Radiology of urinary system
Dr. Sameer Abdul LateefCONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE URINARY TRACT
Renal agenesis Bilateral incompatible with life , Unilateral is rare , I.V.U and sonography showing absence of kidney• .
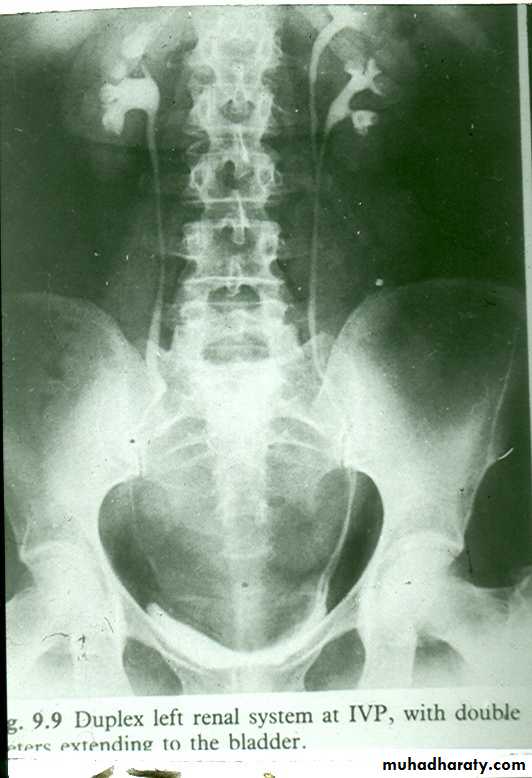
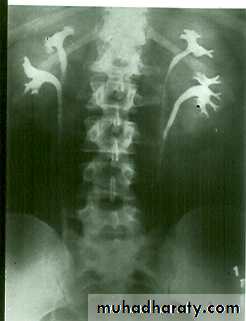
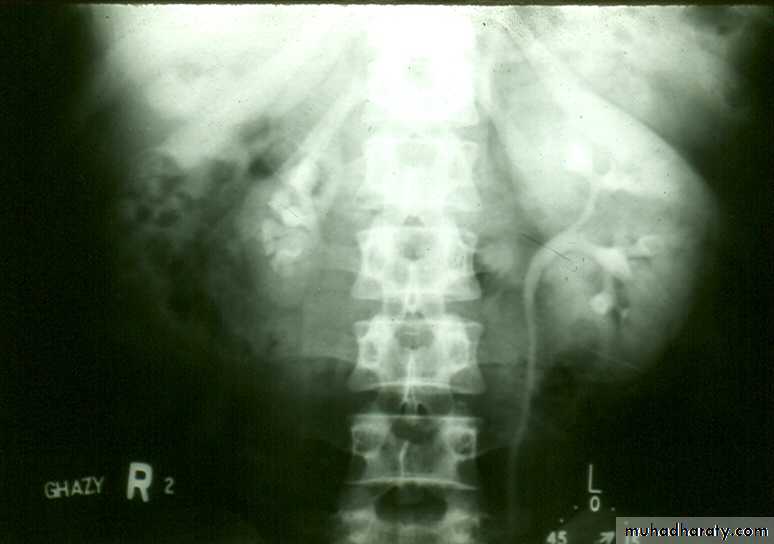
• Renal Duplication :- Common due to division of kidney and ureteric buds.• There are 4 grades
• grade I : Separation of upper pole major calyx from mid and lower poles together with renal pelvis (bifid kidney)
• Grade II : Duplication of kidney and ureter with fusion of two ureters during the coarse .
Grade III : Duplication of kidney and ureter with fusion of two ureters before entry to bladder .
Grade IV : Complete separation with each ureter enter the bladder separately. The orifice of upper moiety ureter is located under the orifice of lower moiety ureter.
Radiological appearance :-
IVU findings
1- Large size kidney .
2- Local indentation of out-line .
