1
Fifth stage
Surgery
عملي
2
د.بسام
30/12/2015
Practical pediatric surgery
#Most important cause of respiratory distress is congenital diaphragmatic hernia
#7 month infant presented with mild respiratory distress with
recurrent chest infection = Eventration of diaphragm (diaphragmatic
paralysis of hemidiaphram usualy the right) the diaphragm is elevated
to the 3
rd
or 4
th
ICS, that’s why during respiration there is paradoxical
movement of the two hemidiaphragms.
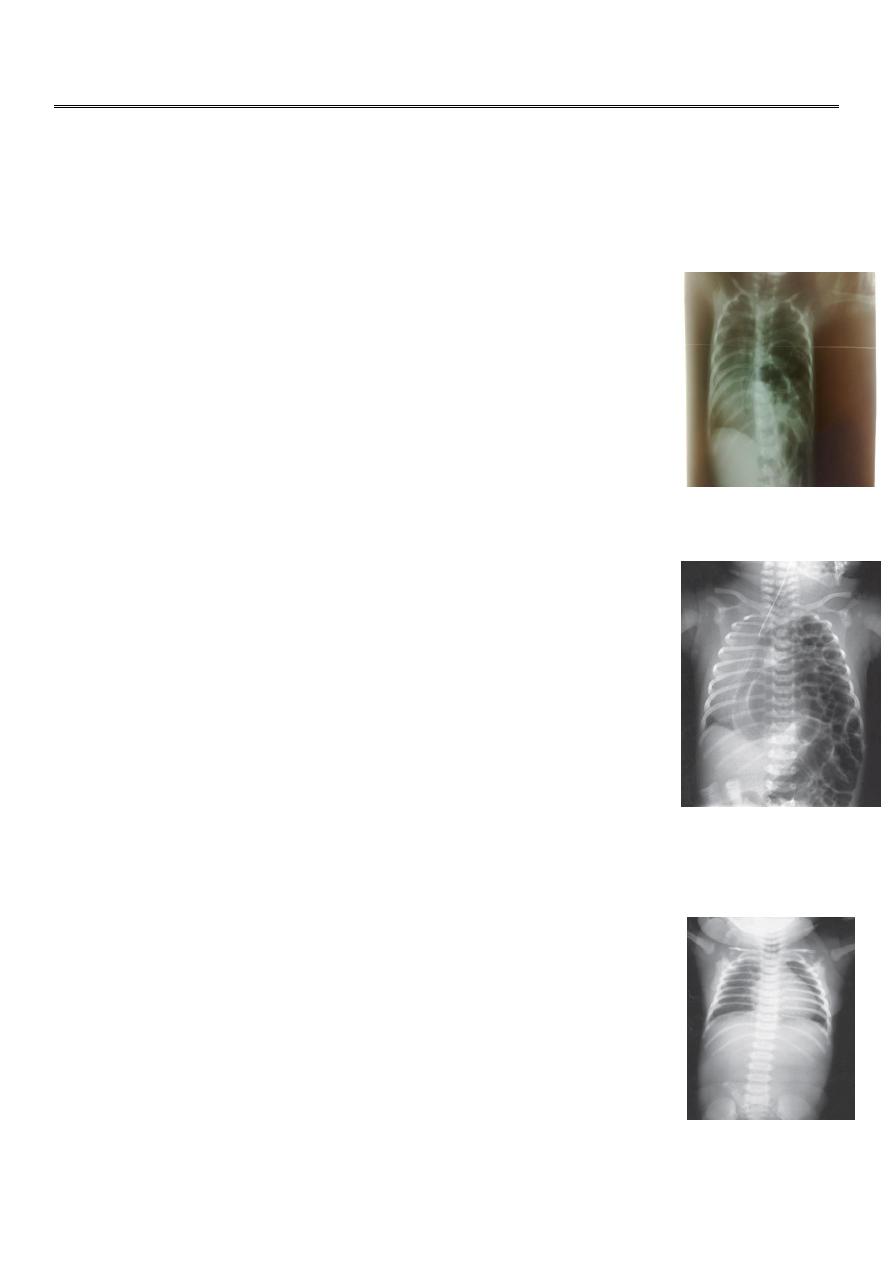
X-ray- elevated diaphragm, presence of lung tissue, bowel loops in
chest + dextrocardia
Diagosis by fluoroscope
Tx; Plication (suturing of the hemidiaphram down) through the chest incision
# One day neonate with severe respiratory distress, very tired and
cynosed with hyperinfalted chest barrel chest, with flat or scaphoid
abdomen
X-ray : bowel loops fill the left side of the chest, sometimes with viscera
with no lung tissue, deviation of the mediastinum with dextrocardia,
endotracheal tube is seen.
Dx; Barium study or X ray = Congenital DH
Tx: Subcostal incision, pull the bowel and close the defect
#The main cause of death, is hypoplastic lung = pulmonary HTN = death
#During operation and after reduction of bowel look for the presence of lung tissue and
inflate the lung to see it if functional or not.
#sometimes there is sac as in other types of hernia which is useful in
repair.
