1
Fifth stage
Radiology
Lec-6
د. هديل
30/3/2016
US of the obstetric & Gyne.
2
3
4
5
6
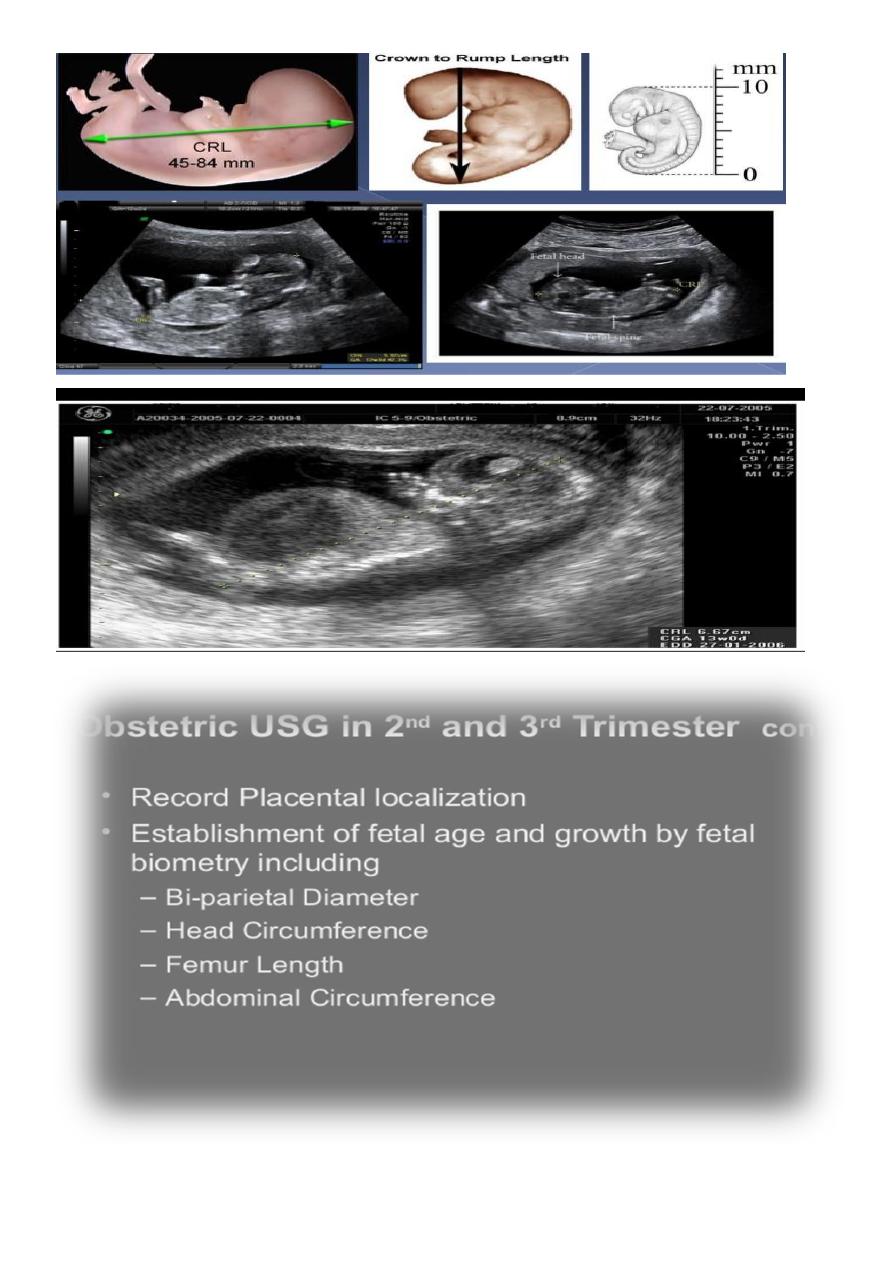
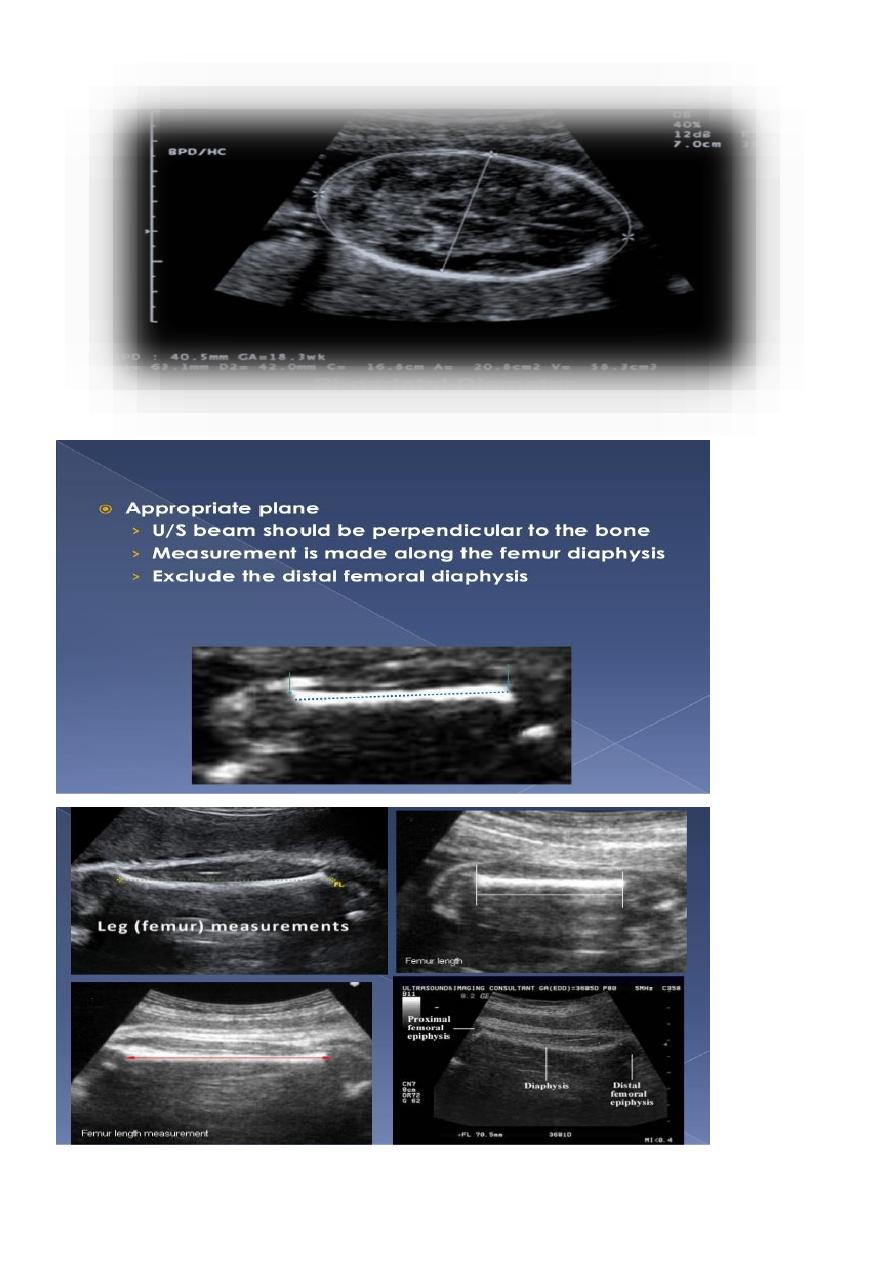
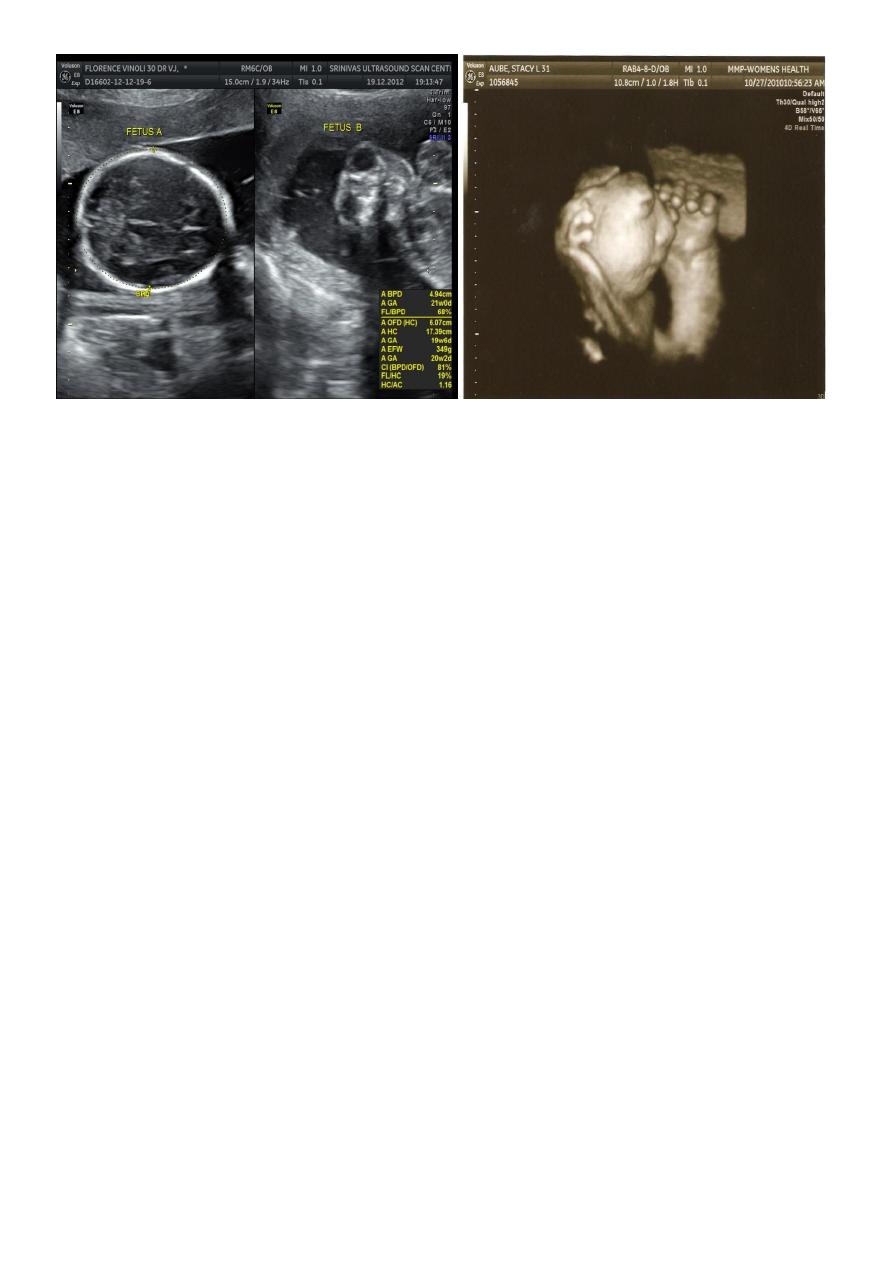
BPD together with head circumference (HC), abdominal circumference (AC), and femur
length (FL) are computed to produce an estimate of fetal weight. In the second trimester
this may be extrapolated to an estimate of gestational age and an estimated due date
(EDD) .
