Otitis media with effusion
SynonymsSecretory otitis media
Non- purulent otitis media
Serous otitis media
Glue ear
Definition: presence of non-purulent fluid within middle ear cleft. Acute or chronic(more than 12 weeks).
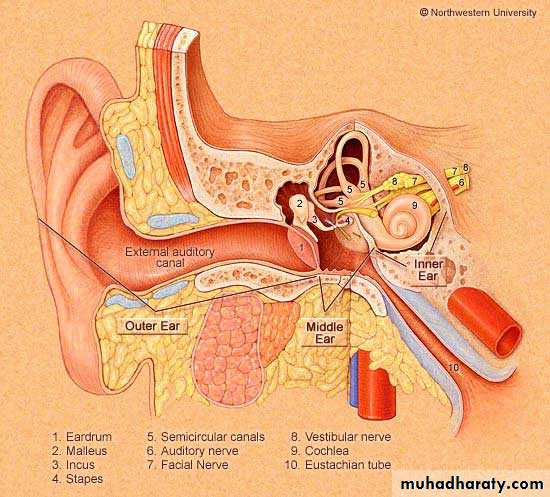
Otitis Media
It is the most common disease of childhood, next to viral URTI.It is acute bacterial infection in 80% (1-6 years)
The most frequent disease treated with antibiotics.Incidence
Children more than adults, peak age:5-6 yearsMale more than female
Winter months
Aetiology
1- Eustachian tube dysfunction
ET has 2 main functions:
1- Regulate ME pressure at atmospheric level.
2- Drainage of ME fluid into nasopharynx.
ET dysfunction may be due to:
A- Up. respiratory tract infection
B- Allergy
C- Cilial abnormality as Kartageners syndrome.
Children have poorer ET function than adults.
2- Cleft palate : muscles which open the ET attached to the soft palate (tensor and levator palate muscles).
3- Adenoid hypertrophy: causes obstruction of ET orifice in the nasopharynx which leads to negative ME pressure and hence ME effusion.
4- Nasopharyngeal tumours: similar mechanism to adenoid hypertrophy.
5- Radiotherapy to neck
6- Idiopathic
7- Barotrauma :as during airplane descent
8- AIDS
Clinical features
1- Deafness : the chief complaint
2- Impaired speech and language development ( in children)
3- Behavioral deterioration and scholastic difficulties (in children)
4- Pain is rare unless there is superadded infection
5- Tinnitus and vertigo
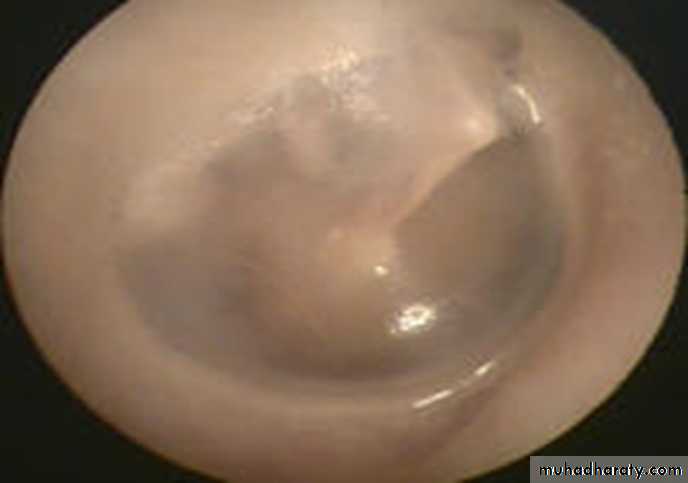
Normal Ear Drum
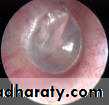
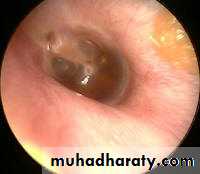
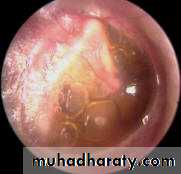
Serous Otitis MediaOn examination of the tympanic membrane by otoscopy:
RetractionLoss of translucency
Color changes: from pale grey to bluish black
Fluid level or air bubbles
Splitting or absent light reflex
Displacement of malleus handle and it become more prominent.