#Two X ray of :
1- X- ray showing coiled NGT failed to pass with radiopaque abdomen =
esophageal atresia without fistula
2-X- ray showing coiled NGT failed to pass, with gas shadow in the
abdomen = TEF
Benefits of X- Ray :
1-Dx and Type of esophageal atresia and fistula

2
2-Condition of the lung aspiration of saliva and milk e.g. chemical
pneumonitis
3-look for right aortic arch
4-Other anomalies, vertebral and ribs
5-length of the defect, measure from the end of pouch to the
carina if 2 cm u can do it primarily if wider it is harder.
#Causes of Double bubble signs
1-Doudenal obstruction
2-Malrotation of bowel e.g. the cecum stop at the right hypochondrium
and there is a band to posterior abdominal wall compressing the
duodenum
3-Annular pancreas
4-Doudenal stenosis
Clinical features of duodenal obstruction:
1-Bileious vomiting
2-Failure to pass meconium
3-Mild epigastria distention which disappear after vomiting
##Associated with down syndrome
30 percent
#Two gas bubble = proximal obstruction.
#Many bubble = distal obstruction.
# We can't differentiate between large or small bowel obstruction on X –ray in neonate.
#Meconium ileus;
@ one of the causes of IO in neonate
@huge dilatation of small bowel usually ileum
@Contain thick sticky tenacious secretions, can't be solubilized by
normal saline ,
@Abdominal doughy mass in the right iliac fossa, with indentation on
pressure
@ no air fluid level on X ray
@Associated with cystic fibrosis
Tx: Surgical excision and re anastomosis
Dx and Tx ; Gastrograffin enema, which can liquefy the meconium and make it easy to pass
out and solve the problem , so it is conservative Tx.

3
##Small bowel atresia
Proximal dilated bowel with distal thin atretic bowel
@Dx: multiple air fluid level
@Tx: Surgical resection with end anastomosis
##Hirschprungs disease
@Barium enema study, showing huge dilatation of the sigmoid up to the
descending colon, and narrowing at rectosgimoid junction, filled with
fecal material
Due to aganglionic segment of bowel lead to spasm..
C/F:
#Neonate; failure to pass meconium with IO,
#Delay in pass meconium with chronic constipation late in life.
#With complication: enterocolitis (diarrhea cuz of ulceration,
perforation)
Types :
Short or long segment of aganglionic colon
Tx:
Pull through surgery, resect the aganglionic segment and pull the normal through the anus
and anastomose it with anus.
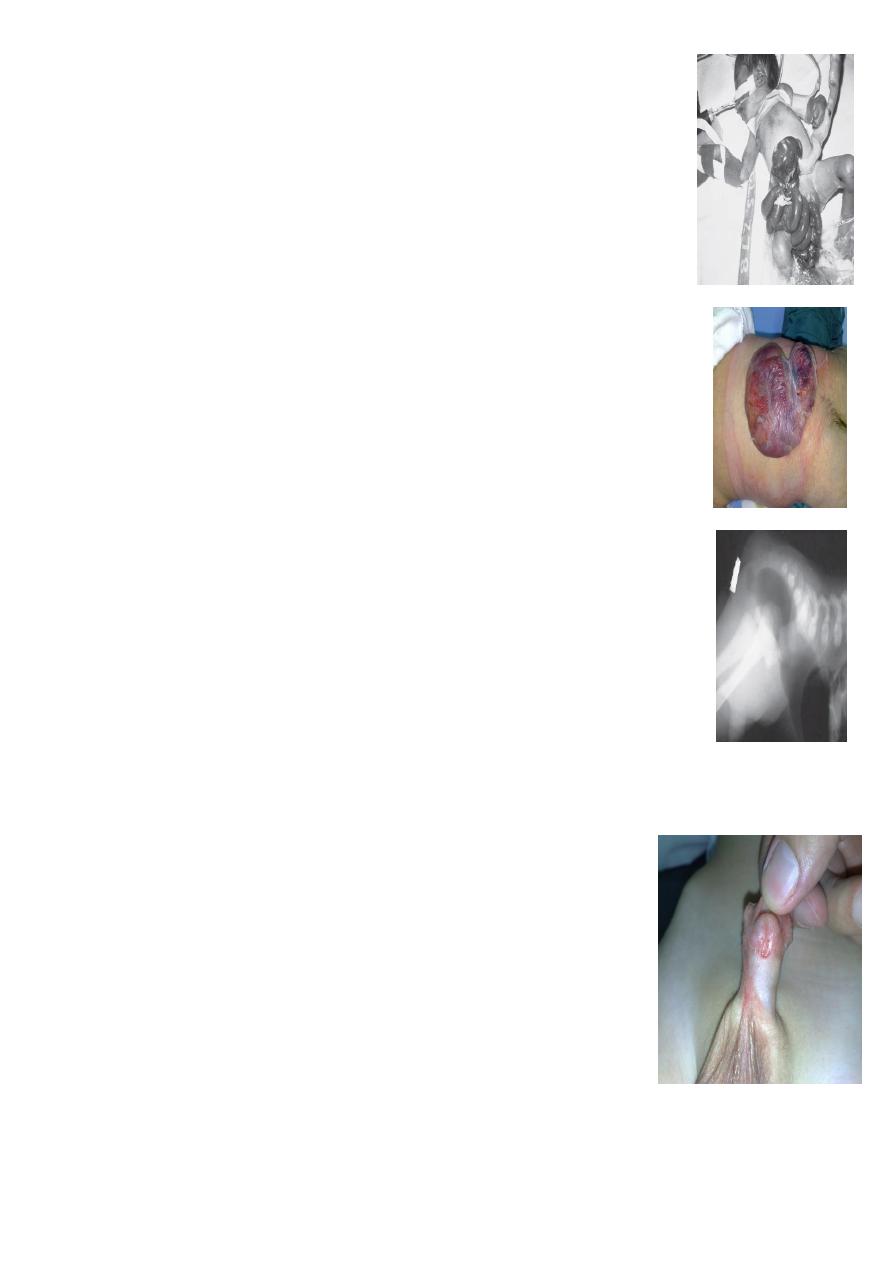
#Omphalocele or exomphale;
##Major: huge mass on the abdomen originate through the
umbilicus about
5-10 cm
, contain small bowel and liver, managed by
using silo bag with gradual twisting to reduce the liver into abdomen
slowly to accommodate for its size.