3- Unilateral or bilateral .
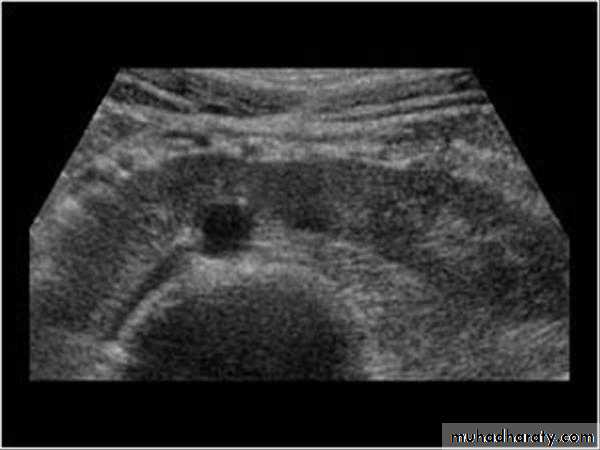
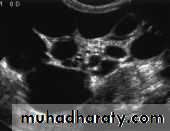
Ultrasound findings:
Division of renal sinus
CONGENITAL ANOMALIES OF THE URINARY TRACT
duplication
Renal Hypoplasia Small but other wise normal kidney.Reduced number of calyces. DDX: Renal ischemia
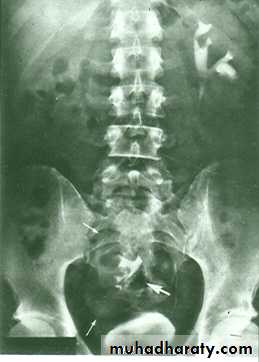
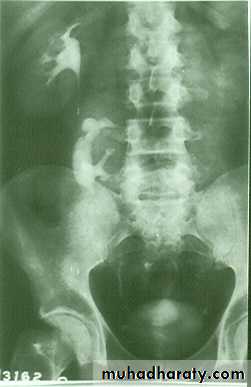
Renal Ectopia
Failure of ascending of kidney with mal –rotation.
The kidney is not seen in it’s proper position and seen at low level ( pre-sacral kidney )
DDX: Renal ptosis
Migration of one kidney to other side (mainly the left ) and fused with lower pole of the normal kidney.
It’s ureteric orifice remain in the same side.
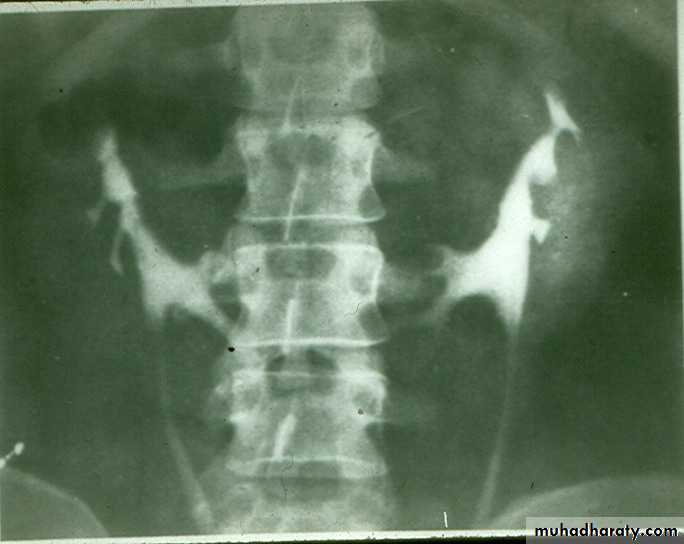
CROSSED ECTOPIA
Fusion of lower pole of both kidneys by bridge of renal tissue (isthmus) crossing in front of aorta, spine and IVC.