Tuning fork tests:
Rinne test :negative(bone conduction better than air)
Weber test: lateralized to diseased side
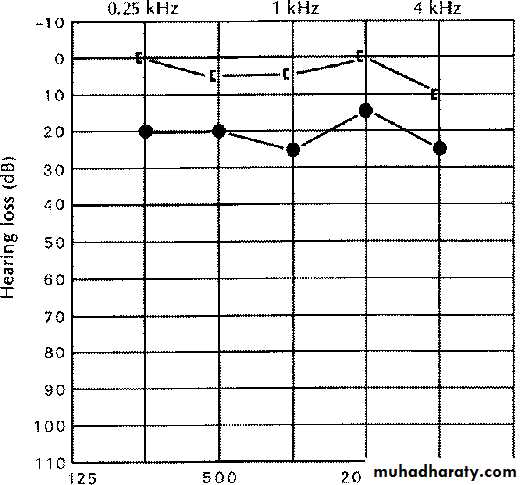
Audiometry:
Pure tone audiometry: air-bone gap
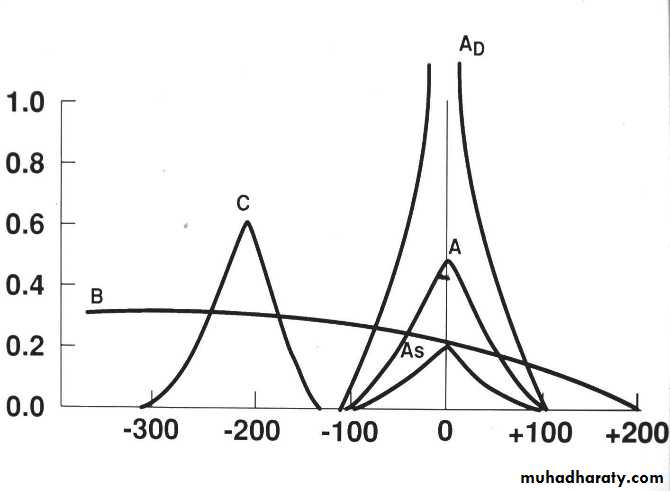
Tympanometry: flat type B curve.
OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSION
Diagnosis
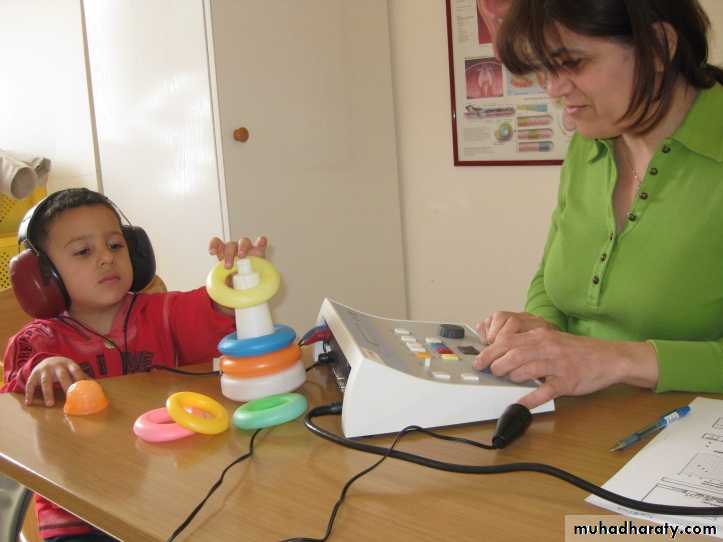
PLAY AUDIOMETRY
AUDIOMETRY
TYMPANOMETRYTreatment
High rate of spontaneous resolution. Only or 5% persist more than 1 year.Medical treatment
A- antibiotics: 10-14 days course
B- antihistamines
C- nasal decongestant
D- steroids: local in the nose or oral short course.