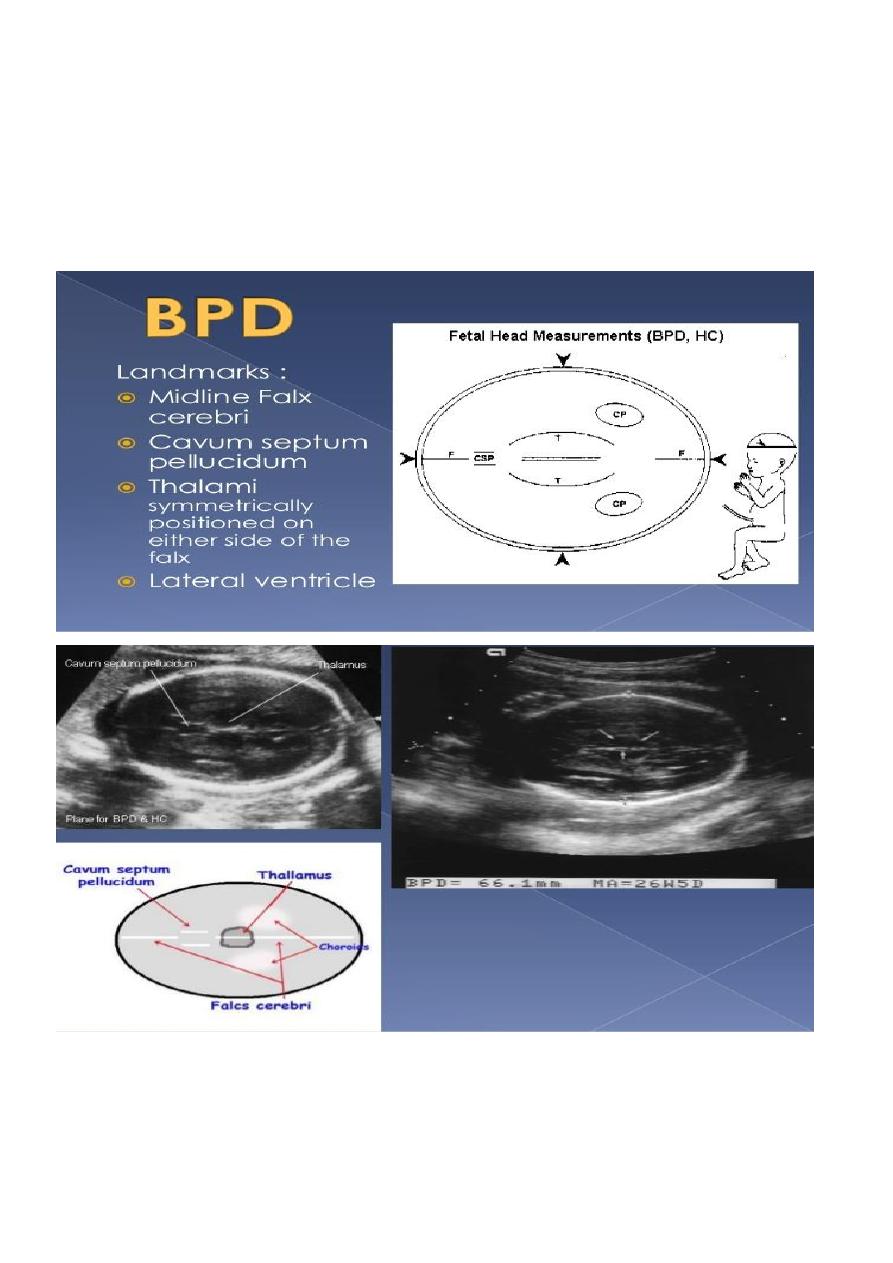
The BPD should be measured on an axial plane that traverses the thalami, and cavum
septum pellucidum. The transducer must be perpendicular to the central axis of the head,
and thus the hemispheres and calvaria should appear symmetric.
7
8
9

10

11

12
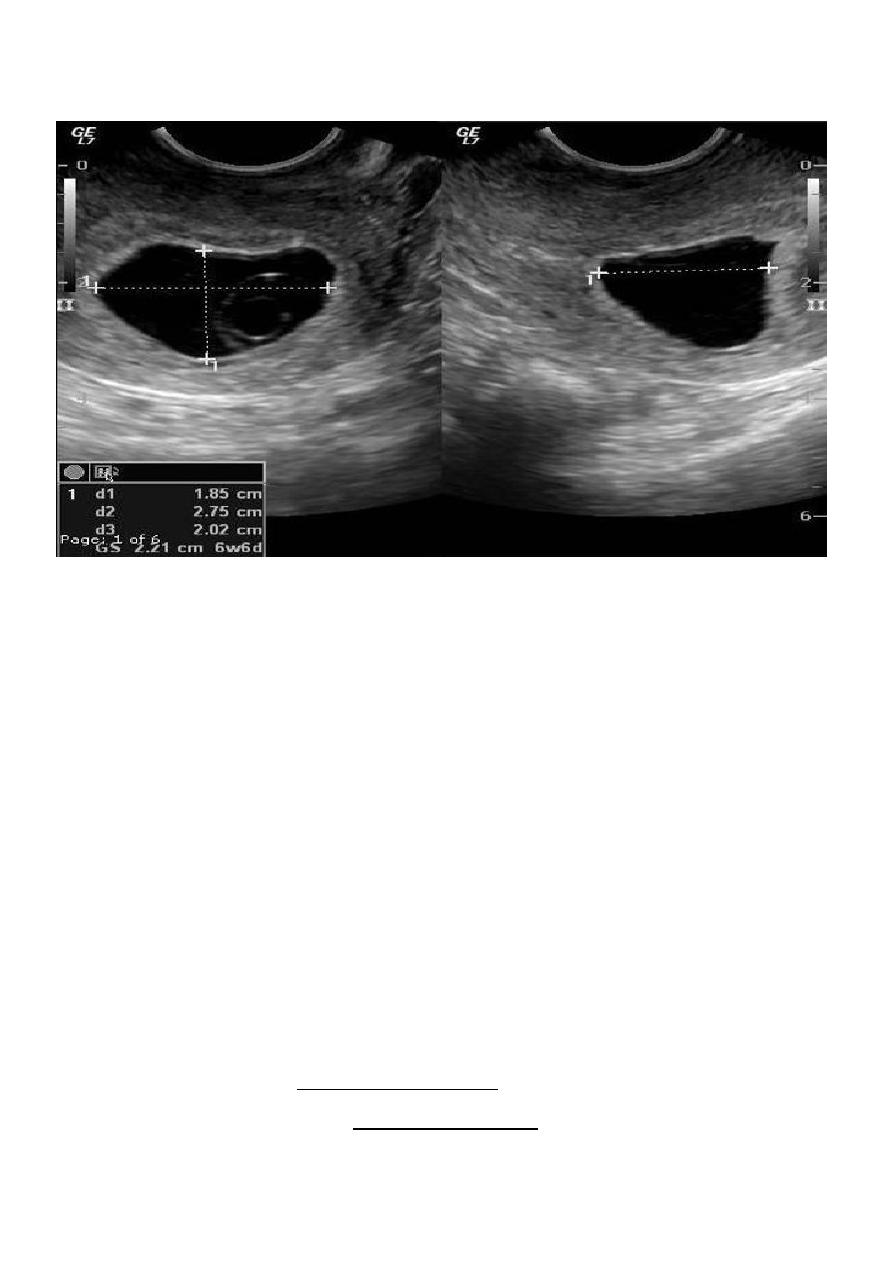
Blighted ovum
Anembryonic pregnancy is a form of a failed early pregnancy, where a gestational sac
develops, but the embryo does not form. The term blighted ovum is synonymous with this,
but is falling out of favour and is best avoided.