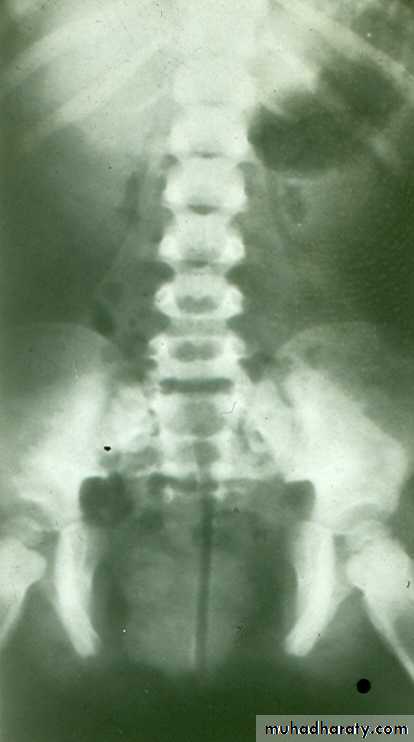
IVU shows :
The kidneys at low position .
Close to the spine with long axis parallel to the spine .
Mal–rotation manifested by medially directed calyces.
The renal pelvis and ureters are anterior and lateral in position .
Fusion of upper poles is rare.
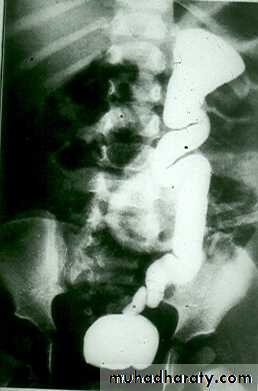
HORSE –SHOE KIDNEY
HORSE SHOE KIDNEY
Adult type :
* Present after the third decade of life .* Familial .
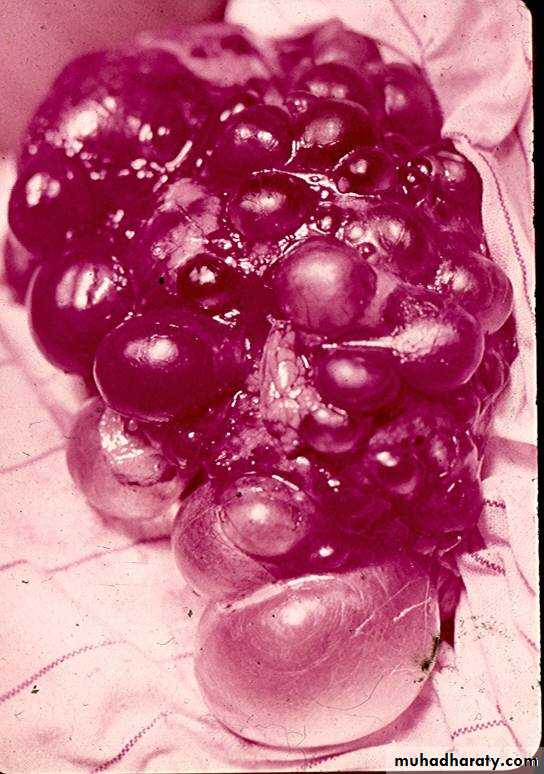
*Renal parenchyma is replaced by numerous cysts containing straw color fluid . The cysts are of variable size .
Clinically renal colic , loin mass , heamaturia and hypertension .
*Renal tissue interposed between the cysts after time destructed ended with renal failure
* Almost bilateral .
* when unilateral – multi-cystic kidney.
poly cystic disease
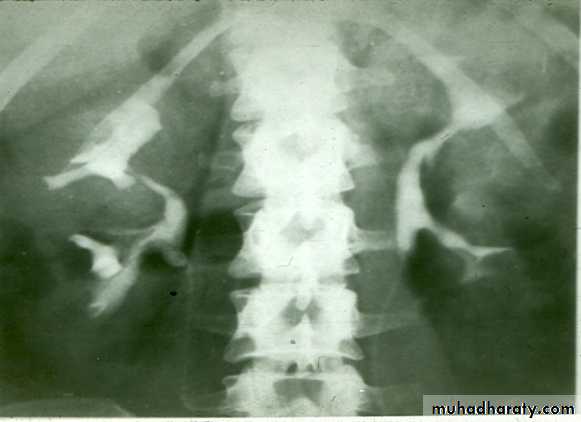
I.V.U.
