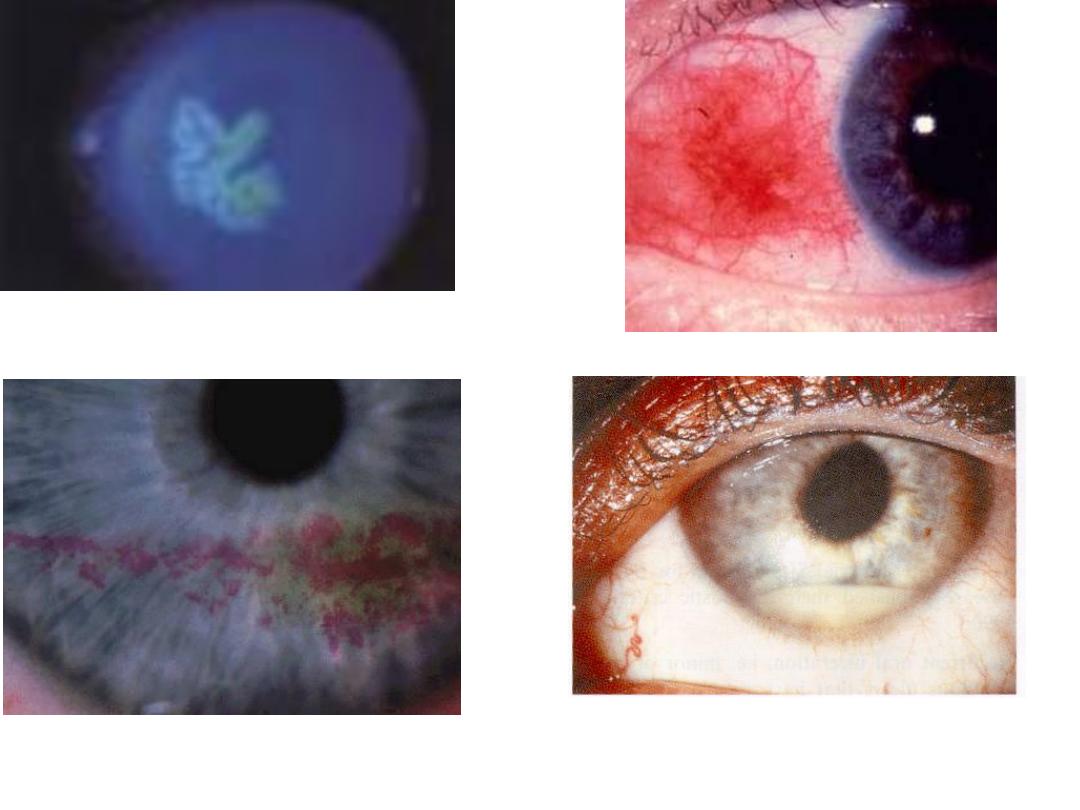
Ameboid ulcer(viral ulcer) due to
mistreatment of dendritic ulcer with
steroid.
episcleritis
Hypopium(pus in the anterior chamber)
causes : 1-keratitis 2-iritis
Dx :Filamentray keratitis
Stain :rose bengal stain
Causes :1-dry eye 2-sjogren syndrome 3- 7 palsy 4-
blepharoptosis
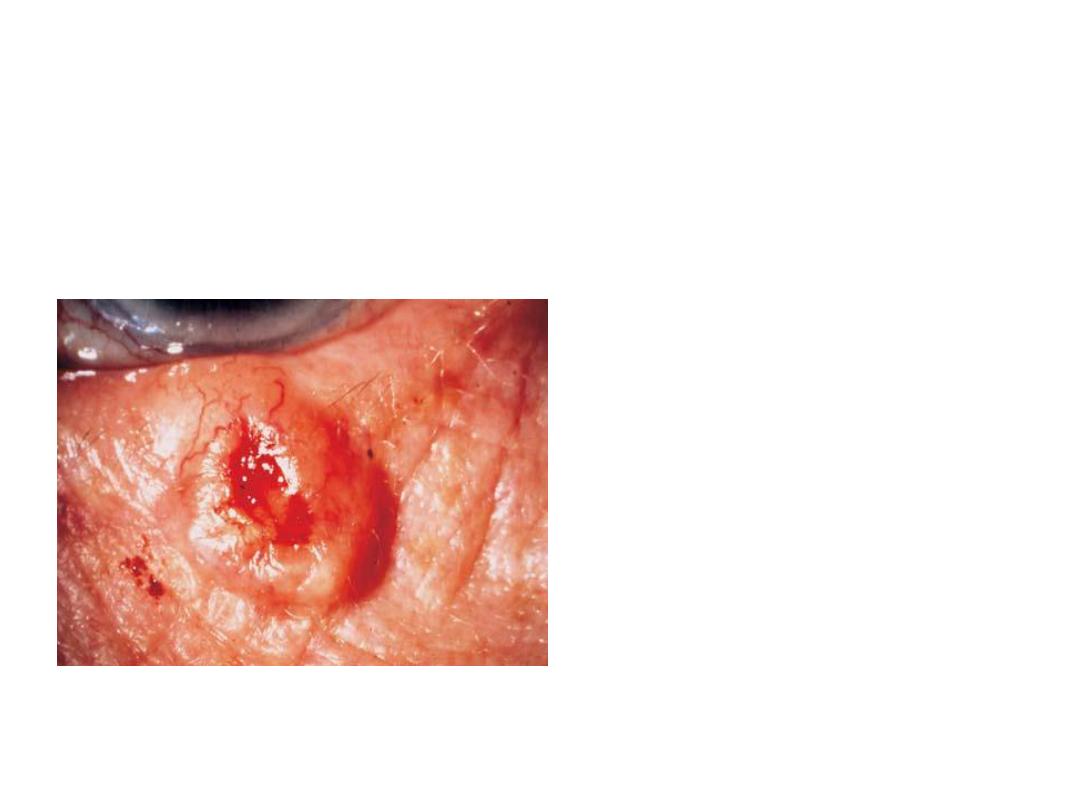
• Describe this lesion?
Oval,elevated,ulcerated,congested,di
rty lesion on the lower lid
• Differential diagnosis?