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
An anembryonic pregnancy may be diagnosed when there is no fetal pole identified on
endovaginal scanning , and:
13
the size of the gestational sac is such that a fetal pole should be seen: MSD ≥25 mm on TVS
(by RCOG criteria)
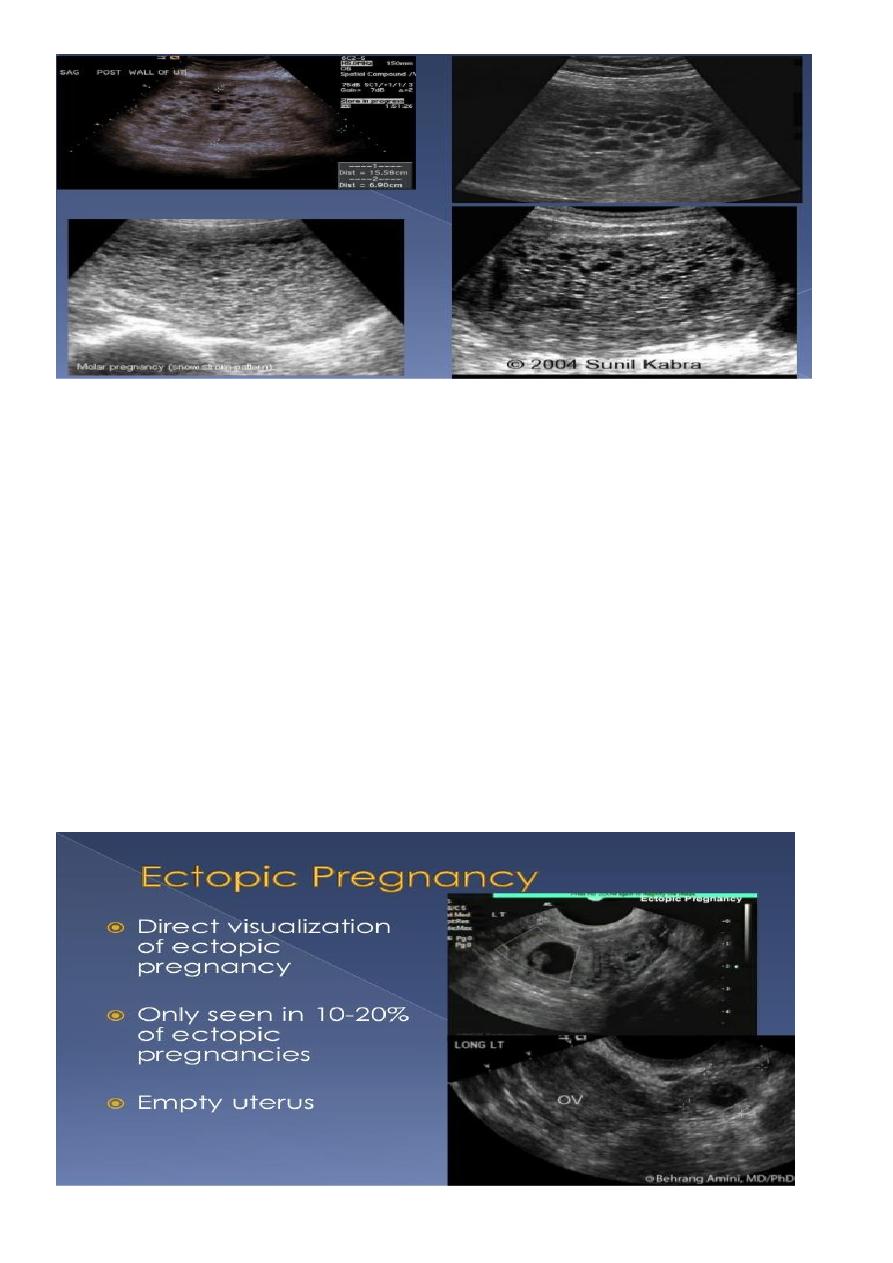
Molar pregnancy
Gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) results from abnormal proliferation of
trophoblastic tissue, and encompasses a wide spectrum of diseases, including:
hydatidiform mole
complete mole
partial mole
invasive mole
Chorio carcinoma (gestational choriocarcinoma)
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
enlarged uterus
classic sonographic appearance is that of a solid collection of echoes with numerous small
(3-10 mm) anechoic spaces (snowstorm appearance).
the molar tissue demonstrates the punch of grapes sign which represents hydropic swelling
of trophoblastic villi.
14
Ectopic pregnancy refers to the implantation of a fertilised ovum outside of the uterine
cavity.
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
The ultrasound exam should be performed both transabdominally and transvaginally. The
transabdominal component provides a wider overview of the abdomen, whereas a
transvaginal scan is important for diagnostic sensitivity.
