
Fifth stage
Radiology
عملي
د. هديل
10/3/2016
All films in chest radiology
=============================================
Chest seminar:
www.muhadharaty.com/lecture/5525
=============================================
Slide 6
important note>>> density of the upper spine is more than density of the lower spine
Slide 8
CXR of adult male
PA and lateral views, it shows :
Normal both lung fields
Central cardiac shadow
Central trachea, central mediastinum
No boney lesions, no soft tissue abnormalities
Slide 9
Costophrenic angle, Cardiophrenic angle
Useful in detection of pleural effusion
Slide 10
right lung has 3 lobes (upper, middle, lower) and 2 fissures ( horizontal, oblique).
Left lung has 2 lobes (upper and lower) and 1 fissure (oblique).
Slide 11
Upper zone>>>> 1
st
and 2
nd
ribs

Middle zone>>>> 3
rd
and 4
th
ribs
Lower zone>>>> 5
th
and 6
th
ribs
Slide 12
Sequence of X ray reading = 5Ds
- Detect
- Describe
- Differential diagnosis
- Discuss
- Diagnosis
Slide 13
How to assess cardiac size??
We take 2 lines the between borders of cardiac shadow and 2 lines between the inner
surface of thoracic cage and the ribs
Cardiothoracic ratio (CTR) =
Cardiac Width : Thoracic Width
A CTR of greater than 1:2 (50%) is considered abnormal.
Slide 14
Right cardiac border =right atrium
Left cardiac border= left ventricle
Slide 15
CXR of adult male , PA view shows:
Enlargement of the cardiac shadow (cardiomegaly)
Enlargement of left atrium
Double density sign: the right side of the enlarged left atrium pushes into the adjacent
lung and creates an addition contour superimposed over the right heart.
Diagnosis= mitral valve disease

Slide 16
CXR of adult , PA view shows:
Cardiomegally
Double density sign of right cardiac border
Enlargement of left atrium, permenant left atrial appendage and relaced mitral valve
(prosthesis)
Diagnosis= mitral valve disease
Slide 17
CXR of adult, PA view shows:
Globular enlargement of the heart
giving a water bottle configuration (globe heart, pumpkin shape heart)
diagnosis= pericardial effusion
Slide 18
CXR of a child, PA view shows:
"boot shaped" heart with an upturned cardiac apex due to right ventricular hypertrophy
and concave pulmonary arterial segment .
Pulmonary oligaemia due to decreased pulmonary arterial flow.
Diagnosis= tetrology of fallot
Slide 19
CXR of a child PA view shows:
cardiomegaly with a cardiac contours classically described as appearing like an "egg on a
string "
apparent narrowing of the superior mediastinum as result of the aortic and pulmonary
arterial configuration.
Diagnosis= transposition of great blood vessels
Slide 20
CXR of a child , PA view shows:

Huge cardiomegaly ( box shaped heart)
Diagnosis= Ebstain anomaly
Slide 21
CXR of adult female , PA view shows:
Cardiac shadow is seen on the right side
Diagnosis= dextrocardia
Slide 22
CT scan (scanogram) ,lateral view of the neck shows:
Widening of retropharyngeal space with air fluid level
Diagnosis= retropharyngeal abscess
Slide 23
CXR of a neonate ,PA view shows thymus gland (normal finding not a disease ) with
indentations
Diagnosis= thymus gland in neonate
Slide 24
CXR of neonate, PA view shows:
Sail sign of thymus gland
Slide 25
CXR , PA view shows:
Widening of the superior mediastinum by soft tissue mass with deviation of the trachea to
the opposite side
Diagnosis= retrosternal goiter
Slide 26
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Widening of the superior mediastinum by soft tissue mass with deviation of the trachea to
the opposite side

Diagnosis= retrosternal goiter
Slide 27
CXR of adult male, PA and lateral views show:
Widening of the middle mediastinum
Diagnosis= lymphoma
Slide 28
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Bilateral hilar and paratracheal regions are enlarged and Prominent
DDX
Infection>>> TB ,sarcoidosis
Metastasis of bronchogenic carcinoma
Lymphoma
Diagnosis= lymphadenopathy
Slide 29
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Hilar lymph nodes are enlarged (bilaterally)
Diagnosis= hilar lymphadenopathy
Slide 30
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
-photo on the right:
homogenus opacity occuies right upper lobe
-photo on the left:
Homogenus opacity occupies right upper lobe with translucent area within the opacity
called air bronchogram , the fissure is normal
Diagnosis= right upper lobar pnemonia

Slide 31
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Bulging fissure sign with homogenus opacity of right upper lobe
No deviation of the trachea
Diagnosis= klebsiella pnemonia
Slide 32
CXR of adult , PA view on the left and lateral view on the right shows:
Triangular Homogenus opacity in the right lower zone (left photo) while in the right photo
the opacity occupies middle lobe of the lung.
Indistinct right cardiac border
Loss of the medial aspect of right hemidiphram
Fissures are at normal position
No deviation of the trachea
Diagnosis= right middle lobe pnemonia
Slide 33
CXR of adult female , lateral view shows:
Homogenus opacity of middle lobe with normal fissures
Diagnosis= right middle lobe pnemonia
Slide 34
CXR of adult , PA and lateral views show:
Complete haziness of the left hemithorax
Homogenus opacification of the left upper lobe
Fissure is normal
No deviation of the trachea
Diagnosis=left upper lobe pnemonia

Slide 35
CXR of adult , PA and lateral views show:
Homogenus opacity of the left lower zone with normal fissure
Diagnosis= left lower lobe pnemonia
Slide 36
CXR of adult ,PA and lateral views show:
Patchy consolidation in both lung fields (diffuse) mainly in the lower zones
Normal heart size
Diagnosis= bronchopnemonia
Slide 37
It is very important to consider that pulmonary edema in normal sized heart have close
similar appearance to bronchpnemonia
The important golden key differentiationis the cardiac size being enlarged in pulmonary
edema.
: من المحاضرة
Septal lines, also known as Kerley lines, are seen when the interlobular septa in the
pulmonary interstitium become prominent. This may be because of lymphatic engorgement
or edema of the connective tissues of the interlobular septa. They usually occur when
pulmonary capillary wedge pressures reach 20-25 mmHg
Classification
Kerley A lines
These are 2-6 cm long oblique lines that are <1 mm thick and course towards the hila. They
represent thickening of the interlobular septa
Kerley B lines
These are 1-2 cm thin lines in the peripheries of the lung. They are perpendicular to and
extend out to the pleural surface . They represent thickened sub pleural interlobular septa
and are usually seen at the lung bases.

Slide 38
CXR of adult , PA view shows:
Bilatral patchy opacity involving mainly lower lung fields with enlargement of cardiac
shadow
Diagnosis=interstitial pulmonary edema
Slide 39
CXR of ault ,PA view shows:
Bilateral patchy opacity mainly in the middle zones of the lungs (Bat wing sign )
Cardiomegaly
Diagnosis=alveolar pulmonary edema
Slide 40
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Bat wing sign
Cardiomegaly
Diagnosis= alveolar pulmonary edema
Slide 41
CXR of adult , PA view shows:
Homogenus opacity of right upper lobe
Elevation of the the horizontal fissure
The trachea is slightly devited to the right
Elevation of ipsilateral hemidiahram
Crowding of the ipsilateral ribs.
Diagnosis= right upper lobe collapse
Slide 42
CXR of adult female, PA view shows:
Homogenus opacity of right upper lobe (consolidation with air bronchogram)

Elevation of horizontal fissure
Elevation of the right hemidiaphram
Crowding of the ribs on the right side
Diagnosis=right upper lobe collapse
Or called collapse consolidation
Slide 43
CXR of adult, PA view shows:
Homogenus oppacity in right upper lobe+ hilar mass lead to bulging of the horizontal fissure
with golden S sign
Shifting of the trachea to the right
Diagnosis= right upper lobe collapse
Slide 44
CXR of adult female ,lateral views
-Photo on the left:
Homogenus opacity of right middle lobe triangular in shape, the fissures are normal
Diagnosis= right middle lobe pnemonia
-Photo on the right:
Homogenus opacity of right middle lobe tongue like with elevation of the fissure
Diagnosis= right middle lobe collapse
Slide 45
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Triangular opacity in the posteromedial aspeect of the left lung
Left hilum is depressed
Loss of the normal left hemidiaphram outline
Elevation of the left hemidiaphram
Crowding of the ribs on the left side

Shifting of the mediastinum to the left
Diagnosis=left lower lobe collapse
Slide 46
CXR of adult male ,PA and lateral views show:
Homogenus opacity in the left lower lobe triangular in shape
In the lateral view the density of the lower vertebrae is more than the upper vetebrae
(abnormal)
Diagnosis=left lower lobe collapse
Slide 47
CXR of adult female ,PA view shows:
Flattening of the hemidiaphrams
Widely spaced ribs
Tenting of the diaphram
Abnormal shape of the heart (tubular)
Increased and irregular radiolucency of the lungs
Vascular changes, paucity of blood vessels (absent pulmonary markings in the outer 1l3 of
the lung fields
There is an emphysmatous bulla (area devoid of lung markings more than 1 cm) in the hilar
area of the right lung .
Diagnosis= emphysema
Slide 48
CXR of adult ,PA view shows:
-Photo on the left:
Homogenus opacity of the right hemithorax with shifting of the trachea to the same side
Diagnosis= total collapse of the right lung
-Photo on the right:
Homogenus opacity of the left hemithorax with central trachea

