
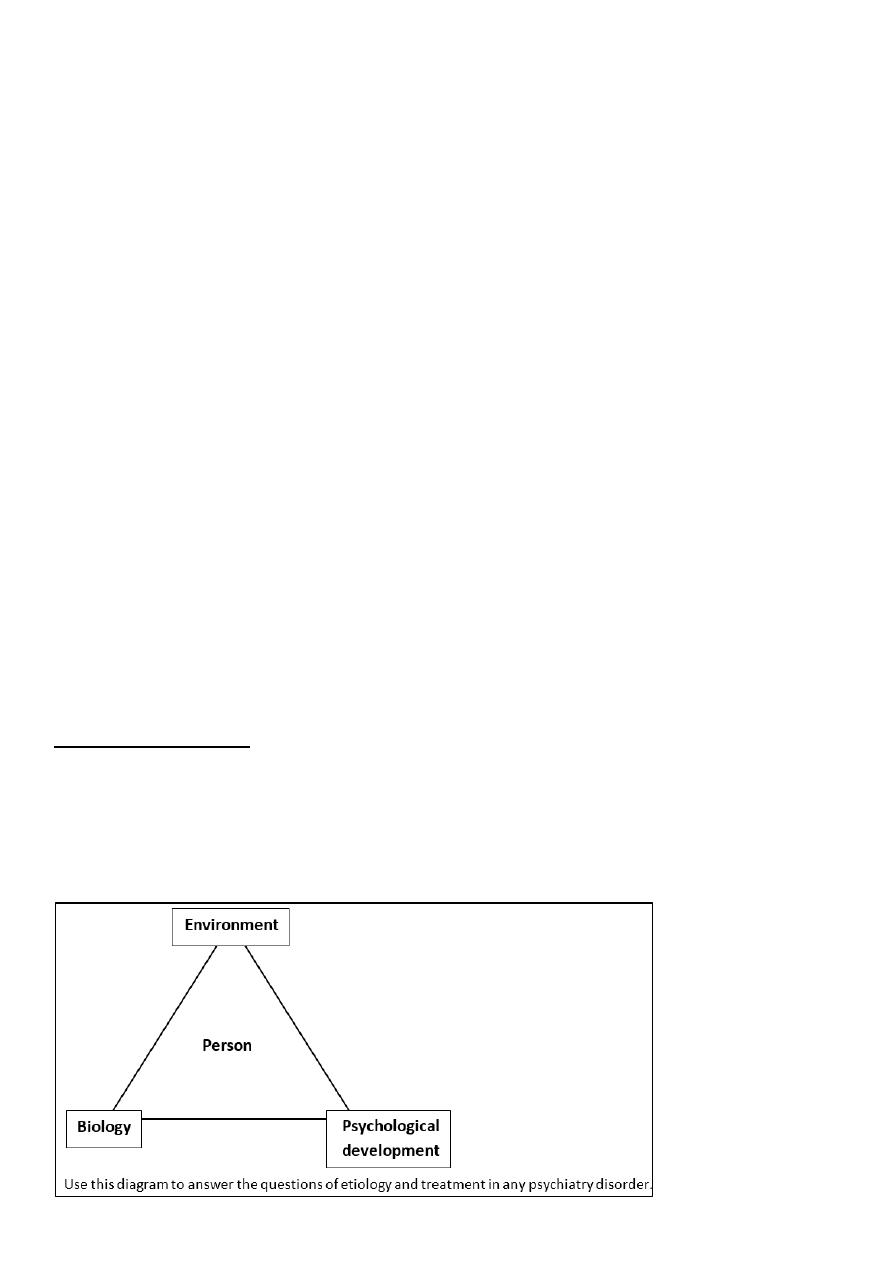
1
Psychiatry sessions
Part1: History
Biographic data:
Name for communication, differentiation, data collection.
Age different diseases for different ages, for example, TCA in old age lead to
anticholinergic side effects like retention due to prostatic hyperplasia.
Sex sexual identity disorders.
Occupation stress of occupation (like anxiety disorders), level of education, effects
of psychiatry diseases on his occupation.
Religion special thoughts, stop some of activities.
Mental state protective psychologically.
Address.
History of presenting complaint:
Chronological order
Duration
Social miliueu
Precipitating events
Attribution of symptoms
Coping with the symptoms
Treatment effect
Effect of symptoms on patient functioning (social, occupational ,interpersonal)
Self-care (eating, sleeping, weight, excretory function)
Substance use
Suicidal thoughts and actions
Do you feel that you have a future?
Do you feel that life`s not worth living?
Do you ever feel completely hopeless?
Do you ever feel you`d be better of dead and away from it all?
Have you made any plan?
Have you ever made an attempt to take your own life?
What prevents you from doing it?
Have you made any arrangementsfor your affairs after your death?
Sleeping
Early morning waking = depression.
2
Night mares.
6-8 h normally.
Interrupted sleep.
Family history:
Mental illness in the family
Suicide.
Personal history:
Family background
Family atmosphere
Infancy and childhood
School
Occupational history
Psychosexual history
Past psychiatric history
Past and current medical and surgical history
Alcohol use
Drug misuse
Medication
Forensic history
Social history
Premorbid personality
Premorbid personality:
Ask the relatives about it.
