Inflammation
Lecture IIDefect in leukocytes function
Defect in adhesionLeukocyte adhesion defect-1 due to defect in integrin.
Leukocyte adhesion defect-2 due to defect in sialyl- Lewis X.
Defect in chemotaxis or phagocytosis
Chediak-Higashi syndrome.
Defect in microbicidal activity
Chronic granulomatous diseaseChemical Mediators
A substances which play a role in genesis and modulation of inflammatory reaction.They are responsible for:
1.Vasodilatation.
2.Increased permeability of the blood vessels.
3.Emigration of WBC (Chemotactic agent).
Mediators of acute inflammation
Plasma factors synthesized mainly in liverPlasma proteins
Factor XII = coagulation system (Hageman factor) activation
Kinin system
Coagulation systemComplementactivation
C3a
C5aC3b
C5b-C9
anaphylatoxins
opsonin
MAC
Chemical Mediators of Inflammation
A/ Vasoactive Amines1) Histamine: secreted from mast cells, basophils & platelets.
2) Serotonin: secreted from platelets, enterochromaffin cells.Effects: arteriolar vasodilatation & increase vascular permeability.
B/ Arachidonic Acid (AA) MetabolitesAA present in the cell membrane phospholipids.
Release from phospholipids through the action of phospholipase enzyme by mechanical, chemical & physical stimuli.AA metabolism proceeds along 1 of 2 pathways
Cyclo-oxygenase pathway------Prostoglandins.Lipo-oxygenase pathway------------Leukotriens.
Arachidonic Acid Metabolites
Cyclo-oxygenase pathway
-Thromboxane A2
VasoconstrictionPlatelet aggregation
-Prostacyclin (PGI2)
Vasodilatation
Inhibits Platelet aggregation
-PGD2, PGE2 & PGF2
VD & edema
-PGE2:
Fever
Pain
Lipo-oxygenase pathway
-HETE:
Chemotaxis-LTB4:
ChemotaxisAggregation of neutrophils
-LTC4, LTD4, LTE4
Vasoconstriction
Bronchospasm
Increase vascular permeability
C/ Platelet-Activating Factor
Synthesized from membrane phospholipids through the action of phospholipase A2 in basophils, endothelial cells & neutrophils.
Effects of platelate –Activating factor
Platelet aggregation.
V.D. & increase vascular permeability.
Chemotaxis.
Smooth muscle contraction.
D) Cytokines
Polypeptides produced by activated lymphocytes & macrophages.It involved in cellular immunity & inflammatory responses.
IL-1 & TNF
Acute phase reaction including fever & Neutrophilia.
Promote endothelial secretion of PG & NO.
Induce fibroblastic proliferation & collagen synthesis.
IT-6
Acute phase reactions.
IT-8
Chemotactant & neutrophil activating agent.
E) Nitric Oxide (NO)
Soluble free radical gas synthesized by endothelial cells, macrophages & specific neurons in the brain.
Effect
Vascular smooth muscle relaxation causing vasodilatation.Decreased platelet aggregation & adhesion.
Microbicidal agent.
F) Lysosomal Constituents
Potentially act as inflammatory mediators when released from neutrophils & macrophages.Effect:
Destruction of ECM.Direct cleavage of C3 & C5.
G) Oxygen Free RadicalsSuperoxide (O2-), OH-, H2O2 & NO
Effects
Endothelial cell damage causing increase vascular permeability.
Activation of proteinases.
Injury to surrounding cells.H/ Plasma Proteases
1)Complement SystemPresent as inactive form in the plasma
Vascular effect (anaphylotaxins): C3a, C5a & C4a causing V.D. & increase vascular permeability.Leukocyte adhesion, chemotaxis & activation: C5a
Phagocytosis: C3b & C3b1 act as opsonin.2) Kinin System
Activated by activation of Hageman factor (XII)
Bradykinin: increase vascular permeability , V.D., pain & smooth muscle contraction.
Kallikrein: has chemotactic activity.3) Clotting System
A cascade activated by Hageman factor (XII) resulting in conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin.Fibrinopeptides: increase vascular permeability & chemotaxis.
4) Fibrinolytic System:Plasmin: lyses fibrin clots, degrades fibrin to fibrin degradation products.
Fibrin degradation products: Increase vascular permeability.Microscopic appearance of acute inflammation
Congestion of blood vessels.Exudation of fluid.
Exudation of inflammatory cells mainly neutrophils.
Types of acute inflammation1. Catarrhal
Acute inflammation + mucus hyper secretion of mucus membrane (common cold).
2. Serous
Low protein content, low cellular fluid (pleural effusion).
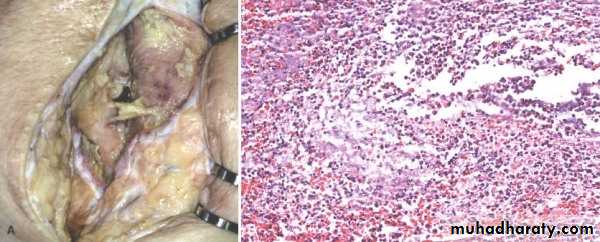
3. Suppurative (Purulent)
Pus: creamy yellow or blood stained fluid consist of N, M.O, & tissue debris (acute appendicitis).
Abscess: Focal localized collection of pus material.
Empyema: Collection of pus in the hallow organ.
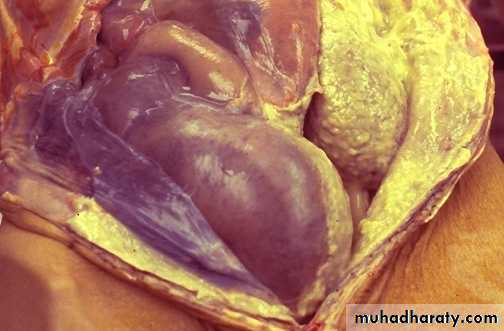
4. Fibrinous
Accumulation of thick exudate rich in fibrin, which may resolve by fibrinolysis or organize into thick fibrous tissue. Fibrinous inflammation –bread &butter appearance to the inflamed serous membrane.
Morphologic patterns of acute inflammation
Serous inflammation:Tissue fluid accumulation indicating a modest increase in vascular permeability
Pleura , pericardium,
peritoneum: effusion
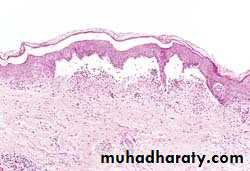
Blister in burns
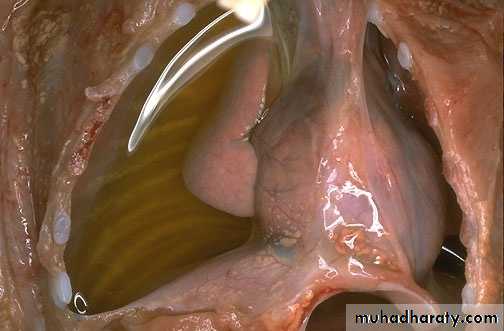
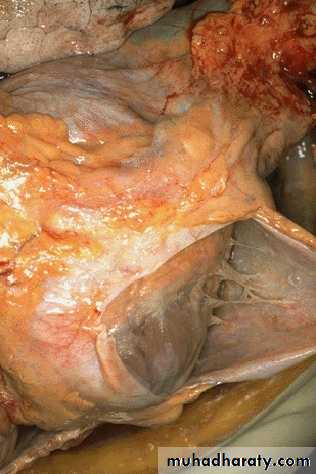
Fibrinous inflammation:
More marked increase in vascular permeability, with exudates containing large amounts of fibrinogenInvolvement of serosal surfaces ( pericardium or pleura) : fibrinous pericarditis or pleuritis
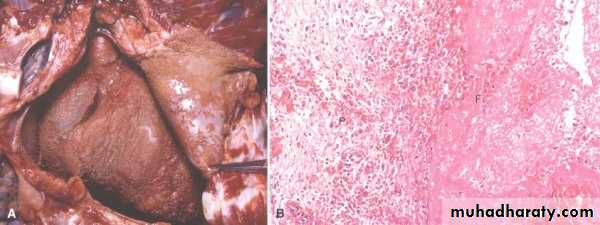
Suppurative or purulent inflammation:
Production of purulent exudates consisting of leukocytes and necrotic cells.An abcess refers to a localized collection of purulent inflammatory tissue accompanied by liquefactive necrosis.