Diagnosis= total consolidation of the left lung
Slide 49
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Homogenus opacity of the left hemithorax with shifting of the trachea to the same side
Diagnosis= total collapse of the left lung
Slide 50
CXR of adult female ,PA view shows:
-Photo on the right:
Homogenus opacity of right lower zone with meniscus sign
Oblitration of right cardiophrenic and costophrenic angles
Diagnosis= right pleural effusion
-Photo on the left:
Homogenus opacity of the right hemithorax
Oblitration of cardiophrenic and costophrenic angles
Shifting of the trachea to the opposite side
Diagnosis= right side pleural effusion
Slide 51
CXR of adult, PA view shows:
Homogenus opacity of right lower lobe with Oblitration of right cardiophrenic and
costophrenic angles.
Meniscus sign
Diagnosis= right side pleural effusion
Slide 52
CXR of adult male ,PA view shows:
Homogenus opacity in the right lung with obtuse angle and obliteration of right
costophrenic angle, normal cardiophrenic angle

Diagnosis= encysted pleural effusion
Note: this x ray has 2 ddx>>> empyema and encysted pleural effusion
Slide 53
CXR of adult male ,PA view shows:
Radiolucent area devoid of lung markings in the upper left lung
Visible viseral pleural edge as very thin sharp white line
Diagnosis= left side pnemothorax
Slide 54
CXR of a child, PA view shows:
-Photo on the left:
Radiolucent area devoid of lung markings in the periphry of the left lung with visible viseral
pleural edge .
-Photo on the right:
Radiolucent area devoid of lung markings in the periphry of the right lung with visible
viseral pleural edge
The mediastinum is pushed to the opposite side
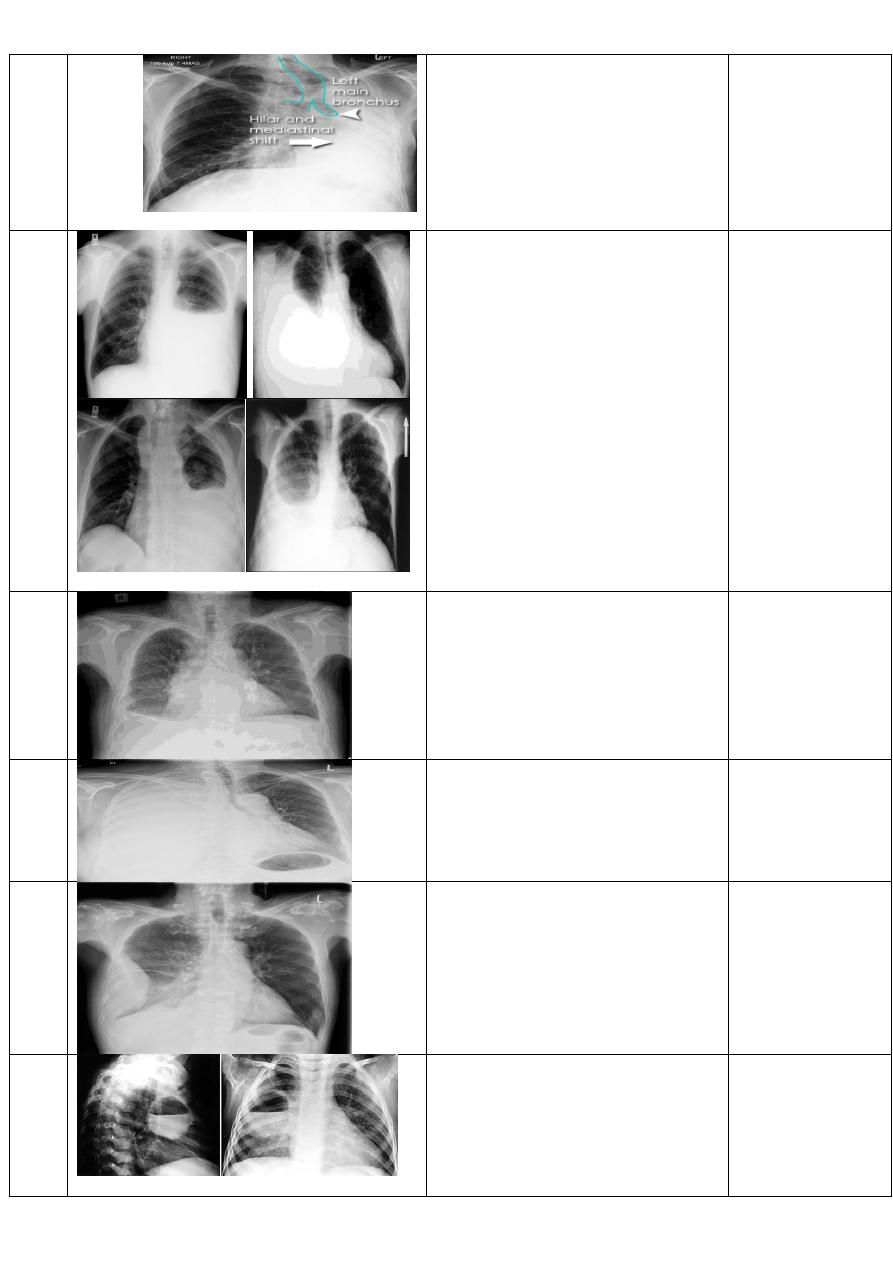
Diagnosis= tension pnemothorax
Slide 55
CX R of adult male, PA view shows:
Radiolucent area devoid of lung markings in the area of the left lung with visible viseral
pleural edge.
Diagnosis= left side pnemothorax
Slide 56
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Radiolucent area devoid of lung markings in the area of the right lung with visible viseral
pleural edge
The mediastinum is pushed to the opposite side

Diagnosis= tension pnemothorax
Slide 58
CXR of adult male in errect position ,PA view shows:
Homogenus opacity in the right lower zone with Horizontal air fluid level .
Diagnosis= hydropnemothorax
Slide 59
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
-Photo on the left:
Many curvilinear opacities in right lung with multiple air fluid levels
Honey comb shadow
Increase in bronchoalveolar markings
Pulmonary vasculature appears ill defined
-Photo on the right:
The same changes seen in the left lung
Diagnosis= bronchiactasis
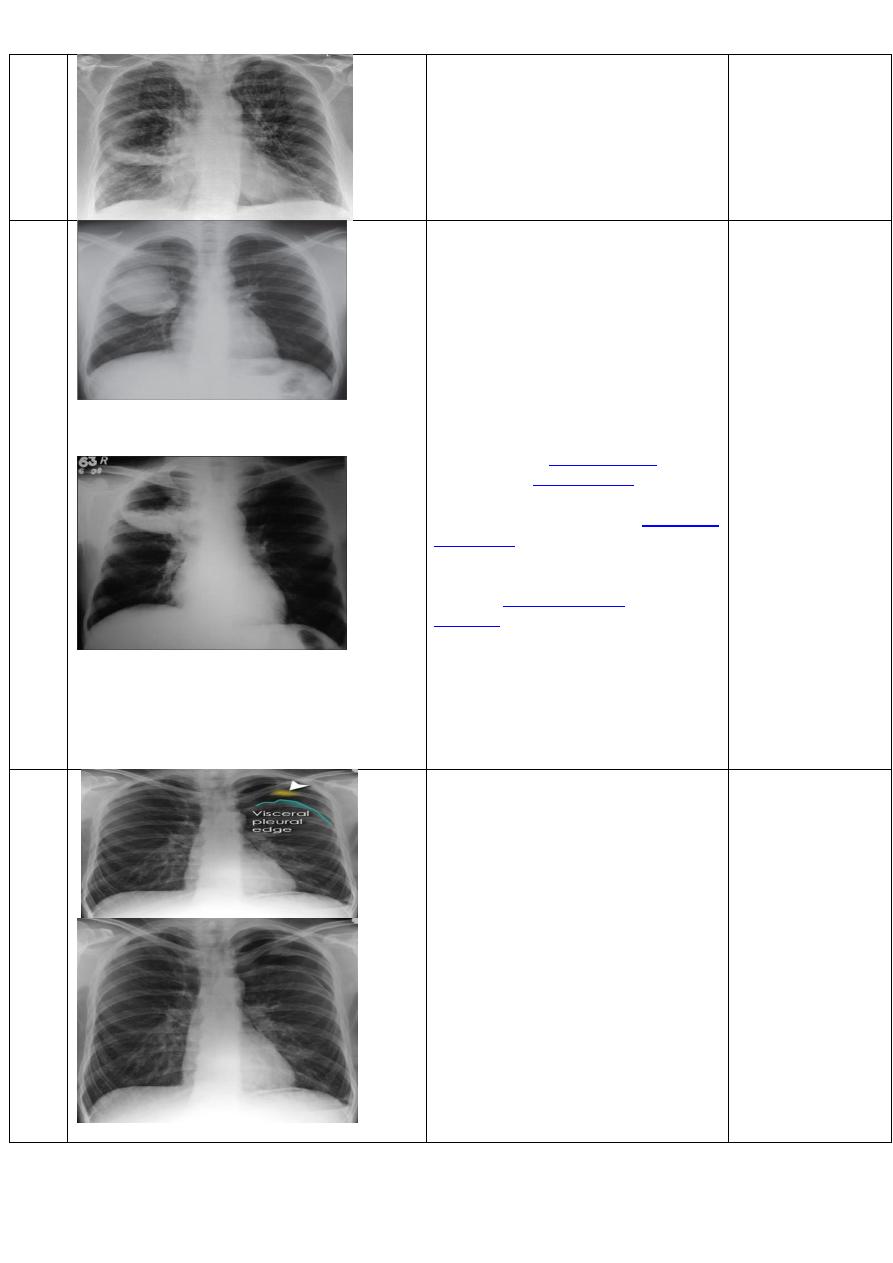
Slide 60
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Bilateral patchy opacities of the upper lobes of the lungs, cotton wool sign.
Diagnosis= post primary TB bronchpnemonia
Slide 61
CXR of adult, PA view shows:
Bilateral Patchy opacification of the lungs involving upper zones, a cavity can be seen in the
right uper lobe( 3
rd
photo)
Diagnosis= post primary TB bronchopnemonia
Slide 62
CXR of adult male , PA view shows:

-Photo on the left:
Bilateral patchy opacity mainly involving lower lung zones
Diagnosis= bronchopnemonia
-Photo on the right:
Bilateral patchy opacity mainly involving upper lung zones
Diagnosis=post primary TB bronchopnemonia
Slide 65
CXR of adult male, PA view show:
Bilateral diffuse tiney nodules1-3 mm in diameter uniform in size and uniformly distributed
involve whole lung fields.
Diagnosis= miliary TB
Slide 66
CXR of a child m PA view shows:
Bilateral diffuse tiney nodules1-3 mm in diameter uniform in size and uniformly distributed
involve whole lung fields.
Diagnosis= miliary TB
Slide 67
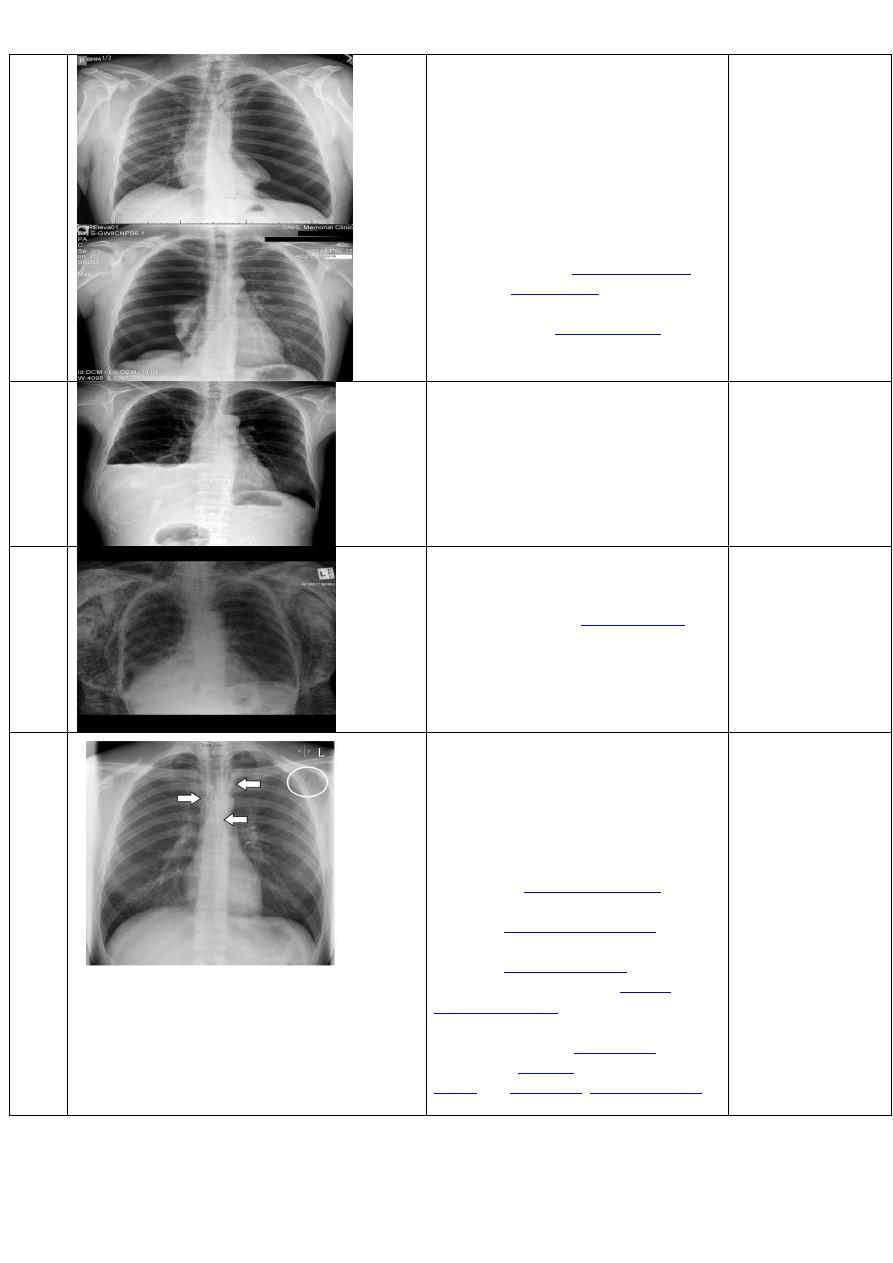
-Photo on the left:
CT scan show cavity with air fluid level inside it in the upper lobe of the right lung.
-Photo on the right:
CXR of adult , PA view show:
Cavity with air fluid level inside in the uper lobe of the right lung
Diagnosis= TB lung abscess
Slide 68
CT scan of the chest show:
Cavity in the upper lobe of the right lung with Well defined rounded opacity in side it

Diagnosis= aspergilloma
Slide 69
CXR of adult male , PA view shows:
-Photo on the left:
Well defined rounded opacity in the middle zone of the right lung, transparent( can see the
ribs through it)
Diagnosis= simple hydatid cyst
-Photo on the right:
The right upper zone show cavity with wavy air fluid level (water lilly sign)
Diagnosis= ruptured hydatid cyst
Slide 70
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
-Photo on the right:
2 Radioopaque lesions can be seen in the right lung one is hilar(central) and the other is
periphral both of them have speculated margins( sun ray appearance)
-Photo on the left:
radioopaque mass with speculated margine can be seen in the upper zone right lung
diagnosis= bronchogenic carcinoma
Slide 71
CXR of adult ,PA view shows:
-Photo on the left
Large radioopaque mass in the left middle zone with sun ray apearance and evidence of
invasion to the chest wall
Note: the film is rotated
-Photo on the right:
Hilar radioopaque mass in the left lung with speculater margin, air fluid level can also be
seen

(pleural effusion).
Diagnosis= bronchogenic carcinoma
Slide 72
-Photo on the right:
CT غير مطلوب
-Photo on the left:
CXR of adult ,PA view shows:
Hilar mass +homogenus opacity in the upper right lobe with elevation of the horizontal
fissure
Golden S sign
Shifting of the trachea to the same side
Diagnosis= bronchogenic carcinoma caused lung collapse
Slide 73
CXR of adult male, PA view shows:
Radioopaque shadoe in the right upper zone
Deviation of the horizontal fissure upward
Deviation of the trachea to the same side
Invasion of the ribs
Diagnosis= pan coast tumor
Note: (lung collapse produce similar picture but there is no rib destruction)
Slide 74
CXR of adult, PA view shows:
Bilateral rounded radioopaque nodules of multiple sizes distributed all over both lung fields
Cannon ball appearance
Diagnosis= secondary metastasis

Slide 76
Well defined rounded radioopaque lesion 3-5 cm in diameter
Ddx=
-simple hydatid cyst
-bronchogenic carcinoma
-TB
-metastasis
Slide 77
CXR of adult male, PA and lateral views show:
Well defined rounded cavitatory lesion in the middle zone of the right lung with air fluid
level inside
Dignosis= lung abscess
Slide 78
CXR of adult male, PA view show:
-Photo on the right:
Well defined rounded lesion in the middle zone of the right lung with air fluid level inside.
-Photo on the left:
Well defined rounded lesion in the upper zone of the right lung with air fluid level inside.
Dignosis= lung abscess
Slide 79
CXR of a child, PA view shows:
-Photo on the left:
Soap bubble appearance in the left hemithorax with shifting of mediastinum to the right
Left hemidiaphram cannot be seen
Presence of nasogasric tube
Diagnosis= congenital diaphramatic hernia( bockdalic type)