##Minor: Small about 2-3 cm with only small bowel inside, treated
primarily by reduction and closure.
##Tx:
Cover the baby and put the baby into incubator and give fluid
therapy (wide body surface area increases evaporation and heat loss
and more risk of hypothermia)
Not emergency for surgery
Associated with more anomalies than gastroschisis.
4
#Gastroschisis:
=bowel exposed completely there is no covering sac
= to right side of umbilicus
=Emergency.
=Associated with less congenital anomalies.
=Tx; reduce and close the defect, sometimes we also may use silo bag to
reduce the bowel gradually.
##Meningomyelocele;
*usually associated with hydrocelphalus.
*lower limb paralysis.
## Lateral invertogram
=pubococcegeal line (below or above gas bubble ) means lower or upper
type of anorectal atresia respectively.
= mark gas distance
=well formed anal dumble associated with low type,
## Cloaca treated as high type IA
##Vestibular fistula = Low type IA
##hypospidias
1-Proximal type(penoscrotal)
2-Distal type (Subcoronal )
Complication:
1-Ventral cordy
2-Psychological in child and adulthood
3-UTI
4-Sterility
Time of operation before
one year unless
there is no
contraindication.
5
#4 month year old presented with severe acute screaming and pulling his
legs toward his abdomen, with sausage like mass to right of umbilicus
with red currant jelly stool = Intucessuption,
Inx : US / barium enema =
coiled spring or claw sign
. Barium enema can
lead to hydrostatic reduction (Dx and Therapeutic), or also pneumatic
enema also used to reduce it, or if failed do laparotomy and reduce it by
pushing from distal to proximal.
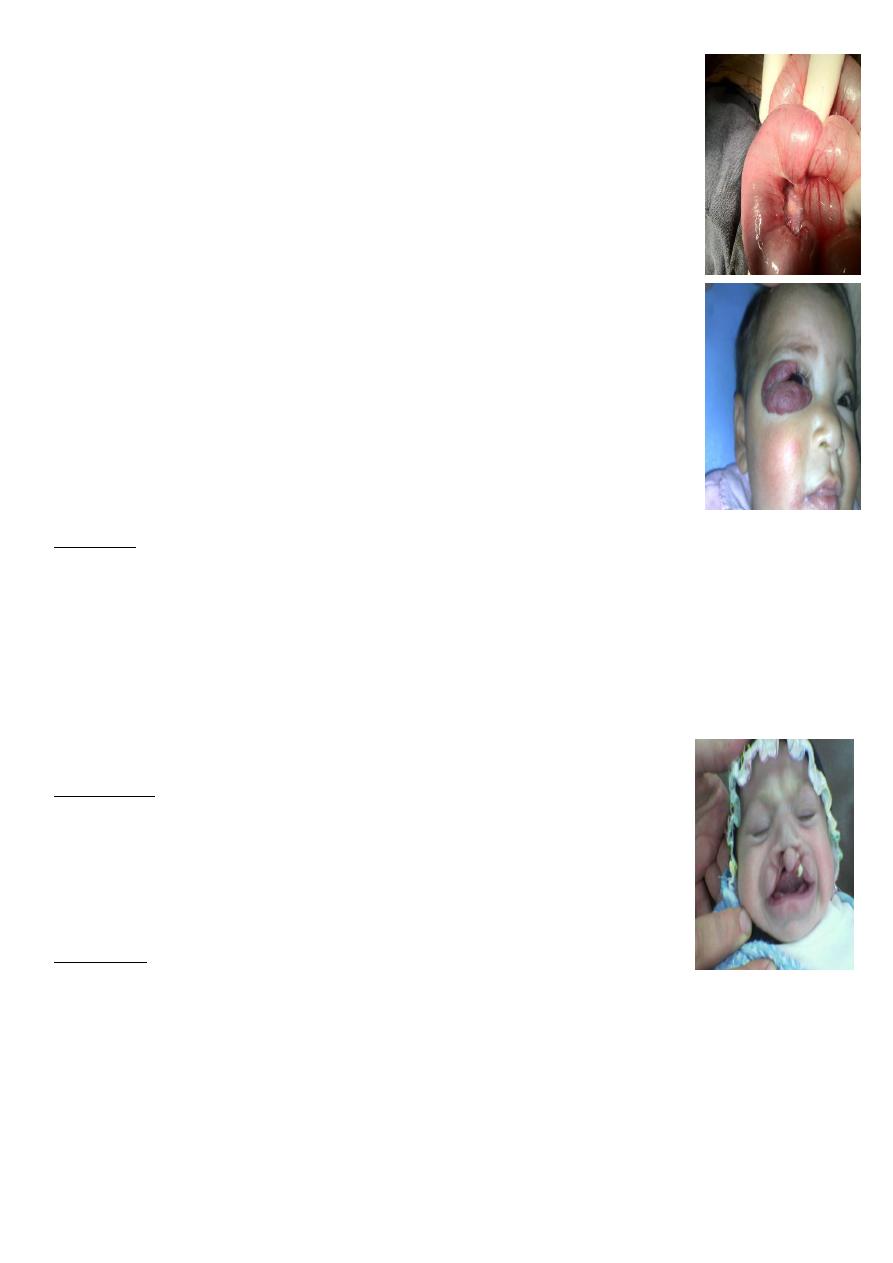
##Cavernous Hemangioma.