Positive sonographic findings include:
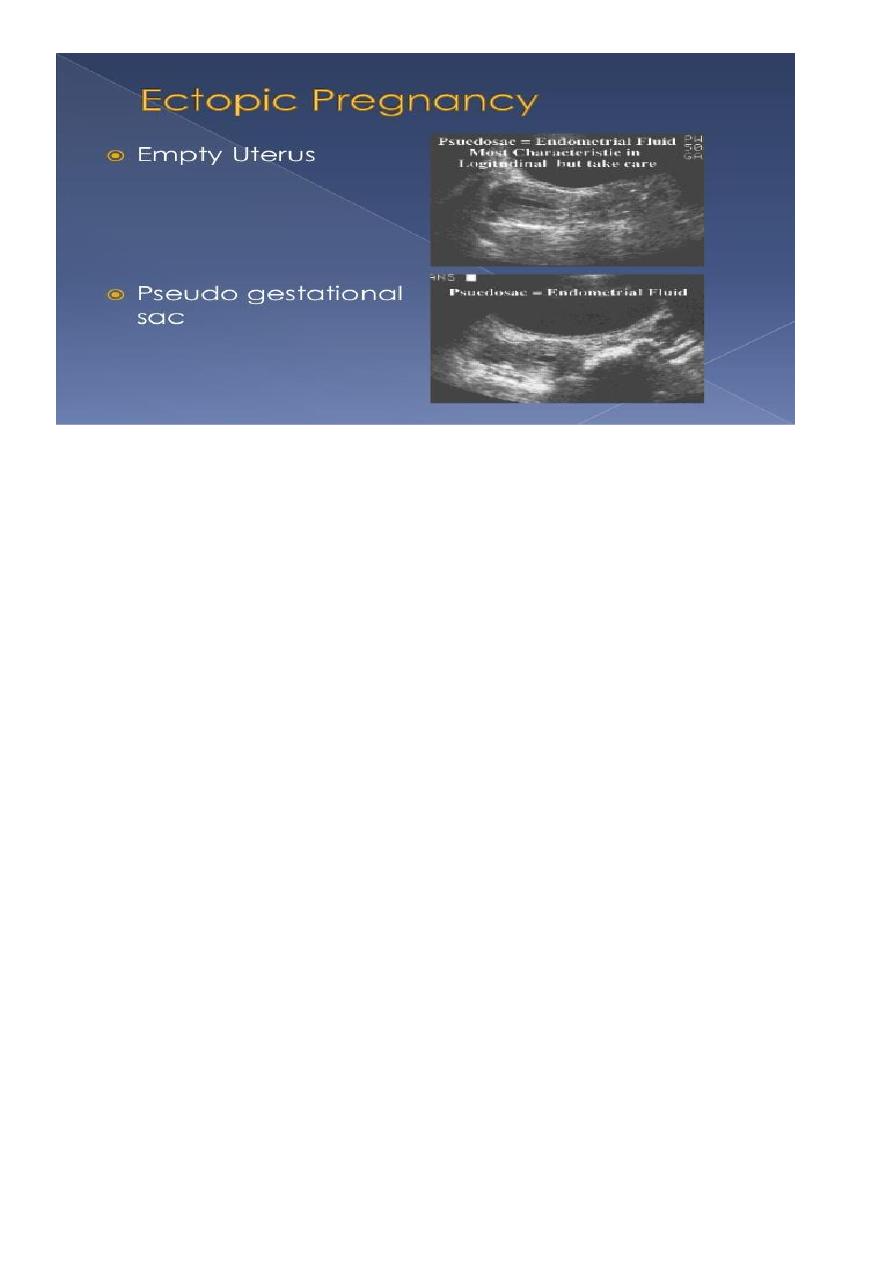
uterus
empty uterine cavity or no evidence of intrauterine pregnancy
Pseudo gestational sac or decidual cyst: may be seen in 10-20% of ectopic pregnancies
Direct visualization of the sac at the adenxia .
15
Anenecephaly >>>> frog sign appearance :
Anencephaly is the most severe form of cranial neural tube defect (NTD) and is
characterized by absence of cortical tissue (although brainstem and cerebellum may be
variably present) as well as absence of the cranial vault.
Associations
As with many other malformations, a number of associated abnormalities are recognized :
other neural tube defects: spina bifida (especially cervical)
congenital heart defects
cleft lip/palate
diaphragmatic hernia(s)
spinal dysraphism
skeletal anomalies: e.g. clubfeet
gastrointestinal abnormalities: e.g. omphalocoele
Radiographic features
Antenatal ultrasound
Anencephaly may be sonographically detectable as early as 11 weeks. Ultrasound can be a
non invasive,
no parenchymal tissue is seen above the orbits and calvarium is absent: parts of the
occipital bone and mid brain may be present urinary tract abnormalities: hydronephrosis
most common
16
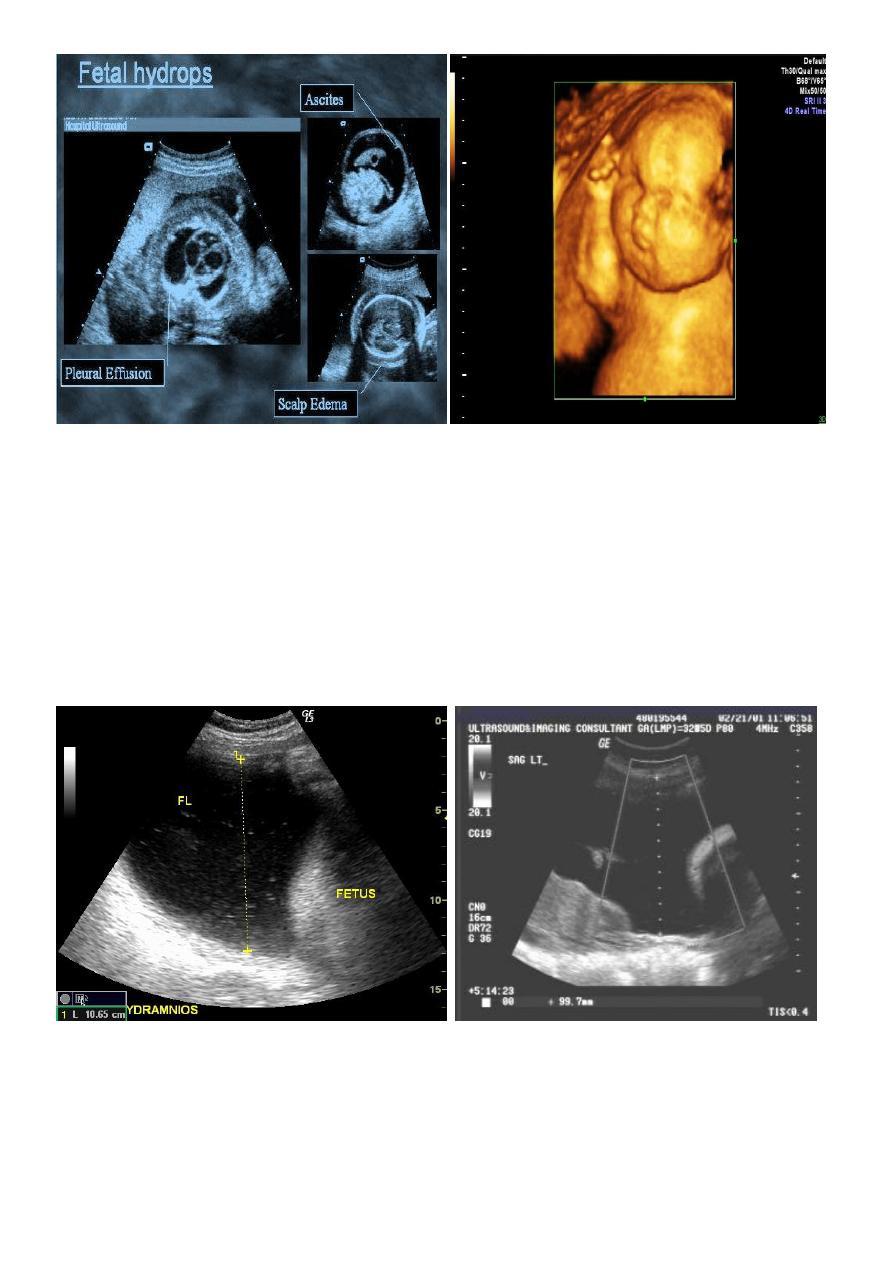
Hydropis fetalis :
Hydrops fetalis is excessive extravasation of fluid due to heart failure, volume overload,
decreased oncotic pressure, or increased vascular permeability.
