Diuretic Drugs
1-Overview2-Classification
3-Indiviual drugsLecture 1
1-Indications of Diuretics.
2-Adverse effects.3-Mannitol and Carbonic Anhydrase inhibitors.
Lecture 2The kidneys
Comprise 0.5% of body weight
But
They receive 25% the cardiac output
Overview
Each day the body produce 180 liter of glomerular filtrate
1.5 liters of urineOverview
If only 1 % of re-absorption is affected ?
Vast increase in urine output“Doubled”
Overview
A diuretic:
Is any drug which causes increase in water and solute excretion in the urine.
Sodium is the most important solute.
Definition:According to the Site of action.
(understanding)According to the Efficacy.
(clinical use)Classification
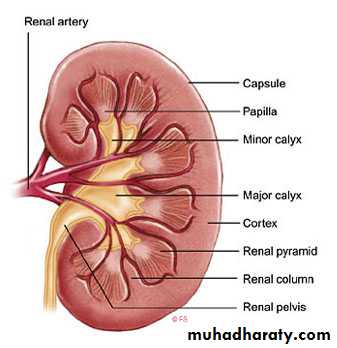
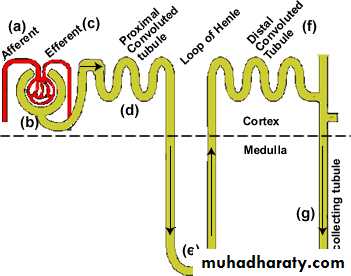
The kidney contains1,000,000 unite
(Nephron)(Basic unite)
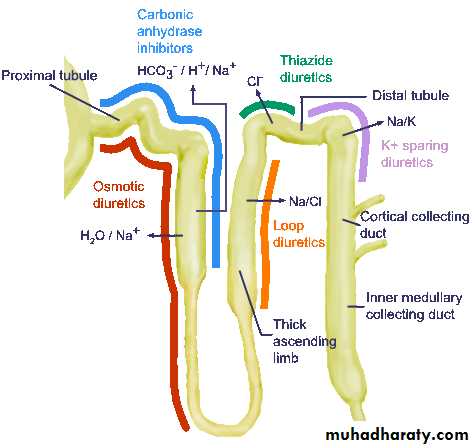
Classification according to the site of action
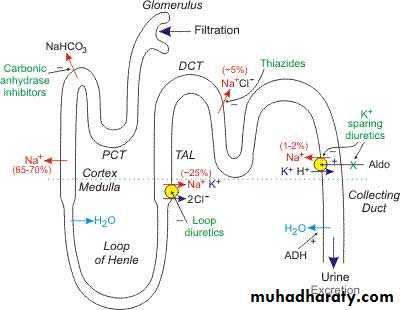
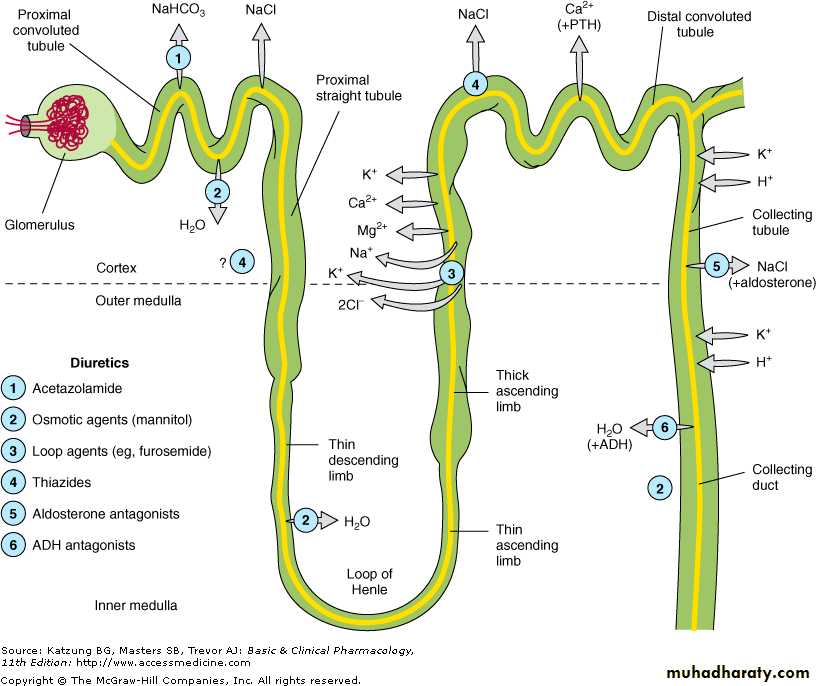
65 % of filtered sodium is reabsorbed in:
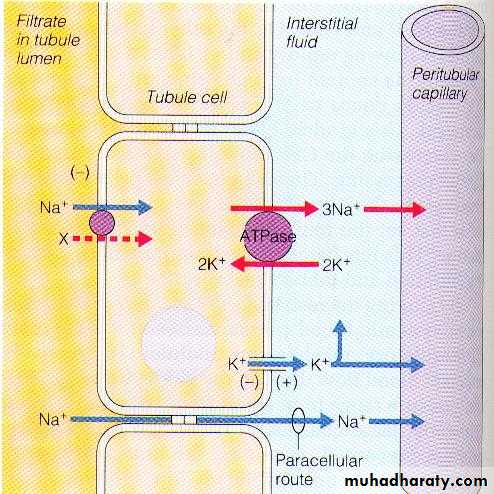
PCTNa-K ATPase
Cl also re-absorbed
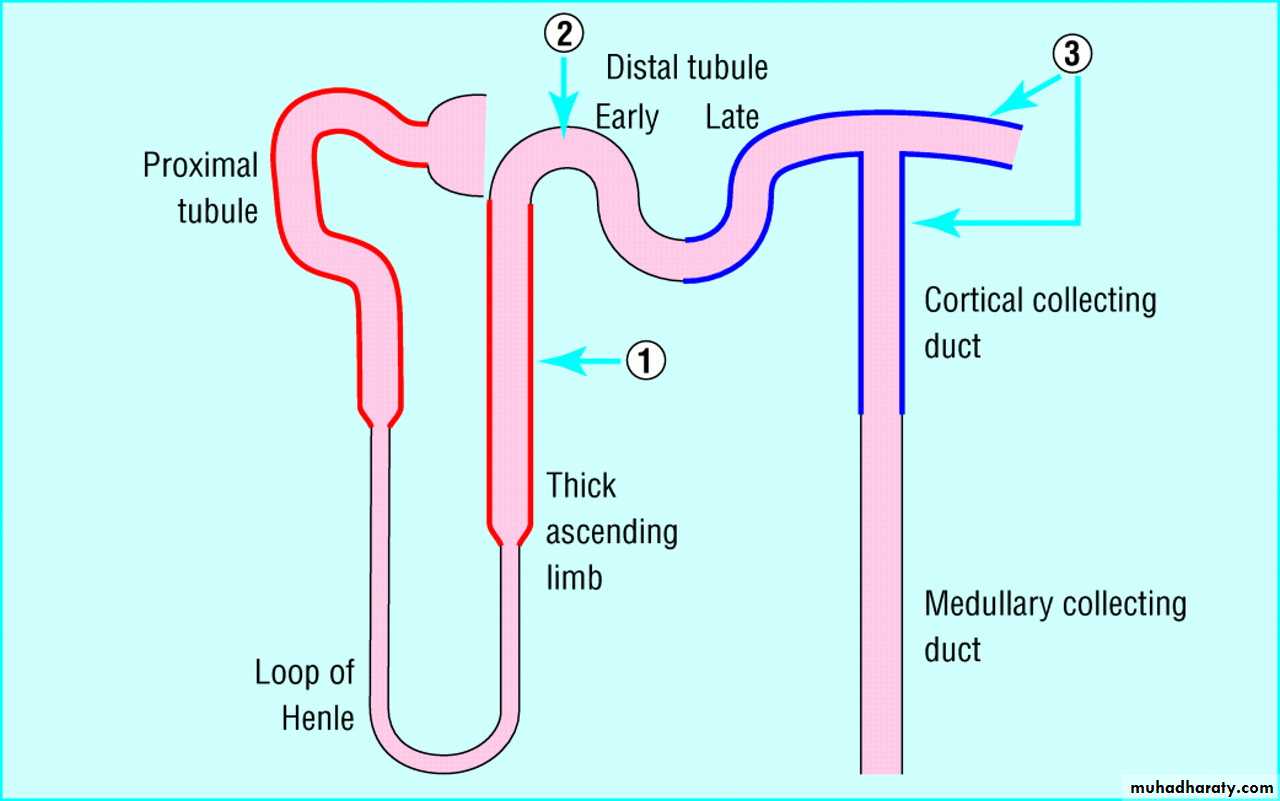
1-Proximal convoluted tubule(PCT)
1-Osmotic diuretic.
2- Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.Proximal convoluted tubule(PCT)
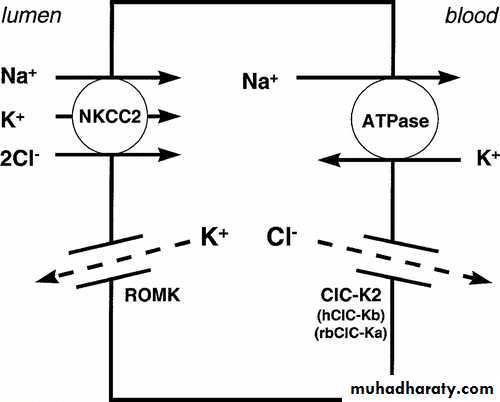
25 % of filtered sodium is re-absorbedAscending (Thick )
Na and Cl“Interstitial concentration”
Hypertonic Medullary Concentration
2-Loop of HenleDescending loop is permeable to water
Loop of Henle is the site of action of“Loop diuretics”
Loop of Henle
Is the site of Thiazide diuretics3-Distal convoluted tubule(DCT)
Na
Is exchanged for
K and H
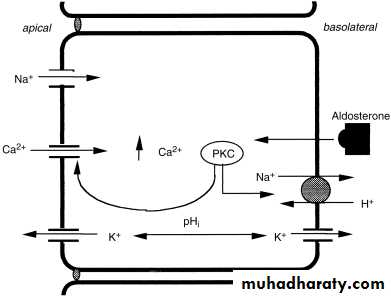
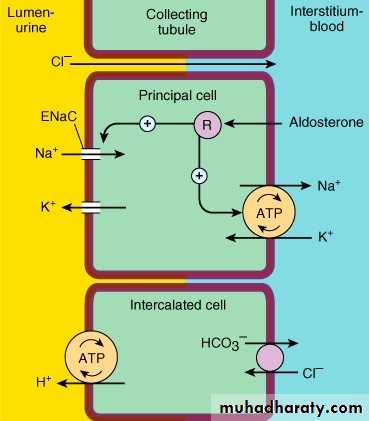
Mineralocorticosteroid
“Aldosterone”4-Collecting duct
Final concentration step is under ADH control
Ethanol decrease ADH hormoneCollecting duct
Is the site of action of Aldosterone antagonists
Spironolactone“K-sparing Diuretics”
Collecting ducts
1- High efficacy
2-Intermediat efficacy3-Low efficacy
Classification acoording to the efficacyFurosemide
FrusemideDecrease the urine concentration mechanism at loop of Henle
Affecting the medullary concentration mechanism25% of filtered sodium excreted
1-High efficacy diureticsFurosemide
FrusemideIncreasing the dose will increase the effect
“No Ceiling”
High efficacy diureticsFurosemide
FrusemideOvertreatment can induce dehydration
It is active even if the GFR is < 10 ml/minNormal GFR = 120 ml/ min
High efficacy diureticsThiazide family drugs
BendrofluazideChlorthalidone
Indapamide
2-Moderate efficacy
Thiazide family drugs
Increasing the dose will NOT increase the effect“Low ceiling”
Ineffective when GFR < 20 ml/ minModerate efficacy
Potassium sparing diuretics
Osmotic diureticSpironolactone (Aldosterone antagonist)
AmilorideTriamterene
3-Law efficacy
Potassium sparing diuretics2-3 % of filtered sodium is excreted by k sparing diuretics
Law efficacy
Furosemide (Lasix)
ThiazidesAmiloride
3-Individual Drugs
Acts on the thick portion of loop of Henle (ascending)
K loss and hypokalemiaMg and calcium loss also occur
Furosemide (Lasix)Well absorbed
Half Life = 2 hours10 hours in renal failure
20- 120 mg / day
20 mg amp
Pharmacokinetics of FurosemideAdverse effects
Uncommonelectrolyte disturbance
Hypotension, nausea rarely deafness which is transientFurosemide (Lasix)
Other Loop Diuretics:
Bumetanide 0.5-2 mg/day
Ethacrynic acid 50 mg/dayFurosemide (Lasix)
DCT increasing k exertionReduce the blood pressure
1- reduction of intravascular volume.