Complication:
1-bleeding
2-Ulcer
3-Infection
4-Pressure effect according to site e.g. eye affect vision, ear may cause
deafness.
5-consumptive coagulopathy due to hemolysis inside the hemangioma =
activation of clot mechanism = consumption = DIC = Casabach syndrome.
On exam:
compressibility, can be compressed and refill after removal of pressure.
Treatment;
Small red spot increases in size rapidly within
2-3
month Up to
1 or 2 increase in size then
become stable
( Platue phase) till the
5 year
start to decrease and
within 7 years
it involute
mostly by itself according to the type and site.
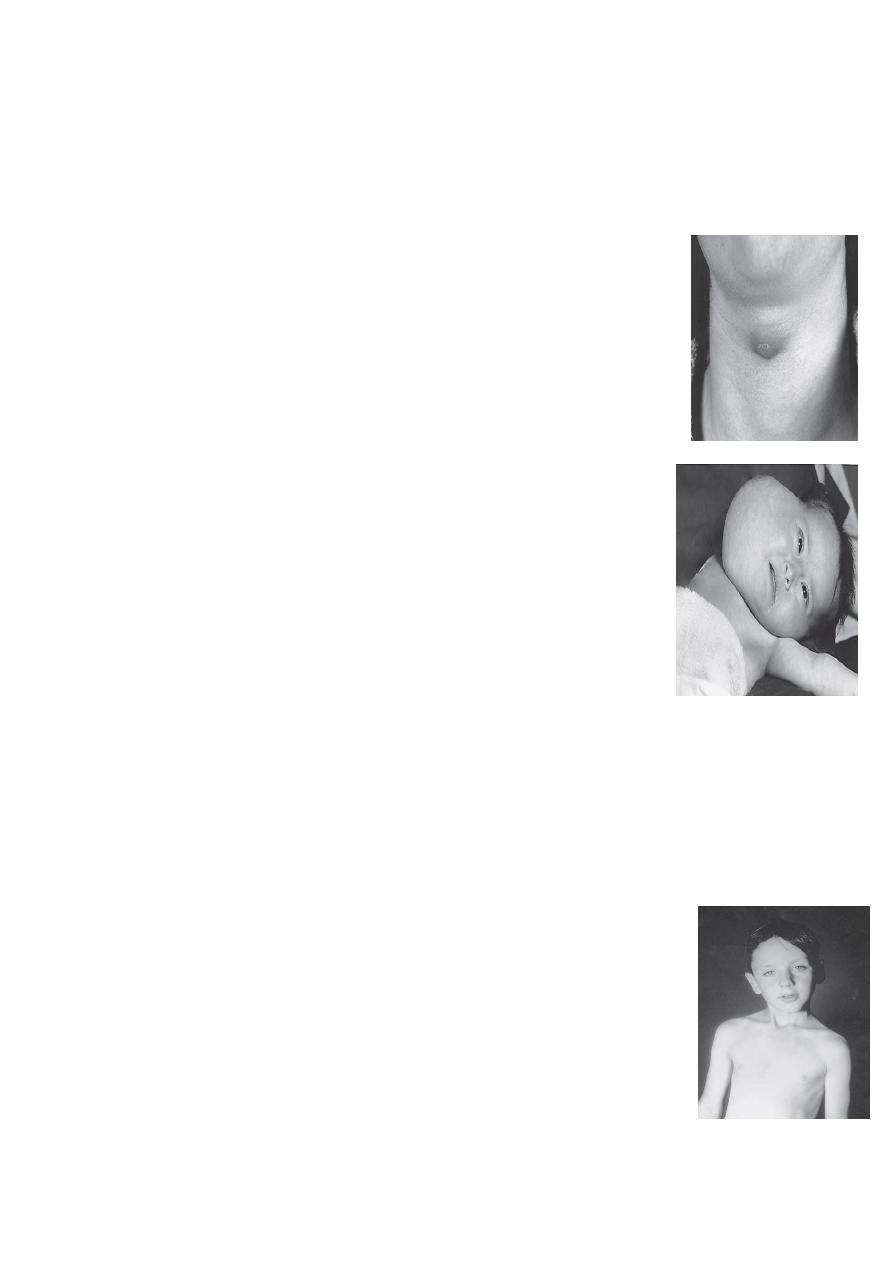
$$ Cleft lip and palate;
$$ Cleft lip :
1-Aspiration (recurrent chest infection) during feeding
*Use special tit.