• 1-basal cell carcinoma
• 2-sequamous cell carcinoma
• 3-sebaeous cell carcinoma
• 4-keratoacanthoma
• 5-malignant melanoma
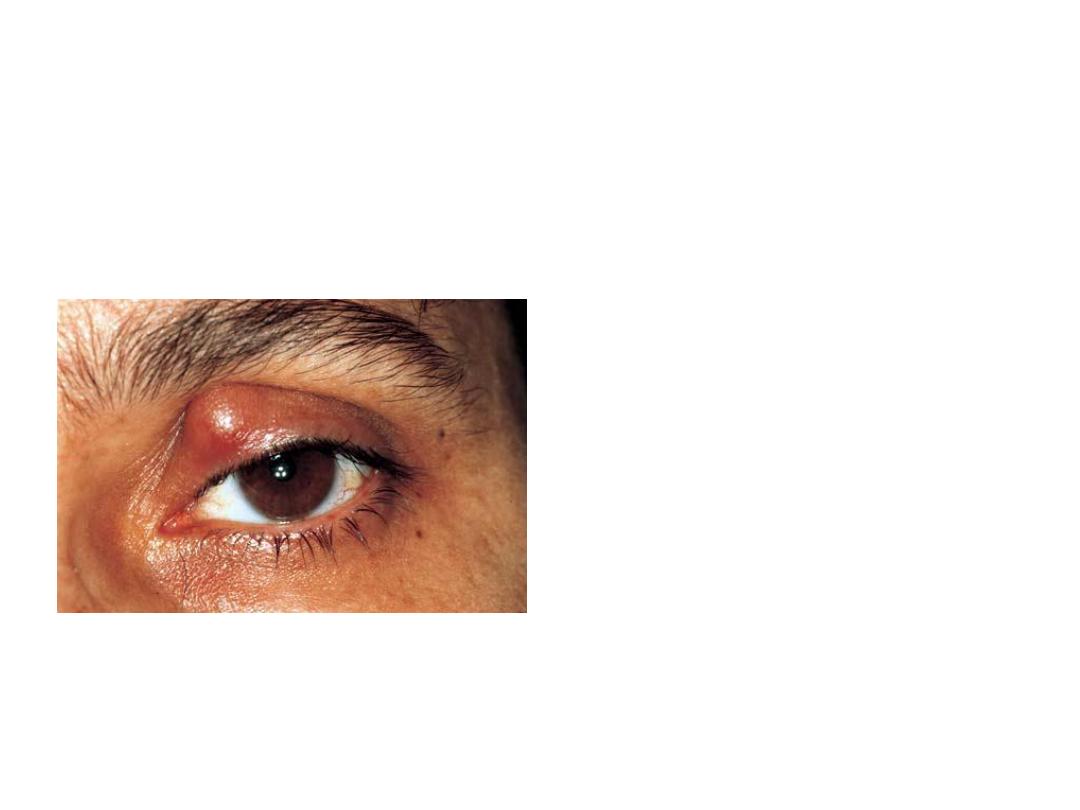
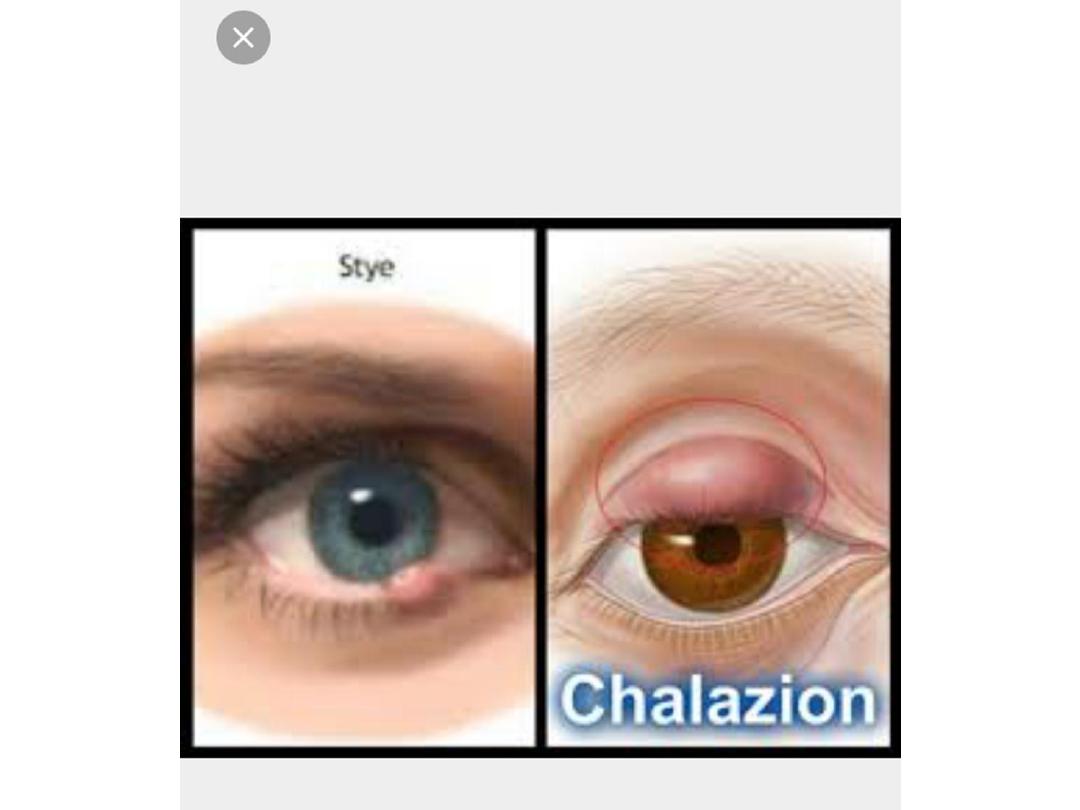
• Describe this lesion
• Localized swelling in the upper lid
with normal skin over it
• Enumerate four causes
• 1-chalazion 2-stye 3-sebaceous
cell carcinoma 4-haemangioma
• What is the most likely
diagnosis ?
• chalazion
• How would you treat it?
•
1-conservative:massage, hot
compress,local AB , local steroid
•
2-surgery.