Ask the patient about friends, habits, trust people, temper, tidiness, coping with life,
how to deal with critisme.
3
Part2: Mental state examination
1- General appearance and patient behavior:
Appearance well dressed, well set.
Behavior look for any abnormal behavior.
2- Speech:
Should be normal steam and flow.
3- Thought ========>
4- Mood:
How he feel.
How he look.
Suicide or not.
5- Hallucination and delusion:
Patient with schizophrenia if he has delusion,
he will do it, so take care.
6- Cognition function:
General information.
Orientation and concentration.
قصة
،قصيرة
،ارقام
ايام
االسبوع
Judgment.
اشارة
مرور
،حمراء
ماذا
سوف
?تفعل
Abstract thinking.
Insight.
المريض
يعلم
ان
لديه
مرض
مثل
5
%
مرضى
انفصام
الشخصية
يعلمةن
انهم
مصابون
Part3: Psychopathology
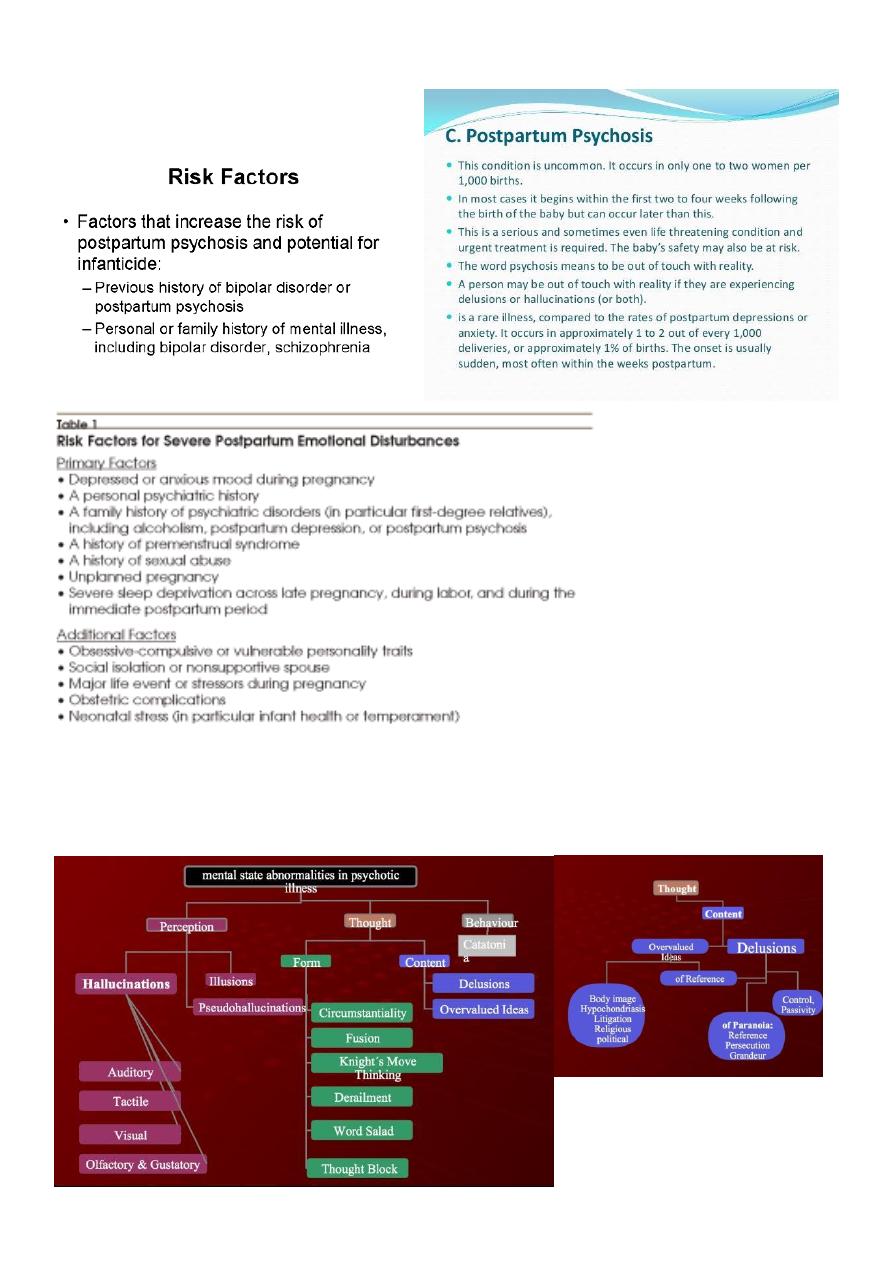
Abnormal beliefs:
A category of disturbance which includes delusions, over-valued ideas.
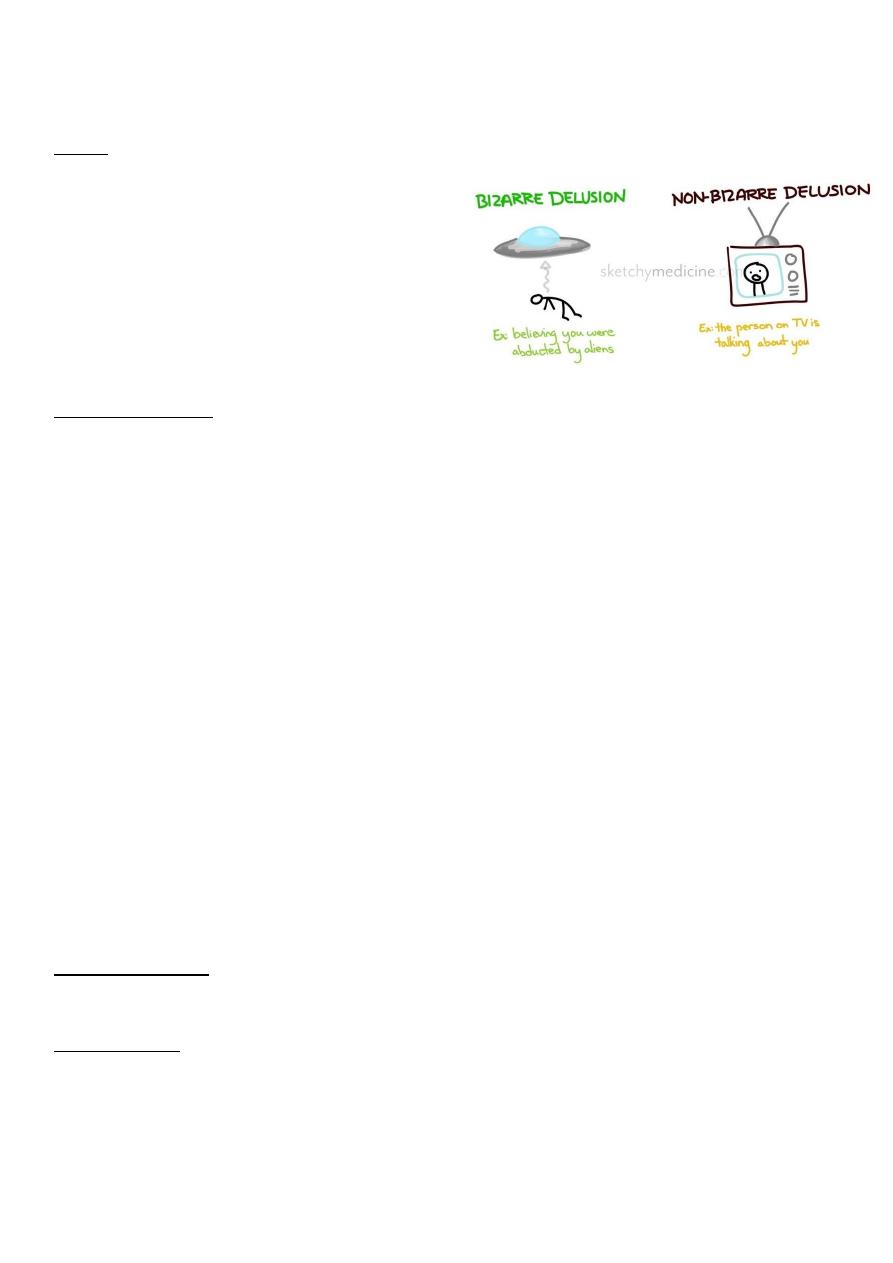
Delusions:
An abnormal belief which is held with absolute subjective certainly, which requires no
external proof, which may be held in the face of contradictory evidence, which has
personal significance and importance to individual concerned.
Excluded are those beliefs which can be understood as part of the subject's cultural or
religious background.
Thought Disorder
1. Disorder of the stream of thought:
o Inhibition of thought. {Depression}
o Pressure of thought. {mania or schizophrenia}
o Flight of Ideas. {mania}
o Thought Blocking. {schizophrenia}
o Incoherence of Thought {schizophrenia}
o Circumstantial pressure of talk. {mania or
schizophrenia}
o Preservation- speech disorder. {dementia}
2. Disorder of the Content of Thought:
o Delusion – A fixed false unchable belief is out
of keeping with person educational and
cultural background, not shared by others.