*Position of baby in semisiting position.
2-Nasal speech.
3-Glue ear, decrease hearing
Role of 10;
1-10 pounds.
2-10 g/dl Hb.
3-10 week of age (6-12 week).
$$Cleft lip
1-cosmotic
time of surgery is before
3 months
, cuz after this the muscles will become more powerful
and this may disrupts the anastomosis after surgery
6
can be:
1-Complete or incomplete.
2-Uni or bilateral.
3-May be associated with cleft palate.
##surgery: Milard surgery
##Cleft palate, time of surgery is from 6 months to 1 year.
## Thyroglossal cyst.
complication :
1-Infection
2-Fistula
3-Malignant transformation after 20 -30 years
Surgery : Sistrunk operation (remove the cyst and the tract completely )
+ removal of the central part of hyoid bone or sometimes completely.
##Cystic hygroma.
Lymphatic obstruction
common sites:
1-Neck, post. Triangle
2-Axilla
3-Groin
complication indicate surgical intervention
1-compression
2- infection may lead to abscess and septicemia or sometimes infection
may lead to healing of it.
3-Bleeding, the child go in shock
During surgery be careful about certain structures
1-cervical nerves
2-Manbdibular branch of trigeminal
3-Hypoglossal nerve
##sternomastoid Torticollis and sternomastoid tumor
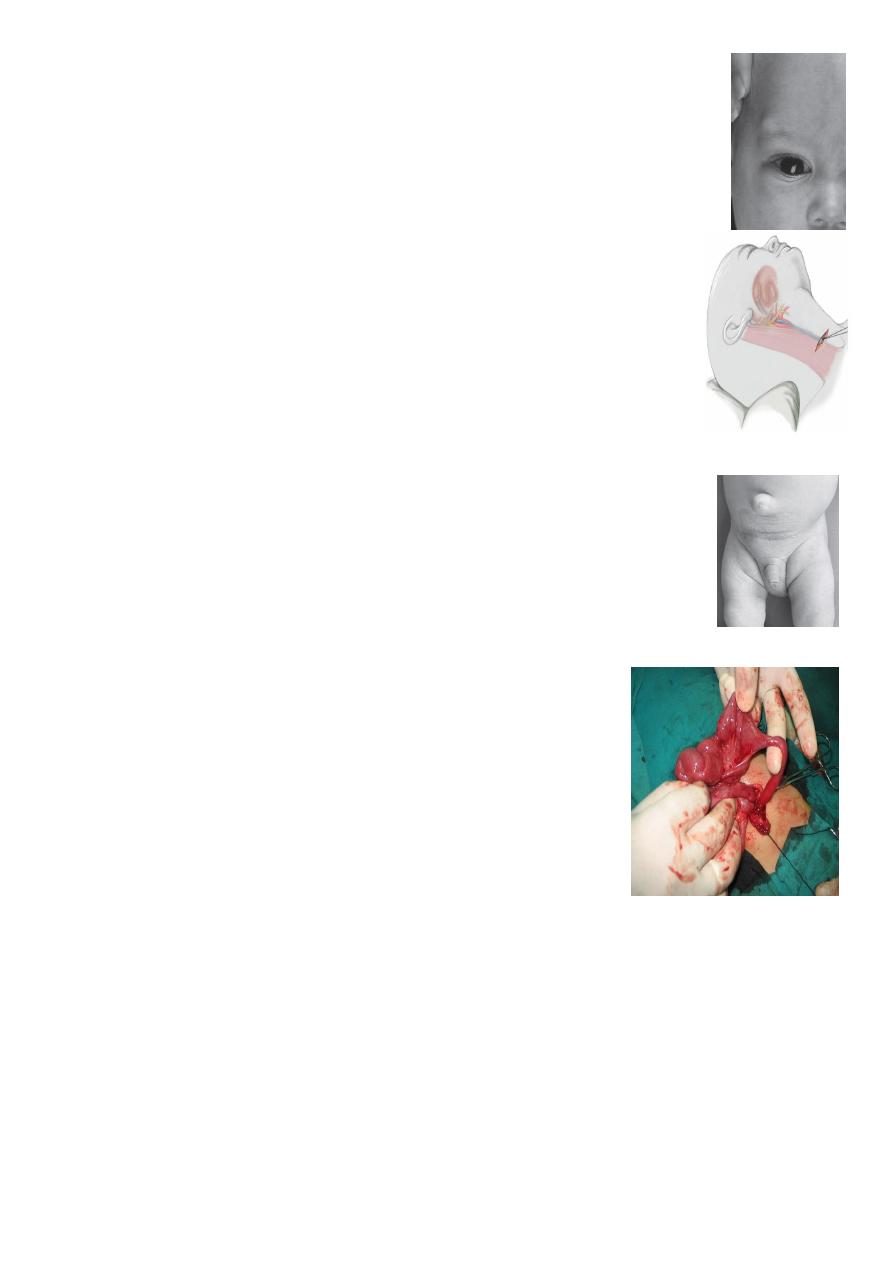
1-Sternomastoid tumor ; two week baby presented with mass, it is a tear
in the muscle, you should ask about obstructive labor, breech
presentation, forceps use, this if not treated probably by physiotherapy
will be torticollis within one year due to shortening of the muscle.
