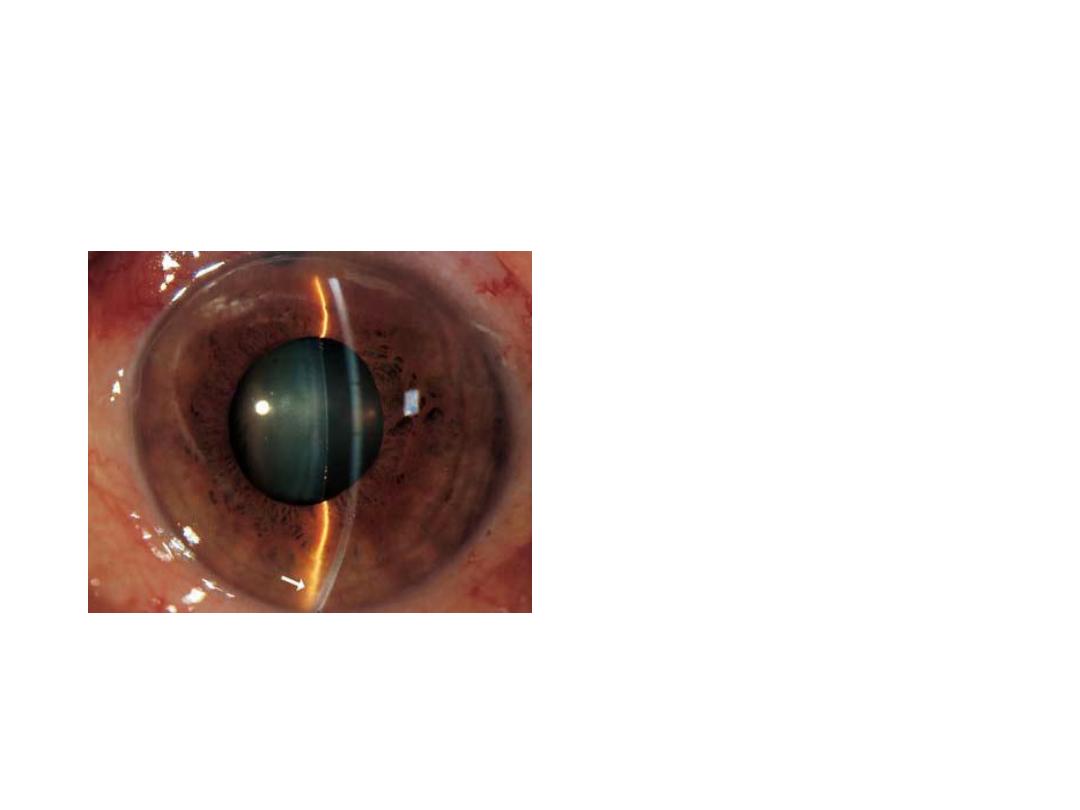
Dx :Red congested
eye(acute angle closure
glucoma) with corneal edema
,ciliary flash and dilated pupli.