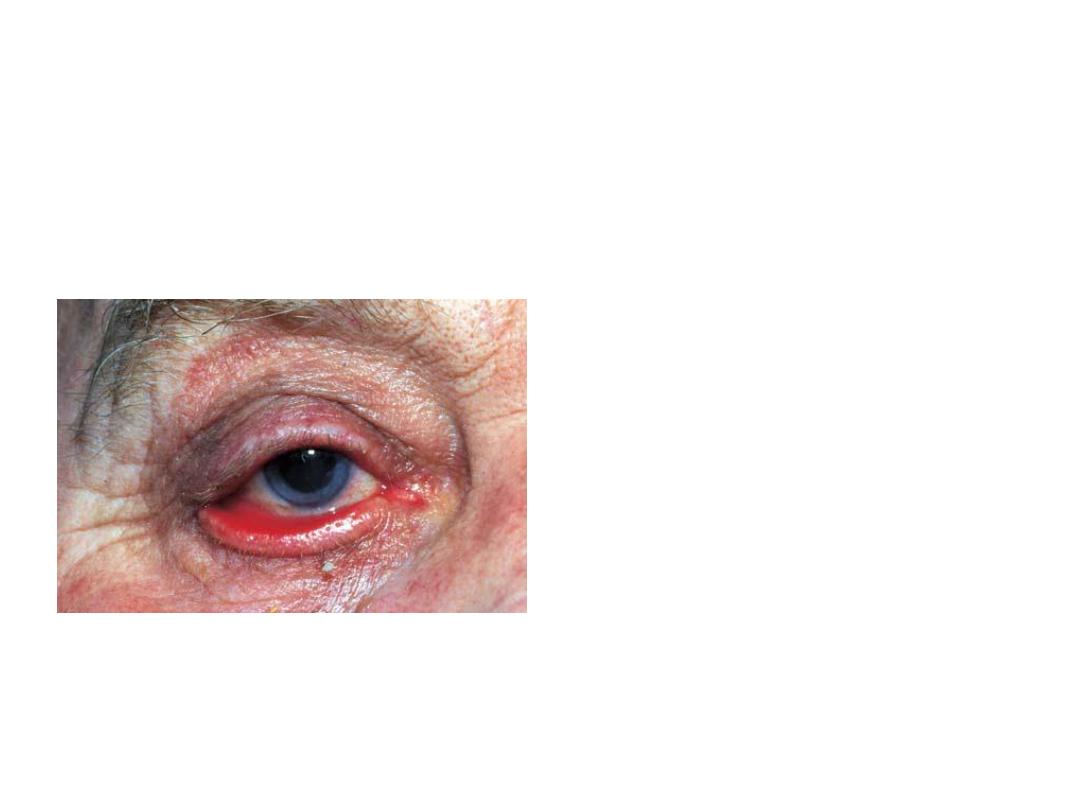
• What is your diagnosis?
•
Ectropion of the R.lower lid
• What is the complaint
of this patient?
•
Lacrimation+congested red
conjunctiva+repeated infections
• What are the possible
causes?
•
1-aging
•
2-congenital
•
3-lower lid scar
•
4-7 palsy , neurofibromas
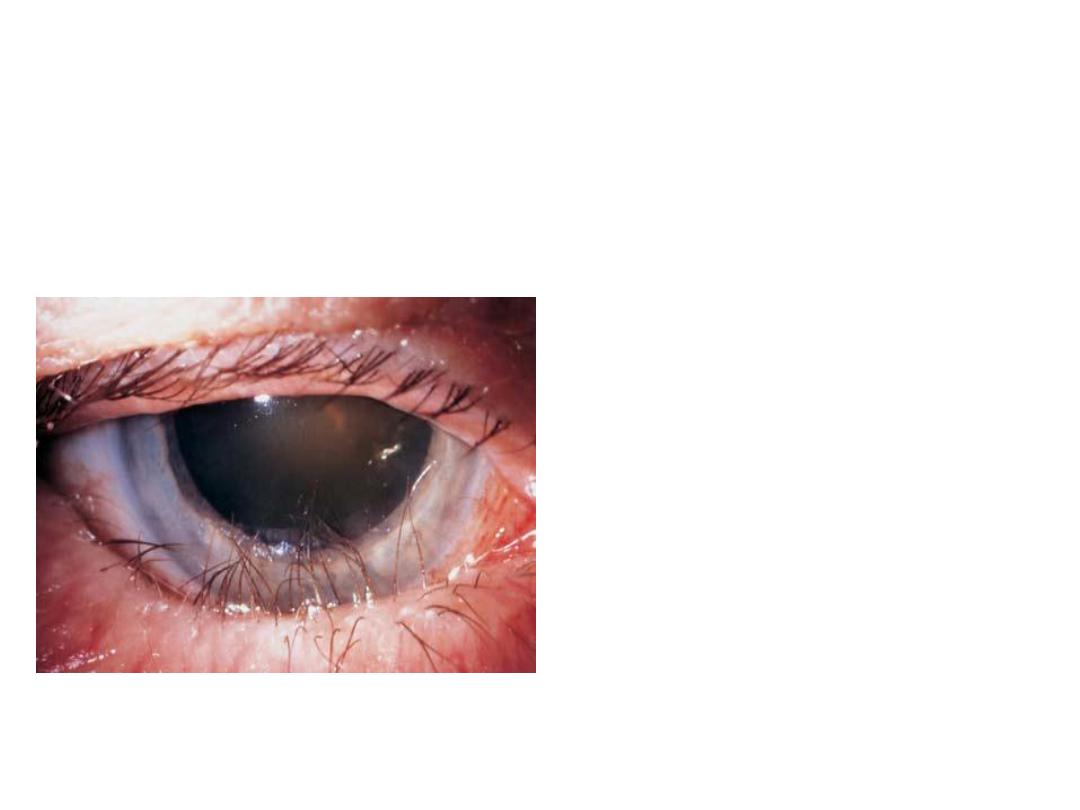
• What is your diagnosis?
• Entropion of the lower lid with
trichiasis
• What are the possible
causes?