Tx: Physiotherapy, twisting the chin right and left with some massage,
might disappear in 90 percent of cases.
2-Torticollis:
you should cut the muscle + physiotherapy
7
##External angular dermoid.
Complication: cosmetic, rupture, infection
Tx; surgical removal of the whole cyst, otherwise it will recur.
##Remanant of second branchial arch = branchial cyst, sinus, or fistula.
Between the upper two third and lower one third of the anterior border of
sternmastoid muscle.
Hx; Whitish sticky discharge.
Complication;
1-infection
2-malignancy (late )
Tx:
Surgical, when baby is
one year
, excision of the total tract till you reach
the tonsil, be careful about hypoglossal nerve and carotid artery.
##Umbilical hernia
Wait don’t rush for surgery might disappear by itself.
##omphalomesenteic duct anomaly
1-Complete communication between skin and bowel = fistula
2- Cyst
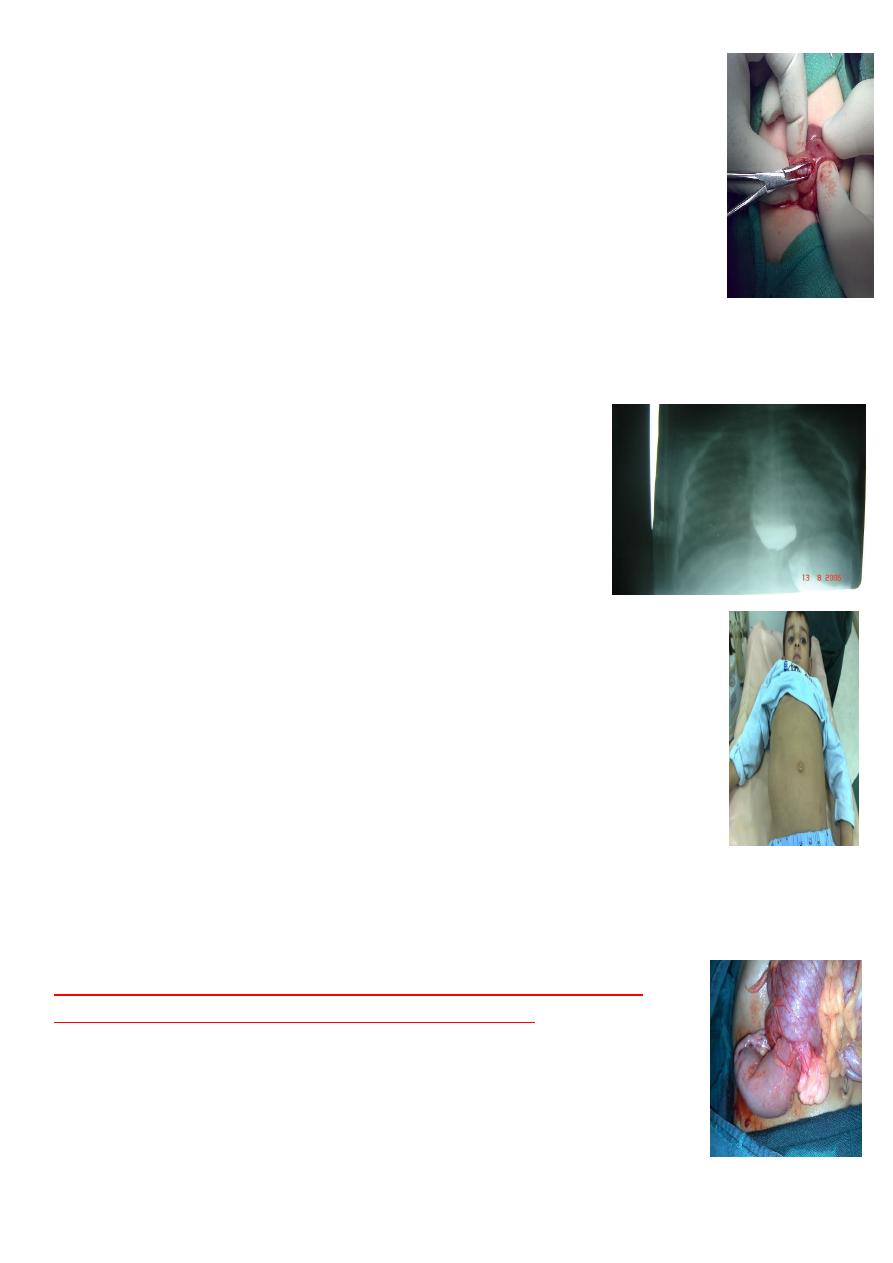
3-Meckles diverticulum:
IT is true diverticulum
Role of 2 :
1- 2 inch in length
2- 2 ft from ileocecal valve
3- 2 percent of population
4- 2 ectopic tissue (gastric or pancreatic)
5- 2 common complication (ulceration and bleeding)
C/F
1-Painless profuse Bright red or marron perectal bleeding
2-intestinal obstruction (valvolus)
3-infection
4-Perforation
5-intussception
6-Abdominal pain
7-incidently during laparotomy for something elese.