o An over – valued idea- an idea that because of
its feeding tone takes precedence overall other
ideas, it may be true or false.
3. Disorder of the form of thought:
o Negative formal thought.
o Positive formal thought Disorder (No abstract
thinking).
o Neologisms.
o Self –reference of thinking.
o Talking past the point ( here the pt. gives a
worong answer
4. Disorder of possession of thought
o Here the individual is compelled to think his
own thought against his will.
4
While the content is usually demonstrably false and bizame in nature, this is not
invariably so.
Belief:
1- Abnormal.
2- Absolute subjective certainly.
3- No external proof.
4- Contradictory evidence.
5- Personal importance and significance.
6- Exclude cultural and religious background.
7- Content usually false and bizame.
Over-valued ideas:
A form of abnormal belief. These are ideas which are reasonable and understandable in
themselves, but which come to unreasonably dominate the patient's life.
Abnormal perceptions:
A category of disturbances which includes:
- Sensory disturbance.
- False perception.
Changes in the perceived intensity as quality if a real external stimulus.
Associated with organic conditions and drug ingestion or withdrawals.
Examples include:
- Hyperacusis
hearing sound as abnormally loud.
- Micropsia
"wrong end of the telescope effect", perceiving objects which are close
as small and far away.
False perceptions: internal perceptions which do not have a corresponding object in the
external or "real" world, Includes: Hallucinations, and Pseudo-hallucinations.
Hallucinations:
An internal percept without a corresponding external object.
The subjective experience of hallucination is that of experiencing a normal percept in
that modality of sensation.