• 1-aging
• 2-congenital
• 3-palpebral conjunctival scaring
• 4-
trachoma,trauma,infection,inflam
mation
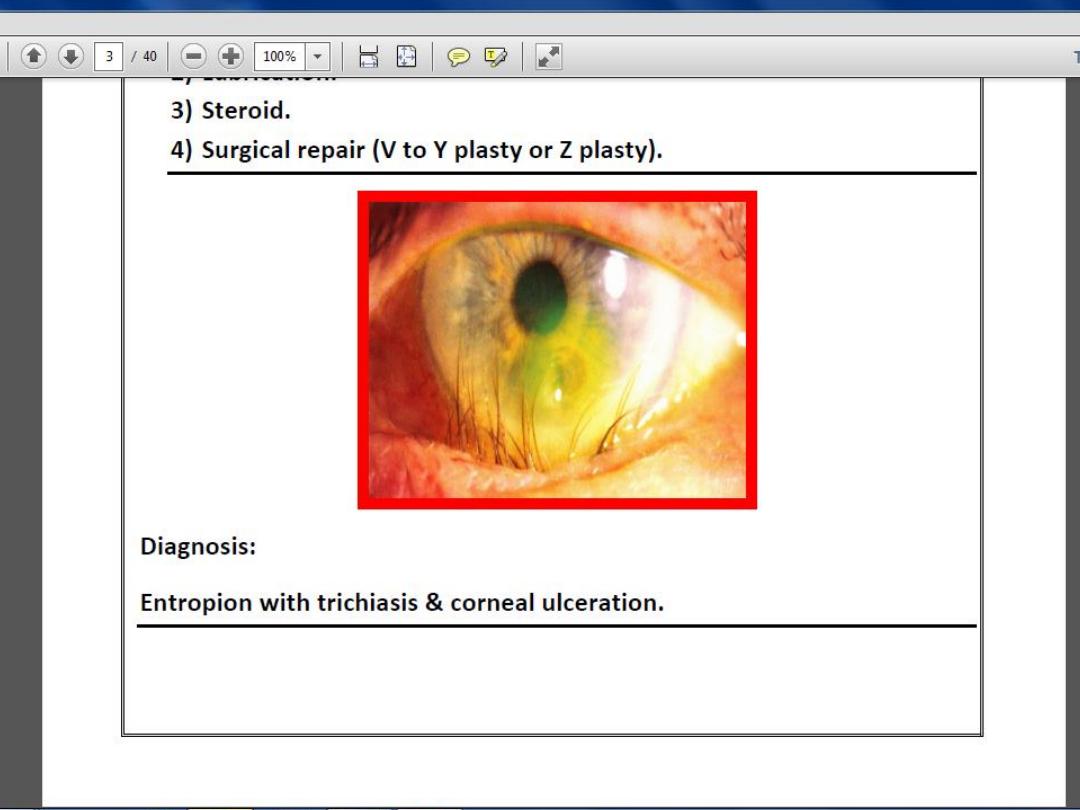
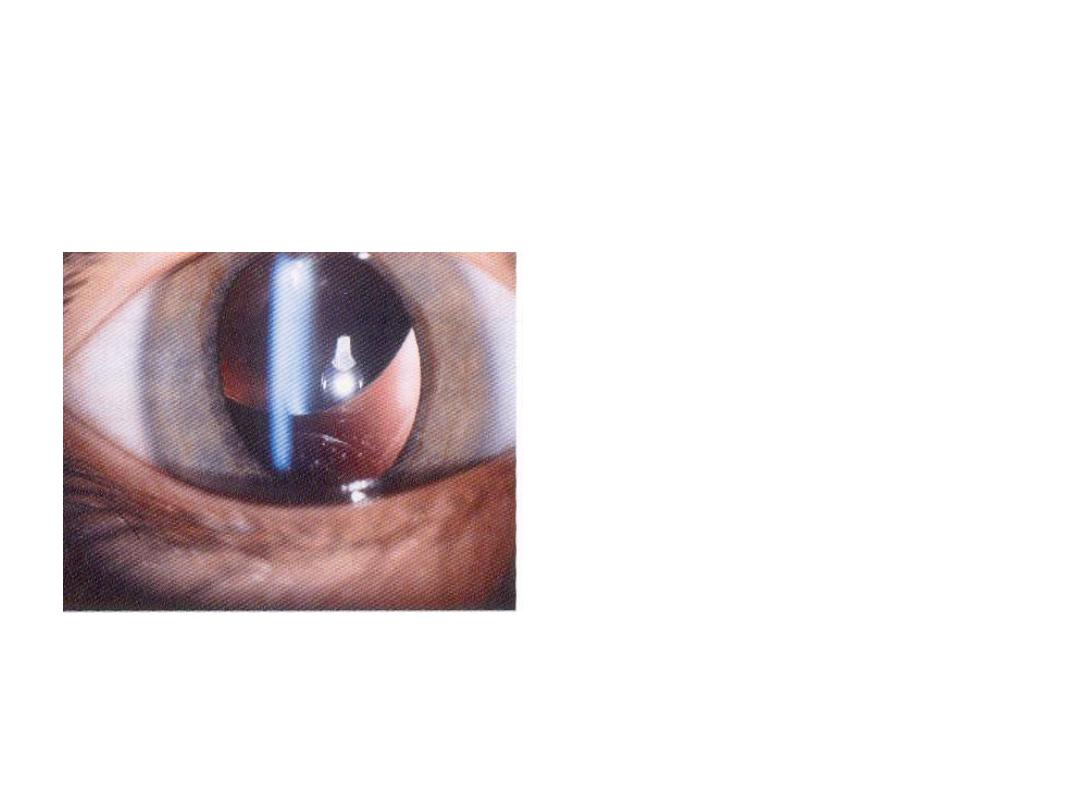
What is this sign ?
Lens dislocation
What are the possible
visual symptoms ?
Blurred vision and diplopia
Enumerate three
possible systemic causes
1-trauma
2-marfan syndrome
3-homocystinuria
4-high myobia(eye problem)
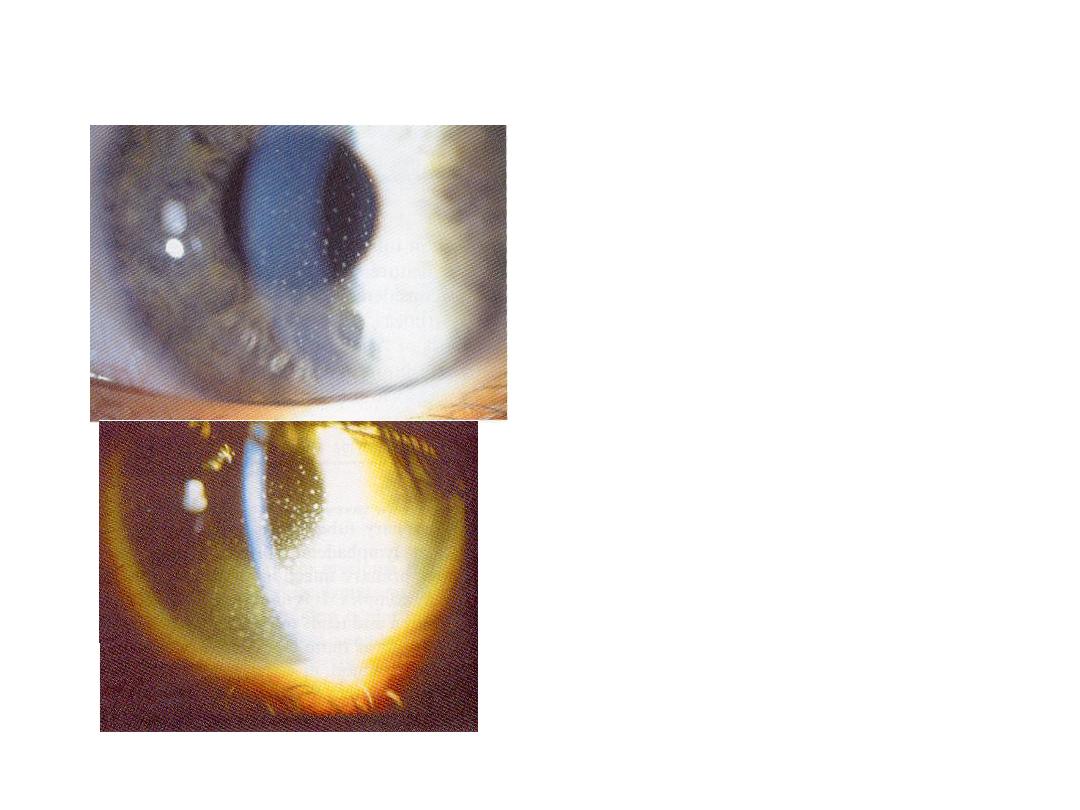
What is the sign shown in the
photo?