* Enlarged kidney.* Lobulated out-line .
* Distortion of pelvi- calyceal system depend on cyst size, number and position.
* In advanced cases there is elongation and stretching of minor and major calyces ( spider leg ).
In advanced cases I.V.U. shows non-functioning kidney .
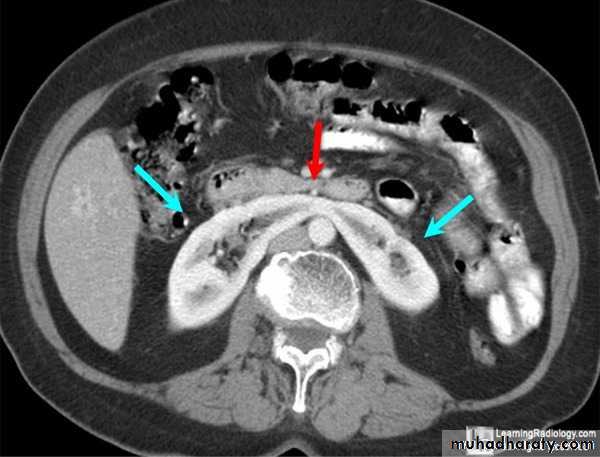
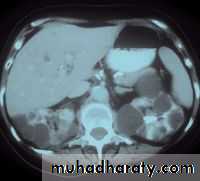
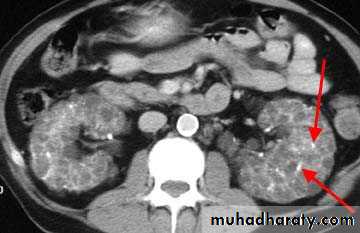
Ultrasound shows enlarged lobulated kidneys full of cysts of variable size.
CT also shows enlarged kidneys with multiple cysts appears as low attinuated areas
Poly cystic kidney
continue.I.V.U.
BilateralLarge kidney due to numerous small cysts ( 1 – 2 mm size ).
* The out-line is not lobulated as in adult.
* I.V.U. may be normal .
* Nephrogram shows minute filling defects.
Infantile poly-cystic disease
*Common anomaly .
* May discovered at adult life .* May be bilateral , more advanced in one side .
I.V.U. shows :
* Marked dilatation of pelvis and may be extra-renal .
*Calyceal dilatation is late and in advanced cases produce parenchymal atrophy .( foot shape pcs ) .
* The ureter is not seen and when it is seen looks normal .
* Delayed film with I.V. diuretic produce gross dilatation .
CONGINTAL HYDRONEPHROSIS
( PUJ obstruction )
Mega ureter
( congenital non-obstructive mega ureter )* Unilateral or bilateral dilatation of the ureter with no evidence of organic obstruction .
* Cause – unknown .
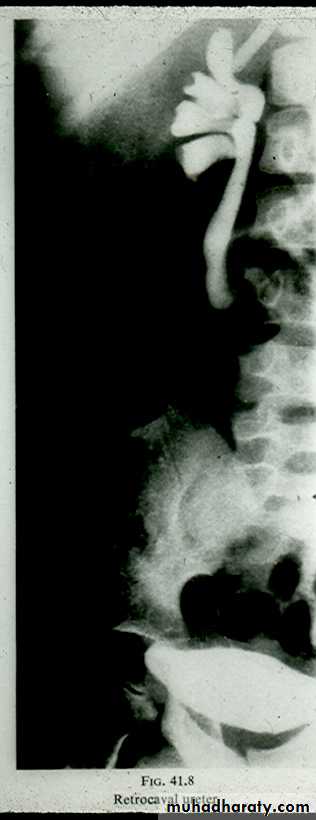
Retro- caval ureter :
* Rare .