-Photo on the right:
Soap bubble appearance in the left hemithorax with air fluid level
Shifting of mediastinum to opposite side
Diagnosis=congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation.
Ddx of soap bubble appearance in the chest:
1- Congenital diaphramatic hernia
2- Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation
The diagnosis
description
The film
No of
slide
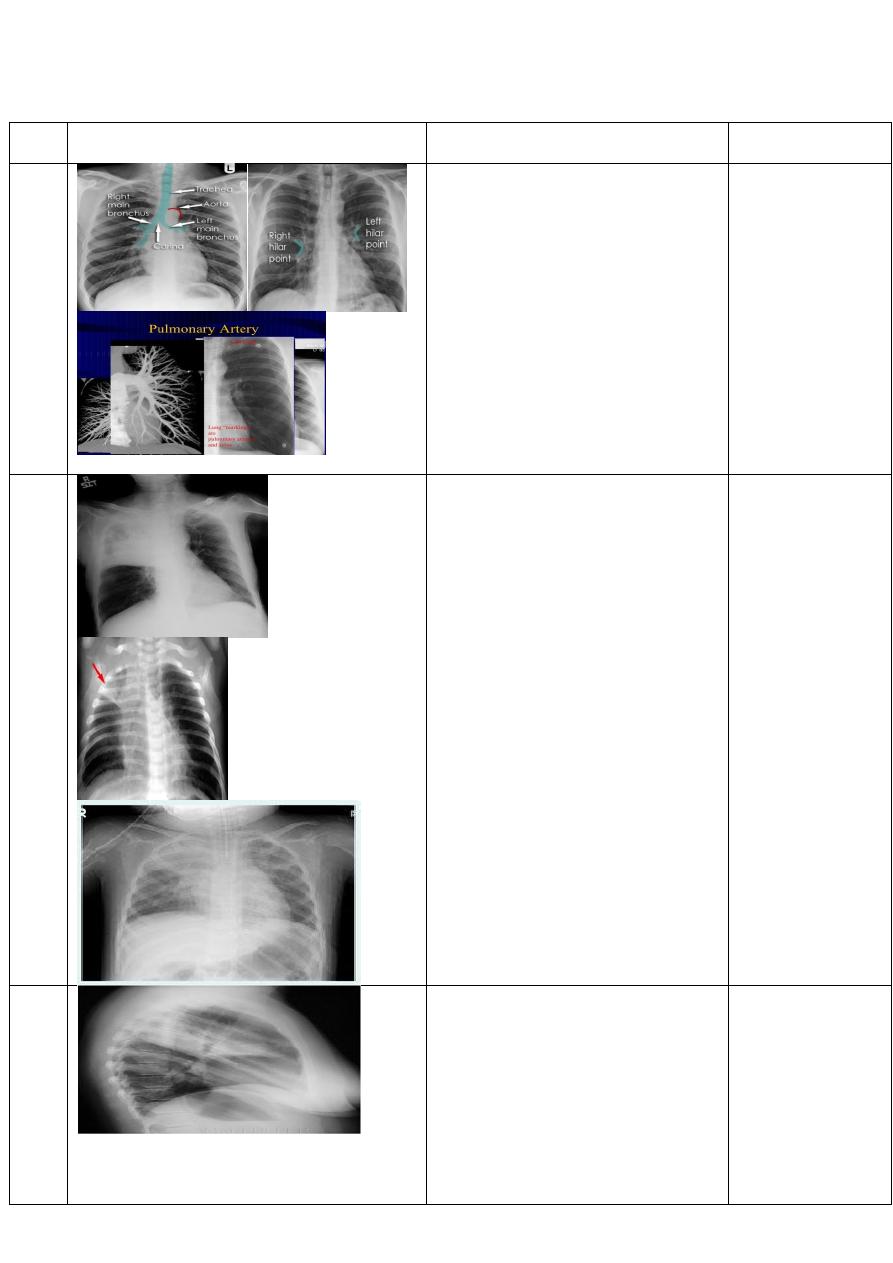
Normal chest x-Ray
Chest x-ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
normal anatomy of hilar region. Each
hilum contains major bronchi and
pulmonary vessels
There are also lymph nodes on each
side(not visible unless abnormal)
The left hilum is often higher than the
right
Both hila should be of similar size and
density. If either hilum is bigger and more
dense, this is a good indication that there
is an abnormality.
12
و
13
Right upper lobe
consolidation
Chest X- Ray, p-A view showing:
an increased opacity within the right
upper lobe. Opacity may be sharply
bordered by the horizontal fissure
Some loss of outline of the upper right
heart border may be apparent.
23
Right upper lobe
consolidation
Chest X- ray ,lateral view of adult female
showing :
Dense opacity seen above the horizontal
fissure.
Air-bronchogram line
The lower border of the consolidation is
sharply delinated by the horizontal fissure
suggesting it lies in the anterior segment
of the RUL.
24
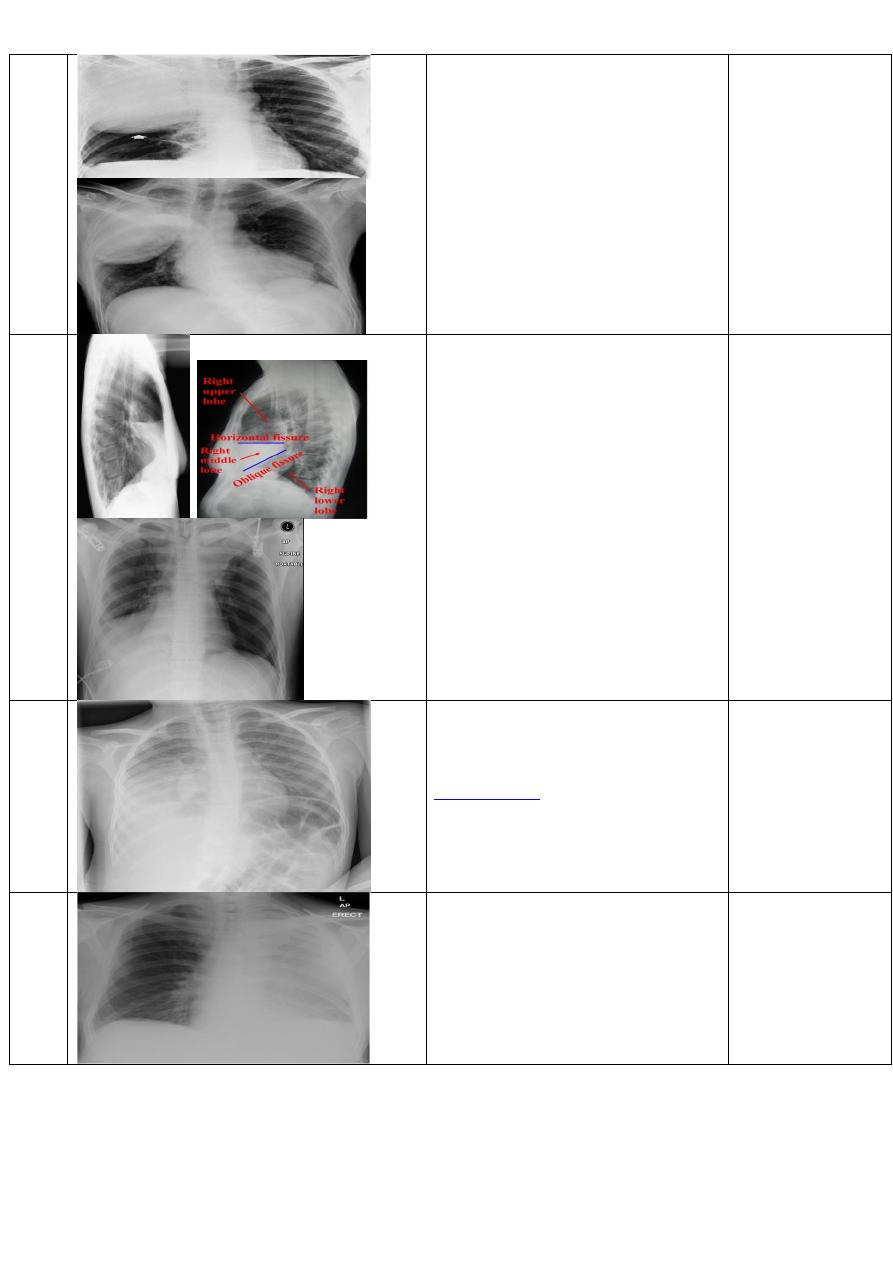
Klebsiella
(Friedlander's)
pneumonia
Chest X- ray ,p-A view of adult male
showing :
an increased opacity within the right
upper lobe with bulging of fissure sign.
27
RT middle lobe
consolidation
Chest x-Ray,lateral and P-A view of adult
male showing:
opacification of the RML
abutting the horizontal
fissure.
indistinct right heart border.
loss of the medial aspect of
the right hemidiaphragm.
28
Right lower lobe
consolidation
Chest x-ray P-A view of adult male
showing:
airspace shadowing that abuts the right
.
obliterating the crisp margin of the.
hemidiaphragm and normal aerated lung.
29
Total Lung
CONSOLIDATION
Chest x-Ray A-P view of adult male
showing :
Homogenous opacification of the left
lung.
30
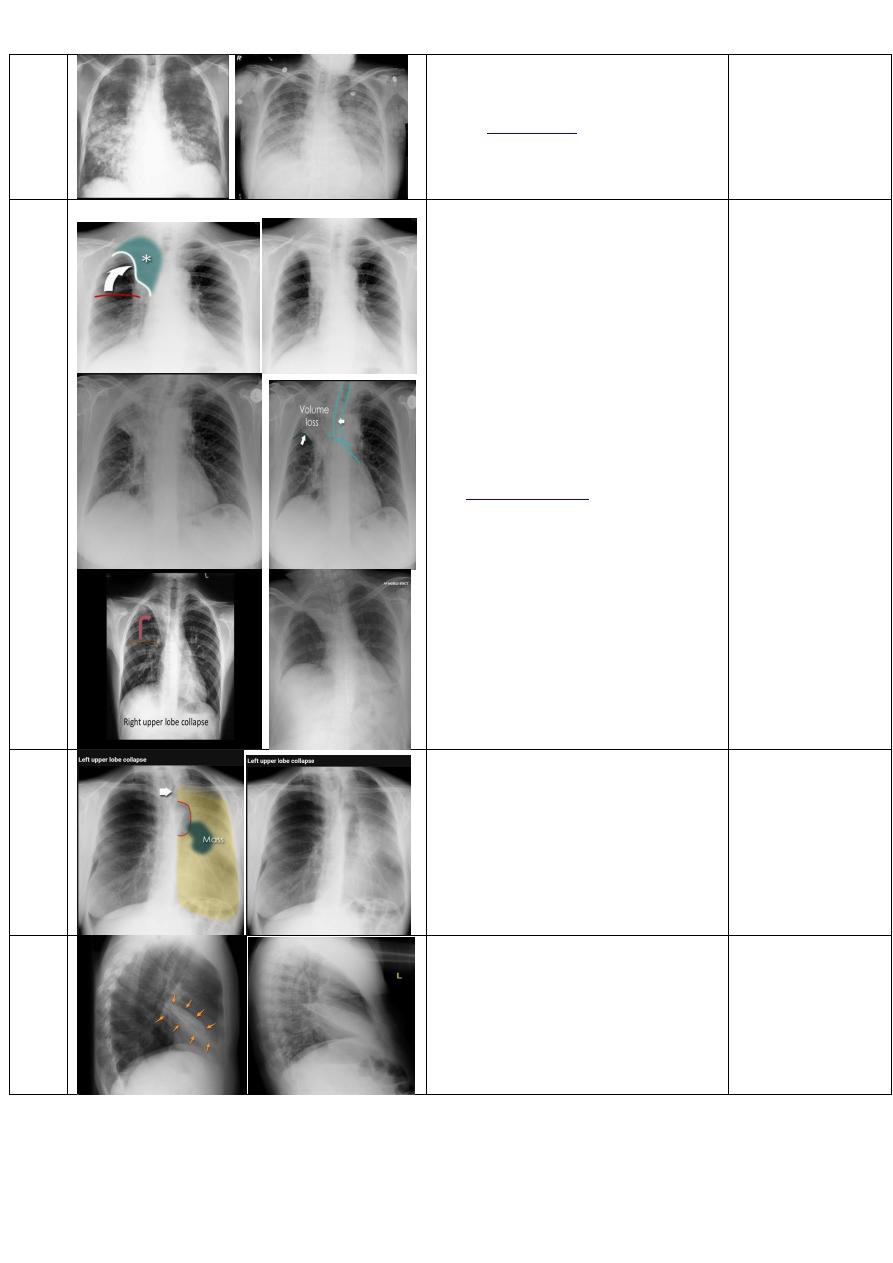
bronchopnemonia
Chest x-ray P-A view of adult male
showing:
of middle and lower
patchy
lobe of right lung.
32
Right upper lobe
collapse
Chest x-ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
•
increased density in the upper
medial aspect of the right
hemithorax
•
elevation of the horizontal fissure
•
loss of the normal right medial
cardiomediastinal contour
•
elevation of the right hilum
•
hyperinflation of the right middle
and lower lobe result in increased
translucency of the mid and lower
parts of the right lung
•
•
note:in the first photo there is
golden s sign which result When a