Keratic precipitate(white dots in cornea)
What is your diagnosis ?
It is afeature of iritis
What do you think the
presentation of this patient
was ?
Blurred vision,photophobia,pain,redness
Tx ?
1-topical:atropin sulphate and
corticosteroid
2-systemic:steroids(severe cases) or AB
(infected cases)
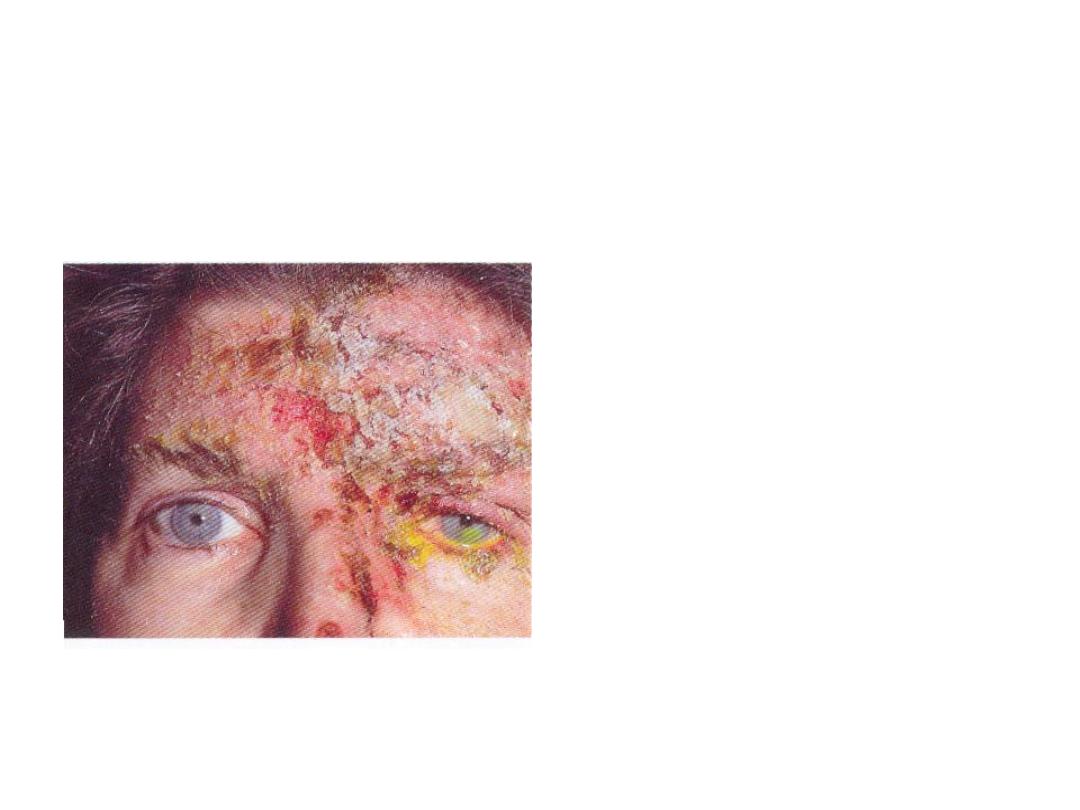
• Q1- Describe the skin
lesion .
•
Erythematous base lesion with
crust,pastule and some sloughing
involving forehead and side of the
nose and upper+lower lid of L. EYE
• Q2- Describe the ocular
lesion.
•
FLOURESCEIN stain showing corneal
ulcer of L.eye+skin lesion involve
upper+lower lid
.
• Q3- What is the cause
of this disease?
•
Herpes zoster virus
• Dx
: herpes zoster ophthalmicus
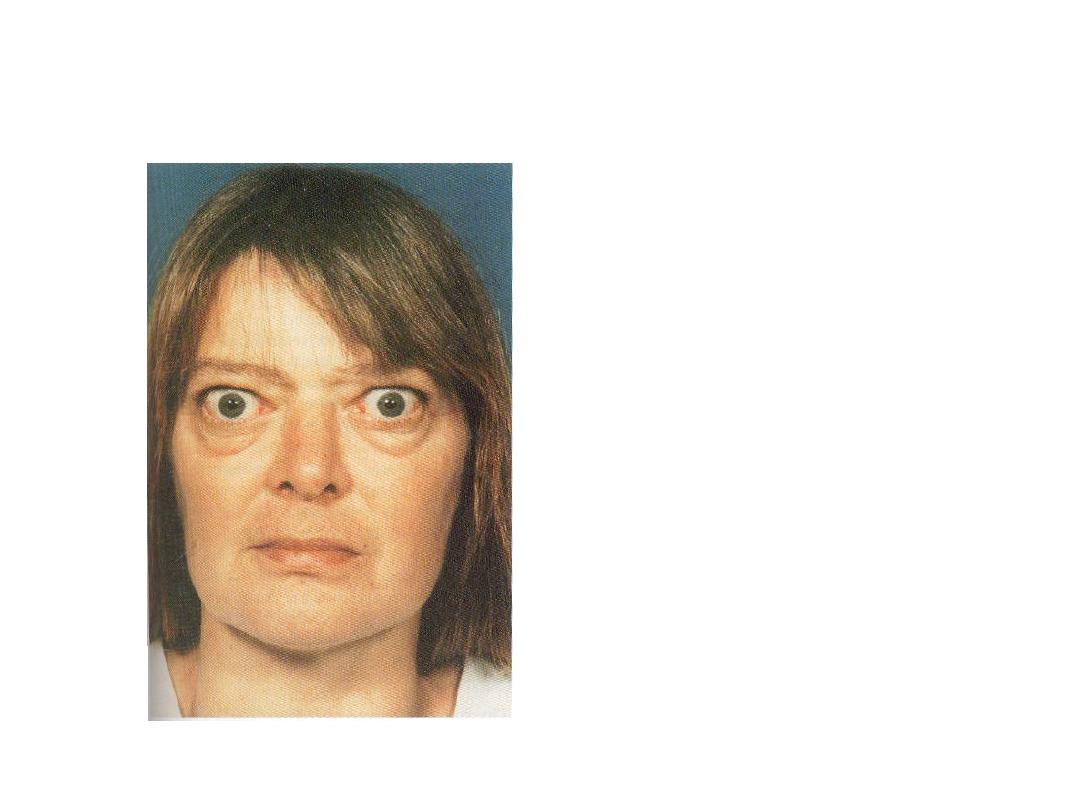
Describe this facies.
