
1
Fifth stage
Surgery
Lec-1
.د
محمد صالح
15/3/2016
Tumors of the brain
Epidemiology:
Incidence of primary brain tumors (benign or malignant) 12.8/100,000
10%–15% of cancer patients develop brain metastases
Etiology:
Primary – unknown
Genetic – hereditary
Metastatic
o 35% - lung
o 20% - breast
o 10% - kidney
o 5% - gastrointestinal tract
Often unknown
Under investigation:
o Genetic changes
o Heredity
o Errors in fetal development
o Ionizing radiation
o Electromagnetic fields (including cellular phones)
o Environmental hazards (including diet)
o Viruses
o Injury or immunosuppression
Classification:
Tissue of origin
Location
Primary or secondary (metastatic)
Grading

2
Tumor grading:
Microscopic appearance
Growth rate
Different for other types of CA
For CNS, per WHO:
o GX Grade cannot be assessed (Undetermined)
o G1 Well-differentiated (Low grade)
o G2 Moderately differentiated (Intermediate grade)
o G3 Poorly differentiated (High grade)
o G4 Undifferentiated (High grade)
Presentation:
Depends on location, size, and type of tumor
Neurological deficit 68%
o 45% motor weakness
o Mental status changes
HA 54%
Seizures 26%
Signs and symptoms of brain tumors:
General
o Cerebral edema
o Increased intracranial pressure
o Focal neurologic deficits
o Obstruction of flow of CSF
o Pituitary dysfunction
o Papilledema (if swelling around optic disk)
Cerebral Tumors
o Headache
o Vomiting unrelated to food intake
o Changes in visual fields and acuity
o Hemiparesis or hemiplegia
o Hypokinesia
o Decreased tactile discrimination
o Seizures
o Changes in personality or behavior

3
Brainstem tumors
o Hearing loss (acoustic neuroma)
o Facial pain and weakness
o Dysphagia, decreased gag reflex
o Nystagmus
o Hoarseness
o Ataxia (loss of muscle coordination) and dysarthria (speech muscle disorder)
(cerebellar tumors)
Cerebellar tumors
o Disturbances in coordination and equilibrium
Pituitary tumors
o Endocrine
o dysfunction
o Visual deficits
o Headache
Frontal Lobe
o Inappropriate behavior
o Personality changes
o Inability to concentrate
o Impaired judgment
o Memory loss
o Headache
o Expressive aphasia
o Motor dysfunctions
Parietal lobe
o Sensory deficits