Dx :
1-Istotope scan : to check for ectopic gastric tissue, by giving special dye that is absorbed by
the parietal cells,
2-Laproscopy : Dx and therapeutic
8
## 1 and half month presend with projectile vomiting and failure to thrive
CHPS
1-Projecticle vomiting non bilioius.
2-Olive mass in the epigastric region.
3-Feeding test positive ( positive peristalsis coming from left to right with
feeding to overcome the obstruction).
Inx
1-US
2-barium meal ( dilated of stomach, failure of barium to pass into
duodenum, sometimes string sign, take again after 4 hours it will stay in stomach)
Tx; Pyloromyotomy
or Ramstids operation
$$ 3-4 years repeated vomiting, halitosis, etc.
Barium swallow. Showing dilated esophagus with narrowing of
the distal segment bird peak sign = Achalasia
Tx: Cardiomytomy
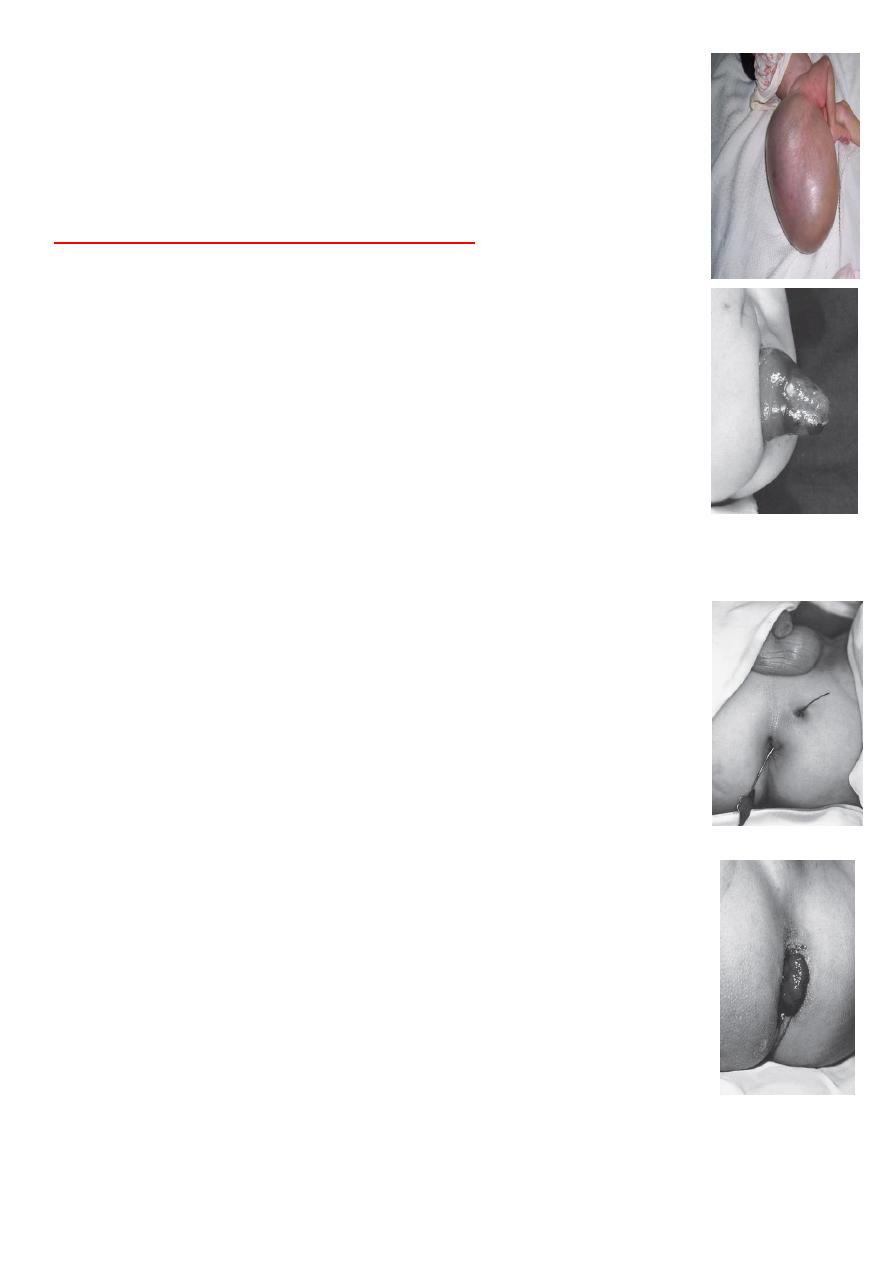
### 5 yers old, presented with filling in the flank
DDx mass in flank
1-Nephroblastoma (wilms tumor)
2-neglected PUJ
3-neuroblastoma
The most common of pediatric renal tumor is Wilms tumor(second is
neuroblastoma) (third is lymphoma non-hogkins), may present as mass,
hematuria, hypertension.
Tx: complete removal of the kidney + post-op chemotherapy
(Hodgkin's in cervical region mostly ,non-Hodgkin also called burkit
lymphoma occur in GIT, may present as intucessuption)
Confirm Dx by fine needle aspiration then start chemotherapy it is as
effective as surgery
The problem in lymphoma is it emergency due to it is rapid growth
(doubling time is high ) if one cm, on second day 2 cm, on third day 4 cm ,,
etc.