Staring facies with periorbital edema
Enumerate four ocular
features of this disease.
1-lid lag 2-lid retraction 3-exophthalmos 4-
excessive lacrimation
Enumerate four systemic
features of this disease
1-sweating 2-palpitation 3-tremor 4-weight
loss
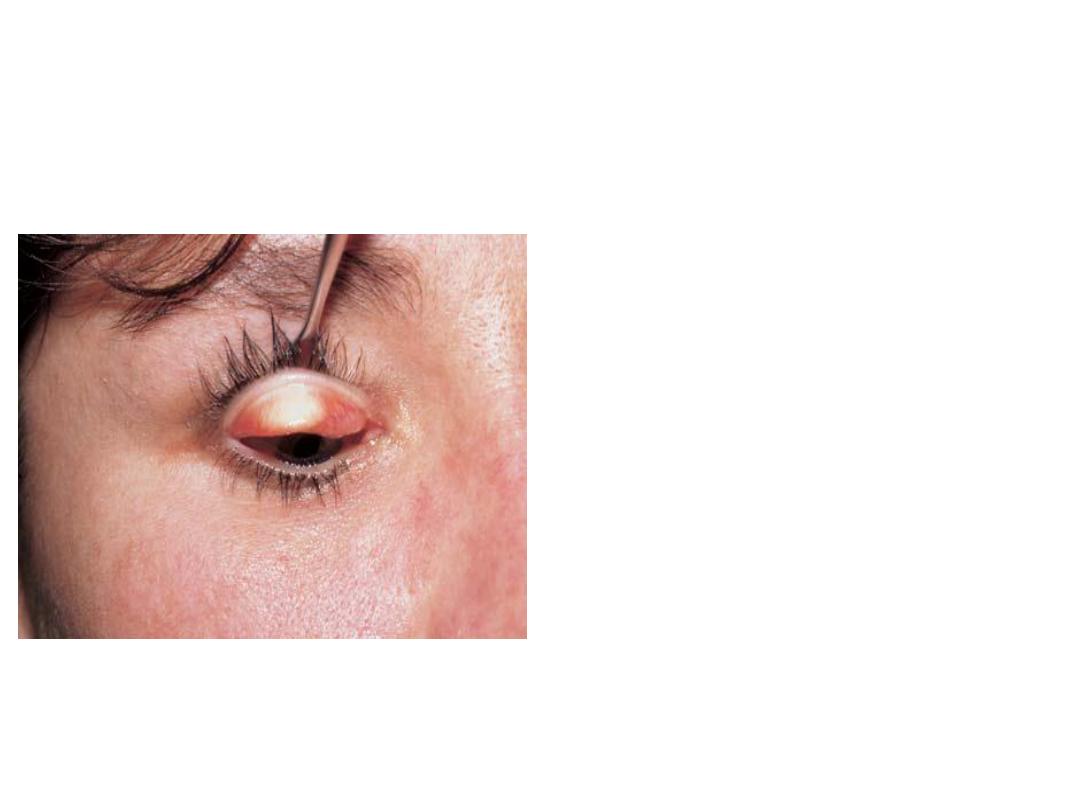
What is this procedure
?
Eversion of upper lid
What are its benefits?
1-very simple
2-F.B. detection
3-papillae detection
4-follicular reaction
detection
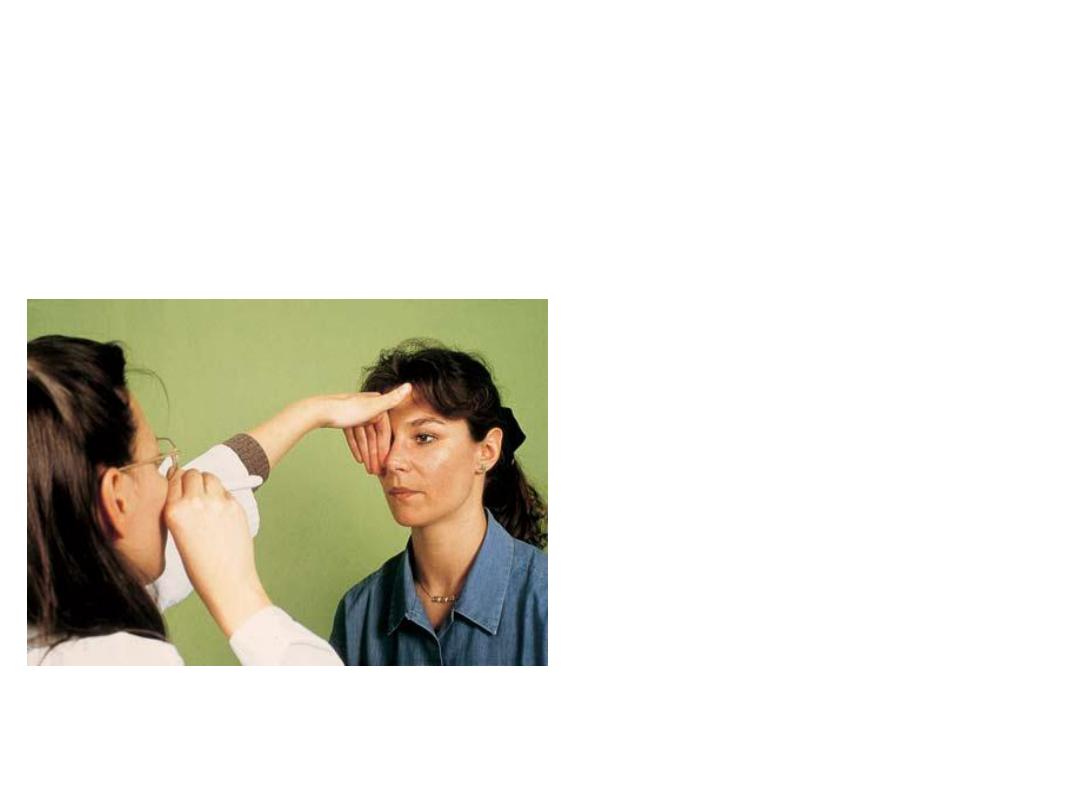
• What is this procedure?