right hilar mass is combined with
collapse of the right upper lobe.
40
و
41
Left upper lobe
collapse.
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
hazy or veiling opacity extending out from
the hilum and fading out inferiorly .
Right middle lobe
collapse
Chest X-Ray ,lateral view of adult male
showing:
opacity is tongue like shape.
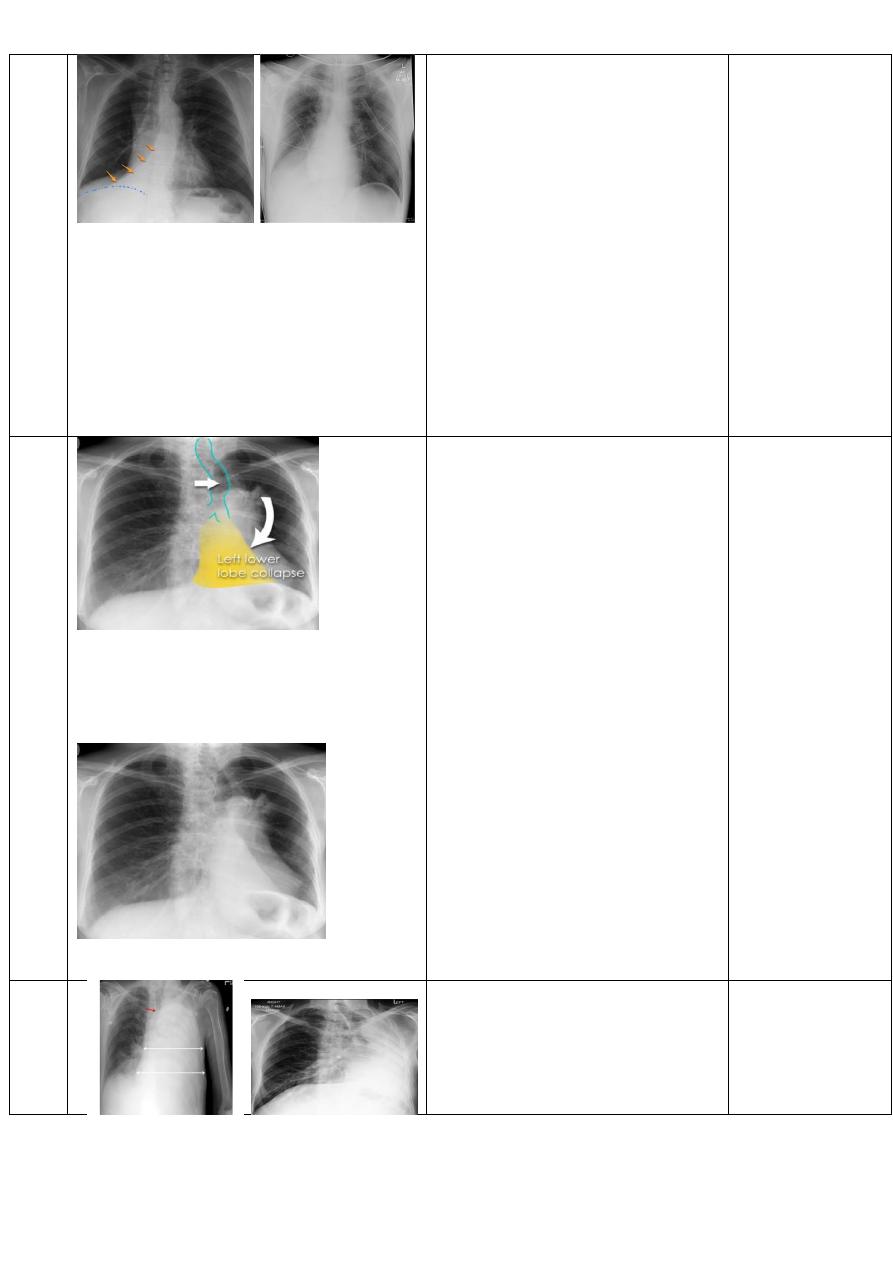
RT lower lobe
collapse
Chest x-ray ,P-A view show:
•
medial aspect of the dome of right
hemidiaphragm is lost.
•
the right hilum is depressed
•
It is important to note that the
right heart border, which is
contacted by the right middle lobe
remains well seen.
•
Non-specific signs indicating right
sided atelectasis may also be
present (although due to the
small size of the right middle lobe
they may well be subtle). They
include:
•
elevation of the hemidiaphragm
•
crowding of the right sided ribs
•
shift of the mediastinum to the
right
Left lower lobe
collapse.
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
•
triangular opacity in the
posteromedial aspect of the left
lung
•
edge of collapsed lung may create
a 'double cardiac contour'
•
left hilum will be depressed
•
loss of the normal left
hemidaphgragmatic outline
•
loss of the outline of the
descending aorta
•
Non-specific signs indicating left
sided atelectasis are usually also
be present including:
•
elevation of the hemidiaphragm
•
crowding of the left sided ribs
•
shift of the mediastinum to the
left
•
On lateral projection the left
hemidiaphragmatic outline is lost
posteriorly and the lower thoracic
vertebrae appear denser than
normal (they are usually more
radiolucent than the upper
vertebrae) .
Total lung collapse.
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
Pleural effusion
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
blunting of the costophrenic
angle.
blunting of the cardiophrenic
angle.
fluid within the horizontal or
oblique fissures.
eventually a meniscus will be
seen, on frontal films seen
laterally and gently sloping
medially.
subpulmonic
effusion
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
Large pleural
effusion.
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
large volume effusions, mediastinal shift
occurs away from the effusion.
Empyema
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
an obtuse angle with the chest wall
unilateral or markedly asymmetric.
lenticular in shape (bi-convex).
Lung abscess
Chest x-ray, lateral and P-A view of adult
male showing:
a cavity containing an air-fluid level. In
general abscesses are round in shape, and
appear similar in both frontal and lateral
projections.
60
Simplr hydatid cyst.
Ruptured or
complicated hydatid
cyst.
Chest x-ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing :
solitary rounded opacity
diameter of 1-20
cm in the right upper lobe.
Chest x-ray P-A view of adult male
showing :
meniscus sign or
onion
The
cumbo sign or
peel sign (also called the cumbo sign) is a
feature seen with complicated
between
in which air lining
the endocyst and pericyst has the
appearance of an onion
is seen in
when there is detachment of
the endocyst membrane which results in
floating membranes within the pericyst
that mimic the appearance of a water lily.
consolidation adjacent to the cyst
(ruptured cyst).
63
pneumothorax
Chest x-ray P-A view of adult male
showing :
visible visceral pleural edge see as a very
thin, sharp white line
no lung markings are seen peripheral to
this line
the peripheral space is radiolucent
compared to adjacent lung.
66
Tension
pnemothorax.
Chest x-ray P-A view of adult male
showing:
visible visceral pleural edge see as a very
thin, sharp white line
no lung markings are seen peripheral to
this line
the peripheral space is radiolucent
compared to adjacent lung.
In addition to:
ipsilateral increased
to the
shift of the
contralateral side
depression of the
68
Hydro pnuemothorax
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing:
air and fluid level in the pleural space on
the right side.
70
Subcutaneous
Emphysema
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing :
tissue fat planes appears as multiple lines
of lucency involving both lungs.
72
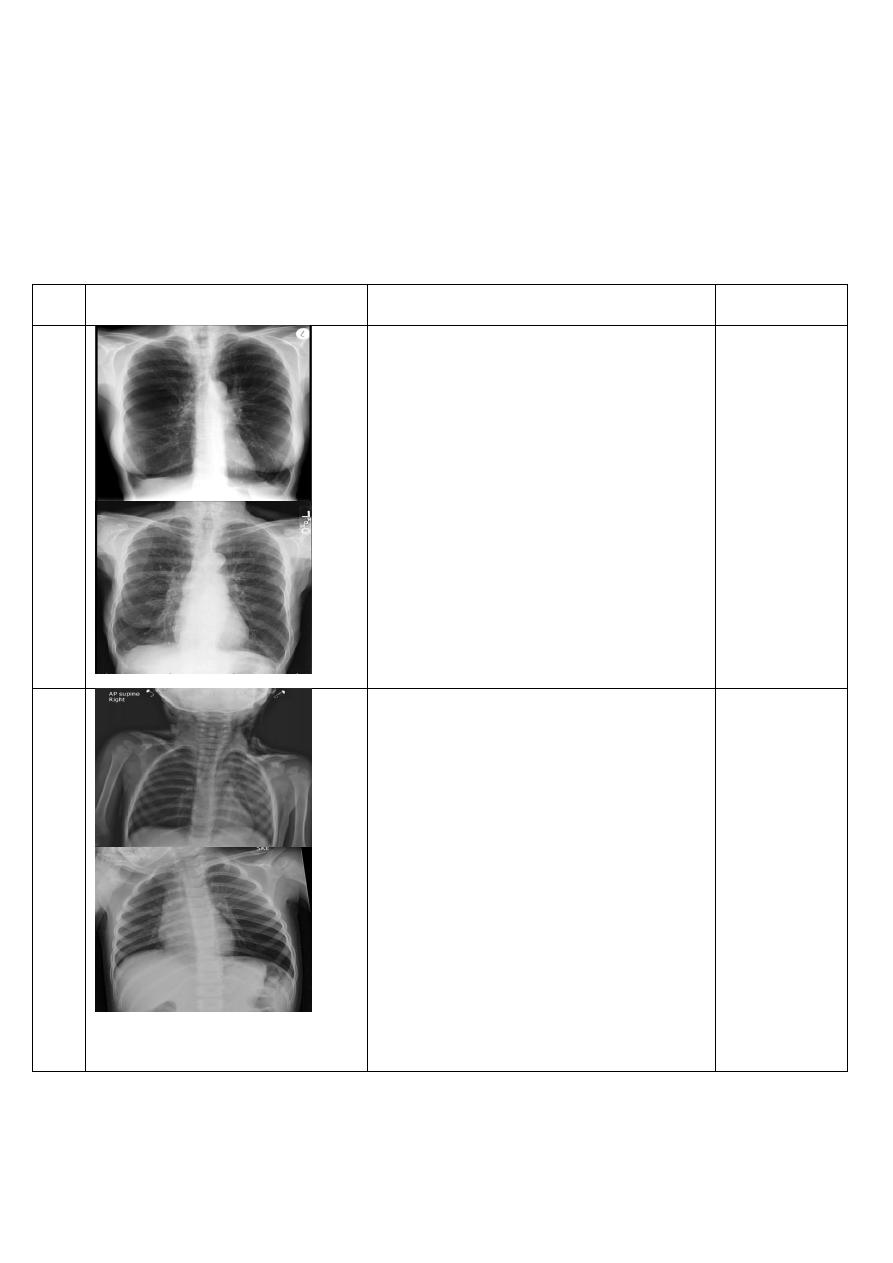
Pneumomediastinum
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male
showing :
Small amounts of air appear as linear or
curvilinear lucencies outlining mediastinal
contours such as:
subcutaneous emphysema
air anterior to
pericardium:
air around pulmonary artery and main
branches:
air outlining major aortic
branches:
air outlining bronchial wall:
continuous diaphragm sign: due to air
trapped posterior to
air between
and
74
=============================================
Lecture2:
www.muhadharaty.com/lecture/5323
=============================================
Diagnosis
description
Films
No.of
slide
emphysema
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult female(1) and
male(2) showing :
1
.
flattened hemidiaphragm(s): most reliable sign
2
.
ncreased and usually irregular radiolucency of
the lungs
3
.
increased retrosternal airspace
4
.
increased antero-posterior diameter of chest
5
.
widely spaced ribs
6
.
sternal bowing
7
.
tenting of the diaphragm
8
.
saber-sheath trachea
9
.
vascular changes paucity of blood vessels (
absent pulmonary markings in outer
1
/
3
of the
lung fields
)
10
.
pulmonary arterial hypertension
pruning of peripheral vessels
increased calibre of central arteries
right ventricular enlargement.
4
emphysema
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view showing:
flattened hemidiaphragm(s): most reliable sign
2
.
ncreased and usually irregular radiolucency of
the lungs
3
.
increased retrosternal airspace
4
.
increased antero-posterior diameter of chest
5
.
widely spaced ribs
6
.
sternal bowing
7
.
tenting of the diaphragm
8
.
saber-sheath trachea
9
.
vascular changes paucity of blood vessels (
absent pulmonary markings in outer
1
/
3
of the
lung fields
)
10
.
pulmonary arterial hypertension
pruning of peripheral vessels
increased calibre of central arteries
right ventricular enlargement.
5
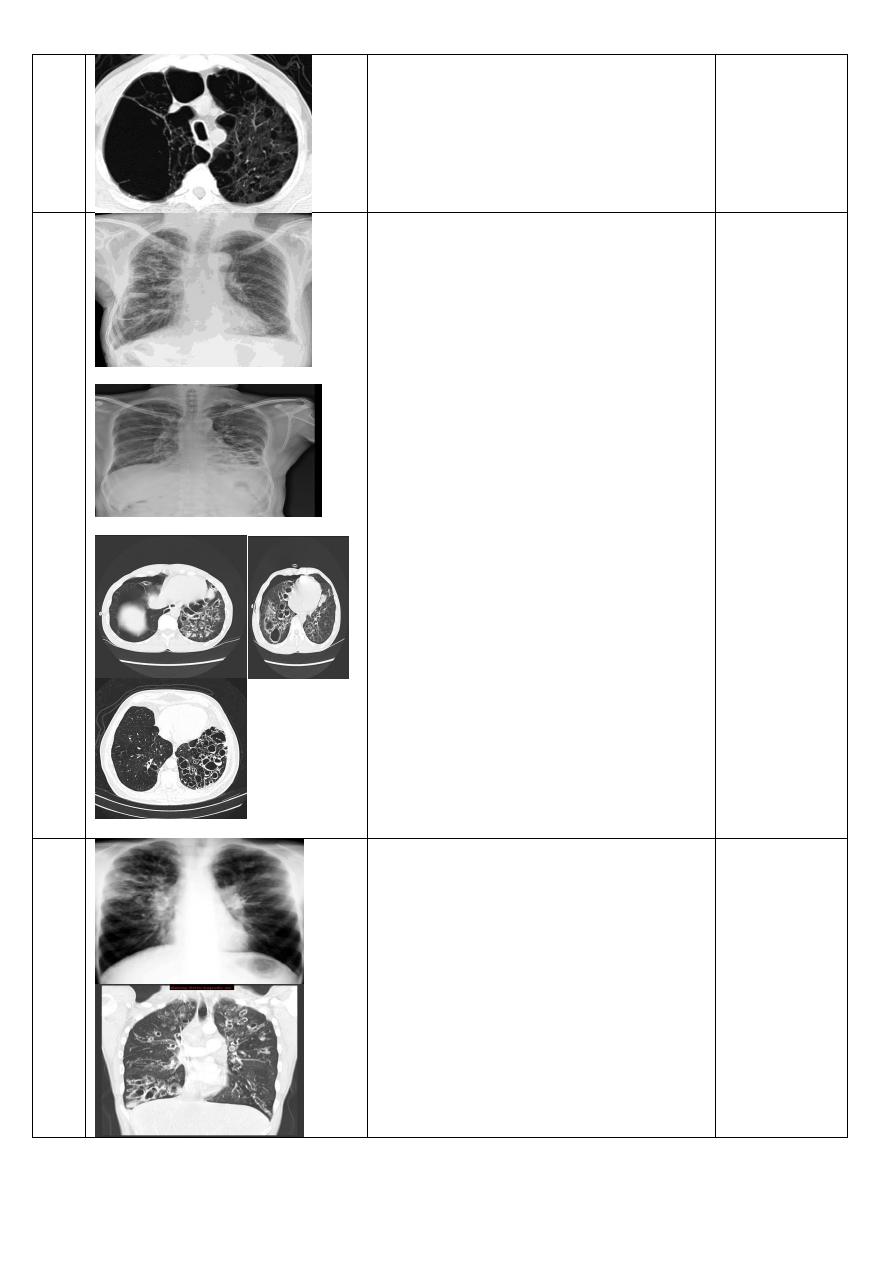
Pulmonary
bullae
C.T scan of the chest (axial view)showing:
focal regions of emphysema with no discenible
wall which measure more than 1cm in diameter.
6
Bronchiactasis
Chest X-Ray P-A view of adult male showing:
Tram-track opacities are seen in cylindrical
bronchiectasis, and air-fluid levels may be seen
in cystic bronchiectasis. Overall there appears to
be an increase in bronchovascular markings, and
bronchi seen end on may appear as ring shadows
. Pulmonary vasculature appears ill-defined,
thought to represent peribronchovascular
fibrosis.
C.T scan,axial view showing:
Multiple small cavities adhere to each other's
resembling honey comb appearance .
10
11
Cystic and
cylindrical
Bronchiactasis
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
.
Tram-track opacities
C.T scan of lung ,coronal view showing:
.
Tram-track opacities
With air fluid level involving both lungs.
12
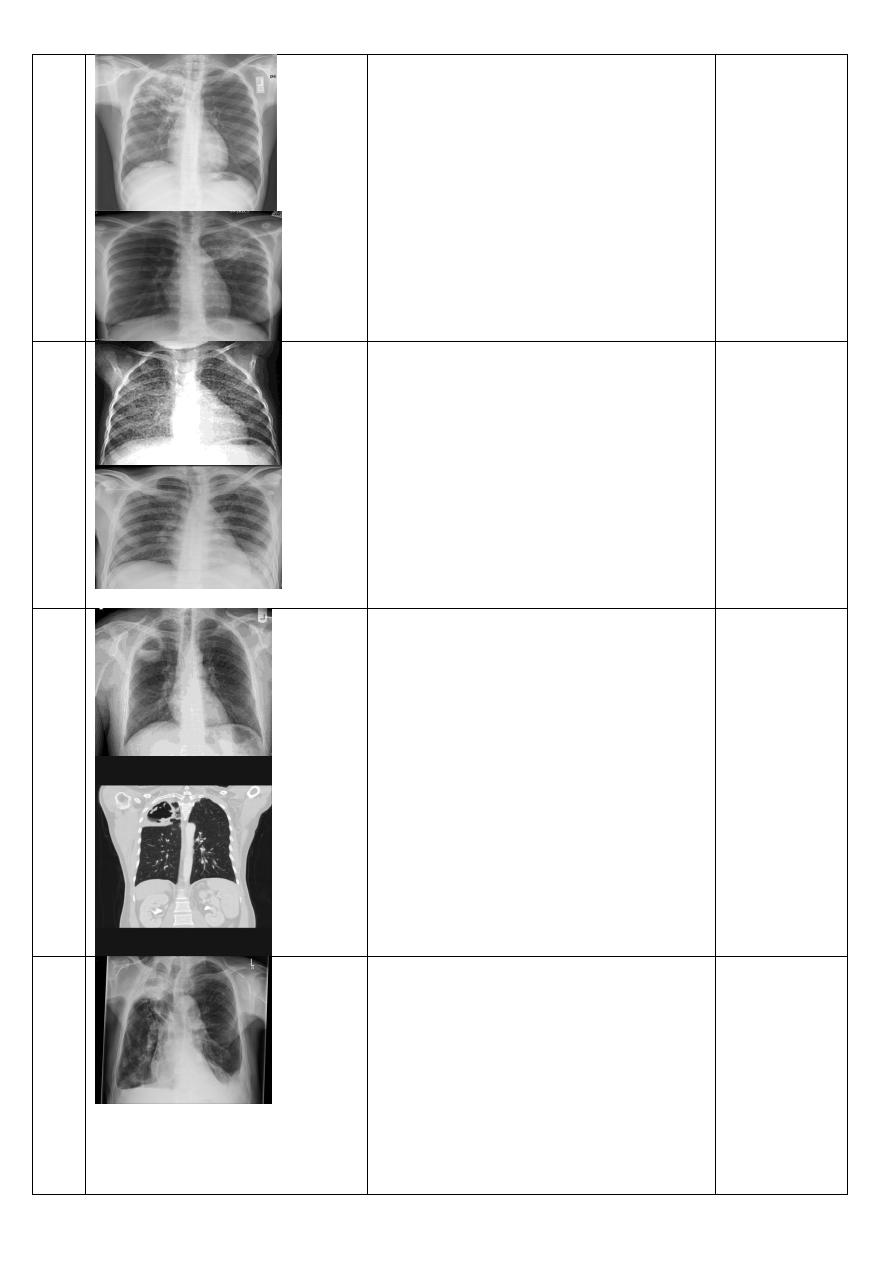
Post primary T.B
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
ill defined patchy consolidation or poorly
defined linear and nodular opacities of right
upper lobe .
17
Military T.B
Chest x-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
1-3 mm diameter nodules . are uniform in size
and uniformly distributed.
18
T.B abcess
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
thin walled air filled (with minimal fluid) rounded
cystic lesion is seen occupying the apical and
posterior segment of right upper lobe. It is
limited by the oblique fissure and surrounded by
area of consolidation with air bronchogram.
Calcified right hilar lymph nodes and esophageal
dilatation are also noted.
C.T scan ,coronal view showing:
rounded cystic lesion is seen occupying the
apical and posterior segment of right upper lobe.
19
Aspergiloma
Chest X-Ray,P-A view of adult male showing:
rounded or ovoid soft tissue attenuating masses
located in a surrounding cavity and outlined by a
crescent of air.
C.T scan coronal view showing:
Cavity with crescent leucency "mobile ball inside
cavity" of right upper lobe
21
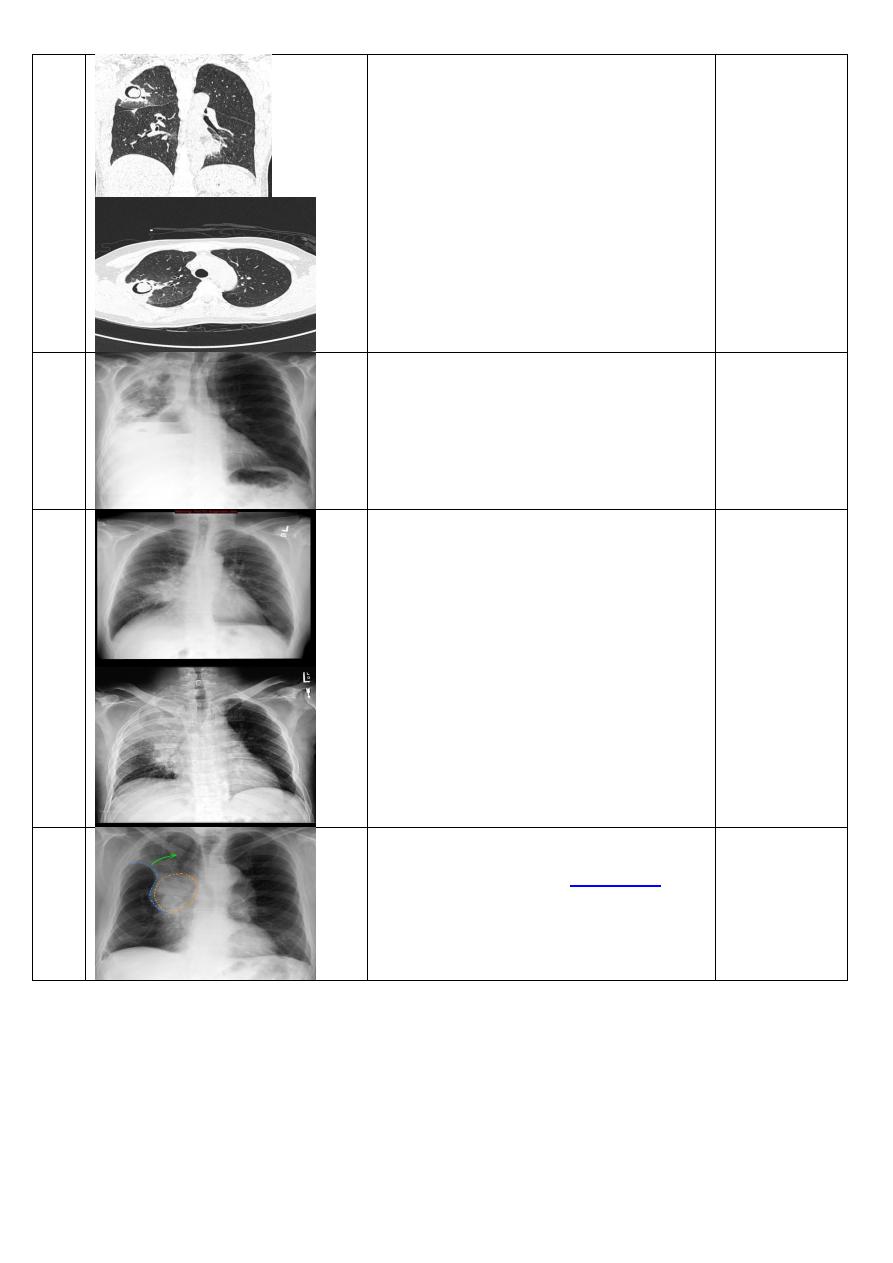
C.T scan axiall view showing:
Cavity with crescent leucency "mobile ball inside
cavity" of rightmiddlrr lobe.
Broncho pleural