9
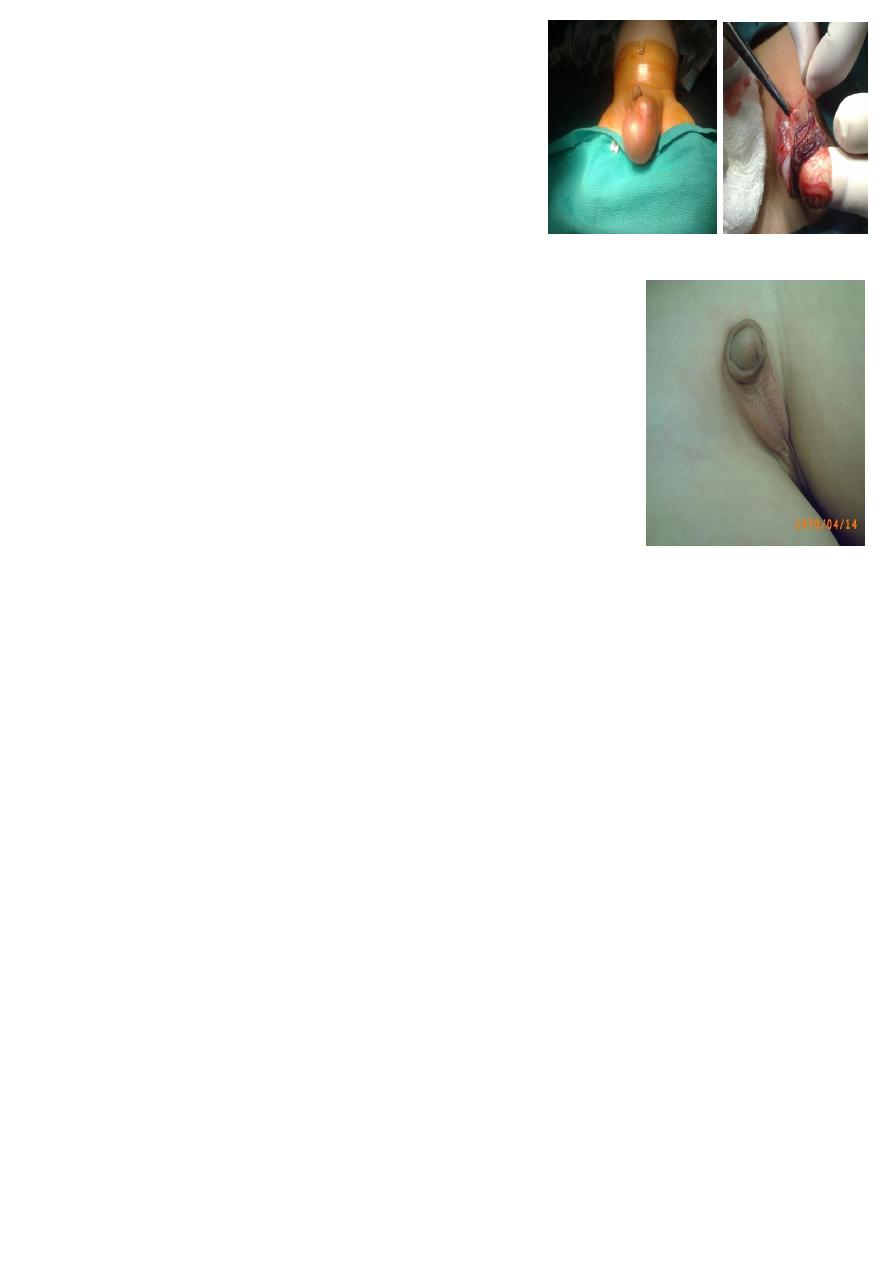
##Sacrococcygeal teratoma:
Problems :
1-Obstructed labor
2-Rupture
3-malignancy (10 percent), if neglected within
two months
will convert to
malignancy.
SHOULD REMOVE COCCYX to prevent recurrence
.
## Rectal prolapse
Causes:
1-constipation
2-Diarhea
3-weakness of pelvic muscles as in meningomyelocele
4-Trichuris trichiura infestation
Grades of prolapse :
1-Prolapse and reduced spontaneously
2-prolapse but reduced by mother
3-Always prolapsed not reduced
*2 and 3
rd
need surgical repair, while 1
st
only conservative.
Surgery is by doing Thursh operation by using subcutaneous suturing.
$$Perianal fistula
Fistulectomy or Fistulotomy
$$ Prolapsing strawberry mass = Juvenile rectal polyp, the cause is due to
infection of the
crypts of Lieberkuhn.
other type as familial polyposis coli.
Tx :
removal by sigmoidscopy
11
$$Hernia and varicocele
$$Undescended testis(empty scrotum) :
1-Unilateral = undescended testis
2-Bilateral = cryptorichidism
Tx: palpable ; orcheopexy if not palpable do laproscopy to see if
present or not, if present laproorecheopexy.
Problems:
1-infection may confused with appendicitis
2-increase incidence malignancy more than other persons
3-Sterility