• Cover/uncover test
• In which disease you
want to use it in your
examination ?
• Used to detect
inapparent squint

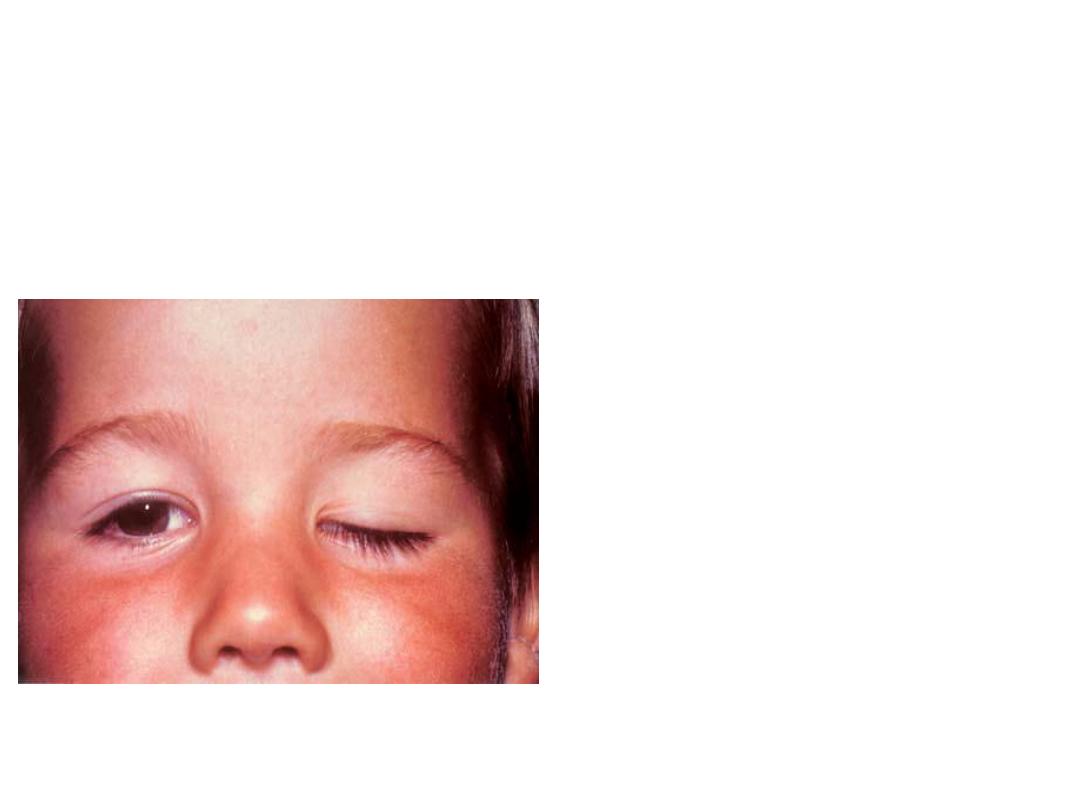
• What is your diagnosis ?
• Left complete ptosis
• What are the possible
causes ?
• 1-3 palsy 2-congenital 3-birth
injury
• Would you go for
surgery for this child ?
• Yes, to avoid amblyopia or
reduction of visual acuity and
here we do sling procedure

لالطالع
•
THIRD NERVE PALSY: 1-PTOSIS. 2-
EXTROPIA OF THE AFFICTED EYE IN
PRIMARY POSITION. 3-LIMITITNG
ADDUCTION. 4-LIMITING
ELEVATION.5-LIMITING DEPRESSION.
6-DILATED PUPIL WITH DEFECTIVE
ACCOMADATION. 7-
Binocular
horizontal diplopia(the most
important
).
•
causes
•
Medical (pupil sparing)
•
• Hypertension
•
• Diabetes
•
Surgical (pupillary involvement)
•
• Aneurysm
•
• Trauma
•
• Uncal herniation
•
TX:
•
1-TREAT THE UNDERLYING CAUSE
•
2-UNIOCULAR OCLUSSION TO AVOID
DIPLOPIA(NEVER UNDER 11 YEARS)
•
3-BOTULINUM TOXIN INJECTION TO THE
LATERAL RECTUS MUSCLE TO PREVENT ITS
CONTRACTURE
•
4-SURGERY.(AFTER 6 MONTH OF ONSET)
•
•
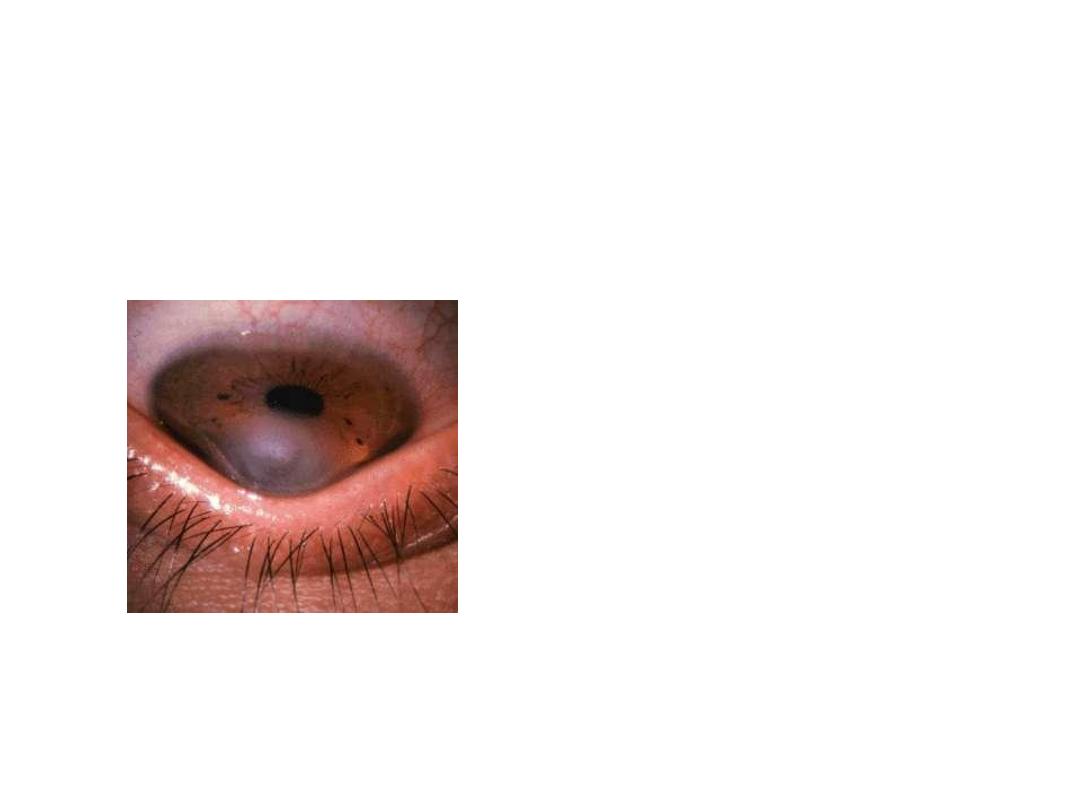
• Q1- Describe what you see.
