
1
Fifth stage
Pediatric
Lec-10
.د
أوس
7/3/2016
Down's syndrome
Clinical features
Down's syndrome is usually suspected at birth because of the baby's facial appearance
Typical craniofacial appearance
1. Round face and flat nasal bridge
2. Upslanted palpebral fissures
3. Epicanthic folds (a fold of skin running across the inner edge of the palpebral fissure)
4. Brushfield spots in iris (pigmented spots)
5. Small mouth and protruding tongue, Small ears
6. Flat occiput and third fontanelle
Other anomalies
1. Short neck
2. Single palmar creases, incurved fifth finger and wide 'sandal' gap between toes
3. Hypotonia
4. Congenital heart defects (40%)
5. Duodenal atresia
6. Hirschsprung's disease
Later medical problems
1. Delayed motor milestones
2. Moderate to severe learning difficulties, Small stature
3. Increased susceptibility to infections
4. Hearing impairment from secretory otitis media
5. Visual impairment from cataracts, squints, myopia

2
6. Increased risk of leukaemia and solid tumours
7. Risk of atlantoaxial instability
8. Hypothyroidism and coeliac disease
9. Epilepsy
10. Alzheimer's disease
Edwards' syndrome (trisomy 18) and Patau's syndrome (trisomy 13)
Although rarer than Down's syndrome (1 in 8000 and 1 in 14 000 live births, respectively),
particular constellations of severe multiple abnormalities suggest the diagnosis at birth and
most affected babies die in infancy
The diagnosis is confirmed by chromosome analysis
Clinical features of Edwards' syndrome (trisomy 18)
Low birthweight
Prominent occiput
Small mouth and chin
Short sternum
Flexed, overlapping fingers
Rocker-bottom feet
Cardiac and renal malformations
Clinical features of Patau's syndrome (trisomy 13)
Structural defect of brain
Scalp defects
Small eyes (microphthalmia) and other eye defects
Cleft lip and palate
Polydactyly
Cardiac and renal malformations
3
Turner's syndrome (45, X)
Usually (>95%) this results in early miscarriage.
In live-born females, the incidence is about 1 in 2500
short stature may be the only clinical abnormality in children.
Clinical features of Turner's syndrome
Lymphoedema of hands and feet in neonate, which may persist
Short stature - cardinal feature
Neck webbing or thick neck
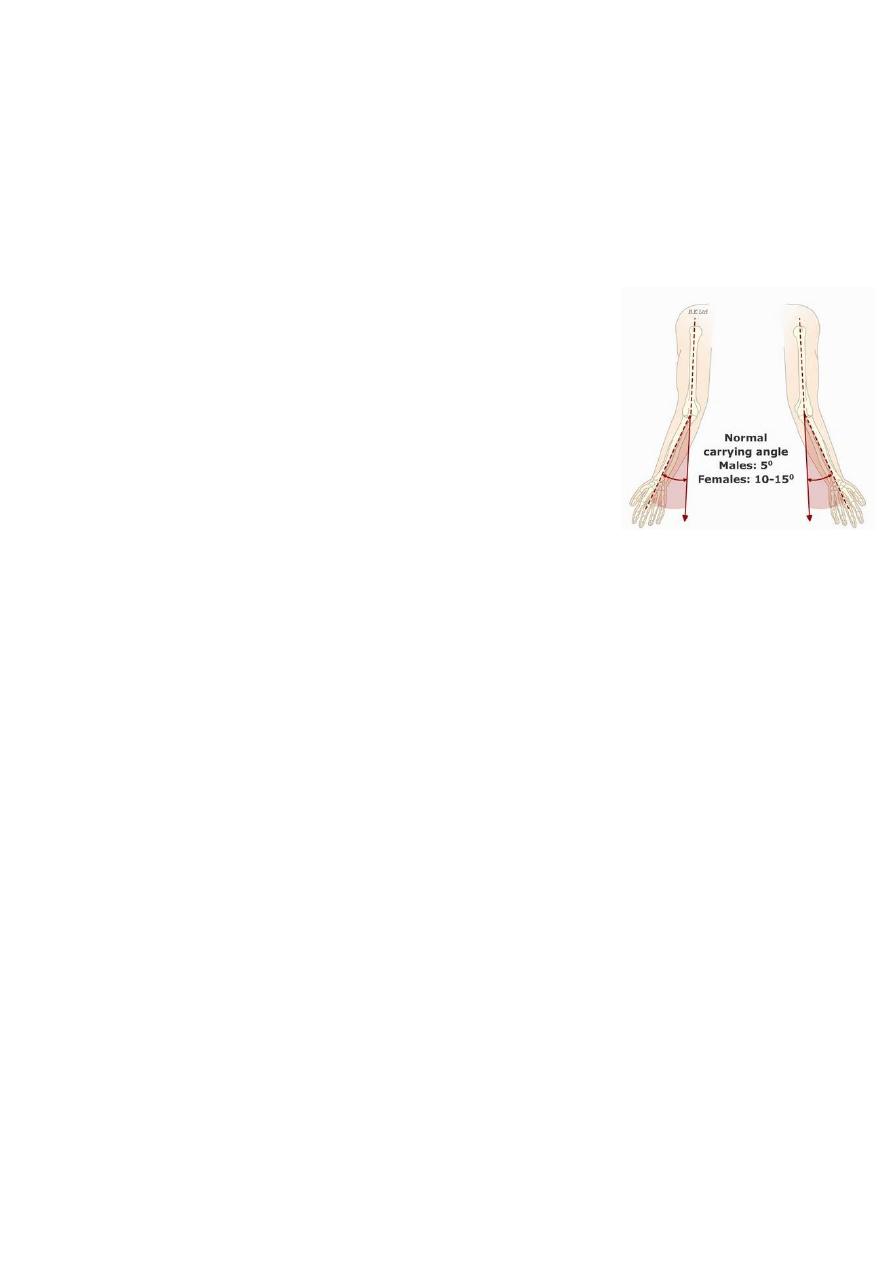
Wide carrying angle (cubitus valgus)
Widely spaced nipples
Congenital heart defects (particularly coarctation of the aorta)
Delayed puberty
Ovarian dysgenesis resulting in infertility, although pregnancy may be possible with in-vitro
fertilisation (IVF) with donated ova
Hypothyroidism
Renal anomalies
Pigmented moles
Recurrent otitis media
Normal intellectual function in most
Treatment
1. growth hormone therapy
2. oestrogen replacement for development of secondary sexual characteristics at the time
of puberty (but infertility persists).