Hydrops fetalis is defined as accumulation of fluid +/- edema involving at least two fetal
components, which may manifest as
fetal pleural effusion
fetal pericardial effusion
fetal ascites
generalized body edema: fetal anasarca /nuchal edema/cystic hygroma
placental enlargement
Poly hydramnious
Sonographic features can be similar for both immune and non-immune hydrops and
include:
increased amniotic fluid volumes
larger placental size (placento megaly)
The maximum thickness considered normal at any stage in pregnancy is often taken at 4
cm.
increased placental thickness (placental edema)
presence of a fetal pleural or pericardial effusion
generalized fetal body swelling : fetal anasarca and skin thickening > 3 mm
17
Poly hydraminous :
Poly hydraminos refers to a situation where the amniotic fluid volume is more than
expected for gestational age.
It is generally defined as:
amniotic fluid index (AFI) > 25 cm
largest fluid pocket depth (maximal vertical pocket (MVP)) greater than 8 cm
overall amniotic fluid volume larger than 1500-2000 cc3
18
UUUUUUs of pelvic organs :
19
20
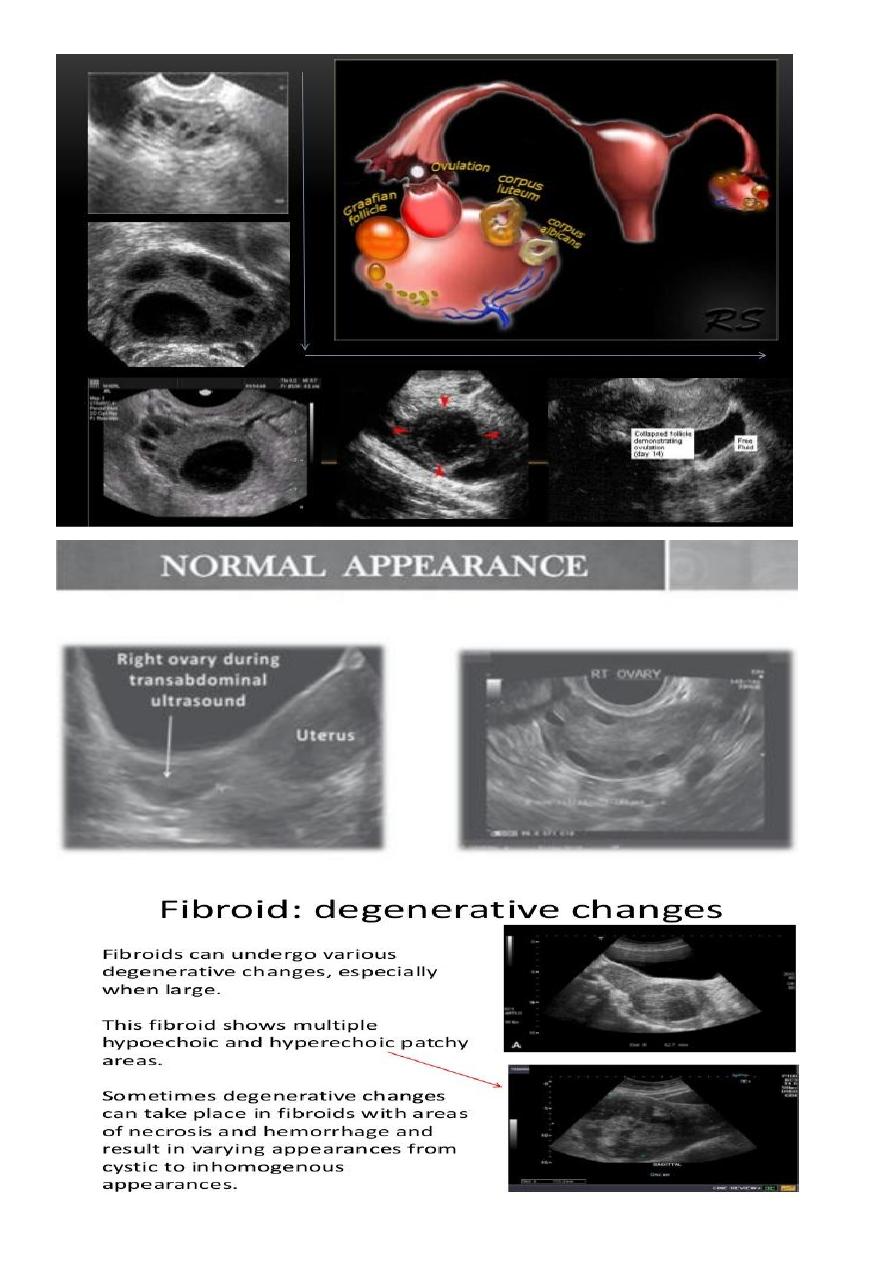
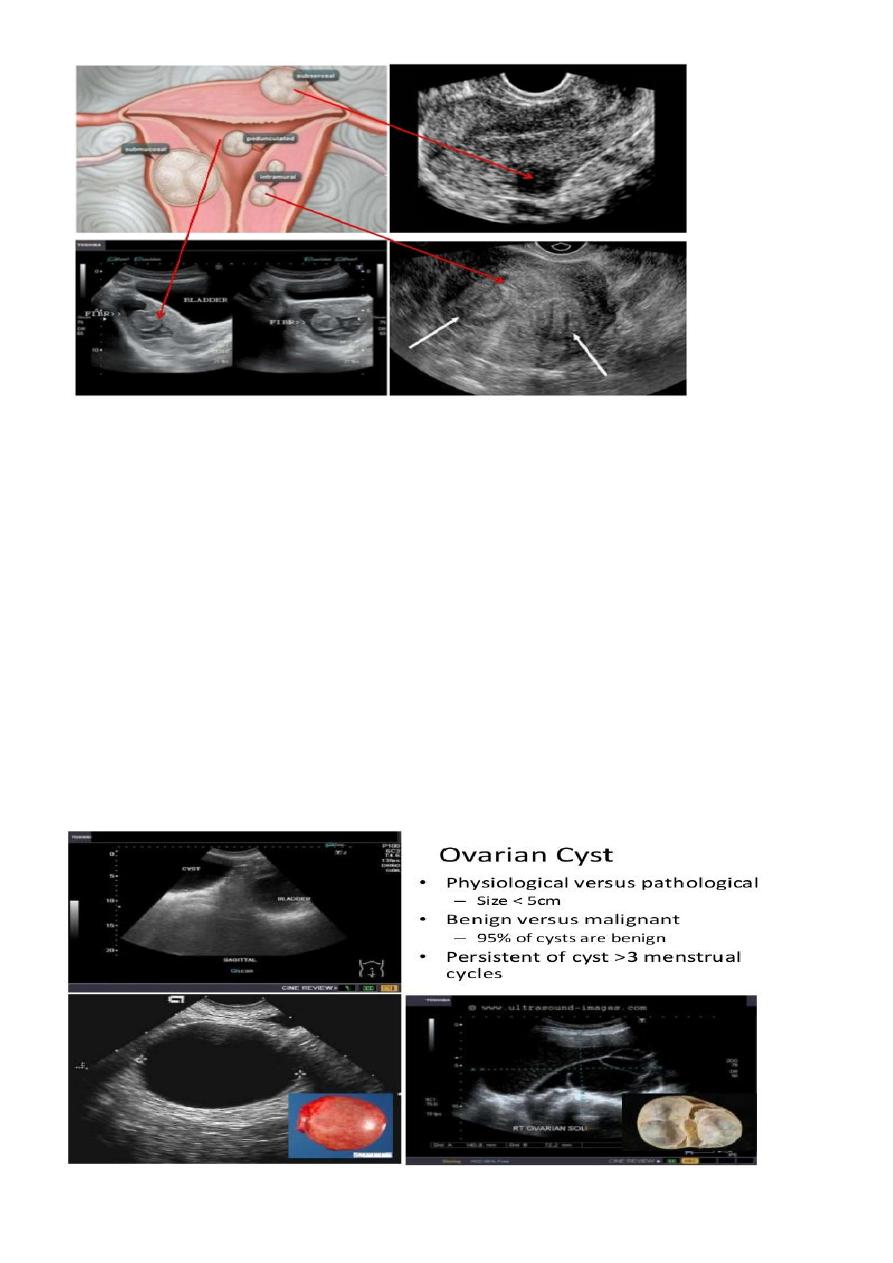
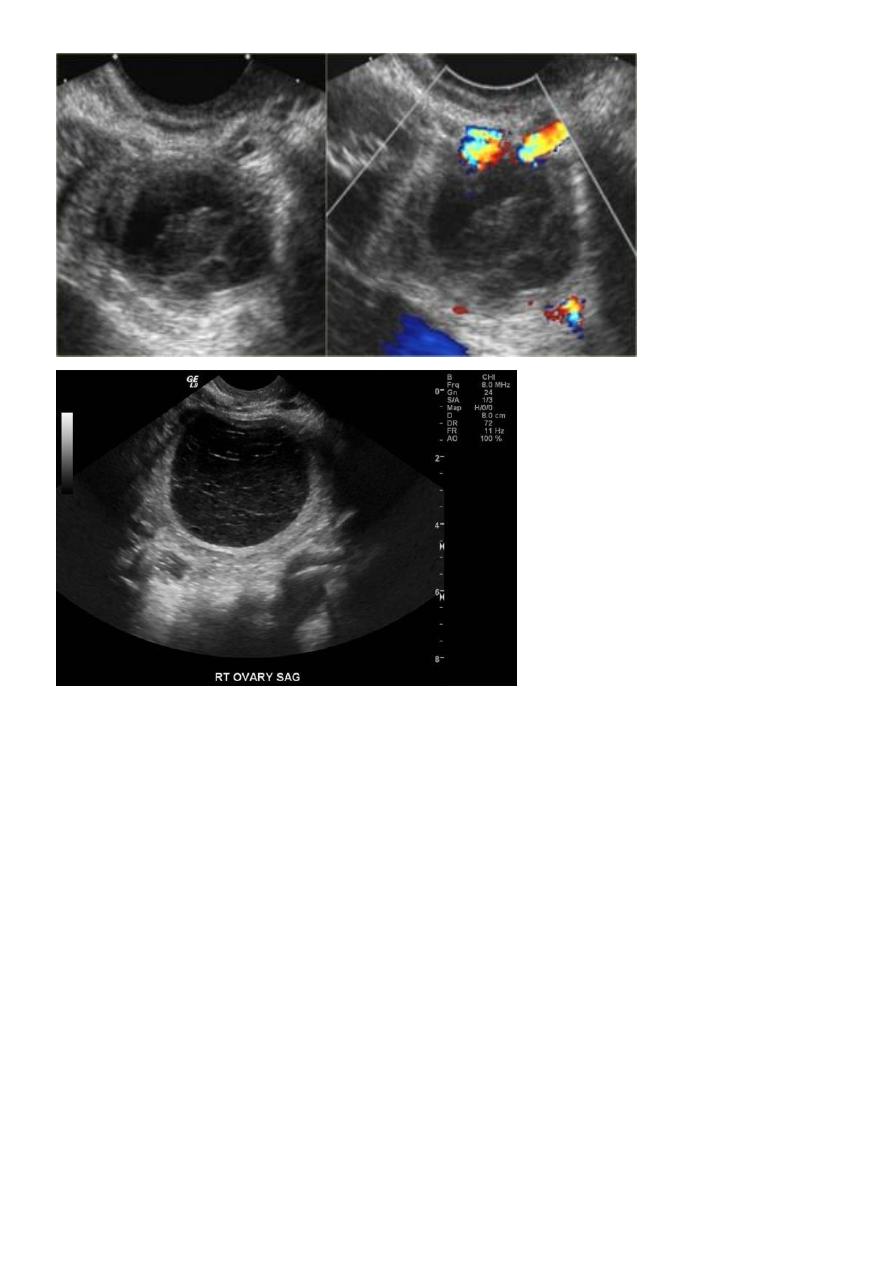
Ovarian cysts :
Ovarian cysts are commonly encountered in gynecological imaging, and vary widely in
etiology, from physiologic, to complex benign, to neoplastic.