•
This patient asked to look down, lower lid is
seen pushed by cornea due to increased corneal
curvature with opacity.
• Q2- What is the disease ?
• Keratoconus with acute hydrops
• What is the name of the sign?
•
Munson sign
• Q3- What are the lines of
treatment for this case ?
• 1-contact lens or patching
• 2-hypertonic drops to cause withdrawal of
hydrops
• 3-corneal graft
Lines of tx of keratoconus in general:
1- Corneal Collagen Cross-linking, in
early cases to arrest the disease
2- Glasses
3- Contact lenses (Rigid)
4- Intra-stromal corneal rings
5- Penetrating keratoplasty or Lamellar
keratoplasty..in advanced cases or corneal
scarring
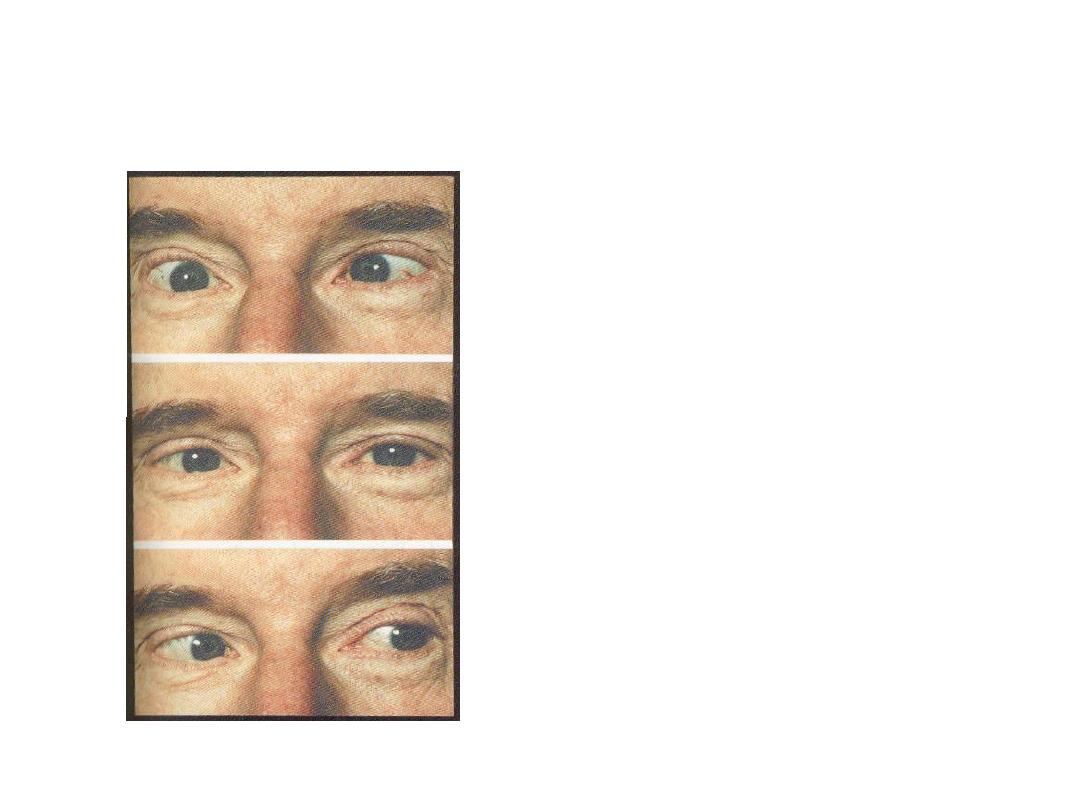
• Q1- Is it a concomitant or
incomitant squint?
• incomitant
• Q2- Which muscle is affected ?
• Right lateral rectus
• Q3- What is the nerve supply ?
• Abducent nerve
• *concomitant:angle of squint
not changed in different visual
directions
• *incomitant:angle changed

لالطالع
•
4
PALSY:1-Binocular vertical or oblique
diplopia . 2-HYPERTROPIA (INCREASED
WITH OPPOSITE SITE GAZE DUE TO
OVERACTIVITY OF I.O.M). 3-LIMITATION
OF DEPRSSION ON ADDUCTION. 4-
NPRMAL ABDUCTION. 5-NORMAL
DEPRESSION. 6-NORMAL ELEVATION. 7-
ABNORMAL HEAD POSTURE TO AVOID
DIPLOPIA.
•
•
CAUSES: 1-CONGENITAL. 2-CAUSES OF 3
PALSY.
•
6 PALSY:1-ESOTROPIA(WORSE FOR
DISTANT TARGET AND LESS OR
ABSENT FOR NEAR TARGET). 2-
LIMITATION OF ABDUCTION 3-
NORMAL ALL OTHER GAZES
•
•
Binocular diplopia