o Paresthesia
o Loss of 2 pt discrimination
o Visual field deficits
Temporal lobe
o Psychomotor seizures – temporal lobe-judgment, behavior, hallucinations, visceral
symptoms, no convulsions, but loss of consciousness
Occipital lobe
o Visual disturbances
Intra-axial:
Gliomas
o Astrocytoma (Grades I & II)
o Anaplastic Astrocytoma
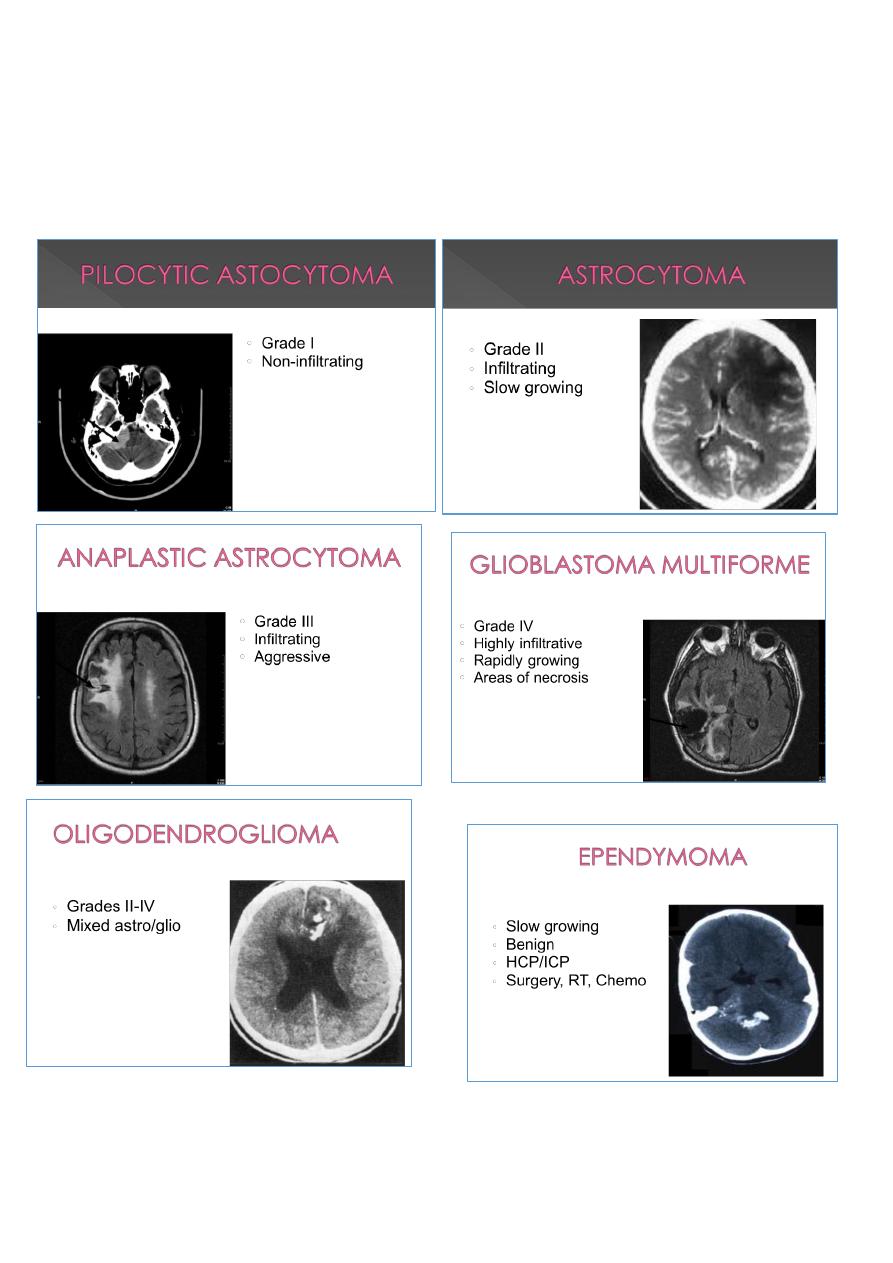
4
o Glioblastoma Multiforme
Oligodendroglioma
Ependymomas
Medulloblastoma
CNS Lymphoma
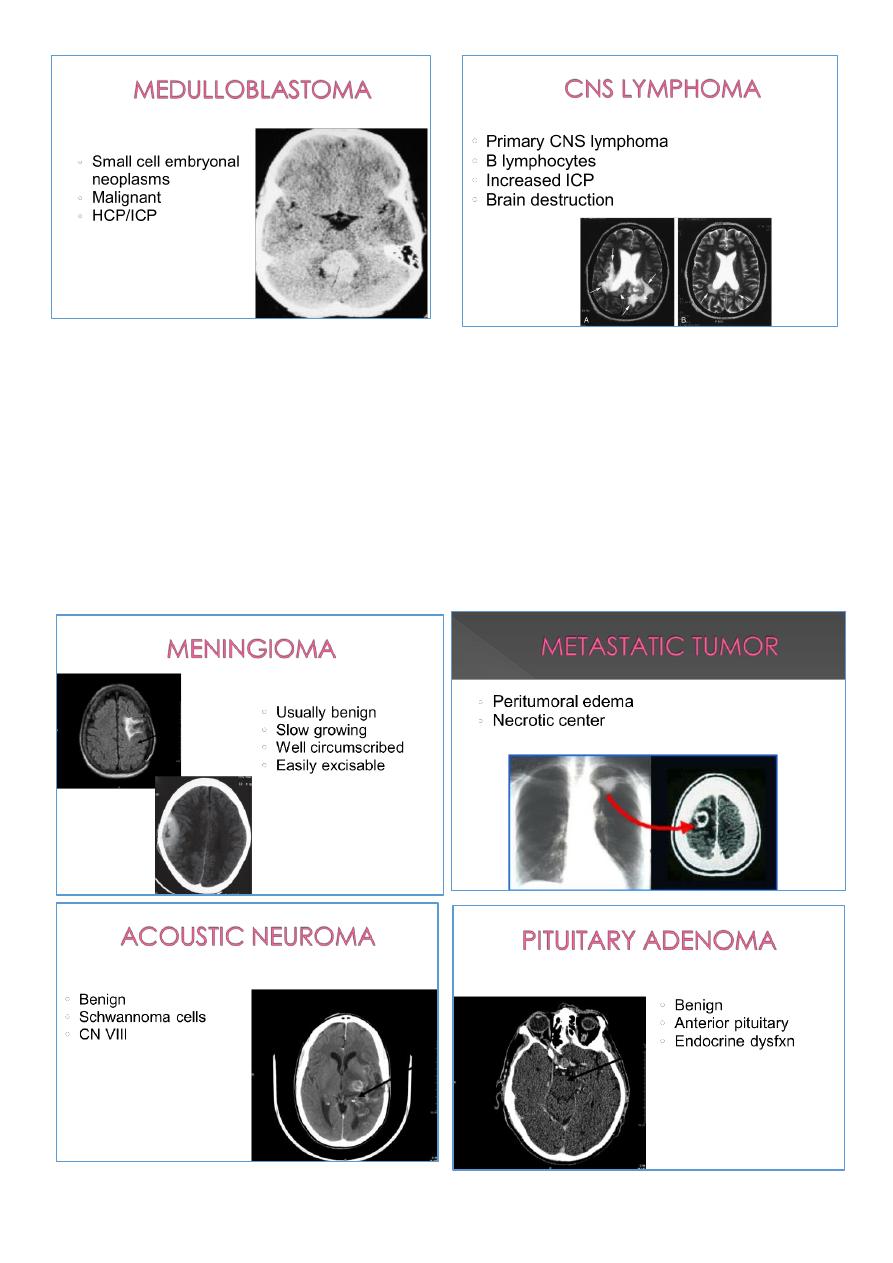
5
Extra axial:
Meningioma
Metastatic
Acoustic neuromas (Schwannoma)
Pituitary adenoma
Neurofibroma
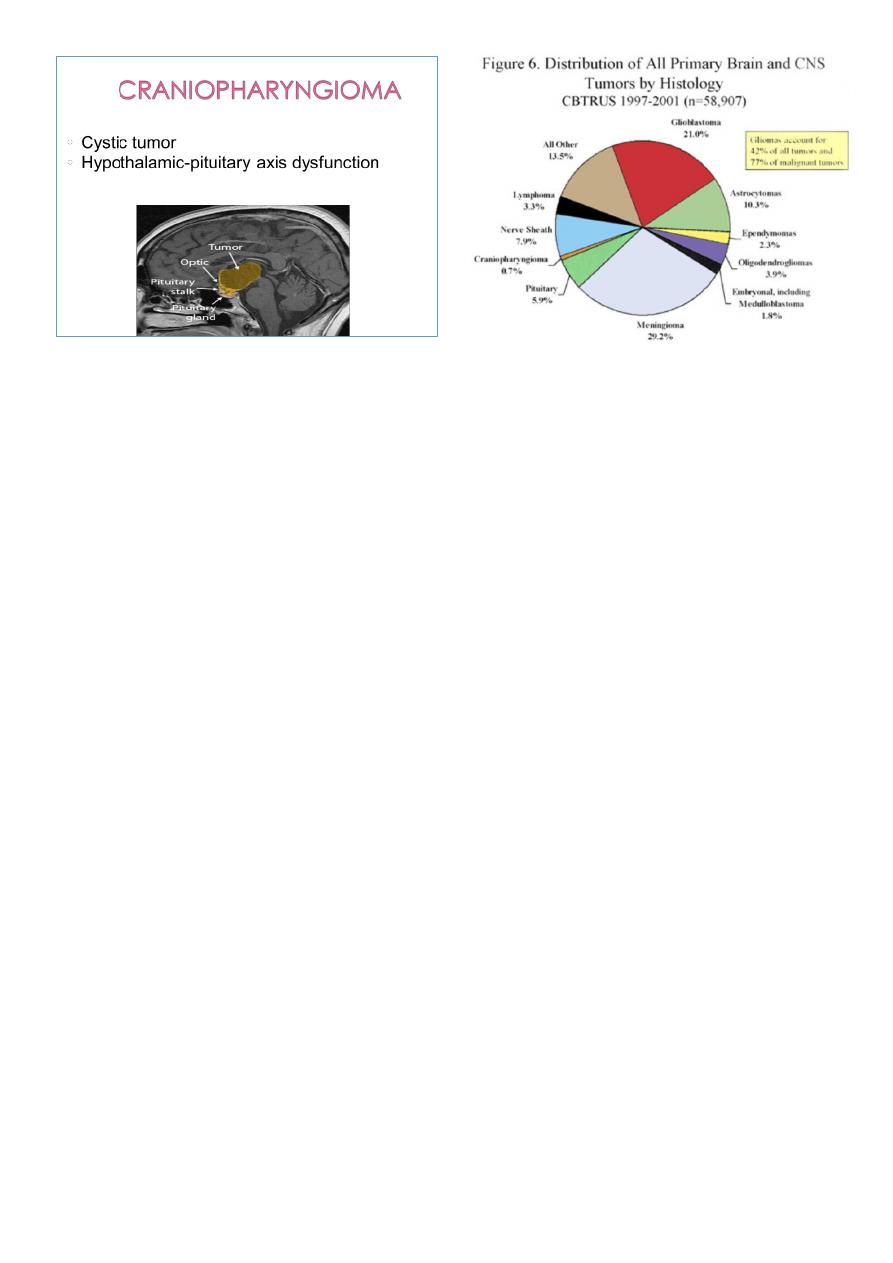
6
Diagnostic procedures:
Radiological Imaging
o Computed Tomography scan (CT scan) with/without contrast
o Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) with/without contrast
o Plain films
o Myelography
o Positron Emission Tomography scan (PET scan)
LP/CSF analysis
Pathology
Surgical treatment:
Resection
Craniotomy
Stereotaxis Surgery
Biopsy
Transsphenoidal
Interventions:
Drug therapy – Palliative
Done for symptom treatment and to prevent complications
o NSAIDs
o Analgesics –
o Steroids (Decadron, medrols, prednisone)
o Anti-seizure medications (phenytoin) Dilantin & Cerebyx

7
o Histamine blockers
o Anti-emetics
o Muscle relaxers (for spasms)
o Mannitol for ICP –New Hypertonic saline
Post-op complications:
Increased ICP
Hematoma
Hypovolemic shock
Hydrocephalus
Atelectasis
Pulmonary edema
Meningitis
Fluid and electrolyte imbalances (ADH)
Wound infection
Seizures
CSF leak
Edema
Discharge planning:
Follow-up appointments and procedures
Medications
Exercise
Diet
o Patient may need referral to dietician to help with diet planning while undergoing
chemotherapy
Seizures
o Are a risk for 1 or more years following surgery
If expecting long term changes, coordinate discharge planning with appropriate
members of health care team
Radiation therapy:
Damages DNA of rapidly dividing cells
4000–6000 Gy total dose
Duration of 4–8 weeks

8
Brachytherapy
Stereotactic radiosurgery
Chemotherapy:
Slows cell growth
Cytotoxic drugs: CCNU, BCNU, PCV, Cisplatin, Etoposide, Vincristine, Temozolomide
(Temodar)