2-reduction in peripheral vascular resistance.Direct effect on vascular smooth muscle.
ThiazidesUsed in:
1-Cardiac failure in combination with other drugs.2-Hypertension.
Thiazides
Well absorbed acting within an hour of administration.Half life less than 4 hours.
ThiazidesAdverse Effects
Rashes and photosensitivity.Thrombocytopenia.
Increase total plasma cholesterol
ThiazidesPhotosensitivity
Bendroflumethiazide 5- 10 mg orally at the morning.
1.25-2.25 mg as anti hypertensive.Hydrochlorthazide 25-100 mg/day
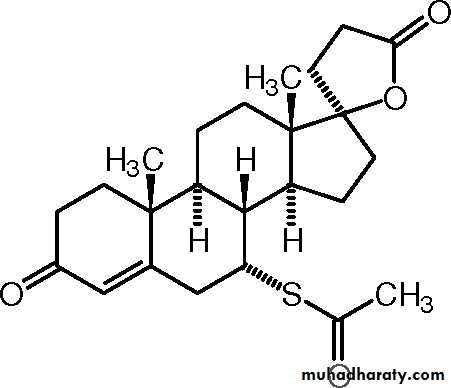
ThiazidesSpironolactone
(Aldactone)Structurally related to Aldosterone
“Competitive inhibitor of Aldosterone”Aldosterone
Spironolactone
Spironolactone (Aldactone)
1-Hepatic cirrhosis and Nehrotic Syndrome.2-Congestive heart failure.
Low efficacy diureticsSpironolactone (Aldactone)
Short half life = 1.6 hoursIneffective alone but more effective when given with other drugs
Spironolactone can be used with loop diureticsImpaired renal function may increase the potassium
Contra indicated
Spironolactone dose is 100- 200 mg
Per day.Spironolactone
Adverse reactions1-Estrogenic effect which is dose dependent.
Breast tenderness and enlargement.
10 % of male patients breast discomfort.
Menstrual irregularity.
2-Carcinogenic in rodents.
Mechanism of action:
Directly blocking the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in the DCT.
Inhibiting sodium re-absorption in the distal convoluted tubule.
Amiloride
Dosage: 5- 10 mg/ day
AmilorideAmiloride + Hydrochlorothiazide
2.5-5 mg Amiloride25-50 mg Hydrochlorothiazide
(Moduretic)
Hypertension and edemaCombination Formulae
High efficacy diuretics acts on:
A-Proximal con. TubuleB-Loop of Henle.
C-Distal Con. Tubule.
D-Collecting Ducts.
MCQs
All the following drugs are potassium sparing diuretics except:
A-Amiloride.B-Spironolactone.
C-Triamterene.
D-Furosemide.
MCQs
Which one of the following diuretics has estrogenic effect?A-Amiloride.
B-Spironolactone.C-Frusemide.
D-Hydrochlorothiazide.
MCQs
The main solute excreted by diuretics is;A-Potassium.
B-Sodium.
C-Chloride.
D-Calcium.
MCQs
Dehydration due to overtreatment is most common with:A-Spironolactone.
B-AmilorideC-Furosemide.
D-Hydrochlorothiazide.
MCQs
It is best to take Furosemide:A-At the morning.
B-At the afternoon.C-Before dinner.
D-At Bedtime.
MCQs
All the following diuretic combinations are wrong except:
A- Furosemide + Ethacrynic acid.B-Hydrochlorothiazide + Amiloride.
C-Amiloride + Spironolactone.
D-Chlorthalidone + Indapamide.
MCQs
Which one of the following diuretics has a significant effect on plasma cholesterol?
A-Furosemide.B-Thiazides
C- Ethacrynic acid.
D-Spironolactone.
MCQs
Which diuretic is structurally similar to Aldosterone?
A-Furosemide.
B-Thiazides
C-Spironolactone.
D-Amiloride.
MCQs
Combination in diuretics are used to:
A-Increase efficacy.
B- Minimize the adverse reactions.C-Improve the patient compliance.
D- All of the above.
MCQs