* The middle third of right ureter curve medially behind the IVC , then laterally to regain it’s normal position , this lead to obstruction of upper third of ureter .
Congenital anomalies of ureter
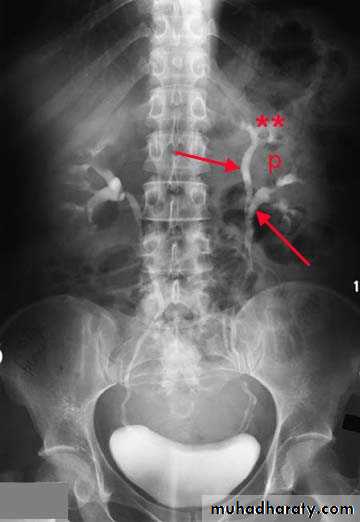
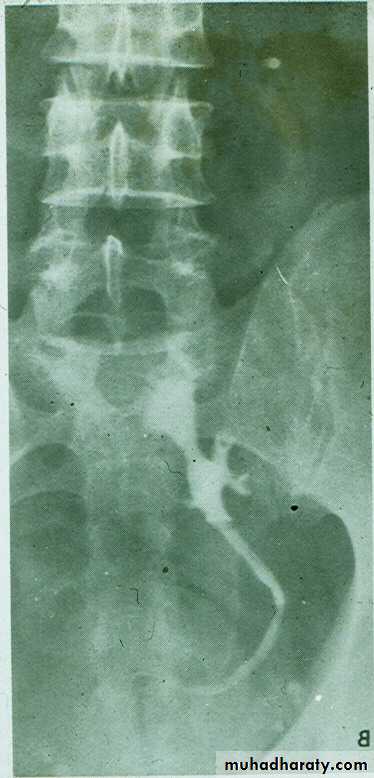
Congenital cystic dilatation of lower end of ureter ( intra-mural part ) due to pin-hole meatus . May be simple or ectopic .
In simple the orifice is in proper position of bladder .
In ectopic the orifice is at the bladder neck, urethra , uterus or vagina .
On IVU :
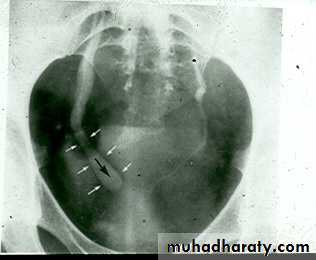
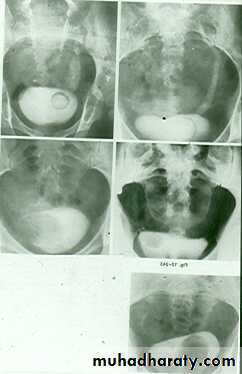
*There is rounded or elliptical dilatation of lower end of ureter with thin lineal filling defect around it , resembling (cobra head appearance) .
*Proximal dilatation of rest of ureter .
* In advanced cases hydronephrosis .
* In obstructed ureterocele filling defect in the bladder
URETEROCELE
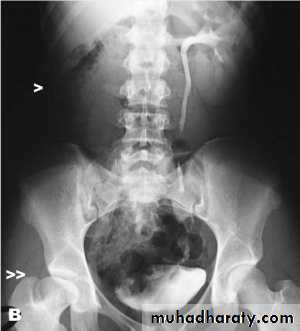
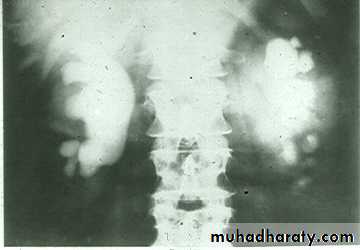
The urinary bladder is located at low position , the plain x-ray shows wide separation of symphysis pubis
ECTOPIA VESICA