Small cystic ovarian structures should be considered normal ovarian follicles unless the
patient is pre-pubertal, post-menopausal, pregnant, or the mean diameter is >3.0 cm
Radiographic features
Ultrasound is usually the first imaging modality for assessment of ovarian lesions. Simple
ovarian follicular cysts are:
anechoic
intraovarian or exophytic;
have an imperceptible wall
21
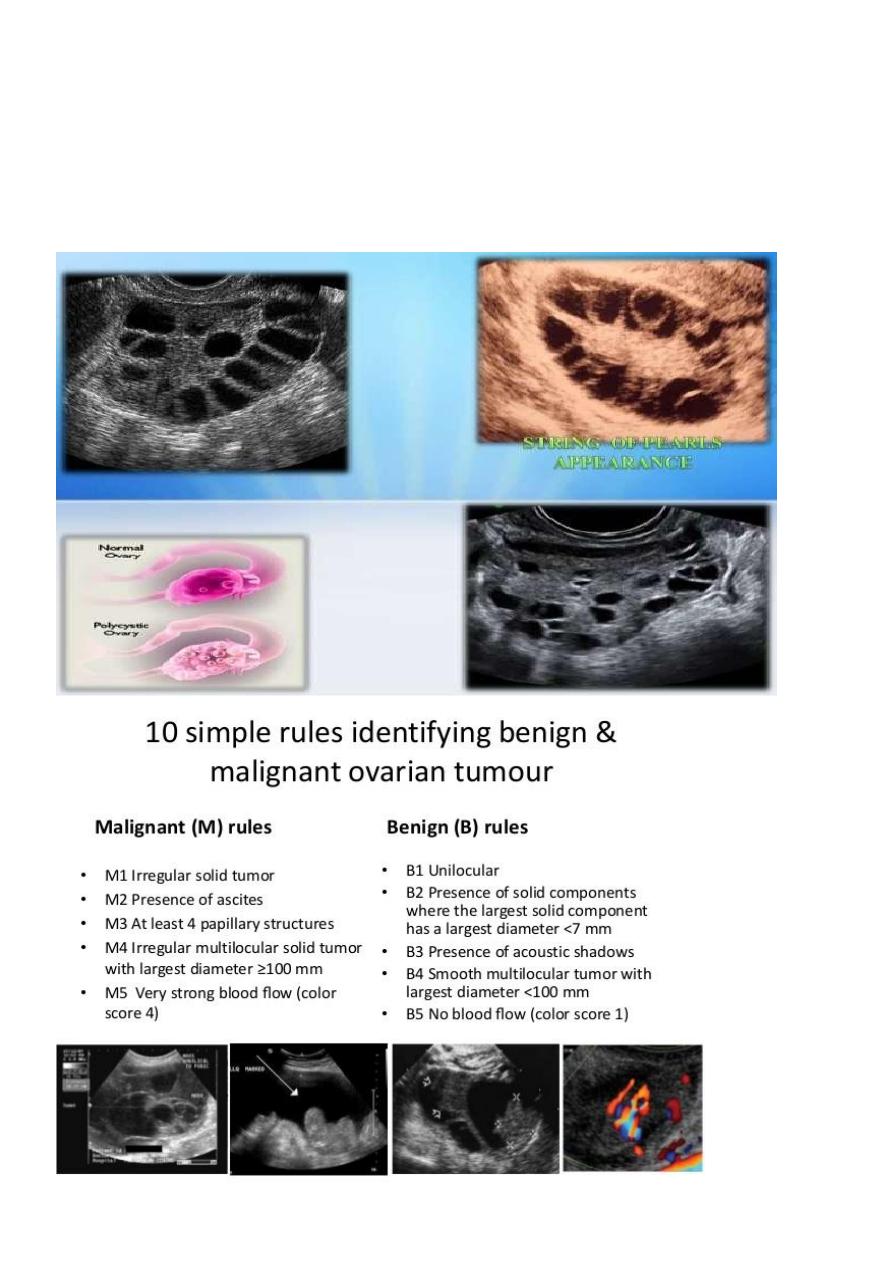
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
is a chronic anovulation syndrome. Sonographic findings alone are not
specific, and the diagnosis is made on the combined clinical, biochemical and
sonographic grounds
The classic triad of PCOS is:
oligomenorrhea
hirsutism
Obesity
Ovaries
may show sonographic features of polycystic ovaries
bilateral enlarged ovaries with multiple small follicles: 50%
increased ovarian size (>10 cc)
12 or more follicles measuring 2-9 mm
22
follicles of similar size
peripheral location of follicles: which can give a string of pearl appearance
hyperechoic central stroma
the ovarian outline may be slightly irregular .