E- autoinflation of the ear by Valsalva maneuver.
Surgical treatment:
If persist more than 12 weeks with no benefit to medical treatment:
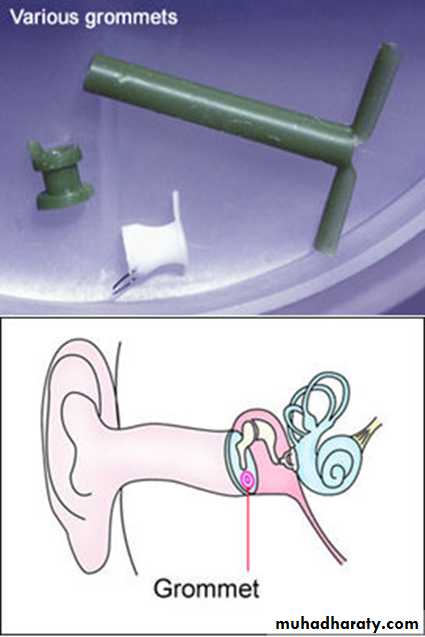
A- myringotomy with or without tympanostomy tube insertion(grommet)
B- adenoidectomy.
C- myringotomy with adenoidectomy
D- cortical mastoidectomy
OTITIS MEDIA WITH EFFUSIONTreatment
Adeno – Tonsellectomy&Myringotomy tube insertion (T&A &TUBES)Otosclerosis
Definition :Hereditary ear disease in which the mature bone is replaced by a woven bone of more cellularity.
Site :
Oval window region is the commonest site of involvement thus leading to fixation of stapes and conductive hearing impairment.
Incidence :
Age :peak 20-30 years
Gender : female more than male
Increased in severity during pregnancy and menopause.
Clinical features:
1- deafness : the main symptom, gradual, conductive in early stages, then mixed conductive and sensorineural. Bilateral2- tinnitus
3- vertigo
On examination: normal tympanic membrane color and mobility, but there may be red flush on the tympanic membrane called flamingo flush or Schwartz sign.
Tuning fork test : Rinne negative and Weber lateralized to affected side.
Audiometry: pure tone audiometry shows air-bone gap and Tympanometry shows normal or shallow curve type As.Differential diagnosis : other causes of conductive deafness:
1- otitis media with effusion2- ossicular disconnection
3- ME fibrosis
4- congenital cholesteatoma
5- osteogenesis imperfecta
Treatment :
1- medical
A- hearing aid
B- sodium fluoride
2- surgical : stapedectomy in which the stapes removed and replaced by a synthetic prosthesis under local or general anesthesia.
Menieres disease
Disease of inner ear in which there is hydropic distension of the endolymphatic system, characterized by episodic vertigo, deafness and tinnitus.Endolymphatic distension(hydrops) could be idiopathic called menieres disease or secondary to chronic otitis media, syphilis, trauma, leukemia, metabolic disease, viral infection, autoimmunity or Otosclerosis.
Clinical features :
1- episodic vertigo associated with vegetative symptoms(nausea and vomiting),last for 2-3 hours, less than 24 hours (24min-24hr).
2- deafness: sensorineural, fluctuate and progressive.
3- tinnitus
4- aural fullness.
Treatment :
1- medical :A- reassurance
B- labyrinthine sedative drugs(vestibular suppressants) :1- phenothiazines : as prochloperazine (stemetel)
2- antihistamines: as cinnarizine (stugeron)
3- benzodiazepines: diazepam and lorazepam
C- prophylaxis: between the attacks: diuretics, salt restriction, vasodilators as betahistine (betaserc) and nitroglycerine
D- steroids and cytotoxic drugs might be helpful
E- hearing aids
2- surgical
Only 10-20% need surgery
A- endolymphatic sac decompression
B- surgical or chemical ablation of vestibular nerve and vestibular end organs
C- labyrinthectomy: total destruction of sensory cells of inner ear.