fistula
22
Bronchogenic
carcinoma.
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
a bulky hilum, representing the tumor and local
nodal involvement the lesion is irregular in
outline have spiky or sun ray speculation.
25
Bronchogenic
carcinoma
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
right upper lobe is collapsed and a hilar mass is
present, this is known as the
26
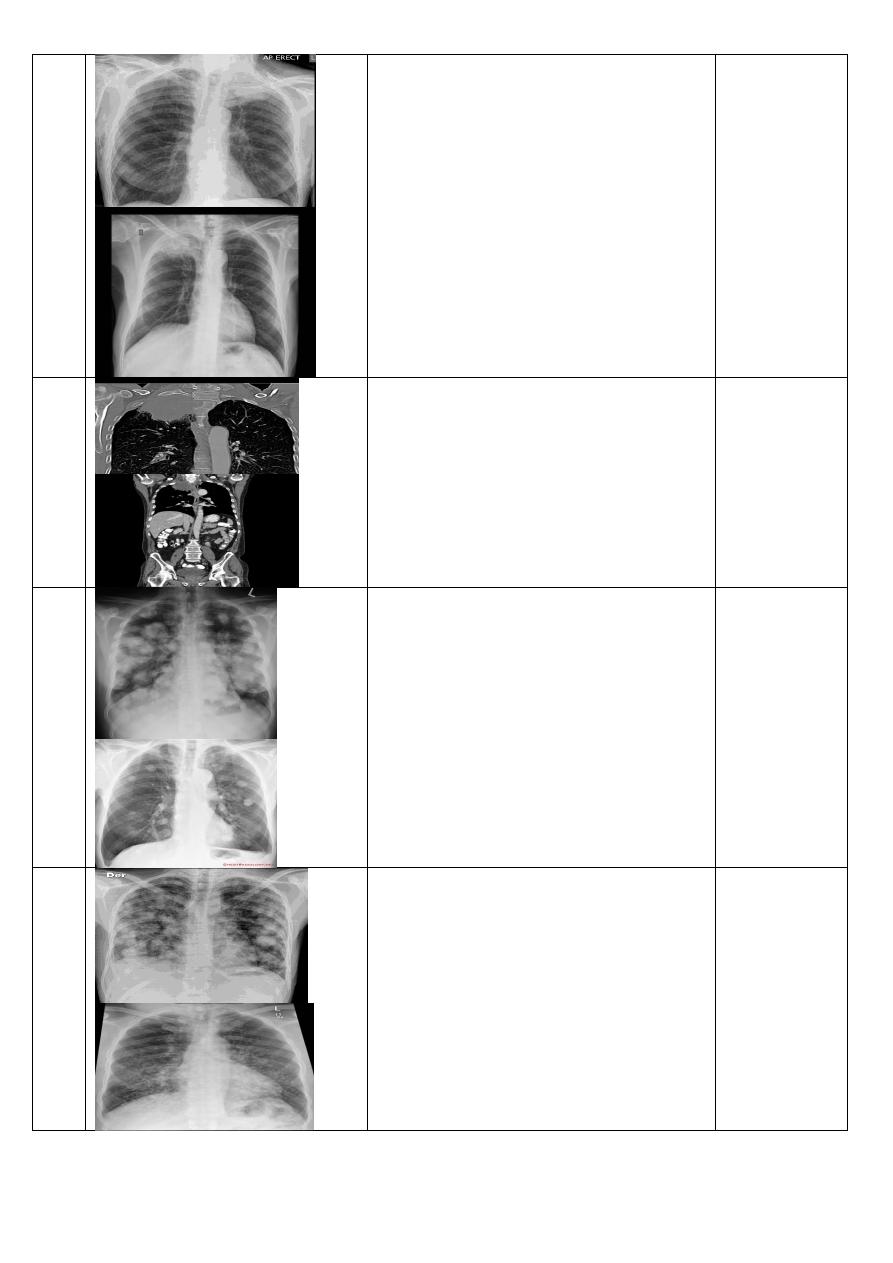
Pancost tumer
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
soft tissue opacity at the apex of the lung.
Occasionally with rib involvement with extension
into the supraclavicular fossa may be evident
with surrounded bony destruction.
28
Pancost tumer
C.T scan (coronal view) showing:
Irregular mass "hyperdense area" at the apex of
the right lung with rib involvement.
28
Cannon ball
metastasis.
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
large well circumscribed, round multiple
opacities with different size and shape like
cannonballs all over the lung field.
30
Secondary
metastasis.
Military T.B
Chest X-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
large well circumscribed, round multiple
opacities with different size and shape like
cannonballs all over the lung field.
Chest x-Ray ,P-A view of adult male showing:
1-3 mm diameter nodules . are uniform in size
and uniformly distributed.( innumerable small
metastases).
31
=============================================
Lecture3: فقط الساليدات التي لم يتم شرحها في العملي
www.muhadharaty.com/lecture/5463
=============================================
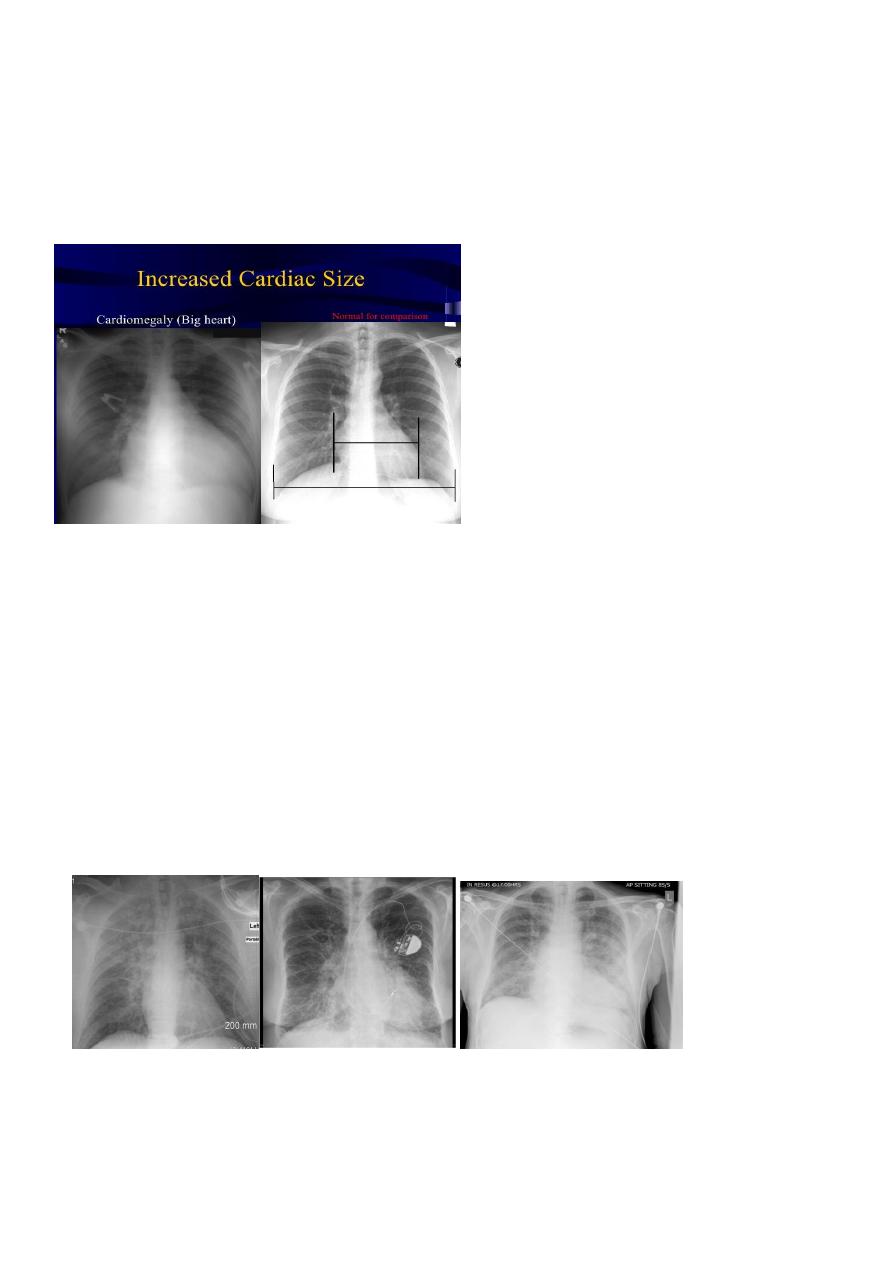
CXR of adult, PA view shows:
Photo on the right:
Normal cardiac shadow, cardiothoracic ratio is less than 50%
Photo on the left:
Increase cardiac shadow
Cardiothoracic ratio is more than 50%
Diagnosis= cardiomegaly
CXR of adult, PA views show:
Bilateral patchy opacities in both lung fields with enlarged cardic shadow
Kerley lines are seen
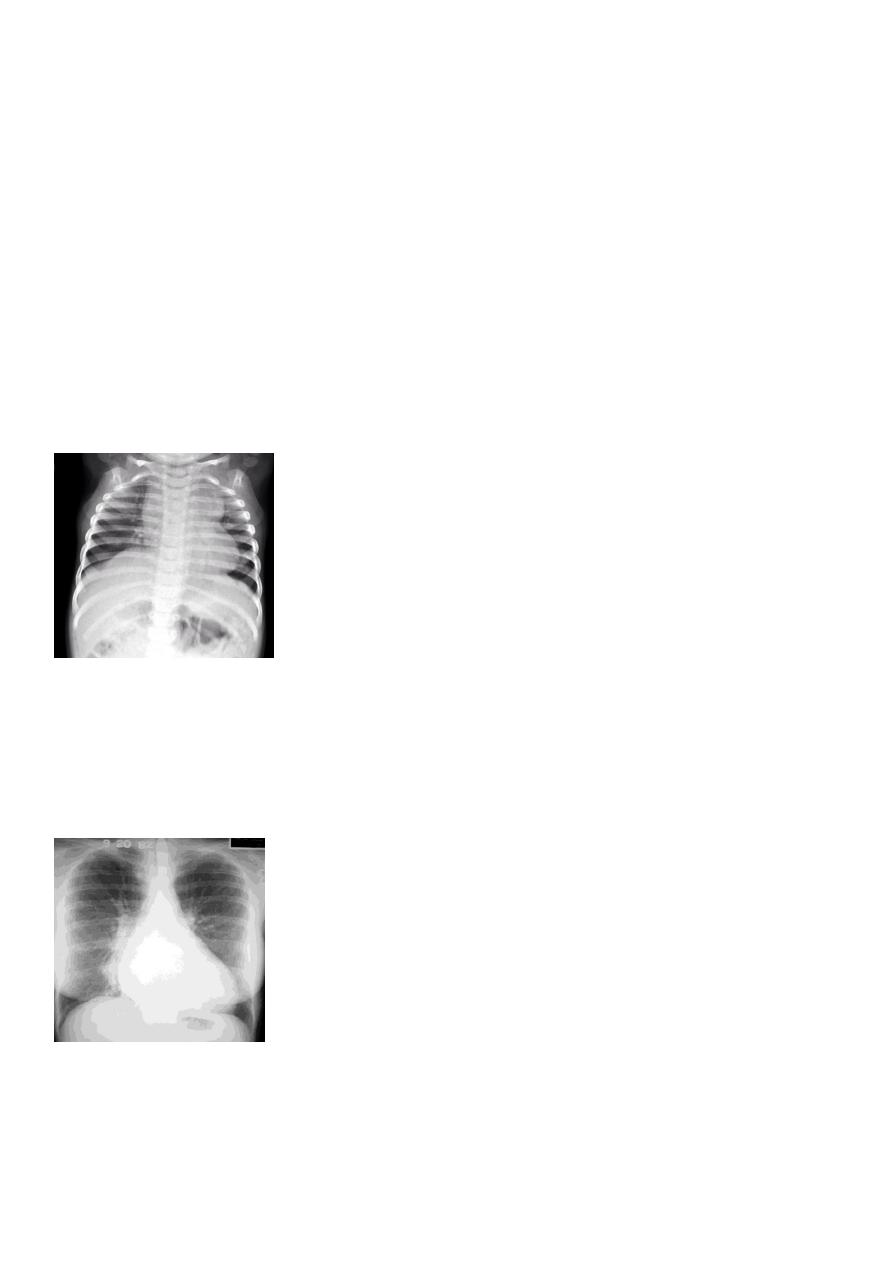
Diagnosis=interstitial pulmonary edema
Note:
Classification of kerley lines:
Kerley A lines
These are 2-6 cm long oblique lines that are <1 mm thick and course towards the hila. They
represent thickening of the interlobular septa
Kerley B lines
These are 1-2 cm thin lines in the peripheries of the lung. They are perpendicular to and
extend out to the pleural surface . They represent thickened sub pleural interlobular septa
and are usually seen at the lung bases.
CXR of a child , PA view shows:
Cardiomegaly with egg on string sign cardiac contour, There is narrowing of the superior
mediastinum .
Diagnosis= transposition of great blood vessels
CXR of adult, PA view shows:
Bilateral upper lobe venous diversion in favour of pulmonary venous hypertension
Diagnosis= pulmonary venous hypertension