5
A true hallucination will be perceived as in external space, distinct from imagined
images, outside conscious control, and as possessing relative permanence.
A pseudo-hallucination will lack one or all of these characteristics.
Hallucinations are subdivided according to their modality of sensation and may be:
auditory, visual, gustatory, tactile, olfactory, or kinesthetic.
Auditory hallucination (voices) schizophrenic patient.
Visual hallucination organic illness.
Pseudo-hallucination:
A false perception which is perceived as occurring as part of one's internal experience,
not as part of the external world.
It may be described an "as if" quality or as being seen with the mind's eye.
Additionally, hallucinations experienced as true hallucination during the active phase of
a patient's illness may become perceived as pseudo-hallucinations as they receves.
They can occur in all modalities of sensation.
They are described in psychotic, organic and drug-induced conditions as well as
occasionally in normal individuals.
The Hallucinations of deceased spouses commonly described by widows and widowers
may have the form of a pseudo-hallucination.
First-rank symptoms of schizophrenia:
A group of symptoms originally described by Schneider which are useful in the diagnosis of
schizophrenia.
They are neither pathognomonic for, nor specific to, schizophrenia and are also ssen in
organic and affective psychoses.
They are 11 symptoms in 4 categories:
Auditory hallucination:
o Voices heard arguing.
o Thought echo.
o Running commentary.
Delusions of thought interference:
o Thought insertion.
o Thought withdrawal.
o Thought broadcasting.
Delusions of control:

6
o Passivity of affect.
o Passivity of impulse.
o Passivity of volition.
o Somatic passivity.
Delusional perception:
o A primary delusion of any content that is reported by the patient as having arisen
following the experience of a normal perception.
Voices heard arguing: A type of auditory hallucination which is first rank symptom of
schizophrenia.
The patient hears two or more voices debating with or another, sometimes about a matter
occur which the patient is agonizing (e.g. he should take the medication, its worked before ,
no not again, he will not take it this time).
Thought echo the experience of an auditory hallucination in which the content is the
individual current thoughts, also knows as gidankelautukule or echo di la pensee.
Running commentary A type of third person auditory hallucination. The patient hears
one or more voices providing a noirative of their current actions he's getting up .. now he's
going towards the window.
Thought insertion the delusional belief that thoughts are being placed in the patient's
head from outside.
Though broadcasting the delusional belief one's thoughts are accessible directly to
others.
Delusions of control:
A group of delusions which are also known as passivity phenomena or delusions of bodily
passivity.
The core feature is the delusional belief that one is no longer in sole control of one's own
body.
The individual delusions are that one is being forced by same external agent to feel
emotions (passivity of affect), to desire to do things (passivity of impulse), to perform
actions (passivity of volition), or to experience bodily sensation (somatic passivity).
Affect The emotional state prevailing in a patient at a particular moment and in
response to a particular event or situation.
7
Mood The subjective emotional state over a longer period of time.
Anergia the subjective feeling of lack of energy and sense of increased effort required to
carry out tasks. Associated with depressive illness.
Anhedonia the feeling of absent or significantly diminished enjoyment of previously
pleasurable activities. A core symptom of depressive illness, also a negative symptom of
schizophrenia.
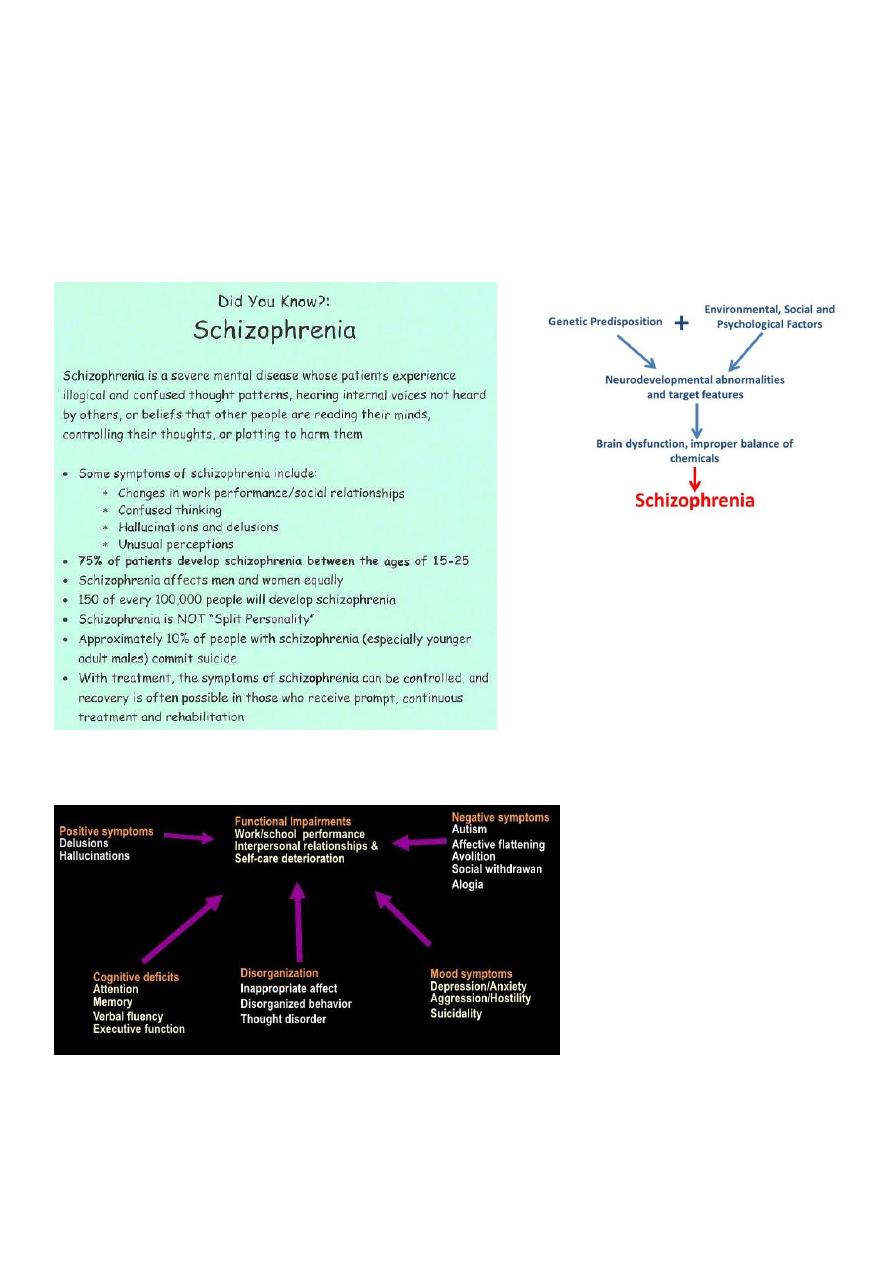
Clinical features of schizophrenia:
Notes:
Monoaminooxidases are dopamine, adrenaline, noradrenaline, acetylcholine, 5-HT.
If dopamine on its receptors increased lead to positive symptoms of schizophrenia.
Negative symptoms occur in chronic case and lead to brain atrophy.
8
Women psychiatry:
Mental state:
9
Alzheimer's:
Drug abuse:

10
Autism:
11
Part4: Treatment in psychiatry

12
Psychosis:
Hallucination.
Delusion.
Disorganized speech (abnormal thinking).
Disorganized behavior.
Loss of insight.
How you examine the insight of the patient?
Ask the patient if he is diseased? If he say no then he is completely loss of insight.
What sort of illness you have? If say physical illness then he is partial loss of insight.
Do you accept psychiatric intervention? If he say yes then he is complete insight.
Antipsychotic:
Atypical more selective, less extra-pyramidal side effects, expensive.
Typical less selective, more extrapyramidal side effects, cheap.
Resistant case:
When use 2 antipsychotics (6 weeks apart) and there is no response despite of good
compliance.
So give clozapine.
Important investigation WBC count because clozapine lead to leukopenia (infection).

13
Notes:
Metoclopramide antipsychotic drug, lead to dystonia.
Procyclidine addictive drug, anticholinergic effect, 5-10 mg orally or equivalent dose
IM.
Acute confusional state (delirious) it is violent behavior due to iatrogenic cause.
Rapid dose of diazepam IV
lead to respiratory attack.
Autonomic dysfunction hypertension, tachycardia, tachypnea, sweating.
Pyrexia 38-39.
Extrapyramidal side effects:
Acute dystonia (hours or days).
Parkinsonism (weeks).
Akanthesia (months) type of restlessness.
Tradative dyskinesia (months or years) continue fine movement of lips.
Neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS) like acute dystonia but more severe.
NMS:
It is a side effect of antipsychotic.
Rare.
High mortality rate.
Medical emergency.
Treatment transferee to medical unit, stop the antipsychotic, give anti-dopamine.
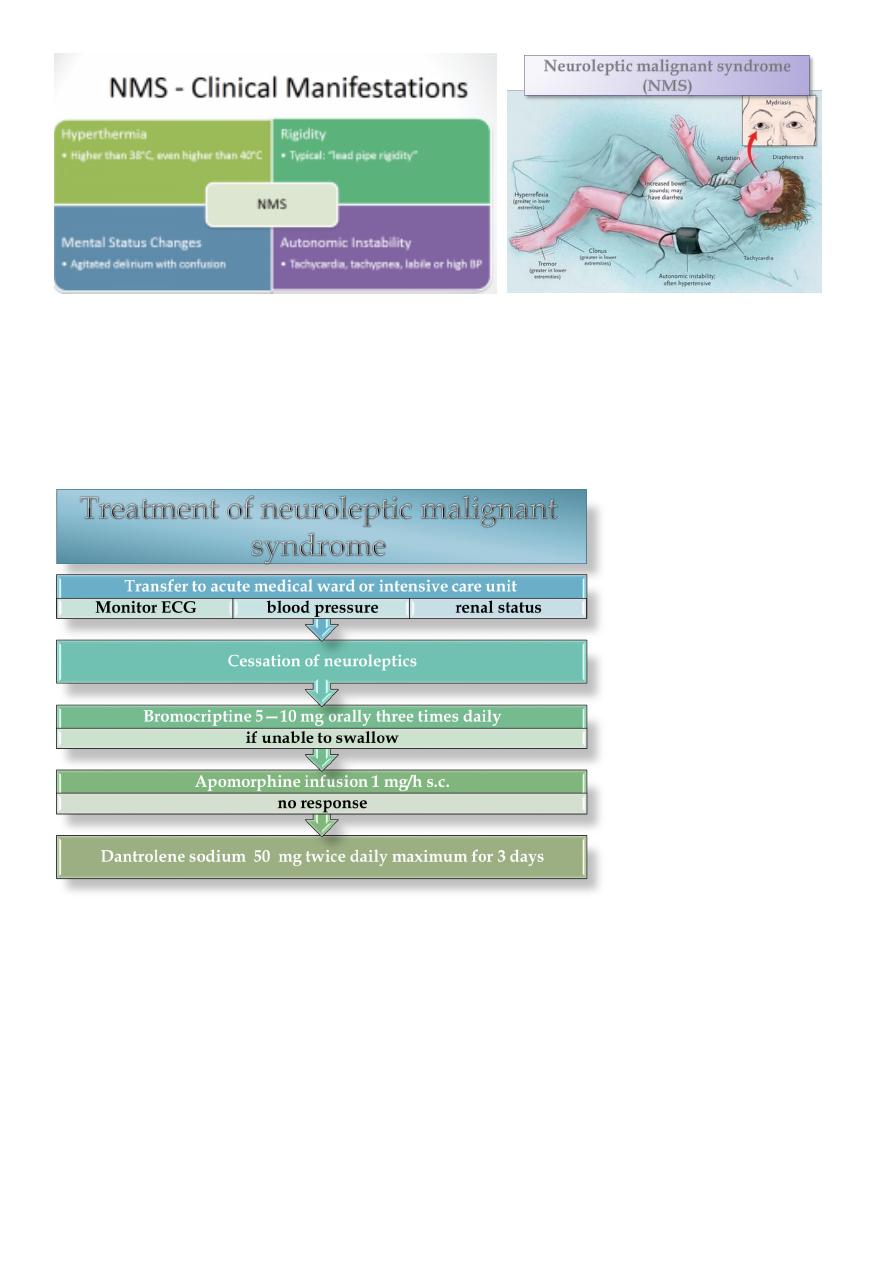
14
NMS has been associated:
larger doses
typical antipsy-chotics
high-potency
Mortality associated with NMS:
autonomic instability (e.g. cardiac arrest)
renal failure due to rhabdornyolysis and myoglobinuria
Lower with atypical antipsychotics
Mortality: 12 -18 %

15
Antidepressant treatment:
reached the therapeutic dose
assessed 4—6 weeks
poor tolerability or inadequate response to the maximum tolerable dose
switch to a different antidepressant
Switching between antidepressants:
abrupt withdrawal should be avoided
cross-tapering should be use
All antidepressants (but especially paroxetine and venlafaxine) have the potential to
cause withdrawal phenomena when stopped abruptly;
they should always be withdrawn slowly, preferably over 4 weeks
Common symptoms of antidepressant discontinuation:
dizziness
electric shock sensations
anxiety and agitation
insomnia
influenza-like symptoms
diarrhoea
abdominal spasms
nausea
paraesthesia
mood swings
low mood
Treatment of withdrawal symptoms:
give reassurance; symptoms rarely last more than 1—2 weeks.
slow the rate of drug withdrawal
return to the last dose tolerated by the patient
If the patient does not respond to a second antidepressant:
check compliance
review the history for social factors
atypical antipsychotic may be added

16
ECT:
Unilateral or bilateral.
Plan ECT or modified ECT (under GA so tonic clonic not
appear).
Dose: 200 voltage at beginning then increased to 400 and 600
until reach 800.
Catatonic schizophrenia need ECT.
Side effects of ECT: dislocation, fractures, confusion amnesia, side effects of GA.
The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidance on ECT
recommends that it be restricted to:
severe depressive illness,
catatonia,
prolonged or severe mania.
postpartum psychoses.
NMS
Severe depressive illness:
treatment resistant
psychomotor retardation
psychotic features such as delusions and/or hallucinations
life-saving if the patient is very acutely suicidal
fails to maintain adequate nutrition or hydration
patient preference
past history of response to ECT
the need for a rapid response to treatment
the risks of other treatments exceed those for ECT
elderly who have not responded to drug treatments or have suffered unpleasant side
effects
Remission rates in clinical trials are 60—70 per cent
Mania:
prolonged or severe mania
the need for a speedy therapeutic response
as a safe alternative to high-dose medications
if patients have drug-resistant