Dx :peripheral laser
iridotomy
Ix : closure angle
glucoma
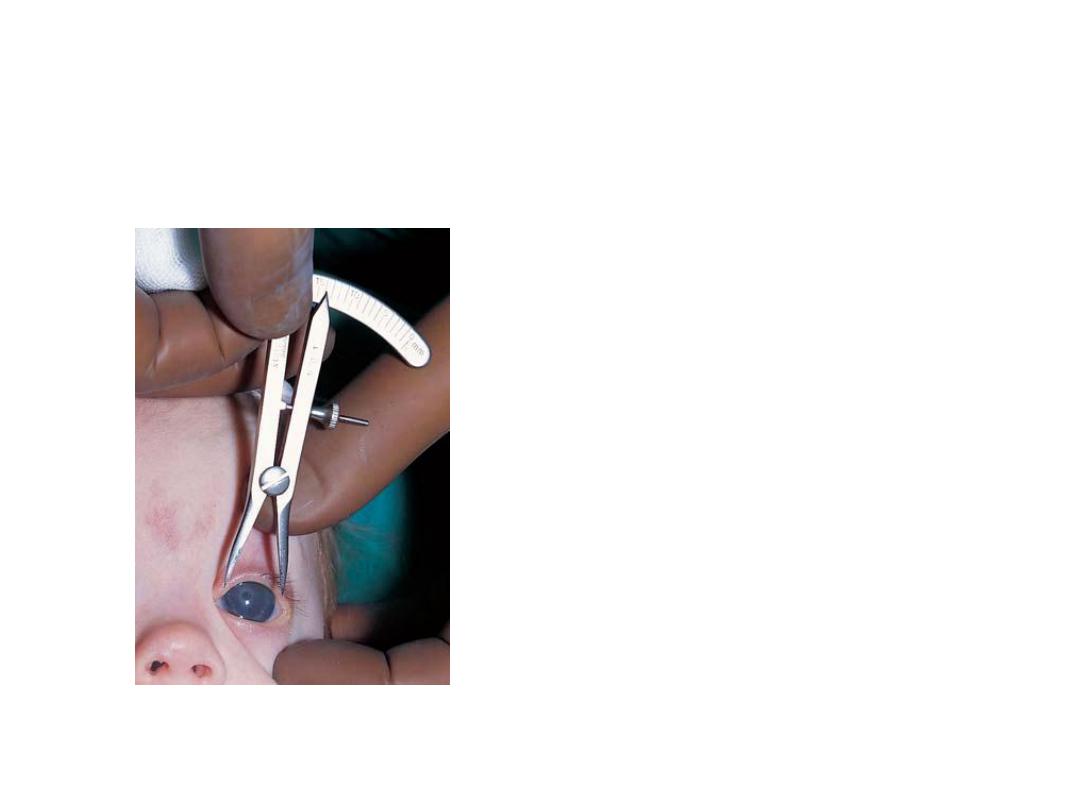
• What is he doing?!
• Measuring corneal diameter by
caliber
• Why?
• To detect and follow up
congenital glucoma(
there is buphthaloms)
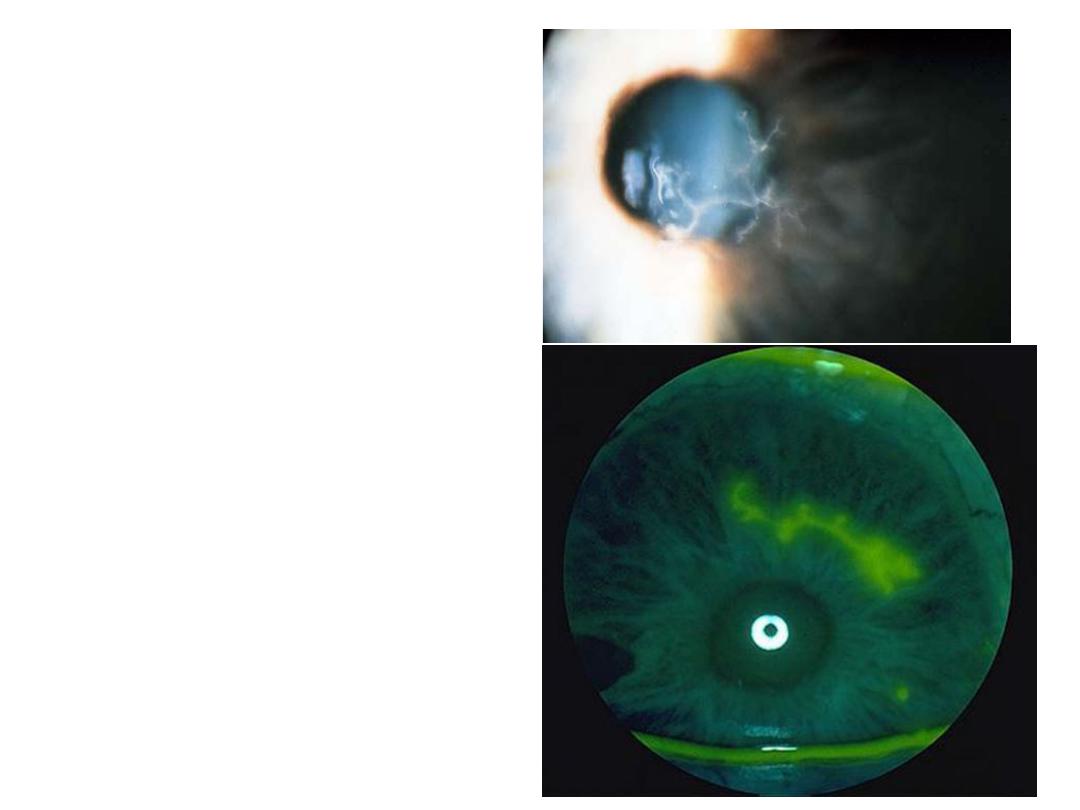
• Describe this corneal
lesion.