17
'rapid cycling' mania
Schizophrenia:
catatonic excitement or immobility
the patient cannot tolerate medications
failed to respond to adequate doses of antipsychotics including clozapine
Part5: Treatment in psychiatry (from the lecture)
1- Antidepressants:
Indications:
Unipolar and bipolar depression,
organic mood disorders,
schizoaffective disorder,
anxiety disorders including OCD, panic, social phobia, PTSD,
premenstrual dysphoric disorder
impulsivity associated with personality disorders.

18
General guidelines
Antidepressant efficacy is similar so selection is based on past history of a response,
side effect profile and coexisting medical conditions.
There is a delay typically of 3-6 weeks after a therapeutic dose is achieved before
symptoms improve.
If no improvement is seen after a trial of adequate length (at least 2 months) and
adequate dose, either switch to another antidepressant or augment with another
agent.
Types:
Mood disorders/Antidepressants
o MAO Inhibitors
o Tricyclics
o Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
o Dual Action Antidepressants
o Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors
o Atypical antidepressant
Mood Stabilizers (Antimanic Agents)
o LithiumCarbonate
o Valproic Acid
o Carbamazepine
o Lamotragine, Topirimate
Side effects:
Orthostatic hypotension, weight gain, dry mouth, sedation, sexual dysfunction and
sleep disturbance.
Hypertensive crisis can develop when MAOI’s are taken with tyramine-rich foods or
sympathomimetics.
Serotonin Syndrome can develop if take MAOI with meds that increase serotonin or
have sympathomimetic actions. Serotonin syndrome sx include abdominal pain,
diarrhea, sweats, tachycardia, HTN, myoclonus, irritability, delirium. Can lead to
hyperpyrexia, cardiovascular shock and death.
TCA leads to more side effects including antihistaminic (sedation and weight gain),
anticholinergic (dry mouth, dry eyes, constipation, memory deficits and potentially
delirium), antiadrenergic (orthostatic hypotension, sedation, sexual dysfunction)
2- Mood Stabilizers:
Indications:
Bipolar, cyclothymia, schizoaffective, impulse control and intermittent explosive
disorders.
Note:
Important questions you should
ask before giving TCA to patient:
1- Epigastric upset and gastric
ulcer.
2- Prostatic hyperplasia.
3- Acute glaucoma.

19
Classes:
Lithium, anticonvulsants, antipsychotics
Lithium side effects:
Most common are GI distress including reduced appetite, nausea/vomiting, diarrhea
Thyroid abnormalities
Non significant leukocytosis
Polyuria/polydypsia secondary to ADH antagonism. In a small number of patients can
cause interstitial renal fibrosis.
Hair loss, acne
Reduces seizure threshold, cognitive slowing, intention tremor
Lithium toxicity:
Mild- levels 1.5-2.0 see vomiting, diarrhea, ataxia, dizziness, slurred speech,
nystagmus.
Moderate-2.0-2.5 nausea, vomiting, anorexia, blurred vision, clonic limb movements,
convulsions, delirium, syncope
Severe- >2.5 generalized convulsions, oliguria and renal failure
3- Antipsychotics
Indications:
schizophrenia, schizoaffective disorder, bipolar disorder- for mood stabilization
and/or when psychotic features are present, delirium,
psychotic depression, dementia, trichotillomania, augmenting agent in treatment
resistant anxiety disorders.
Types:
Typical:
o Chlorpromazine
o Trifluperazine Thorazine
o Haloperidol – (Haldol)
Atypical:
o Risperdal - Risperidone
o Olanzepine - Zyprexia
o Quetiapine - Seroquel
o Ziprasidone – Geodon
o Aripiprazole – Abilify
o Paliperidone – Invega

20
Side effects:
Extrapyramidal side effects (EPS): Acute dystonia, Parkinson syndrome, Akathisia
Parkinson-like symptoms of bradykinesia, rigidity, and tremor
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS): Characterized by severe muscle rigidity,
fever, altered mental status, autonomic instability, elevated WBC, CPK and lfts.
Hyperprolactinaemia, sedation, weight gain
CV& cerebrovascular events
postural hypotension , sexual dysfunction
photosensitivity, agranulocytosis
constipation, reduction of fit threshold
orthostatic hypotension, light-headedness, poikilothermia
The neuroleptics depress the hypothalamus, affecting thermoregulation, and causing
amenorrhea, galactorrhea, gynecomastia, infertility, and impotence
4- Anxiolytic:
Indications:
Treat anxiety disorders
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Panic Disorder
PTSD
OCD
Social Anxiety Disorder (SAD)
Used to treat many diagnoses including panic disorder,
generalized Anxiety disorder,
substance-related disorders and their withdrawal,
insomnias and parasomnias.
Example:
Benzodiazepines
Side effects:
Somnolence
Cognitive deficits
Amnesia
Disinhibition
Tolerance
Dependence

21
Part5: Photos
Delusion of Grandiosity:
The patient think himself is very important or god or
prophet.
Occur in mania, schizophrenia, delusional disorder
(person has only delusion, no other diseases).
Erotomania:
Delusion in love.
Male to female ratio is 1:10.
Occur in schizophrenia and delusional disorder.
Delusion of Jealousy (othello syndrome):
Called delusion of intendancy.
Occur in middle age males.
Occur in schizophrenia and delusional disorders and in
alcoholic.
May lead to kill other people.
Thought withdrawal:
Occur in schizophrenia.
It is one of criteria of schizo (First rank).
Thought broadcast:
Not digital delusion.