• Dendritic ulcer
• What is the most likely
diagnosis?
• HSV type 1
• How would you treat?
• Antiviral drugs(acyclovir ,
trifluoridine and idoxuridine)
*avoid steroids.
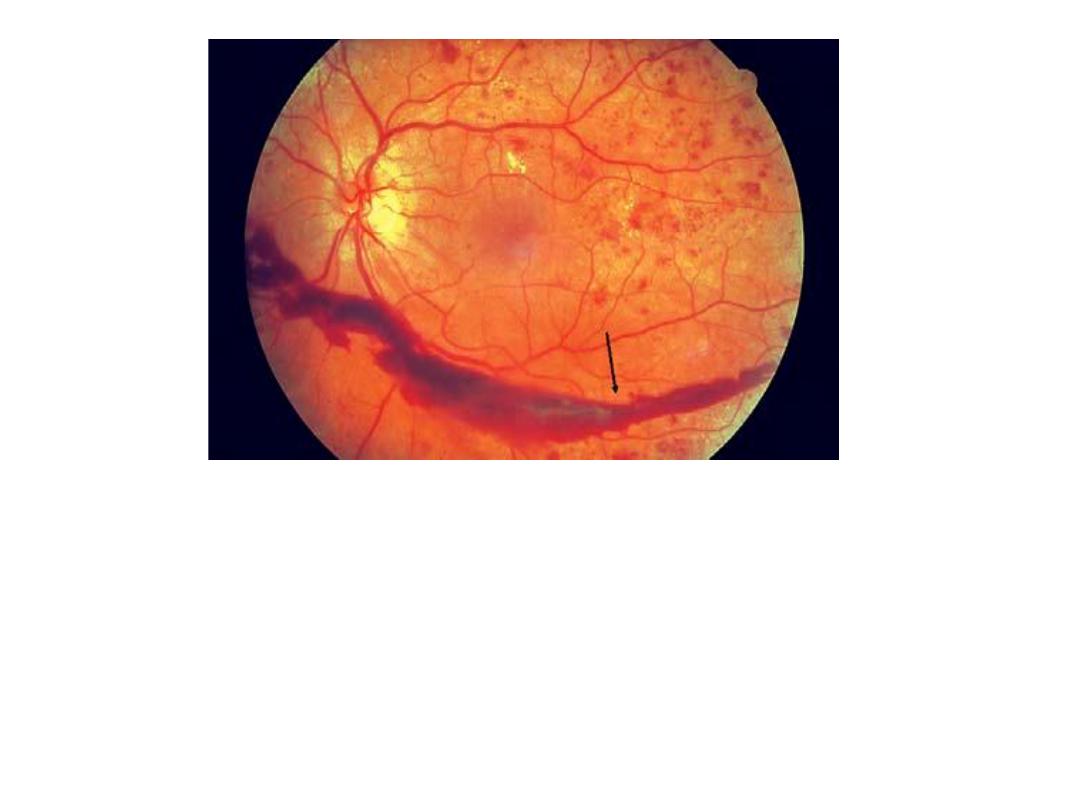
Subhaloid hemorrhage(hemorrhage
between retina & vitreous).
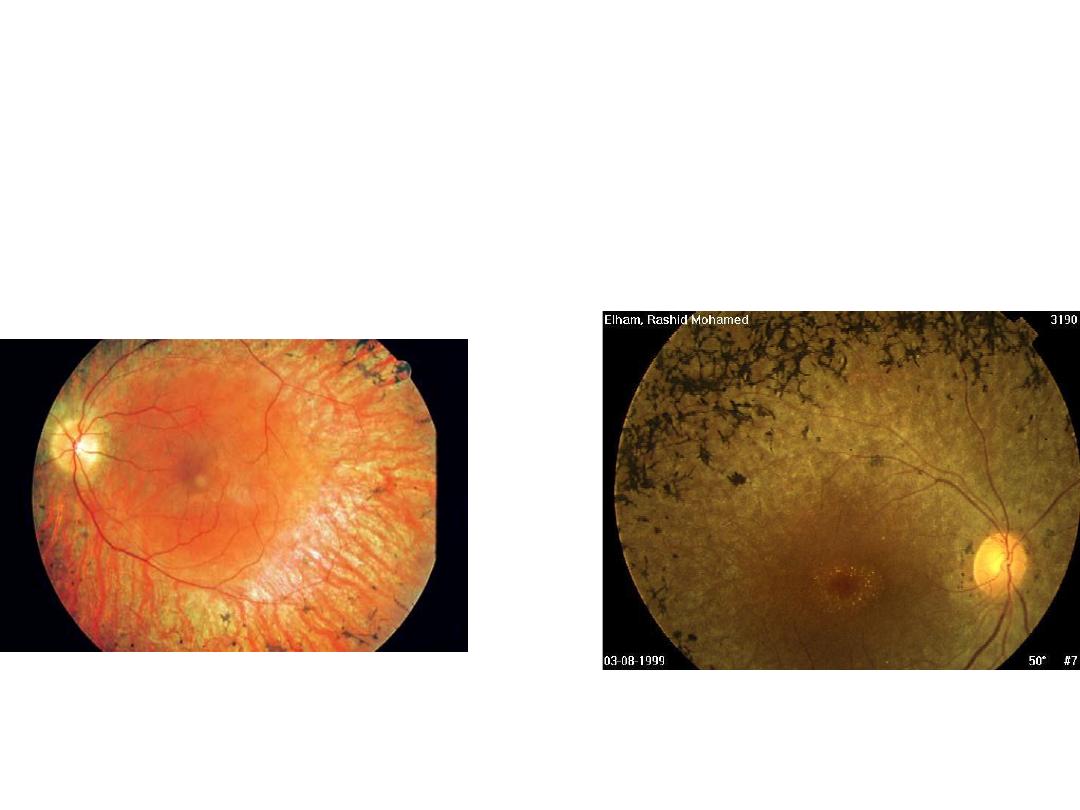
# Dx : Retinitis pigmentosa
:
# Patient complains
1-night blindness
2-visual loss
3-seeing flashes of light
# mention 2 syndromes associated with it.
1-bardet biedl syndrome
2-refsum syndrome
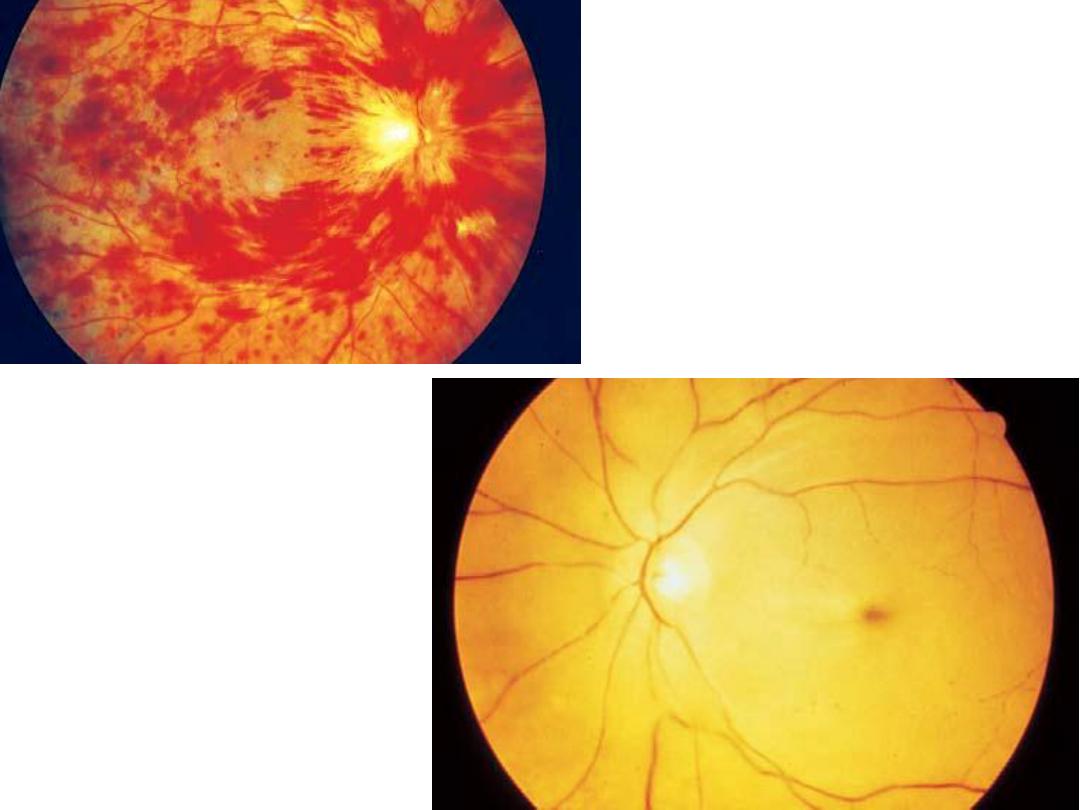
CRVO
CRAO
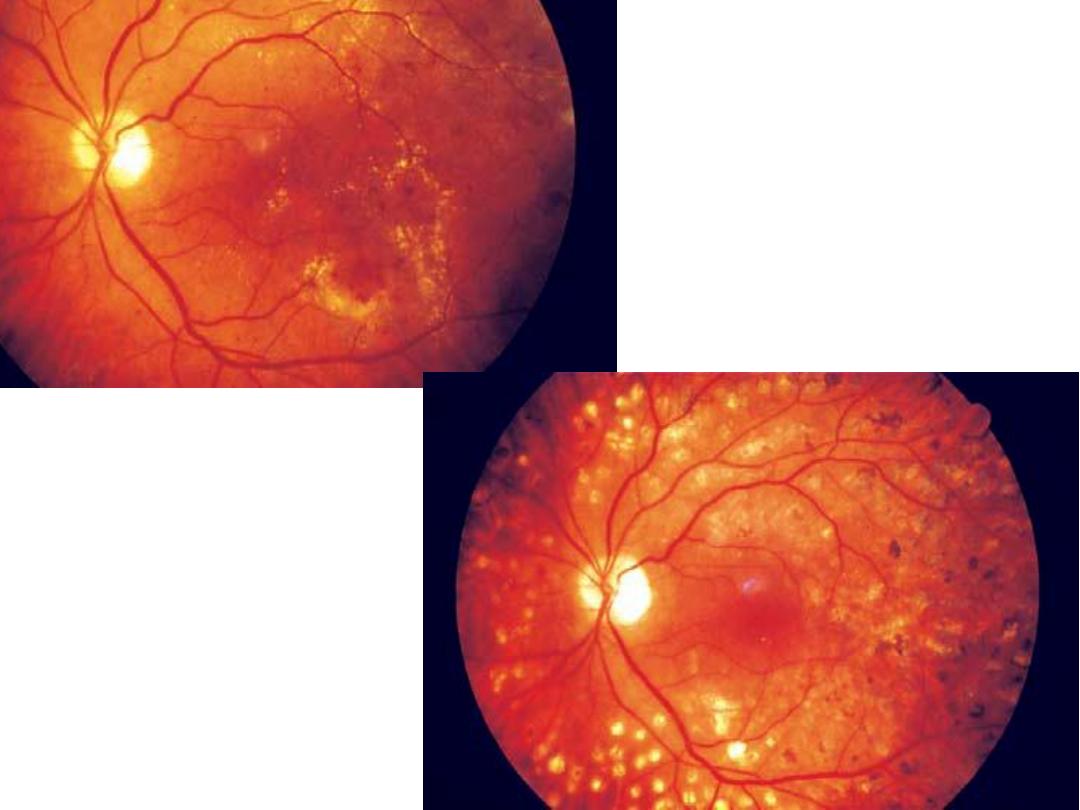
NON
PROLIFERATIVE
DIABETIC
RETINOPATHY
PROLIFERATIVE
DIABETIC
RETINOPATHY