22
Delusion of reference:
Occur in schizophrenia.
Facial expression of patient with paranoid
delusion:
Paranoid delusion occur in delusional disorders and
schizophrenia.
Nihilistic delusion وهم العدمية:
Patient feels that part of his body is not present or all
parts of his body not present.
Occur in delusional disorders and schizophrenia.
Delusion of infestation:
Occur in addict patients.
Body dysmorphic delusion
Hallucination:
It is perception without stimulant.
Types:
Gustatory.
Visual.
Tactile.
Auditory.

23
Auditory delusion:
Occur in schizophrenia and depression and any
psychotic disorder.
Psychosis:
Loss of insight.
Delusion.
Hallucination.
Disorganized speech.
Disorganized behaviors.
Hallucination
Auditory hallucination:
Punish him.
Distressing.
Commentary voices (suicide or homicide).
Mania اصوات طيبة
Visual and auditory hallucination:
Occur in delusion and schizophrenia.
Tactile (somatic) hallucination
Illusion:
False perception of real stimulus.

24
Pass suicide or real suicide:
Bleeding from hand, continuously bleeding, cuts and
bandages on hand, mostly by patient himself using
knife.
Suicide:
Adult man, angry, try to kill himself by gun, aggressive,
abnormal personality or addict or psychotic problem
like schizophrenia.
Management by modifying environmental and
psychological and mental factors.
Worry:
Try to avoid multiple ideas, fear from something,
multiple thinking.
Obsessional thinking or depression (black dog
type):
Thought that fall his brain.
Aggressive patient with schizophrenia
ECT:
Adult female, lying down, give O2, under general
anesthesia.
ECT:
Middle age male, lying down, monitoring, mouth gag,
try to give him electrical shock.
25
Tonic phase during ECT
ECT:
Indications:
Acute phase of schizophrenia
Mania
Post partum psychosis
Major depression
Depression with suicide
Contraindications:
Physical cardiac infarction, old age, first trimester
pregnancy, recent CVA, osteoporosis.
Psychological
neurotic disorders, hysteria, drug
dependence, personality changes.
Post partum depression:
Risk of Infenticidal.
It is emergency in psychiarty and should treat
immediately, do ECT twice weekly because drugs need
long duration to start acting and secreted in breast
milk and affecting the baby.
Take care of mother and baby.
26
Depression:
Management:
Take full history.
Do examinations.
Thinck of the DDx.
Treatment by social support, psychological treatment,
give antidepressant.
Anroxia nervosa:
Over estimation of her wieght (abnormal self image).
She is very active.
Cheeting in weight.
Cook for her family but don’t eat.
She is mannequin and Ballerina.
The problem is in her family.
She is very childish in her thinking.
Paranoid idea in schizophrenia:
Grandiosity delusion.
Hallusination of voice and touch.
Ideas of refernce and influence.
Schizophrenia:
Delusion of infestation.
Visual hallusination.
Auditory hallusination.
Somatic hallusionation.
Delusion.
Passivity.
Major depression:
Elderly.
Setting alone.
Has signs and symptoms of depression.
Treatment by antidepressant or ECT.
27
Mania:
Give a lot of information, Very clear, Happy life.
Spend mony, Hyperactive, Hypersexual.
Treatment:
ECT twice per day because it is very dangerous
condition.
Haloperidol (I.V) high dose.
Glue sniffing addict:
Lead to cerebral or renal damage.
Drug addit
Depression of old age or dementia (alzheimer)
PTSD:
Clinical features divided into 3 groups:
1- Hyper arousal (persistent anxiety, irritability,
insomnia, and poor concentration)
2- Intrusions (intense intrusive imagery, flashbacks,
and recurrent distressing dreams)
3- Avoidance (difficulty in recalling stressful events at
will, avoidance of reminders of the events,
detachment, inability to feel emotion “numbness”,
and diminished interest in activities
Supportive and cognitive therapy.

28
Obssessive thought (OCD):
A common, chronic condition, often associated with
marked anxiety and depression, characterised by
obsessions and compulsions
Clinical features Thoughts, Ruminations, Impulses,
'Phobias', Compulsive rituals, Abnormal slowness,
Anxiety, Depression, Depersonalization
Treatment
Antidepressants SSRIs, Clomipramine,
psychosurgery, ECT, behavioural therapy
Obssessive cleaning
Depression
Phobia

29
Alcohol depression
Acute dystonia:
